
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (9): 991-1004.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230105
Special Issue: 【能源环境】钙钛矿(202312); 【能源环境】太阳能电池(202312)
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Yu1,2( ), LIN Puan1,2, CAI Bing2(
), LIN Puan1,2, CAI Bing2( ), ZHANG Wenhua1,2(
), ZHANG Wenhua1,2( )
)
Received:2023-03-02
Revised:2023-05-30
Published:2023-09-20
Online:2023-06-16
Contact:
CAI Bing, PhD. E-mail: bingcai@caep.cn;About author:CHEN Yu (1993-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: 434980565@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
CHEN Yu, LIN Puan, CAI Bing, ZHANG Wenhua. Research Progress of Inorganic Hole Transport Materials in Perovskite Solar Cells[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 991-1004.
| Material | Hole concentration, N/cm-3 | Hole mobility, μ/(cm2·V-1·s-1) | Conductivity, σ/(S·cm-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sprio-OMeTAD with Li-TFSI, etc. | 7.13×1015[ | 0.779[ | 1.53×10-3[ |
| NiO | 5.3×1018[ | 0.12[ | 1.66×10-4[ |
| Cu:NiO | 7.3×1019[ | ~0.2[ | 1.25×10-3[ |
| Ni0.8Li0.05Mg0.15O | 6.46×1018[ | - | 2.23×10-3[ |
| CuGaO2 | 3.098×1019[ | - | 4.625×10-3[ |
| Zn:CuGaO2 | 1.328×1020[ | - | 1.39×10-2[ |
| CuCrO2 | - | 0.1-1.0[ | 2.9×10-2[ |
| In:CuCrO2 | 7.1×1018[ | 0.75[ | 6.9×10-2[ |
| CuScO2 | - | - | 2.11×10-3[ |
| CuSCN | - | 1.2×10-3[ | - |
| Co3O4 | - | 1.49×10-2[ | - |
| Co3O4-SrCO3 | - | 6.33×10-2[ | - |
Table 1 Properties of inorganic hole transport materials (Spiro-OMeTAD for comparison)
| Material | Hole concentration, N/cm-3 | Hole mobility, μ/(cm2·V-1·s-1) | Conductivity, σ/(S·cm-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sprio-OMeTAD with Li-TFSI, etc. | 7.13×1015[ | 0.779[ | 1.53×10-3[ |
| NiO | 5.3×1018[ | 0.12[ | 1.66×10-4[ |
| Cu:NiO | 7.3×1019[ | ~0.2[ | 1.25×10-3[ |
| Ni0.8Li0.05Mg0.15O | 6.46×1018[ | - | 2.23×10-3[ |
| CuGaO2 | 3.098×1019[ | - | 4.625×10-3[ |
| Zn:CuGaO2 | 1.328×1020[ | - | 1.39×10-2[ |
| CuCrO2 | - | 0.1-1.0[ | 2.9×10-2[ |
| In:CuCrO2 | 7.1×1018[ | 0.75[ | 6.9×10-2[ |
| CuScO2 | - | - | 2.11×10-3[ |
| CuSCN | - | 1.2×10-3[ | - |
| Co3O4 | - | 1.49×10-2[ | - |
| Co3O4-SrCO3 | - | 6.33×10-2[ | - |
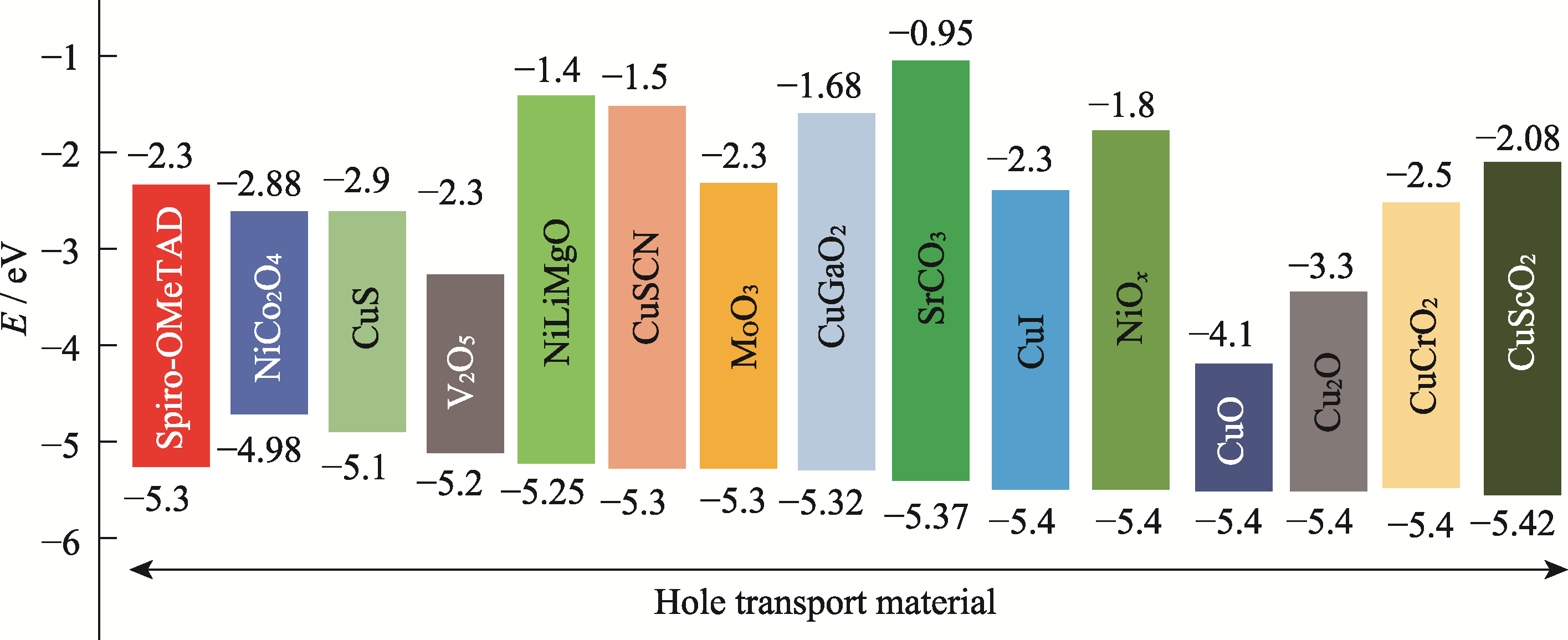
Fig. 2 Highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) (or valence-band) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) (or conduction-band) energy levels relative to the vacuum of representative inorganic hole transport materials (HOMO and LUMO of Spiro-OMeTAD for comparison)[18]

Fig. 3 Physical morphology, synthesis process and related properties of nickel-based oxide materials (a) Comparison of conductivity mapping results for NiO (left) and Li0.05Mg0.15Ni0.8O (right) films[21]; (b) J-V curve of NiOx-based PSCs with molecular doping of F6TCNNQ[34]; (c) Synthetic process of the SRE NiOx (top), Ni species changed with different synthetic processes (bottom-left) and spectrum changes in Ni species caused by SRE (bottom-right), and (d) champion J-V curves of PSCs[35]; (e) Schematic diagram of synthesis process and (f) high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of NiCo2O4 nanocrystals, as well as (g) J-V curves of the champion PSCs[37]. Colorful figures are available on website

Fig. 4 Morphology and related properties of copper-based oxide materials (a) Cross-sectional SEM image and (b) stability performance of the device with different HTL (Spiro-OMeTAD and Cu2O)[26]; (c) Preparation technology, device structure, energy level diagram and (d) J-V curves of Cu2O and CuO films[40]; (e) TEM image of CuGaO2 nanocrystals and (f) stability of the device[45]; (g) J-V curves, structure diagram (PC61BM: [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester) and (h) stability of device based on mp-CuGaO2[39]; (i) Schematic diagram of nanocrystalline structure and (j) stability of devices based on CuCrO2[46]; (k) TEM image of CuScO2 nanocrystals and (l) J-V curves of PSCs[28]. Colorful figures are available on website
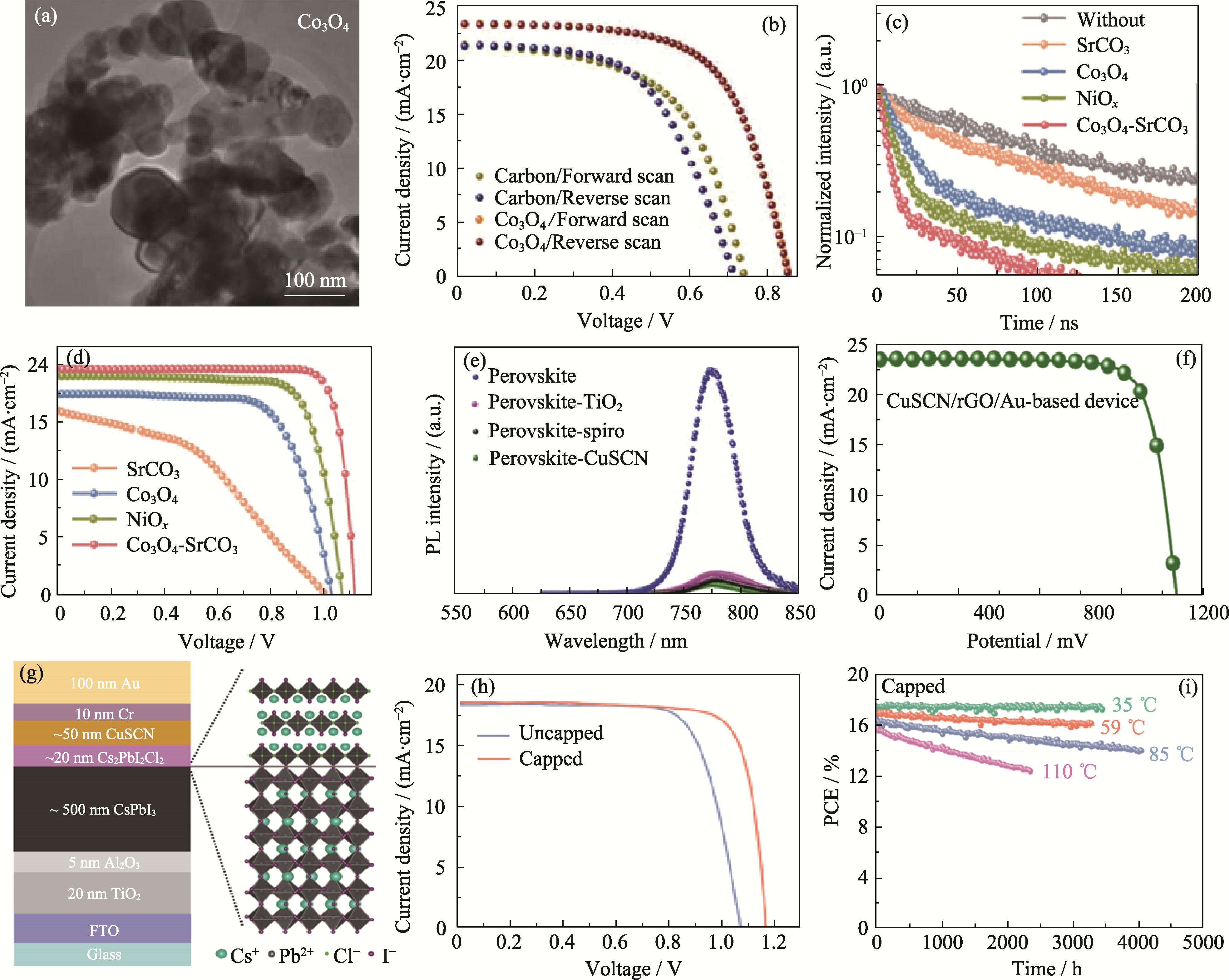
Fig. 5 Physical morphology and related properties of other oxides and non-oxides (a) High-resolution TEM image of Co3O4 and (b) J-V curves of PSCs[47]; (c) Time-resolved photoluminescence (TRPL) spectra and (d) J-V curves of PSCs based on Co3O4-SrCO3[50]; (e) PL absorption spectra and (f) J-V curve of PSCs based on CuSCN HTL[16]; (g) Diagram of device structure, (h) J-V curves and (i) light stability of capped PSCs (under constant illumination and different temperature) based on CuSCN HTL and 2D Cs2PbI2Cl2 capping layers[55]
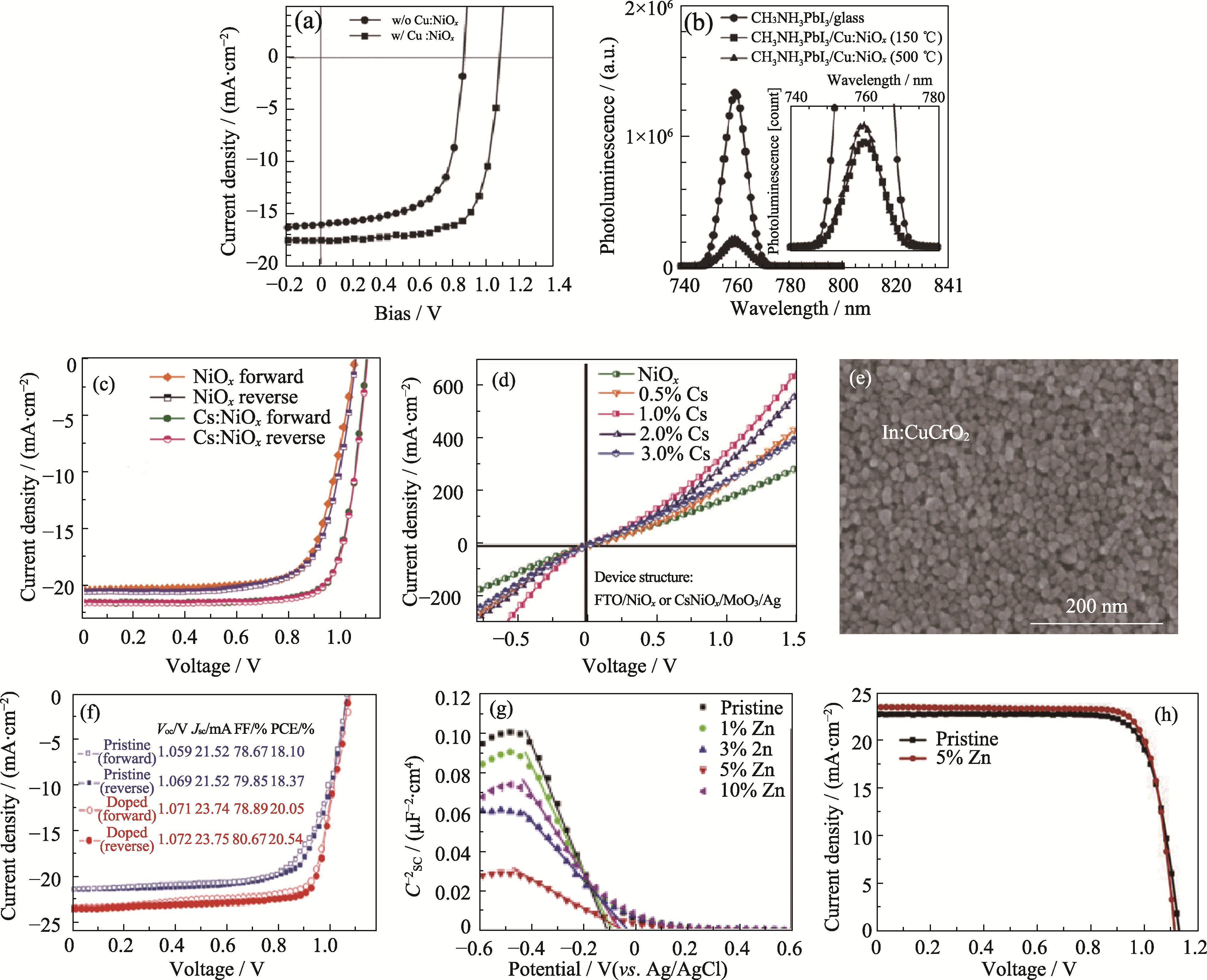
Fig. 6 Effect of element doping on device performance (a) J-V curves and (b) PL spectra of PSCs based on Cu:NiOx HTL[23]; (c) J-V curves of PSCs and (d) electrical conductivity of Cs:NiOx film[27]; (e) SEM image of In doped CuCrO2 film and (f) J-V curves of PSCs[57]; (g) Mott-Schottky curves and (h) J-V curves of PSCs based on the Zn doped CuGaO2[25]
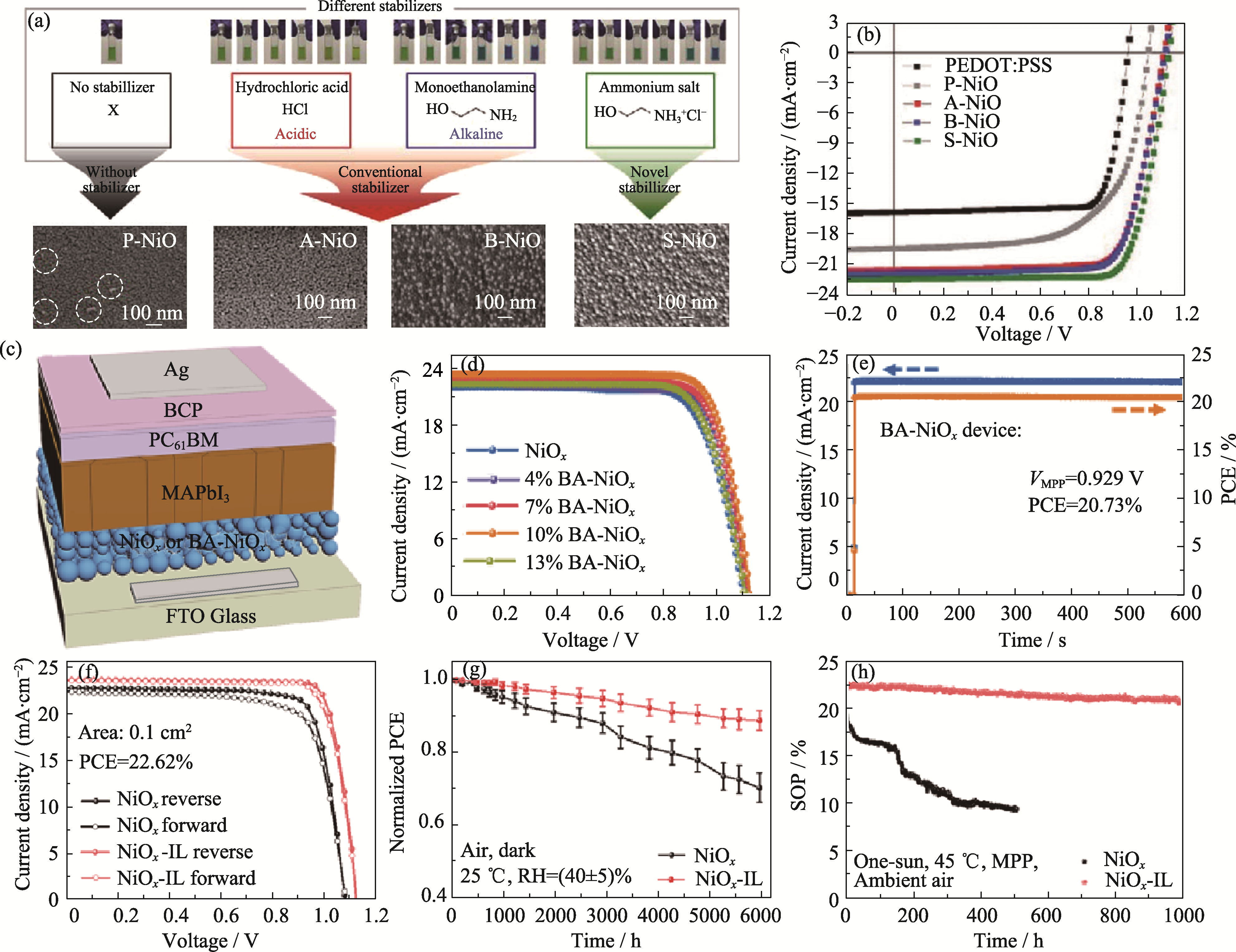
Fig. 7 Effect of additive engineering on device performance (a) SEM images of NiO film with different ammonium stabilizers and different concentrations and (b) J-V curves of PSCs[30]; (c) Schematic structure, (d) J-V curves and (e) I-t curves of PSCs based on NiO film with boric acid[59]; (f) J-V curves, (g) long-term stability and (h) maximum power output stability of PSCs based on ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of NiO NPs[60]; BCP: Bathocuproin; VMPP: Output voltage at maximum power. Colorful figures are available on website
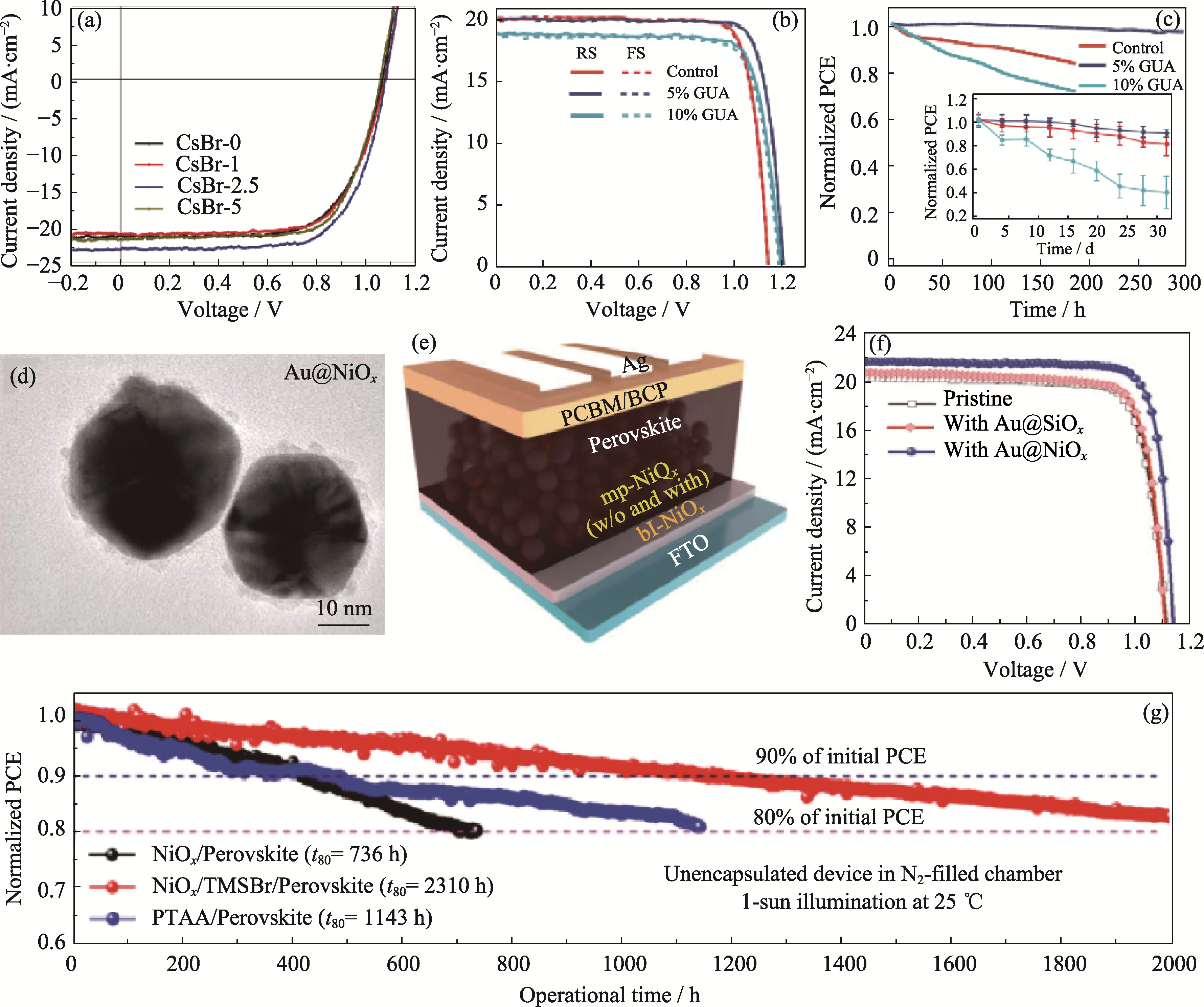
Fig. 8 Effect of interface engineering on device performance (a) J-V curves of devices based on surface modification with different concentrations of CsBr, and stability of PSCs[63]; (b) J-V curves and (c) MPP stability of PSCs based on GUAI surface modification at different concentrations (in molar) with inset showing environmental stability[64]; (d) High-resolution TEM images of Au@NiOx NPs, (e) corresponding structure diagram and (f) J-V curves of PSCs[65]; (g) MPP stability of devices with TMSBr surface modification[66]; CsBr-2.5: 2.5 mg/mL CsBr; RS: reverse scan; FS: forward scan; T80: the time maintaining 80% initial PCE. Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] | The National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Best research cell efficiency chart[2023-06-05]. https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cellefficiency.html. |
| [2] |
MENG W, ZHANG K, OSVET A, et al. Revealing the strain- associated physical mechanisms impacting the performance and stability of perovskite solar cells. Joule, 2022, 6(2): 458.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN R, ZHANG W, GUAN X, et al. Rear electrode materials for perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(26): 2200651.
DOI URL |
| [4] | NAZIR G, LEE S Y, LEE J H, et al. Stabilization of perovskite solar cells: recent developments and future perspectives. Adv. Mater., 2022, 34(50): e2204380. |
| [5] |
BING J, CARO L G, TALATHI H P, et al. Perovskite solar cells for building integrated photovoltaics-glazing applications. Joule, 2022, 6(7): 1446.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
PARK H H. Efficient and stable perovskite solar cells based on inorganic hole transport materials. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(1): 112.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHANG X, ZHANG H, LI Y, et al. Recent progress in hole-transporting layers of conventional organic solar cells with p-i-n structure. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(44): 2205398.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CAI B, XING Y, YANG Z, et al. High performance hybrid solar cells sensitized by organolead halide perovskites. Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6(5): 1480.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHANG T, WANG F, KIM H B, et al. Ion-modulated radical doping of Spiro-OMeTAD for more efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Science, 2022, 377(6605): 495.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
CHEN Y, WANG Q, TANG W, et al. Heterocyclic amino acid molecule as a multifunctional interfacial bridge for improving the efficiency and stability of quadruple cation perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy, 2023, 107: 108154.
DOI URL |
| [11] | GAO D, LI B, LI Z, et al. Highly efficient flexible perovskite solar cells through pentylammonium acetate modification with certified efficiency of 23.35%. Adv. Mater., 2023, 35(3): e2206387. |
| [12] |
LI Z, LI B, WU X, et al. Organometallic-functionalized interfaces for highly efficient inverted perovskite solar cells. Science, 2022, 376(6591): 416.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
NGUYEN W H, BAILIE C D, UNGER E L, et al. Enhancing the hole-conductivity of Spiro-OMeTAD without oxygen or lithium salts by using Spiro(TFSI)2 in perovskite and dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(31): 10996.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZAI H, MA Y, CHEN Q, et al. Ion migration in halide perovskite solar cells: mechanism, characterization, impact and suppression. J. Energy Chem., 2021, 63: 528.
DOI |
| [15] |
LUO X, LIN X, GAO F, et al. Recent progress in perovskite solar cells: from device to commercialization. Sci. China Chem., 2022, 65(12): 2369.
DOI |
| [16] |
ARORA N, DAR M I, HINDERHOFER A, et al. Perovskite solar cells with CuSCN hole extraction layers yield stabilized efficiencies greater than 20%. Science, 2017, 358(6364): 768.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
LEE J H, JIN I S, NOH Y W, et al. A solution-processed spinel CuCo2O4 as an effective hole transport layer for efficient perovskite solar cells with negligible hysteresis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2019, 7(21): 17661.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG Q, LIN Z, SU J, et al. Recent progress of inorganic hole transport materials for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Nano Select, 2021, 2(6): 1055.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LIU J, PATHAK S K, SAKAI N, et al. Identification and mitigation of a critical interfacial instability in perovskite solar cells employing copper thiocyanate hole-transporter. Adv. Mater. Interf., 2016, 3(22): 1600571.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
CHEN W Y, JENG J S, HUANG K L, et al. Modulation of Ni valence in p-type NiO films via substitution of Ni by Cu. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A, 2013, 31(2): 021501.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
CHEN W, WU Y, YUE Y, et al. Efficient and stable large-area perovskite solar cells with inorganic charge extraction layers. Science, 2015, 350(6263): 944.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
EUVRARD J, YAN Y, MITZI D B. Electrical doping in halide perovskites. Nat. Rev. Mater., 2021, 6(6): 531.
DOI |
| [23] |
JUNG J W, CHUEH C C, JEN A K Y. A low-temperature, solution- processable, Cu-doped nickel oxide hole-transporting layer via the combustion method for high-performance thin-film perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(47): 7874.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
BOYD C C, SHALLCROSS R C, MOOT T, et al. Overcoming redox reactions at perovskite-nickel oxide interfaces to boost voltages in perovskite solar cells. Joule, 2020, 4(8): 1759.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
CHEN Y, YANG Z, JIA X, et al. Thermally stable methylammonium- free inverted perovskite solar cells with Zn2+ doped CuGaO2 as efficient mesoporous hole-transporting layer. Nano Energy, 2019, 61: 148.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
NEJAND B A, AHMADI V, GHARIBZADEH S, et al. Cuprous oxide as a potential low-cost hole-transport material for stable perovskite solar cells. ChemSusChem, 2016, 9(3): 302.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
CHEN W, LIU F Z, FENG X Y, et al. Cesium doped NiOx as an efficient hole extraction layer for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, 7(19): 1700722.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
CHEN Y, SHEN Y, TANG W, et al. Ion compensation of buried interface enables highly efficient and stable inverted MA-free perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(44): 2206703.
DOI URL |
| [29] | CHEN Y, YANG Z, WANG S, et al. Design of an inorganic mesoporous hole-transporting layer for highly efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(52): e1805660. |
| [30] |
PARK S, KIM D W, PARK S Y. Improved stability and efficiency of inverted perovskite solar cell by employing nickel oxide hole transporting material containing ammonium salt stabilizer. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(28): 2200437.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
JENG J Y, CHEN K C, CHIANG T Y, et al. Nickel oxide electrode interlayer in CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite/PCBM planar-heterojunction hybrid solar cells. Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(24): 4107.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZHU Z, BAI Y, ZHANG T, et al. High-performance hole-extraction layer of Sol-Gel-processed NiO nanocrystals for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(46): 12571.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
CHEN W, WU Y, LIU J, et al. Hybrid interfacial layer leads to solid performance improvement of inverted perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci., 2015, 8(2): 629.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
CHEN W, ZHOU Y, WANG L, et al. Molecule-doped nickel oxide: verified charge transfer and planar inverted mixed cation perovskite solar cell. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(20): 1800515.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
DU M, ZHAO S, DUAN L, et al. Surface redox engineering of vacuum-deposited NiOx for top-performance perovskite solar cells and modules. Joule, 2022, 6(8): 1931.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ZHANG Y, LI C, BI E, et al. Efficient inverted perovskite solar cells with a low-dimensional halide/perovskite heterostructure. Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(48): 2202191.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
OUYANG D, XIAO J, YE F, et al. Strategic synthesis of ultrasmall NiCo2O4 NPs as hole transport layer for highly efficient perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(16): 1702722.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
JING X, ZHANG Z, CHEN T, et al. Review of inorganic hole transport materials for perovskite solar cells. Energy Technol., 2023, 11(2): 2201005.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
BIDIKOUDI M, KYMAKIS E. Novel approaches and scalability prospects of copper based hole transporting materials for planar perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2019, 7(44): 13680.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ZUO C, DING L. Solution-processed Cu2O and CuO as hole transport materials for efficient perovskite solar cells. Small, 2015, 11(41): 5528.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
SUN W, LI Y, YE S, et al. High-performance inverted planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells based on a solution-processed CuOx hole transport layer. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(20): 10806.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
SCANLON D O, WALSH A. Polymorph engineering of CuMO2 (M = Al, Ga, Sc, Y) semiconductors for solar energy applications: from delafossite to wurtzite. Acta Crystallogr. B, 2015, 71(6): 702.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
XIONG D, XU Z, ZENG X, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of ultrasmall CuCrO2 nanocrystal alternatives to NiO nanoparticles in efficient p-type dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(47): 24760.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
ROBERTSON J, PEACOCK P W, TOWLER M D, et al. Electronic structure of p-type conducting transparent oxides. Thin Solid Films, 2002, 411(1): 96.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
ZHANG H, WANG H, CHEN W, et al. CuGaO2: a promising inorganic hole-transporting material for highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(8): 1604984.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
ZHANG H, WANG H, ZHU H, et al. Low-temperature solution- processed CuCrO2 hole-transporting layer for efficient and photostable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(13): 1702762.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
BASHIR A, SHUKLA S, LEW J H, et al. Spinel Co3O4 nanomaterials for efficient and stable large area carbon-based printed perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(5): 2341.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
TSENG Z L, CHEN L C, CHIANG C H, et al. Efficient inverted-type perovskite solar cells using UV-ozone treated MoOx and WOx as hole transporting layers. Sol. Energy, 2016, 139: 484.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
CHENG M, LI Y, SAFDARI M, et al. Efficient perovskite solar cells based on a solution processable nickel(II) phthalocyanine and vanadium oxide integrated hole transport layer. Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, 7(14): 1602556.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
GE B, ZHOU Z R, WU X F, et al. Self-organized Co3O4-SrCO3 percolative composites enabling nanosized hole transport pathways for perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(46): 2106121.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
CHRISTIANS J A, FUNG R C M, KAMAT P V. An inorganic hole conductor for organo-lead halide perovskite solar cells. Improved hole conductivity with copper iodide. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(2): 758.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
SUN W, YE S, RAO H, et al. Room-temperature and solution- processed copper iodide as the hole transport layer for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(35): 15954.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
RAO H, SUN W, YE S, et al. Solution-processed CuS NPs as an inorganic hole-selective contact material for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2016, 8(12): 7800.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
WIJEYASINGHE N, ANTHOPOULOS T D. Copper(I) thiocyanate (CuSCN) as a hole-transport material for large-area opto/electronics. Semicond. Sci. Tech., 2015, 30(10): 104002.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
ZHAO X, LIU T, BURLINGAME Q C, et al. Accelerated aging of all-inorganic, interface-stabilized perovskite solar cells. Science, 2022, 377(6603): 307.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
CHEN W, WU Y, FAN J, et al. Understanding the doping effect on NiO: toward high-performance inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(19): 1703519.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
YANG B, OUYANG D, HUANG Z, et al. Multifunctional synthesis approach of In:CuCrO2 nanoparticles for hole transport layer in high-performance perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29(34): 1902600.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
HUYNH U N, LIU Y, CHANANA A, et al. Transient quantum beatings of trions in hybrid organic tri-iodine perovskite single crystal. Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1): 1428.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
GE B, LIN Z Q, ZHOU Z R, et al. Boric acid mediated formation and doping of NiOx layers for perovskite solar cells with efficiency over 21%. Sol. RRL, 2021, 5(4): 2000810.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
WANG S, LI Y, YANG J, et al. Critical role of removing impurities in nickel oxide on high-efficiency and long-term stability of inverted perovskite solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2022, 61(18): e202116534.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
CHEN J, PARK N G. Materials and methods for interface engineering toward stable and efficient perovskite solar cells. ACS Energy Lett., 2020, 5(8): 2742.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
GAO Z W, WANG Y, CHOY W C H. Buried interface modification in perovskite solar cells: a materials perspective. Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(20): 2104030.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
ZHANG B, SU J, GUO X, et al. NiO/perovskite heterojunction contact engineering for highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Adv. Sci., 2020, 7(11): 1903044.
DOI URL |
| [64] | CHEN B, CHEN H, HOU Y, et al. Passivation of the buried interface via preferential crystallization of 2D perovskite on metal oxide transport layers. Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(41): e2103394. |
| [65] |
LIU Z, LI Q, CHEN K, et al. Tailoring carrier dynamics in inverted mesoporous perovskite solar cells with interface-engineered plasmonics. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9(4): 2394.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
WU T, ONO L K, YOSHIOKA R, et al. Elimination of light- induced degradation at the nickel oxide-perovskite heterojunction by aprotic sulfonium layers towards long-term operationally stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci., 2022, 15(11): 4612.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
LI C, WANG X, BI E, et al. Rational design of Lewis base molecules for stable and efficient inverted perovskite solar cells. Science, 2023, 379(6633): 690.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | ZHANG Yuchen, LU Zhiyao, HE Xiaodong, SONG Guangping, ZHU Chuncheng, ZHENG Yongting, BAI Yuelei. Predictions of Phase Stability and Properties of S-group Elements Containing MAX Borides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(2): 225-232. |
| [2] | HU Mengfei, HUANG Liping, LI He, ZHANG Guojun, WU Houzheng. Research Progress on Hard Carbon Anode for Li/Na-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 32-44. |
| [3] | KE Xin, XIE Bingqing, WANG Zhong, ZHANG Jingguo, WANG Jianwei, LI Zhanrong, HE Huijun, WANG Limin. Progress of Interconnect Materials in the Third-generation Semiconductor and Their Low-temperature Sintering of Copper Nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 17-31. |
| [4] | DONG Siyin, TIE Shujie, YUAN Ruihan, ZHENG Xiaojia. Research Progress on Low-dimensional Halide Perovskite Direct X-ray Detectors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1017-1030. |
| [5] | FANG Wanli, SHEN Lili, LI Haiyan, CHEN Xinyu, CHEN Zongqi, SHOU Chunhui, ZHAO Bin, YANG Songwang. Effect of Film Formation Processes of NiOx Mesoporous Layer on Performance of Perovskite Solar Cells with Carbon Electrodes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1103-1109. |
| [6] | ZHANG Lun, LYU Mei, ZHU Jun. Research Progress of Cs2AgBiBr6 Perovskite Solar Cell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1044-1054. |
| [7] | DONG Yiman, TAN Zhan’ao. Research Progress of Recombination Layers in Two-terminal Tandem Solar Cells Based on Wide Bandgap Perovskite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1031-1043. |
| [8] | GUO Huajun, AN Shuailing, MENG Jie, REN Shuxia, WANG Wenwen, LIANG Zishang, SONG Jiayu, CHEN Hengbin, SU Hang, ZHAO Jinjin. Research Progress of Photoelectric Resistive Switching Mechanism of Halide Perovskite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1005-1016. |
| [9] | HU Zhongliang, FU Yuntian, JIANG Meng, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Thermal Stability of Nb/Mg3SbBi Interface [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 931-937. |
| [10] | LIU Jian, WANG Lingkun, XU Baoliang, ZHAO Qian, WANG Yaoxuan, DING Yi, ZHANG Shengtai, DUAN Tao. Nd-doped ZrSiO4 Ceramics: Synthesis in Molten Salt at Low Temperature, Phase Evolution and Chemical Stability [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 910-916. |
| [11] | DING Haoming, LI Mian, LI Youbing, CHEN Ke, XIAO Yukun, ZHOU Jie, TAO Quanzheng, Johanna Rosen, YIN Hang, BAI Yuelei, ZHANG Bikun, SUN Zhimei, WANG Junjie, ZHANG Yiming, HUANG Zhenying, ZHANG Peigen, SUN Zhengming, HAN Meikang, ZHAO Shuang, WANG Chenxu, HUANG Qing. Progress in Structural Tailoring and Properties of Ternary Layered Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 845-884. |
| [12] | XIAO Yani, LYU Jianan, LI Zhenming, LIU Mingyang, LIU Wei, REN Zhigang, LIU Hongjing, YANG Dongwang, YAN Yonggao. Hygrothermal Stability of Bi2Te3-based Thermoelectric Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 800-806. |
| [13] | DING Ling, JIANG Rui, TANG Zilong, YANG Yunqiong. MXene: Nanoengineering and Application as Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [14] | WANG Bo, YU Jian, LI Cuncheng, NIE Xiaolei, ZHU Wanting, WEI Ping, ZHAO Wenyu, ZHANG Qingjie. Service Stability of Gd/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 Thermo-electro-magnetic Gradient Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 663-670. |
| [15] | YANG Zhuo, LU Yong, ZHAO Qing, CHEN Jun. X-ray Diffraction Rietveld Refinement and Its Application in Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||