
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 521-528.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220627
Special Issue: 【能源环境】水体污染物去除(202309); 【信息功能】Max层状材料、MXene及其他二维材料(202309)
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Shiyi1,2( ), FENG Aihu2, LI Xiaoyan1(
), FENG Aihu2, LI Xiaoyan1( ), YU Yun2(
), YU Yun2( )
)
Received:2022-10-25
Revised:2022-12-02
Published:2023-01-11
Online:2023-01-11
Contact:
LI Xiaoyan, associate professor. E-mail: lixiaoyan@usst.edu.cn;About author:WANG Shiyi (1996-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: wsysues051115114@163.com
CLC Number:
WANG Shiyi, FENG Aihu, LI Xiaoyan, YU Yun. Pb (II) Adsorption Process of Fe3O4 Supported Ti3C2Tx[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 521-528.

Fig. 2 (a) Diagram of Ti3C2Tx MXene doped with Fe3O4; SEM images of (b)Ti3AlC2, (c)Ti3C2Tx and (d) FeMX1-1 sample; (e)Elements distributions of FeMX1-1 sample Colorful figures are available on website
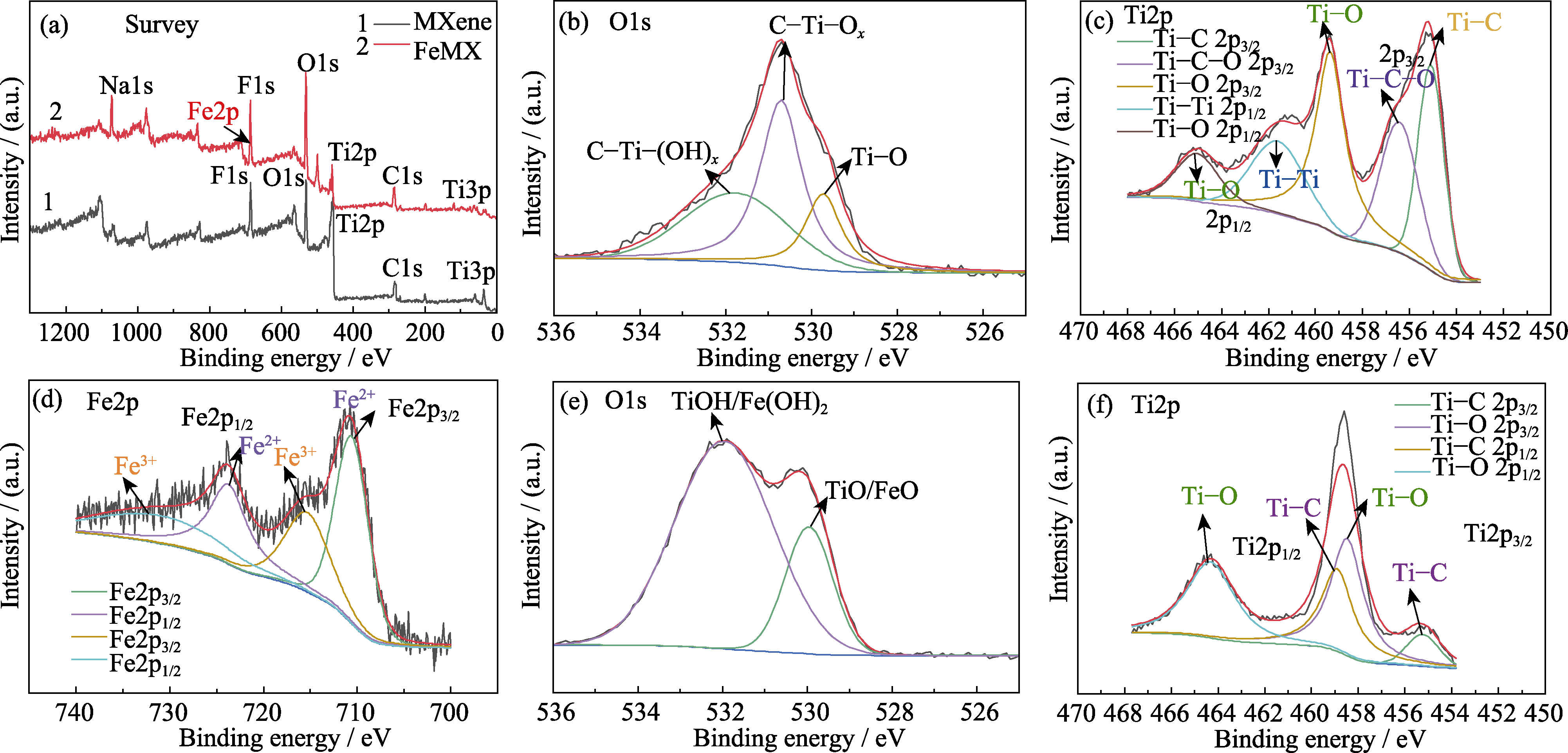
Fig. 4 (a) XPS spectra of FeMX before and after doping; (b) O1s and (c) Ti2p spectra of MXene materials; (d) Fe2p, (e) O1s and (f) Ti2p spectra of FeMX composite
| Temperature | Langmiur | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Qm/(mg·g-1) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| 30 ℃ | 0.05 | 110.54 | 0.8327 | 32.80 | 0.20 | 0.9881 |
| 40 ℃ | 0.21 | 126.04 | 0.8854 | 76.09 | 0.12 | 0.9435 |
| 50 ℃ | 0.29 | 120.24 | 0.9190 | 62.61 | 0.09 | 0.9934 |
Table 1 Fitting parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich isothermal adsorption models for Pb (II) adsorption by FeMX1-1 at different temperatures
| Temperature | Langmiur | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Qm/(mg·g-1) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| 30 ℃ | 0.05 | 110.54 | 0.8327 | 32.80 | 0.20 | 0.9881 |
| 40 ℃ | 0.21 | 126.04 | 0.8854 | 76.09 | 0.12 | 0.9435 |
| 50 ℃ | 0.29 | 120.24 | 0.9190 | 62.61 | 0.09 | 0.9934 |
| Absorbance | Langmiur | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Qm/(mg·g-1) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| MXene | 0.0177 | 110.23 | 0.86006 | 15.8026 | 0.30 | 0.9106 |
| FeMX0.5-1 | 0.1652 | 149.63 | 0.99028 | 67.9776 | 0.14 | 0.90833 |
| FeMX1-1 | 0.2781 | 126.04 | 0.88536 | 76.0907 | 0.09 | 0.94345 |
| FeMX2-1 | 0.0139 | 210.54 | 0.97478 | 22.1793 | 0.36 | 0.91117 |
Table S2 Fitting parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich isothermal adsorption models for Pb (II) adsorption by FeMX with different doping ratios
| Absorbance | Langmiur | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Qm/(mg·g-1) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| MXene | 0.0177 | 110.23 | 0.86006 | 15.8026 | 0.30 | 0.9106 |
| FeMX0.5-1 | 0.1652 | 149.63 | 0.99028 | 67.9776 | 0.14 | 0.90833 |
| FeMX1-1 | 0.2781 | 126.04 | 0.88536 | 76.0907 | 0.09 | 0.94345 |
| FeMX2-1 | 0.0139 | 210.54 | 0.97478 | 22.1793 | 0.36 | 0.91117 |
| Absorbance | Pseudo first-order reaction | Pseudo second-order reaction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min-1 | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | k2/(g·(mg·min) -1) | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | |
| MXene | 2.0966 | 104.22 | 0.98786 | 0.4378 | 108.85 | 0.99402 |
| FeMX0.5-1 | 0.6308 | 173.65 | 0.95009 | 0.0039 | 201.10 | 0.98103 |
| FeMX1-1 | 0.7447 | 148.66 | 0.90406 | 0.0053 | 171.57 | 0.95077 |
| FeMX2-1 | 1.1093 | 184.59 | 0.97027 | 0.0076 | 204.46 | 0.99135 |
Table S3 Fitting parameters of pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic adsorption models for Pb (II) adsorption by FeMX composites with different doping ratios
| Absorbance | Pseudo first-order reaction | Pseudo second-order reaction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min-1 | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | k2/(g·(mg·min) -1) | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | |
| MXene | 2.0966 | 104.22 | 0.98786 | 0.4378 | 108.85 | 0.99402 |
| FeMX0.5-1 | 0.6308 | 173.65 | 0.95009 | 0.0039 | 201.10 | 0.98103 |
| FeMX1-1 | 0.7447 | 148.66 | 0.90406 | 0.0053 | 171.57 | 0.95077 |
| FeMX2-1 | 1.1093 | 184.59 | 0.97027 | 0.0076 | 204.46 | 0.99135 |

Fig. 7 (a) XPS spectra of FeMX before and after Pb (II) adsorption ; (b) Pb4f and (c) O1s spectra of FeMX1-1 sample after Pb(II) adsorption; (d)Na1s spectra of FeMX1-1 sample before and after Pb(II) adsorption Colorful figures are available on website
| Absorbance | Condition | Adsorption property/ (mg·g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite A based on blast furnace slag | Shake for 60 min at room temperature, C0=50 mg/L | 39.37 | [S1] |
| MXene (Ti3C2Tx) | T=293 K, pH 6, C0=2 mg/L, 2 min contact time | ~90 | [S2] |
| Bead-supported MnFe2O4 nanoparticles | T=298 K, pH 5, C0= 20 mg/L, 2 h equilibrium time | 11.98 | [S3] |
| Polyhydroxyl-aluminum | T=298 K, shake for 270 min, C0=1500 mg/L, 150 min equilibrium time | 3.99 | [S4] |
| Peanut shell-based biochar | T=293 K, pH 5.5, C0=100 mg/L, 180 min contact time | 56.5 | [S5] |
| MnO2 modified magnetic graphitic carbon nitride composite | T=298 K, pH 6, C0=250 mg/L, shake for 270 min | 187.6 | [S6] |
| FeMX2-1 | T=313 K, pH 6, C0=500 mg/L, 3 h equilibrium time | 210.54 | This work |
Table S4 Comparison of Pb(II) adsorption properties of existing adsorption materials and FeMX
| Absorbance | Condition | Adsorption property/ (mg·g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite A based on blast furnace slag | Shake for 60 min at room temperature, C0=50 mg/L | 39.37 | [S1] |
| MXene (Ti3C2Tx) | T=293 K, pH 6, C0=2 mg/L, 2 min contact time | ~90 | [S2] |
| Bead-supported MnFe2O4 nanoparticles | T=298 K, pH 5, C0= 20 mg/L, 2 h equilibrium time | 11.98 | [S3] |
| Polyhydroxyl-aluminum | T=298 K, shake for 270 min, C0=1500 mg/L, 150 min equilibrium time | 3.99 | [S4] |
| Peanut shell-based biochar | T=293 K, pH 5.5, C0=100 mg/L, 180 min contact time | 56.5 | [S5] |
| MnO2 modified magnetic graphitic carbon nitride composite | T=298 K, pH 6, C0=250 mg/L, shake for 270 min | 187.6 | [S6] |
| FeMX2-1 | T=313 K, pH 6, C0=500 mg/L, 3 h equilibrium time | 210.54 | This work |
| [1] |
FU L, YAN Z, ZHAO Q, et al. Novel 2D Nanosheets with potential applications in heavy metal purification: a review. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2018, 5(23): 1801094.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
WANG X, YANG S, SHI W, et al. Different interaction mechanisms of Eu (III) and (243) Am (III) with carbon nanotubes studied by batch, spectroscopy technique and theoretical calculation. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49(19): 11721.
DOI URL |
| [3] | CAI Y, WU C, LIU Z, et al. Fabrication of a phosphorylated graphene oxide-chitosan composite for highly effective and selective capture of U(VI). Environmental Science: Nano, 2017, 4(9): 1876. |
| [4] |
LIU Y, LÜ H, LIU Y, et al. Progresses on electrospun metal- organic frameworks nanofibers and their wastewater treatment applications. Materials Today Chemistry, 2022, 25: 100974.
DOI URL |
| [5] | LIU J, WEN X, ZHAO S Q, et al. Synthesis of the Zeolite a based on blast furnace slag and adsorption of Pb2+ ions. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2019, 48(6): 1129. |
| [6] |
LIU X, VERMA G, CHEN Z, et al. Metal-organic framework nanocrystal-derived hollow porous materials: synthetic strategies and emerging applications. The Innovation, 2022, 3(5): 100281.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHANG Y, LIU H, GAO F, et al. Application of MOFs and COFs for photocatalysis in CO2 reduction, H2 generation, and environmental treatment. EnergyChem, 2022, 4(4): 100078.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHEN X, ZHAO Y, LI L, et al. MXene/Polymer nanocomposites: preparation, properties, and applications. Polymer Reviews, 2020, 61(1): 80.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
IBRAHIM Y, KASSAB A, EID K, et al. Unveiling fabrication and environmental remediation of MXene-based nanoarchitectures in toxic metals removal from wastewater: strategy and mechanism. Nanomaterials, 2020, 10: 885.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V, et al. Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(37): 4248.
DOI URL |
| [11] | IHSANULLAH I. MXenes (two-dimensional metal carbides) as emerging nanomaterials for water purification: progress, challenges and prospects. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 388: 124300. |
| [12] |
CHEN J, HUANG Q, HUANG H, et al. Recent progress and advances in the environmental applications of MXene related materials. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(6): 3574.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
GHIDIU M, LUKATSKAYA M R, ZHAO M Q, et al. Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide 'clay' with high volumetric capacitance. Nature, 2014, 516(4): 78.
DOI |
| [14] | SHI W, WANG H, WANG L, et al. Adsorption of Eu(III) on alkalized Ti3C2Tx MXene studied by batch experiment and mechanism investigation. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 35(1): 65. |
| [15] |
WANG L, TAO W, YUAN L, et al. Rational control of the interlayer space inside two-dimensional titanium carbides for highly efficient uranium removal and imprisonment. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(89): 12084.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
GóMEZ-PASTORA J, DOMINGUEZ S, BRINGAS E, et al. Review and perspectives on the use of magnetic nanophotocatalysts (MNPCs) in water treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 310: 407.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
JANG J, SHAHZAD A, WOO S H, et al. Magnetic Ti3C2Tx (MXene) for diclofenac degradation via the ultraviolet/chlorine advanced oxidation process. Environmental Research, 2020, 182: 108990.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
YANG X, LIU Y, HU S, et al. Construction of Fe3O4@MXene composite nanofiltration membrane for heavy metal ions removal from wastewater. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2020, 32(3): 1000.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SHAHZAD A, RASOOL K, MIRAN W, et al. Mercuric ion capturing by recoverable titanium carbide magnetic nanocomposite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 344: 811.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
CUI Y, LIU M, HUANG H, et al. A novel one-step strategy for preparation of Fe3O4-loaded Ti3C2 MXenes with high efficiency for removal organic dyes. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(8): 11593.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
CUI Y, ZHANG D, SHEN K, et al. Biomimetic anchoring of Fe3O4 onto Ti3C2 MXene for highly efficient removal of organic dyes by fenton reaction. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(5): 104369.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHANG Q, TENG J, ZOU G, et al. Efficient phosphate sequestration for water purification by unique sandwich-like MXene/ magnetic iron oxide nanocomposites. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(13): 7085.
DOI URL |
| [23] | YU S, TANG H, ZHANG D, et al. MXenes as emerging nanomaterials in water purification and environmental remediation. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 811: 152280. |
| [24] | ZHANG P, XIANG M, LIU H, et al. Novel two-dimensional magnetic titanium carbide for Methylene Blue removal over a wide pH range: insight into removal performance and mechanism. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(27): 24027. |
| [25] |
DU Y, MA W, LIU P, et al. Magnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles supported on titanate nanotubes (CoFe2O4/TNTs) as a novel heterogeneous catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation and degradation of organic pollutants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 308: 58.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
JIN L, WANG J, WU F, et al. Tailoring MXene-based materials for sodium-ion storage: synthesis, mechanisms, and applications. Electrochemical Energy Reviews, 2020, 3(4): 766.
DOI |
| [27] |
YANG G, HU X, LIANG J, et al. Surface functionalization of MXene with chitosan through in-situ formation of polyimidazoles and its adsorption properties. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 419: 126220.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZHANG C, PINILLA S, MCEVOY N, et al. Oxidation stability of colloidal two-dimensional titanium carbides (MXenes). Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29: 4848.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
YANG H, LU M, CHEN D, et al. Efficient and rapid removal of Pb2+ from water by magnetic Fe3O4@MnO2 core-shell nanoflower attached to carbon microtube: adsorption behavior and process study. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 563: 218.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
LI S S, JIANG M, JIANG T J, et al. Competitive adsorption behavior toward metal ions on nano-Fe/Mg/Ni ternary layered double hydroxide proved by XPS: evidence of selective and sensitive detection of Pb(II). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 338: 1.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
JUN B M, PARK C M, HEO J, et al. Adsorption of Ba2+ and Sr2+on Ti3C2Tx MXene in model fracking wastewater. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 256: 109940.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
LIU F, JIN Y, LIAO H, et al. Facile self-assembly synthesis of titanate/Fe3O4 nanocomposites for the efficient removal of Pb2+ from aqueous systems. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(3): 805.
DOI URL |
| [1] | FANG Wanli, SHEN Lili, LI Haiyan, CHEN Xinyu, CHEN Zongqi, SHOU Chunhui, ZHAO Bin, YANG Songwang. Effect of Film Formation Processes of NiOx Mesoporous Layer on Performance of Perovskite Solar Cells with Carbon Electrodes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1103-1109. |
| [2] | CHEN Yu, LIN Puan, CAI Bing, ZHANG Wenhua. Research Progress of Inorganic Hole Transport Materials in Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 991-1004. |
| [3] | HU Zhongliang, FU Yuntian, JIANG Meng, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Thermal Stability of Nb/Mg3SbBi Interface [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 931-937. |
| [4] | LIU Jian, WANG Lingkun, XU Baoliang, ZHAO Qian, WANG Yaoxuan, DING Yi, ZHANG Shengtai, DUAN Tao. Nd-doped ZrSiO4 Ceramics: Synthesis in Molten Salt at Low Temperature, Phase Evolution and Chemical Stability [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 910-916. |
| [5] | DING Haoming, LI Mian, LI Youbing, CHEN Ke, XIAO Yukun, ZHOU Jie, TAO Quanzheng, Johanna Rosen, YIN Hang, BAI Yuelei, ZHANG Bikun, SUN Zhimei, WANG Junjie, ZHANG Yiming, HUANG Zhenying, ZHANG Peigen, SUN Zhengming, HAN Meikang, ZHAO Shuang, WANG Chenxu, HUANG Qing. Progress in Structural Tailoring and Properties of Ternary Layered Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 845-884. |
| [6] | XIAO Yani, LYU Jianan, LI Zhenming, LIU Mingyang, LIU Wei, REN Zhigang, LIU Hongjing, YANG Dongwang, YAN Yonggao. Hygrothermal Stability of Bi2Te3-based Thermoelectric Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 800-806. |
| [7] | DING Ling, JIANG Rui, TANG Zilong, YANG Yunqiong. MXene: Nanoengineering and Application as Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [8] | WANG Bo, YU Jian, LI Cuncheng, NIE Xiaolei, ZHU Wanting, WEI Ping, ZHAO Wenyu, ZHANG Qingjie. Service Stability of Gd/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 Thermo-electro-magnetic Gradient Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 663-670. |
| [9] | LI Yue, ZHANG Xuliang, JING Fangli, HU Zhanggui, WU Yicheng. Growth and Property of Ce3+-doped La2CaB10O19 Crystal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 583-588. |
| [10] | MA Rundong, GUO Xiong, SHI Kaixuan, AN Shengli, WANG Ruifen, GUO Ruihua. S-type Heterojunction of MOS2/g-C3N4: Construction and Photocatalysis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1176-1182. |
| [11] | WAN Jiabao, ZHANG Minghui, SU Huaiyu, CAO Zhijun, LIU Xuechao, XIE Jiansheng, WANG Xiangyuan, SHI Yinghui, WANG Liang, LEI Shuijin. Structural, Thermal, and Optical Properties of GeO2-La2O3-TiO2 Glasses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1230-1236. |
| [12] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Mesoporous Organic-inorganic Hybrid Siliceous Hollow Spheres: Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [13] | JIANG Yiyi, SHEN Min, SONG Banxia, LI Nan, DING Xianghuan, GUO Leyi, MA Guoqiang. Effect of Dual-functional Electrolyte Additive on High Temperature and High Voltage Performance of Li-ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 710-716. |
| [14] | LUO Shilin, ZHANG Shengtai, XU Baoliang, WANG Lingkun, DUAN Siyihan, DING Yi, ZHAO Qian, DUAN Tao. Immobilizing Behavior of Trivalent Actinide Nuclides by YIG Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 757-763. |
| [15] | XIAO Meixia, LI Miaomiao, SONG Erhong, SONG Haiyang, LI Zhao, BI Jiaying. Halogenated Ti3C2 MXene as High Capacity Electrode Material for Li-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 660-668. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||