
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 1301-1308.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230170
Special Issue: 【能源环境】光催化(202312)
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIA Xin1,2( ), LI Jinyu1,2, DING Shihao1,2, SHEN Qianqian1,2, JIA Husheng1,2, XUE Jinbo1,2(
), LI Jinyu1,2, DING Shihao1,2, SHEN Qianqian1,2, JIA Husheng1,2, XUE Jinbo1,2( )
)
Received:2023-04-06
Revised:2023-06-26
Published:2023-07-17
Online:2023-07-17
Contact:
XUE Jinbo, associate professor. E-mail: xuejinbo@tyut.edu.cnAbout author:About author: JIA Xin (1995-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 547623834@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
JIA Xin, LI Jinyu, DING Shihao, SHEN Qianqian, JIA Husheng, XUE Jinbo. Synergy Effect of Pd Nanoparticles and Oxygen Vacancies for Enhancing TiO2 Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1301-1308.
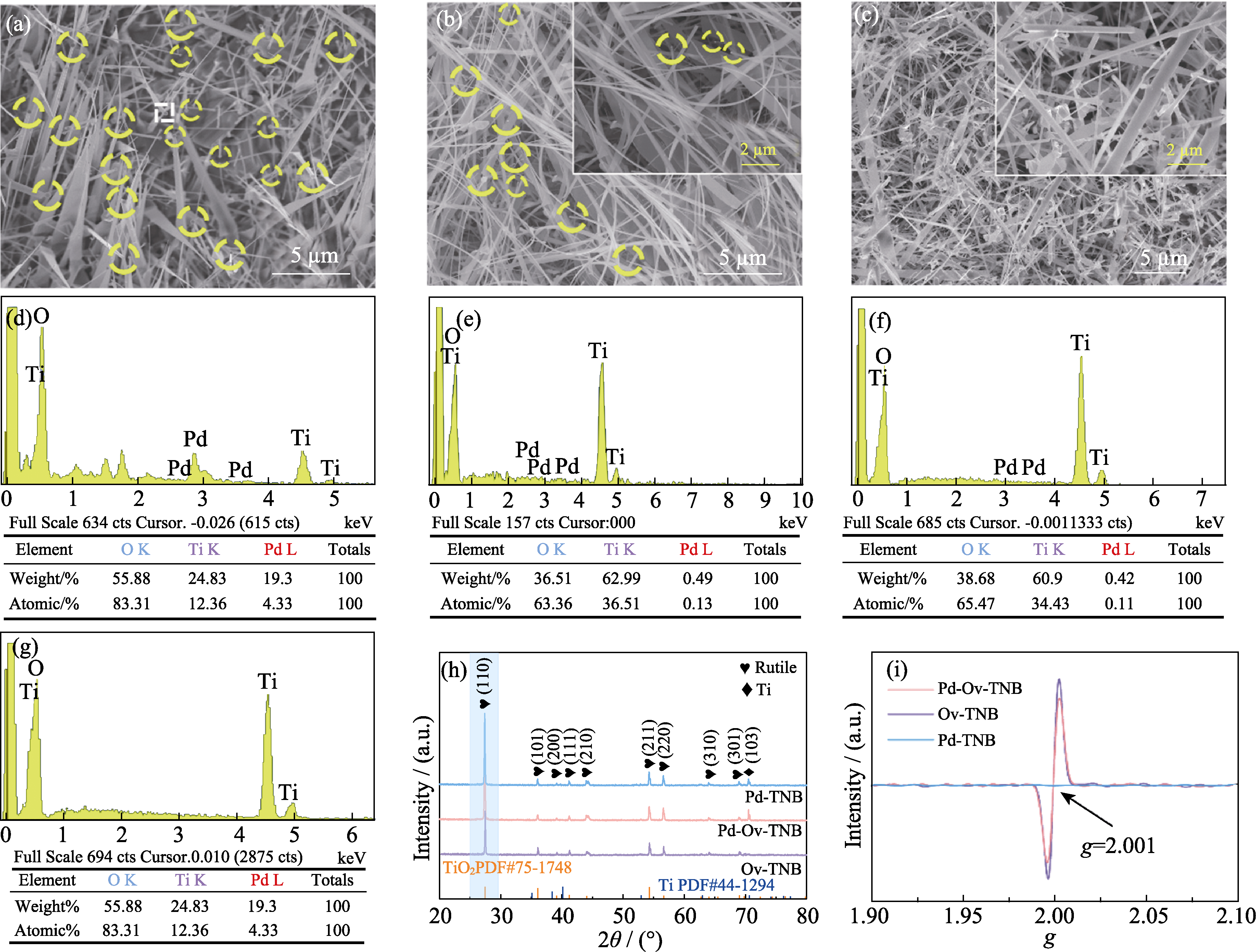
Fig. 1 (a-c) SEM images, (e-g)EDS spectra, (h) XRD patterns and (i) EPR spectra of (a, e) Pd-Ov-TNB, (b, f) Pd-TNB and (c, g) Ov-TNB; (d) Analytical mapping of EDS point of square area in (a)
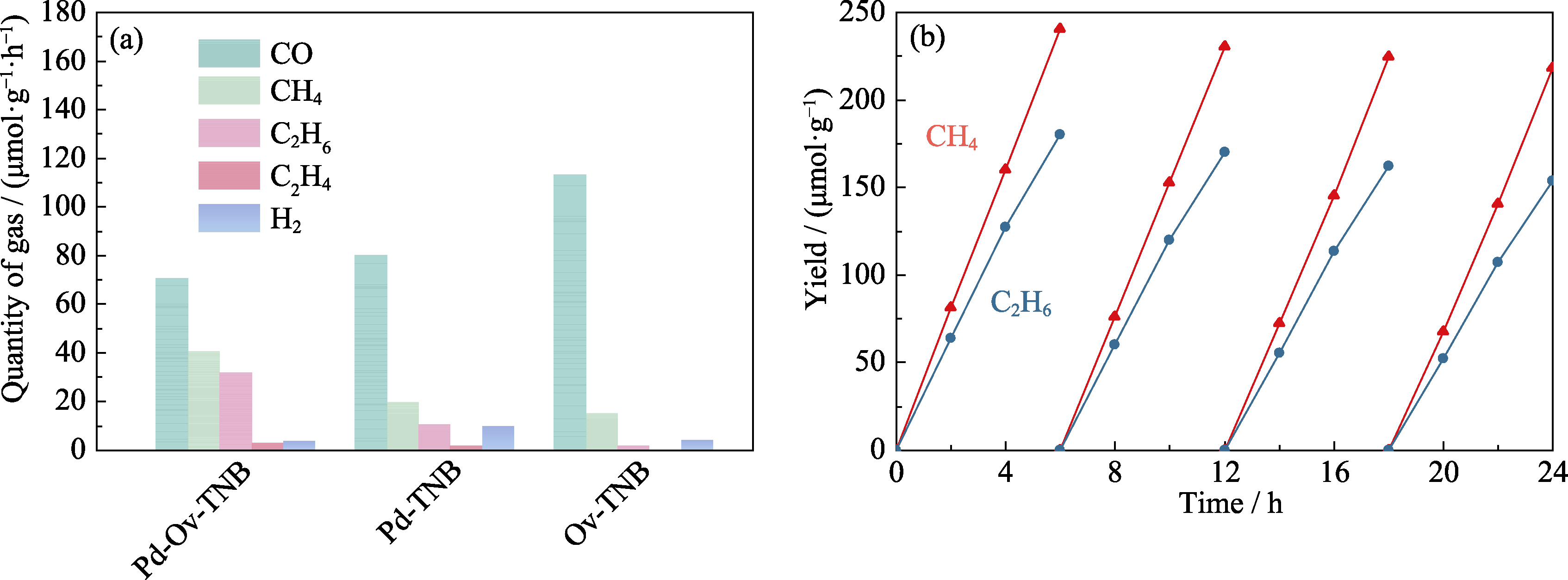
Fig. 4 (a) Photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance of Pd-Ov-TNB, Ov-TNB and Pd-TNB and (b) recycling curves of Pd-Ov-TNB for photocatalytic CO2 reduction Colorful figures are available on website
| Photocatalyst | Productivity/(μmol·g-1·h-1) | Selectivity for hydrocarbon products/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | CH4 | C2H6 | C2H4 | H2 | ||
| Pd-Ov-TNB | 70.7 | 40.8 | 32.09 | 3.09 | 3.69 | 84.52 |
| Pd-TNB | 80.21 | 19.92 | 10.71 | 2.02 | 10.04 | 64.88 |
| Ov-TNB | 113.58 | 15.32 | 2.071 | 0 | 4.25 | 39.14 |
Table 1 Activities and selectivities for photocatalytic reduction of CO2 over the obtained samples
| Photocatalyst | Productivity/(μmol·g-1·h-1) | Selectivity for hydrocarbon products/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | CH4 | C2H6 | C2H4 | H2 | ||
| Pd-Ov-TNB | 70.7 | 40.8 | 32.09 | 3.09 | 3.69 | 84.52 |
| Pd-TNB | 80.21 | 19.92 | 10.71 | 2.02 | 10.04 | 64.88 |
| Ov-TNB | 113.58 | 15.32 | 2.071 | 0 | 4.25 | 39.14 |
| Photocatalyst | Productivity / (μmol·g-1·h-1) | Selectivity for hydrocarbon products/% | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | CH4 | C2H6 | C2H4 | H2 | |||
| Pd-Ov-TNB | 70.7 | 40.8 | 32.09 | 3.087 | 3.69 | 84.52 | This work |
| 1%Ru-TiO2-x | 5.06 | 31.36 | - | - | - | 96.12 | [ |
| In-TiO2 | 81 | 244 | 2.78 | 0.06 | - | 92.48 | [ |
| In-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 2.32 | 7.31 | - | 1.41 | - | 94.20 | [ |
| Au6Pd1/TiO2 | 10.9 | 12.7 | 0.8 | 0.7 | - | 84.75 | [ |
| Cuδ+/CeO2-TiO2 | 3.47 | 1.52 | - | 4.51 | - | 90.52 | [ |
| Pd/Mn-TiO2 | 17.88 | 5.51 | 1.32 | - | - | 55.21 | [ |
| PdNRs-TiO2 | 12.6 | 3.0 | - | - | 8.826 | 35.90 | [ |
| Ti3C2/P25 | 11.74 | 16.61 | - | - | 35.0 | 58.70 | [ |
| ZXN-TC | 1296.4 | 98.11 | 41.07 | 2.25 | - | 34.85 | [ |
Table 2 Photocatalytic performance of CO2 reduction of photocatalysts in literature
| Photocatalyst | Productivity / (μmol·g-1·h-1) | Selectivity for hydrocarbon products/% | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | CH4 | C2H6 | C2H4 | H2 | |||
| Pd-Ov-TNB | 70.7 | 40.8 | 32.09 | 3.087 | 3.69 | 84.52 | This work |
| 1%Ru-TiO2-x | 5.06 | 31.36 | - | - | - | 96.12 | [ |
| In-TiO2 | 81 | 244 | 2.78 | 0.06 | - | 92.48 | [ |
| In-TiO2/g-C3N4 | 2.32 | 7.31 | - | 1.41 | - | 94.20 | [ |
| Au6Pd1/TiO2 | 10.9 | 12.7 | 0.8 | 0.7 | - | 84.75 | [ |
| Cuδ+/CeO2-TiO2 | 3.47 | 1.52 | - | 4.51 | - | 90.52 | [ |
| Pd/Mn-TiO2 | 17.88 | 5.51 | 1.32 | - | - | 55.21 | [ |
| PdNRs-TiO2 | 12.6 | 3.0 | - | - | 8.826 | 35.90 | [ |
| Ti3C2/P25 | 11.74 | 16.61 | - | - | 35.0 | 58.70 | [ |
| ZXN-TC | 1296.4 | 98.11 | 41.07 | 2.25 | - | 34.85 | [ |
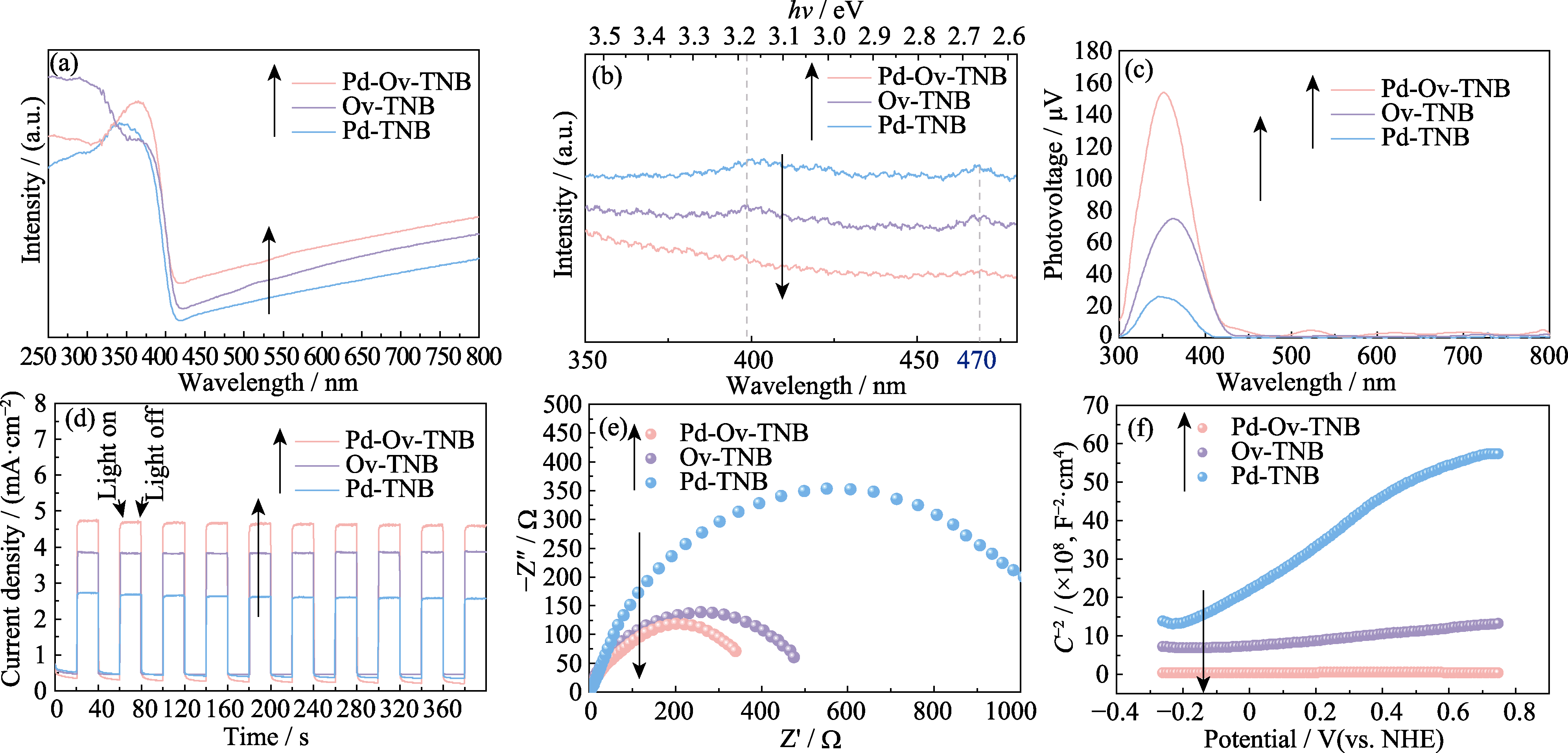
Fig. 5 (a) UV-Vis DRS spectra, (b) PL emission spectra, (c) SPV spectra, (d) I-t curves, (e) EIS plots, and (f) Mott-Schottky plots of Pd-Ov-TNB, Ov-TNB and Pd-TNB
| [1] |
SHEN Q Q, XUE J B, LI Y, et al. Construction of CdSe polymorphic junctions with coherent interface for enhanced photoelectrocatalytic hydrogen generation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 282: 119552.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LI C J, XUE Y, ZHOU X X, et al. BiZnx/Si photocathode: preparation and CO2 reduction performance. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1093.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
XU S Z, CARTER E A. Theoretical insights into heterogeneous (photo) electrochemical CO2 reduction. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(11): 6631.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
PANG Q H, LIAO G F, HU X Y, et al. Porous bamboo charcoal/ TiO2 nanocomposites: preparation and photocatalytic property. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 219.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
HAO L, HUANG H W, ZHANG Y H, et al. Oxygen vacant semiconductor photocatalysts. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(25): 2100919.
DOI URL |
| [6] | VERBRUGGEN A W, MASSCHAELE K, MOORTGAT E, et al. Factors driving the activity of commercial titanium dioxide powders towards gas phase photocatalytic oxidation of acetaldehyde. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2012, 2: 2311. |
| [7] |
KERI Q, KOCSIS E, KARAJZ D A, et al. Photocatalytic crystalline and amorphous TiO2 nanotubes prepared by electrospinning and atomic layer deposition. Molecules, 2021, 26(19): 5917.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
BUNSHO O, YOSHIMASA O, SEIICHI N. Photocatalytic activity of amorphous anatase mixture of titanium(IV) oxide particles suspended in aqueous solutions. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1997, 101(19): 3746.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
BELLARDITA M, PAOLA A D, MEGNA B, et al. Absolute crystallinity and photocatalytic activity of brookite TiO2 samples. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 201: 150.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WANG S Q, ZHANG Z L, HUO W Y, et al. Preferentially oriented Ag-TiO2 nanotube array film: an efficient visible-light-driven photocatalyst. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 399: 123016.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
DENG Z S, JI J H, XING M Y, et al. The role of oxygen defects in metal oxides for CO2 reduction. Nanoscale Advances, 2020, 2: 4986.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
JIANG W B, LOH H Y, LOW B Q L, et al. Role of oxygen vacancy in metal oxides for photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2023, 321: 122079.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
JI Y F, LUO Y. New mechanism for photocatalytic reduction of CO2 on the anatase TiO2(101) surface: the essential role of oxygen vacancy. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(49): 15896.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZHANG T, LOW J X, YU J G, et al. A blinking mesoporous TiO2-x composed of nanosized anatase with unusually long-lived trapped charge carriers. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(35): 15000.
DOI URL |
| [15] | GAO J Q, SHEN Q Q, GUAN R F, et al. Oxygen vacancy self- doped black TiO2 nanotube arrays by aluminothermic reduction for photocatalytic CO2 reduction under visible light illumination. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2020, 35: 205. |
| [16] | GAO J Q, XUE J B, JIA S F, et al. Self-doping surface oxygen vacancy-induced lattice strains for enhancing visible light-driven photocatalytic H2 evolution over black TiO2. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(16): 18758. |
| [17] |
WANG Y Y, QU Y, QU B H, et al. Construction of six-oxygen- coordinated single Ni sites on g-C3N4 with boron-oxo species for photocatalytic water-activation-induced CO2 reduction. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(48): 2105482.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG Z Q, ZHU J C, ZU X L, et al. Selective CO2 photoreduction to CH4 via Pdδ+-assisted hydrodeoxygenation over CeO2 nanosheets. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(30): e202203249.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHANG W J, SHEN Q Q, XUE J B, et al. Preparation and photoelectrochemical water oxidation of hematite nanobelts containing highly ordered oxygen vacancies. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1290.
DOI |
| [20] |
WANG L L, YANG T, PENG L J, et al. Dual transfer channels of photo-carriers in 2D/2D/2D sandwich-like ZnIn2S4/g-C3N4/Ti3C2 MXene S-scheme/Schottky heterojunction for boosting photocatalytic H2 evolution. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2022, 43: 2720.
DOI URL |
| [21] | CAI S C, CHEN J, LI Q, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction with photothermal effect by cooperative effect of oxygen vacancy and Au cocatalyst. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(12): 14221. |
| [22] |
XIANG Q J, LÜ K L, YU J G. Pivotal role of fluorine in enhanced photocatalytic activity of anatase TiO2 nanosheets with dominant (001) facets for the photocatalytic degradation of acetone in air. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2010, 96(3/4): 557.
DOI URL |
| [23] | MANIVANNAN S, AN S, JEONG J, et al. Hematite/M (M=Au, Pd) catalysts derived from a double-hollow Prussian blue microstructure: simultaneous catalytic reduction of o- and p-nitrophenols. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(15): 17557. |
| [24] |
ZHOU Y M, ZHANG Q X, SHI X L, et al. Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into CH4 over Ru-doped TiO2: synergy of Ru and oxygen vacancies. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 608: 2809.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
TAHIR M, AMIN N S. Indium-doped TiO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic CO2 reduction with H2O vapors to CH4. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 162: 98.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
PARK J, LIU H, PIAO G X, et al. Synergistic conversion of CO2 into C1 and C2 gases using hybrid In-doped TiO2 and g-C3N4 photocatalysts. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 437: 135388.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
CHEN Q, CHEN X J, FANG M L, et al. Photo-induced Au-Pd alloying at TiO2 {101} facets enables robust CO2 photocatalytic reduction into hydrocarbon fuels. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7: 1334.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WANG T, CHEN L, CHEN C, et al. Engineering catalytic interfaces in Cuδ+/CeO2-TiO2 photocatalysts forsynergistically boosting CO2 reduction to ethylene. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(2): 2306.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
CAO C, YAN Y B, YU Y L, et al. Modification of Pd and Mn on the surface of TiO2 with enhanced photocatalytic activity for photoreduction of CO2 into CH4. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(1): 270.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZHU Y Z, XU Z X, JIANG W Y, et al. Engineering on the edge of Pd nanosheet cocatalysts for enhanced photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to fuels. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5: 2619.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
YE M H, WANG X, LIU E Z, et al. Boosting the photocatalytic activity of P25 for carbon dioxide reduction by using a surface- alkalinized titanium carbide MXene as cocatalyst. ChemSusChem, 2018, 11(10): 1606.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
NI B X, JIANG H, GUO W Y, et al. Tailoring the oxidation state of metallic TiO through Ti3+/Ti2+ regulation for photocatalytic conversion of CO2 to C2H6. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 307: 121141.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ASCHAUER U, PFENNINGER R, SELBACH S M, et al. Strain- controlled oxygen vacancy formation and ordering in CaMnO3. Physical Review B, 2013, 88(5): 054111.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
LIU Q Q, HE X D, PENG J J, et al. Hot-electron-assisted S- scheme heterojunction of tungsten oxide/graphitic carbon nitride for broad-spectrum photocatalytic H2 generation. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2021, 42(9): 1478.
DOI URL |
| [35] | YANG T, DENG P K, WANG L L, et al. Simultaneous photocatalytic oxygen production and hexavalent chromium reduction in Ag3PO4/C3N4 S-scheme heterojunction. Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry, 2022, 41(6): 2206023. |
| [1] | LI Yuejun, CAO Tieping, SUN Dawei. Bi4O5Br2/CeO2 Composite with S-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and CO2 Reduction Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 963-970. |
| [2] | GAO Wa, XIONG Yujie, WU Congping, ZHOU Yong, ZOU Zhigang. Recent Progress on Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction with Ultrathin Nanostructures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 3-14. |
| [3] | ZHANG Wenjin, SHEN Qianqian, XUE Jinbo, LI Qi, LIU Xuguang, JIA Husheng. Preparation and Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation of Hematite Nanobelts Containing Highly Ordered Oxygen Vacancies [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1290-1296. |
| [4] | WU Fan, ZHAO Ziyan, LI Bangxin, DONG Fan, ZHOU Ying. Interfacial Oxygen Vacancy of Bi2O2CO3/PPy and its Visible-light Photocatalytic NO Oxidation Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 541-548. |
| [5] | LU Qing, HUA Luo-Guang, CHEN Yi-Lin, GAO Bi-Fen, LIN Bi-Zhou. Preparation and Property of Oxygen-deficient Bi2WO6-x Photocatalyst Active in Visible Light [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(4): 413-419. |
| [6] | ZHAO Qian, WU Ping. Ferromagnetism Induced by Defects in Cr-doped TiO2 Nanopowders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(10): 1098-1102. |
| [7] | ZHOU Zhi-Gang,TANG Zi-Long. Chemistry and Physics of Point Defects in Advanced Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(3): 417-426. |
| [8] | LI Bao-Shan,ZHU Zhi-Gang,LI Guo-Rong,YIN Qing-Rui,DING Ai-Li. Sintering Behavior of PMnN-PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2005, 20(4): 993-999. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||