
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (10): 1223-1229.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230091
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Xiaofan1,2( ), CHEN Xiaowu1,2, JIN Xihai1,2(
), CHEN Xiaowu1,2, JIN Xihai1,2( ), KAN Yanmei1,2, HU Jianbao1,2, DONG Shaoming1,2(
), KAN Yanmei1,2, HU Jianbao1,2, DONG Shaoming1,2( )
)
Received:2023-02-22
Revised:2023-04-20
Published:2023-10-20
Online:2023-05-15
Contact:
JIN Xihai, professor. E-mail: jinxihai@hotmail.com;About author:SUN Xiaofan (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 2487801767@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
SUN Xiaofan, CHEN Xiaowu, JIN Xihai, KAN Yanmei, HU Jianbao, DONG Shaoming. Fabrication and Properties of AlN-SiC Multiphase Ceramics via Low Temperature Reactive Melt Infiltration[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1223-1229.
| Material | Mass percent of LCP/% | Mass percent of HCP/% |
|---|---|---|
| α-Si3N4 | 20.17 | 15.66 |
| Carbon black | 8.65 | 6.71 |
| Phenolic resin | 17.29 | 26.85 |
| Dibutyl phthalate (DBP) | 5.76 | 4.47 |
| Polyvinyl butyral (PVB) | 7.20 | 5.59 |
| Castor oil | 0.58 | 0.45 |
| Ethanol absolute | 40.35 | 40.27 |
Table 1 Chemical composition of the slurries used for different types of C-Si3N4 infiltration preform preparation
| Material | Mass percent of LCP/% | Mass percent of HCP/% |
|---|---|---|
| α-Si3N4 | 20.17 | 15.66 |
| Carbon black | 8.65 | 6.71 |
| Phenolic resin | 17.29 | 26.85 |
| Dibutyl phthalate (DBP) | 5.76 | 4.47 |
| Polyvinyl butyral (PVB) | 7.20 | 5.59 |
| Castor oil | 0.58 | 0.45 |
| Ethanol absolute | 40.35 | 40.27 |
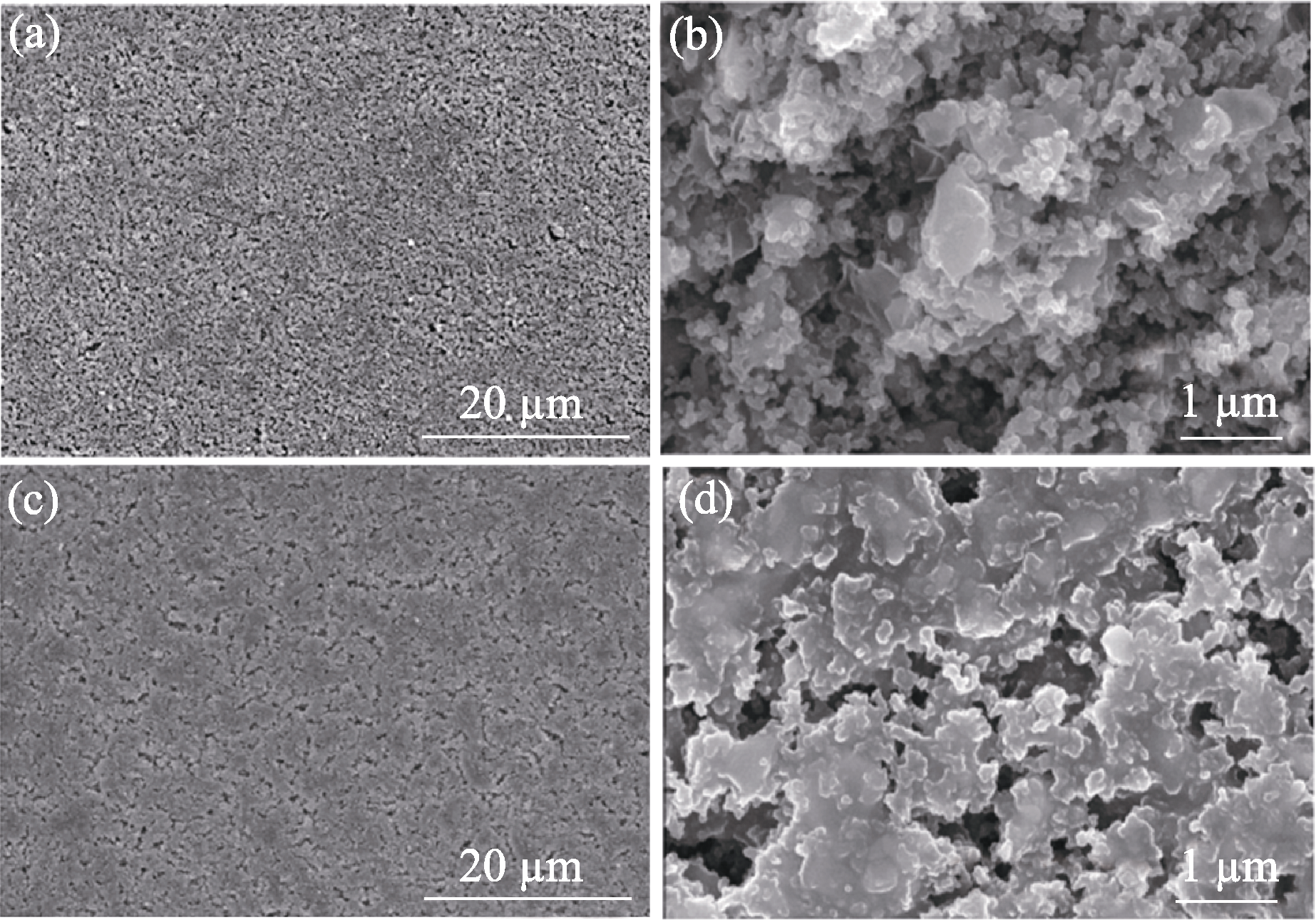
Fig. 1 SEM images of porous C-Si3N4 infiltration preforms with different carbon contents (a, b) Low carbon content preform (LCP); (c, d) High carbon content preform (HCP)
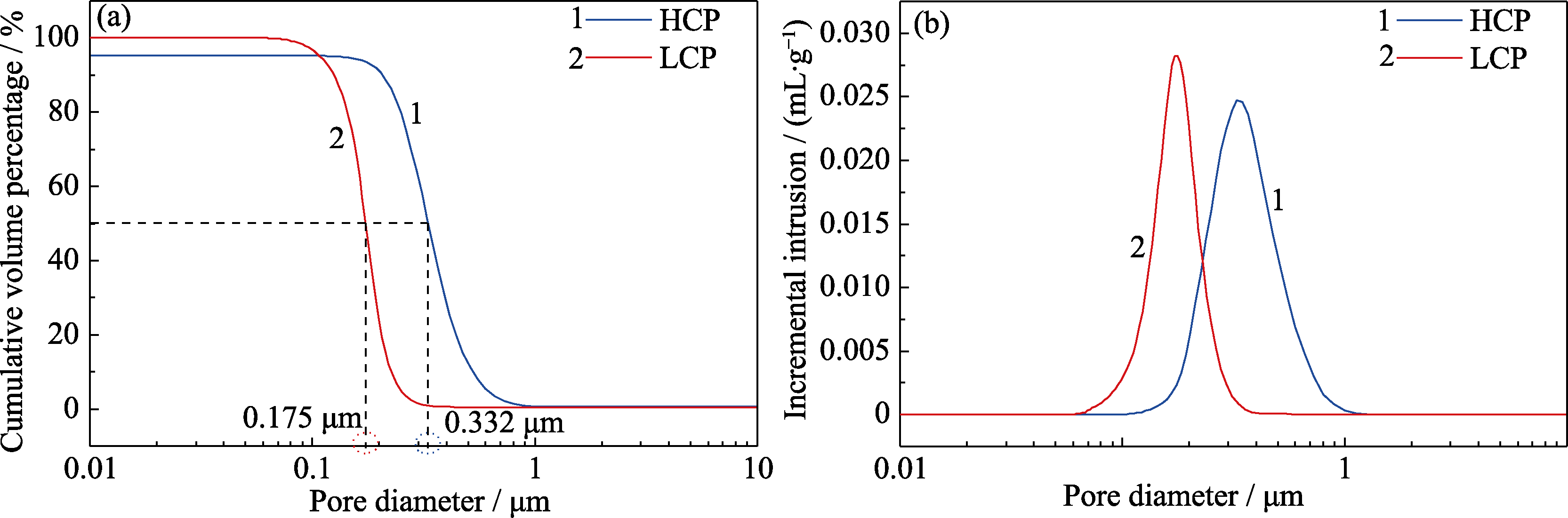
Fig. 2 Mercury porosimetry curves of the C-Si3N4 infiltration preforms with different carbon contents (a) Cumulative volume percentage vs pore diameter; (b) Incremental intrusion vs pore diameter

Fig. 3 SEM image and EDS line scanning of the melt/preform interface region in the post melt infiltrated Si-Al/C-Si3N4 system, using (a, b) Si-Al ingot and (c, d) Si-Al powder as infiltration medium Colorful figures are available on the website
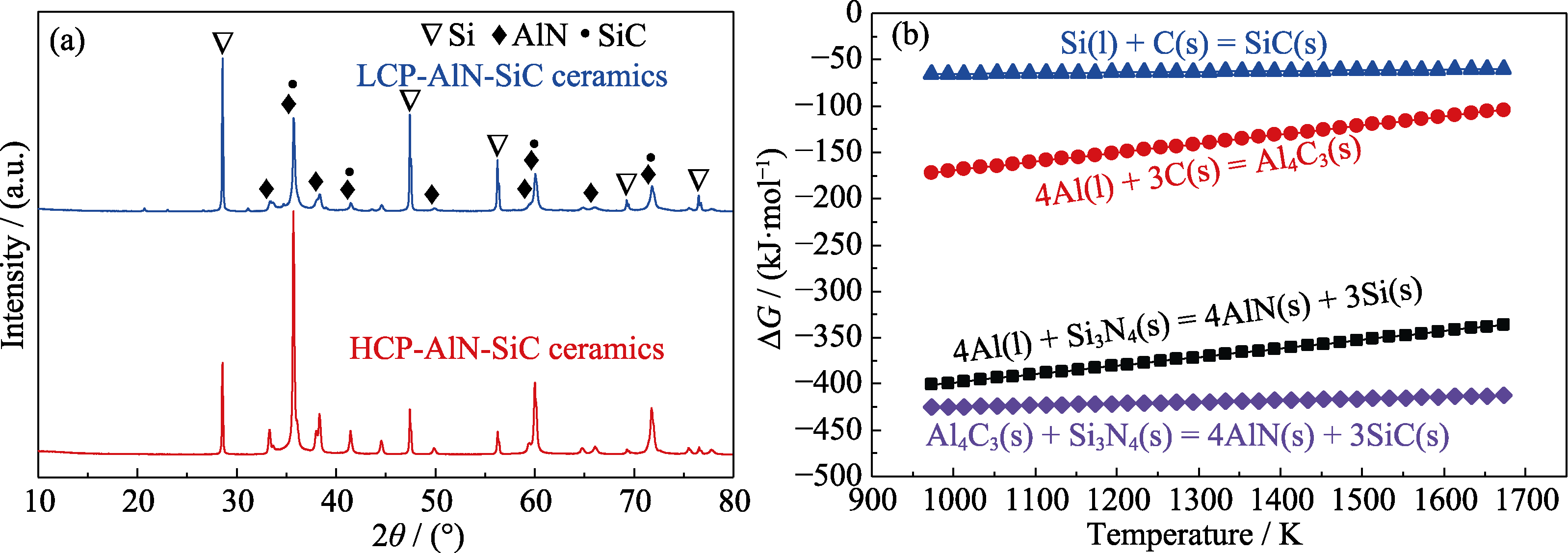
Fig. 4 (a) XRD patterns of AlN-SiC multiphase ceramics prepared from different types of C-Si3N4 preform, and (b) changes of standard Gibbs free energy of reaction (3-6) as a function of temperatures calculated with HSC 6.0 software
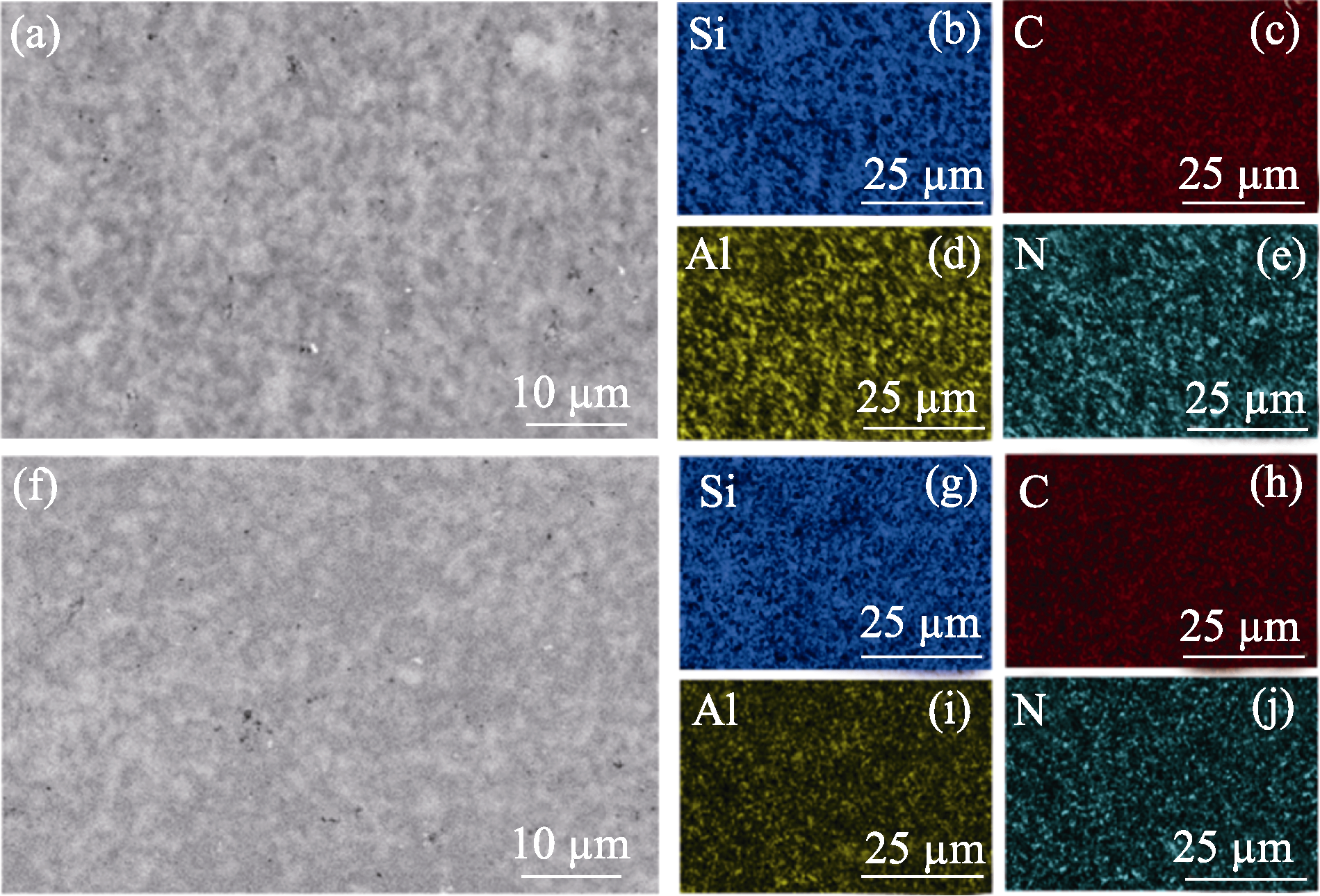
Fig. 5 SEM images of AlN-SiC multiphase ceramics prepared from different C-Si3N4 preforms and their corresponding EDS mapping (a-e) Low carbon content preform; (f-j) High carbon content preform
| Preform type | Bulk density/ (g·cm-3) | Hardness/GPa | Bending strength/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| LCP | 2.83 | 12.8±0.2 | 198.3±4.6 |
| HCP | 2.95 | 16.9±0.4 | 320.1±25.1 |
Table 2 Density and mechanical properties of AlN-SiC multiphase ceramics prepared from different types of C-Si3N4 preform
| Preform type | Bulk density/ (g·cm-3) | Hardness/GPa | Bending strength/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| LCP | 2.83 | 12.8±0.2 | 198.3±4.6 |
| HCP | 2.95 | 16.9±0.4 | 320.1±25.1 |
| [1] |
SHEN X, LI M, DAI Y, et al. The effects of preparation temperature on the SiCf/SiC 3D4d woven composite. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(9): 13088.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LIU Y, CHAI N, QIN H, et al. Tensile fracture behavior and strength distribution of SiCf/SiC composites with different SiBN interface thicknesses. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(1): 1609.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
YANG B, ZHOU X, CHAI Y. Mechanical properties of SiCf/SiC composites with PyC and the BN interface. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(5): 7185.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHONG Q, ZHANG X, DONG S, et al. Reactive melt infiltrated Cf/SiC composites with robust matrix derived from novel engineered pyrolytic carbon structure. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(7): 5832.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CHEN B W, NI D W, WANG J X, et al. Ablation behavior of Cf/ZrC-SiC-based composites fabricated by an improved reactive melt infiltration. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(15): 4617.
DOI URL |
| [6] | MU Y, ZHOU W, WANG H, et al. Mechanical and dielectric properties of 2.5D SiCf/SiC-Al2O3composites prepared via precursor infiltration and pyrolysis. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 596: 64. |
| [7] |
SUN X, LIU H, LI J, et al. Effects of CVD SiBCN interphases on mechanical and dielectric properties of SiCf/SiC composites fabricated via a PIP process. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(1): 82.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
WU P, LIU Y, XU S, et al. Mechanical properties and strengthening mechanism of SiCf/SiC mini-composites modified by SiC nanowires. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(2): 1819.
DOI URL |
| [9] | SANTORO U, NOVITSKAYA E, KARANDIKAR K, et al. Phase stability of SiC/SiC fiber reinforced composites: the effect of processing on the formation of α and β phases. Materials Letters, 2019, 241: 123. |
| [10] |
CHEN X, FENG Q, GAO L, et al. Interphase degradation of three-dimensional Cf/SiC-ZrC-ZrB2composites fabricated via reactive melt infiltration. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(10): 4816.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
CAO X, YIN X, MA X, et al. The microstructure and properties of SiC/SiC-based composites fabricated by low-temperature melt infiltration of Al-Si alloy. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(8): 10144.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
TAO P, WANG Y. Improved thermal conductivity of silicon carbide fibers-reinforced silicon carbide matrix composites by chemical vapor infiltration method. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(2): 2207.
DOI URL |
| [13] | AOKI T, OGASAWARA T, OKUBO Y, et al. Fabrication and properties of Si-Hf alloy melt-infiltrated Tyranno ZMI fiber/SiC- based matrix composites. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2014, 66: 155. |
| [14] | AOKI T, OGASAWARA T. Tyranno ZMI fiber/TiSi2-Si matrix composites for high-temperature structural applications. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2015, 76: 102. |
| [15] |
GAO Y, LIU Y, WANG J, et al. Formation mechanism of Si-Y-C ceramic matrix by reactive melt infiltration using Si-Y alloy and properties of C/Si-Y-C composites. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(11): 18976.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LI Z, GUO R, LI L, et al. Improvement in high-temperature oxidation resistance of SiC nanocrystalline ceramics by doping AlN. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(21): 30999.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
FUJII H, NAKAE H, OKADA K. Interfacial reaction wetting in the boron nitride/molten aluminum system. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1993, 41(10): 2963.
DOI URL |
| [1] | NI Xiaoshi, LIN Ziyang, QIN Muyan, YE Song, WANG Deping. Bioactivity and Mechanical Property of PMMA Bone Cement: Effect of Silanized Mesoporous Borosilicate Bioglass Microspheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 971-977. |
| [2] | WANG Shuling, JIANG Meng, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. n-Type Pb-free AgBiSe2 Based Thermoelectric Materials with Stable Cubic Phase Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 807-814. |
| [3] | CHEN Qiang, BAI Shuxin, YE Yicong. Highly Thermal Conductive Silicon Carbide Ceramics Matrix Composites for Thermal Management: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | ZHANG Shuo, FU Qiangang, ZHANG Pei, FEI Jie, LI Wei. Influence of High Temperature Treatment of C/C Porous Preform on Friction and Wear Behavior of C/C-SiC Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 561-568. |
| [5] | FU Shi, YANG Zengchao, LI Jiangtao. Progress of High Strength and High Thermal Conductivity Si3N4 Ceramics for Power Module Packaging [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1117-1132. |
| [6] | WU Dongjiang, ZHAO Ziyuan, YU Xuexin, MA Guangyi, YOU Zhulin, REN Guanhui, NIU Fangyong. Direct Additive Manufacturing of Al2O3-TiCp Composite Ceramics by Laser Directed Energy Deposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1183-1192. |
| [7] | AN Wenran, HUANG Jingqi, LU Xiangrong, JIANG Jianing, DENG Longhui, CAO Xueqiang. Effect of Heat-treatment Temperature on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of LaMgAl11O19 Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 925-932. |
| [8] | FU Shi, YANG Zengchao, LI Honghua, WANG Liang, LI Jiangtao. Mechanical Properties and Thermal Conductivity of Si3N4 Ceramics with Composite Sintering Additives [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 947-953. |
| [9] | HU Jiajun, WANG Kai, HOU Xinguang, YANG Ting, XIA Hongyan. Boron Phosphide with High Thermal Conductivity: Synthesis by Molten Salt Method and Thermal Management Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 933-940. |
| [10] | LI Wenjun, WANG Hao, TU Bingtian, CHEN Qiangguo, ZHENG Kaiping, WANG Weiming, FU Zhengyi. Preparation and Property of Mg0.9Al2.08O3.97N0.03 Transparent Ceramic with Broad Optical Transmission Range [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 969-975. |
| [11] | ZHANG Ye, ZENG Yuping. Progress of Porous Silicon Nitride Ceramics Prepared via Self-propagating High Temperature Synthesis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 853-864. |
| [12] | WANG Pengjiang, KANG Huijun, YANG Xiong, LIU Ying, CHENG Cheng, WANG Tongmin. Inhibition of Lattice Thermal Conductivity of ZrNiSn-based Half-Heusler Thermoelectric Materials by Entropy Adjustment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 717-723. |
| [13] | HONG Du, NIU Yaran, LI Hong, ZHONG Xin, ZHENG Xuebin. Tribological Properties of Plasma Sprayed TiC-Graphite Composite Coatings [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 643-650. |
| [14] | XU Puhao, ZHANG Xiangzhao, LIU Guiwu, ZHANG Mingfen, GUI Xinyi, QIAO Guanjun. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SiC Joint Brazed by Al-Ti Alloys as Filler Metal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 683-690. |
| [15] | DING Jianxiang, ZHANG Kaige, LIU Dongming, ZHENG Wei, ZHANG Peigen, SUN Zhengming. Ag-based Electrical Contact Material Reinforced by Ti3AlC2 Ceramic and Its Derivative Ti3C2Tx [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 567-573. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||