
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 469-476.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220591
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles
WANG Lei1( ), LI Jianjun1,2(
), LI Jianjun1,2( ), NING Jun3, HU Tianyu1,2, WANG Hongyang1, ZHANG Zhanqun1, WU Linxin1
), NING Jun3, HU Tianyu1,2, WANG Hongyang1, ZHANG Zhanqun1, WU Linxin1
Received:2022-10-09
Revised:2022-11-27
Published:2023-04-20
Online:2022-12-30
Contact:
LI Jianjun, professor. E-mail: ljj.hero@126.comAbout author:WANG Lei (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: wangleidreamer@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Lei, LI Jianjun, NING Jun, HU Tianyu, WANG Hongyang, ZHANG Zhanqun, WU Linxin. Enhanced Degradation of Methyl Orange with CoFe2O4@Zeolite Catalyst as Peroxymonosulfate Activator: Performance and Mechanism[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 469-476.
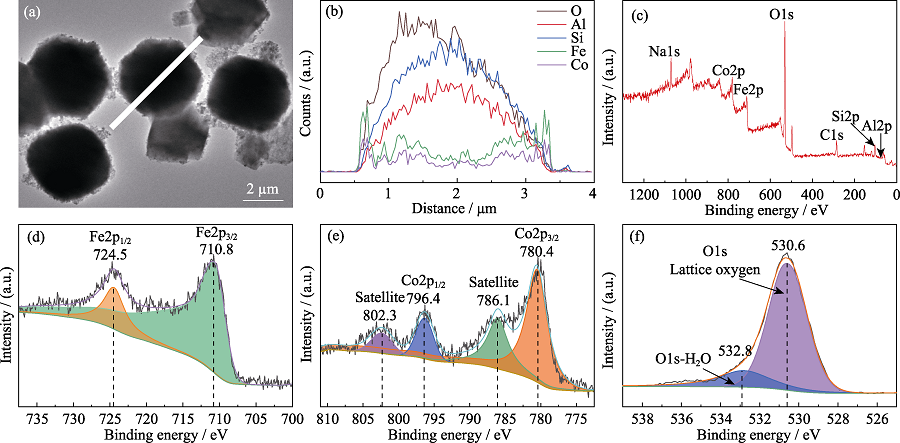
Fig. 3 (a) TEM image and (b) elemental line scanning spectra of CFZ, as well as XPS spectra of (c) survey, (d) Fe2p, (e) Co2p, and (f) O1s of CFZ Colorful figures are available on website

Fig. 4 (a) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distributions of the prepared zeolite and CFZ, (c) removal of MO in different systems (0.2 g/L CFZ, [PMS] = 0.6 mmol/L, [MO] = 0.2 g/L, pH 8, T = 25 ℃), and effects of (d) catalyst dosage, (e) initial solution pH and (f) PMS concentration on MO removal (0.2 g/L CFZ, [PMS] = 1 mmol/L, [MO] = 50 mg/L, pH 8, T = 25 ℃) Colorful figures are available on website
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/ (cm3·g-1) | Pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite | 30.13 | 0.08 | 15.00 |
| CFZ | 107.06 | 0.33 | 16.24 |
Table 1 SBET and pore size analysis data of the prepared zeolite and CFZ
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/ (cm3·g-1) | Pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite | 30.13 | 0.08 | 15.00 |
| CFZ | 107.06 | 0.33 | 16.24 |
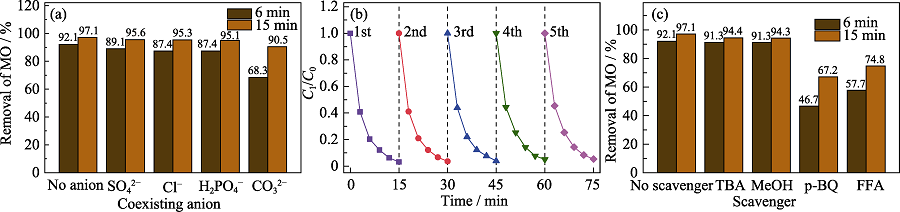
Fig. 5 Effects of (a) coexisting anions on MO removal, (b) cyclic experiments and (c) ROS quenching tests (0.2 g/L CFZ, under the conditions of [PMS] = 1 mmol/L, [MO] = [coexisting anions] = 50 mg/L, pH 8, T = 25 ℃, [scavengers] = 100 mmol/L) Colorful figures are available on website
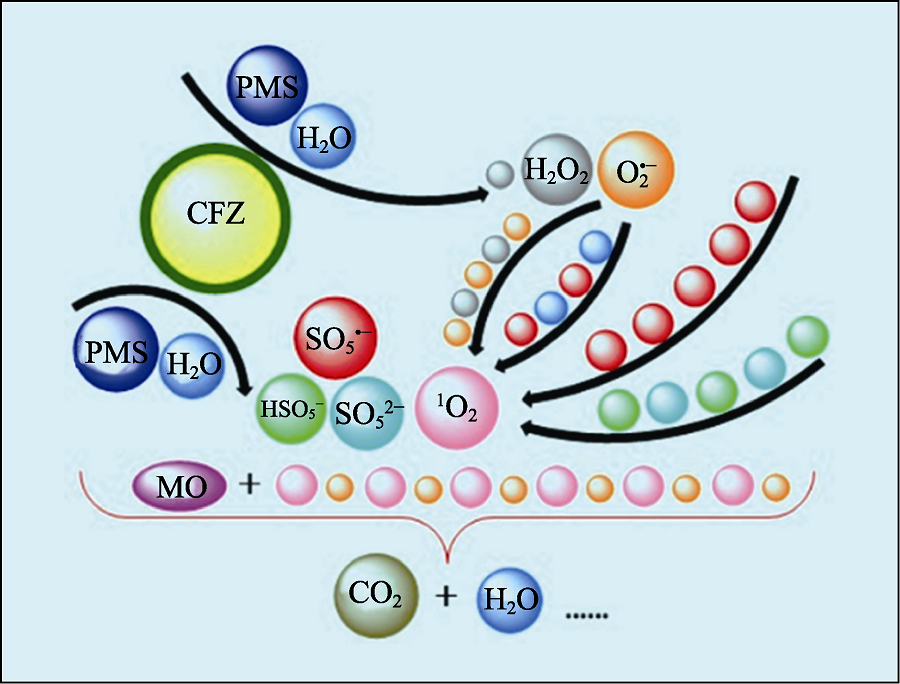
Fig. 6 Schematic of ROS generation and MO degradation The black arrows show the generation route of ROS and the balls with colors correspond to different reactants, intermediates or products Colorful figures are available on website
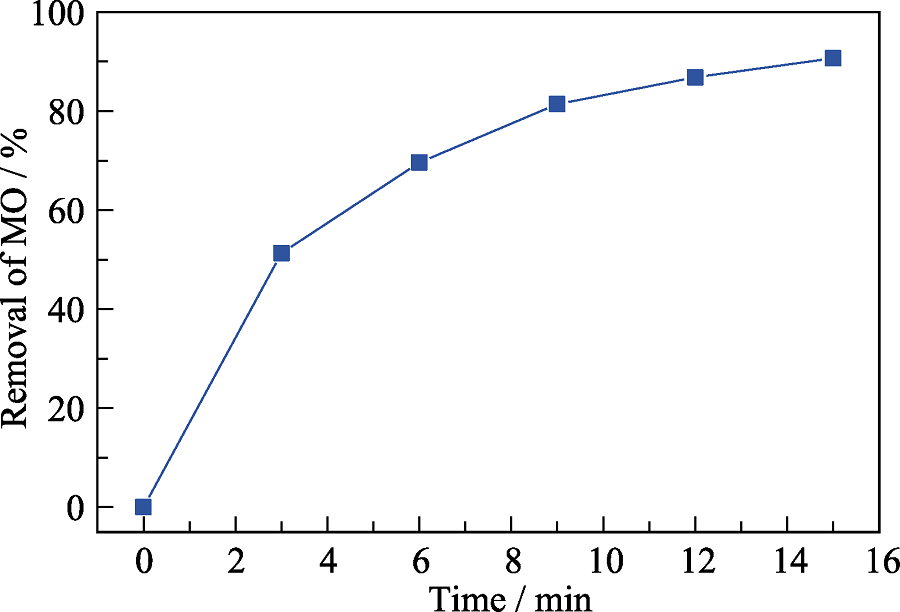
Fig. S2 Effect of high-concentration coexisting anions ([MO]=50 mg/L, [SO42-]=[CO32-]=[Cl-]=[H2PO42-]=1000 mg/L, 0.2 g/L CFZ, [PMS]=1 mmol/L, pH 7, T=25 ℃)
| pH | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Removal efficiency/% | 73.96 | 91.83 | 94.22 | 93.99 | 94.96 |
Table S1 Removal efficiency of MB under different pH conditions
| pH | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Removal efficiency/% | 73.96 | 91.83 | 94.22 | 93.99 | 94.96 |
| [1] | LYU W, LI J, TRCHOVA M, et al. Fabrication of polyaniline/poly (vinyl alcohol)/montmorillonite hybrid aerogels toward efficient adsorption of organic dye pollutants. J. Hazard Mater., 2022, 435: 129004. |
| [2] | SUN B, YUAN Y, LI H, et al. Waste-cellulose-derived porous carbon adsorbents for methyl orange removal. Chem. Eng. J., 2019, 371: 55. |
| [3] |
ZHANG S, LIU Y, MA R, et al. Molybdenum (VI)-oxo clusters incorporation activates g-C3N4 with simultaneously regulating charge transfer and reaction centers for boosting photocatalytic performance. Adv. Fun. Mater., 2022, 32(38):2204175.
DOI URL |
| [4] | ISSAKA E, AMU-DARKO J N, YAKUBU S, et al. Advanced catalytic ozonation for degradation of pharmaceutical pollutants-a review. Chemosphere, 2022, 289: 133208. |
| [5] | LIU B, JI J, ZHANG B, et al. Catalytic ozonation of VOCs at low temperature: a comprehensive review. J. Hazard Mater., 2022, 422: 126847. |
| [6] | OYEKUNLE D T, GENDY E A, IFTHIKAR J, et al. Heterogeneous activation of persulfate by metal and non-metal catalyst for the degradation of sulfamethoxazole: a review. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 437: 135277. |
| [7] | PENG Y, TANG H, YAO B, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) by spinel ferrite and their composites in degradation of organic pollutants: a review. Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 414: 128800. |
| [8] | ZHANG S, LIU Y, GU P, et al. Enhanced photodegradation of toxic organic pollutants using dual-oxygen-doped porous g-C3N4: mechanism exploration from both experimental and DFT studies. Appl.Catal. B: Environ., 2019, 248: 1. |
| [9] |
ZHANG S, SONG S, GU P, et al. Visible-light-driven activation of persulfate over cyano and hydroxyl group co-modified mesoporous g-C3N4 for boosting Bisphenol A degradation. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(10):5552.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
PARK J, CHOE J K, LEE W, et al. Highly fast and selective removal of nitrate in groundwater by bimetallic catalysts supported by fly ash-derived zeolite Na-X. Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2020, 7(11):3360.
DOI URL |
| [11] | LI J, GOU G, ZHAO H, et al. Efficient peroxymonosulfate activation by CoFe2O4-CeO2 composite: performance and catalytic mechanism. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 435: 134840. |
| [12] | BALAKRISHNAN R M, ILANGO I, GAMANA G, et al. Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and peroxymonosulfate system for the removal of ampicillin from aqueous solution. J. Water Proc. Eng., 2021, 40: 101823. |
| [13] | GHANBARI F, MORADI M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: review. Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 310: 41. |
| [14] | ZHENG X, NIU X, ZHANG D, et al. Metal-based catalysts for persulfate and peroxymonosulfate activation in heterogeneous ways: a review. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 429: 132323. |
| [15] | WANG Q, SHAO Y, GAO N, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by Al2O3-based CoFe2O4 for the degradation of sulfachloropyridazine sodium: kinetics and mechanism. Separ. and Purif. Tech., 2017, 189: 176. |
| [16] | KEFENI K K, MAMBA B B. Photocatalytic application of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and nanocomposites in wastewater treatment: review. Sustain. Mater. Tech., 2020, 23: e00140. |
| [17] | SONG L, LI J, ZHANG Z, et al. La-containing magnetic zeolite synthesized from gangue by ball-milling method. Mater. Lett., 2021, 303: 130542. |
| [18] |
MARTINEZ-VARGAS S, MARTÍNEZ A I, HERNÁNDEZ- BETETA E E, et al. Arsenic adsorption on cobalt and manganese ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52(11):6205.
DOI URL |
| [19] | CHAGAS C A, DE SOUZA E F, DE CARVALHO M C N A, et al. Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for the preferential oxidation of CO. Appl. Catal. A: Gener., 2016, 519: 139. |
| [20] | LIU Z, GAO Z, WU Q. Activation of persulfate by magnetic zirconium-doped manganese ferrite for efficient degradation of tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 423: 130283. |
| [21] | PENIDO E S, MELO L C A, GUILHERME L R G, et al. Cadmium binding mechanisms and adsorption capacity by novel phosphorus/magnesium-engineered biochars. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 671: 1134. |
| [22] | JI Y, LU J, WANG L, et al. Non-activated peroxymonosulfate oxidation of sulfonamide antibiotics in water: kinetics, mechanisms, and implications for water treatment. Water Res., 2018, 147: 82. |
| [23] | LIU L, MI H, ZHANG M, et al. Efficient moxifloxacin degradation by CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles activated peroxymonosulfate: kinetics, pathways and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 407: 127201. |
| [24] | CHEN L, DING D, LIU C, et al. Degradation of norfloxacin by CoFe2O4-GO composite coupled with peroxymonosulfate: a comparative study and mechanistic consideration. Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 334: 273. |
| [25] | DU Y, MA W, LIU P, et al. Magnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles supported on titanate nanotubes (CoFe2O4/TNTs) as a novel heterogeneous catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation and degradation of organic pollutants. J. Hazard Mater., 2016, 308: 58. |
| [26] | HUNG C M, CHEN C W, HUANG C P, et al. Removal of 4-nonylphenol in activated sludge by peroxymonosulfate activated with sorghum distillery residue-derived biochar. Bioresour Technol., 2022, 360: 127564. |
| [27] | DUNG N T, TRANG T T, THAO V D, et al. Enhanced degradation of organic dyes by peroxymonosulfate with Fe3O4-CoCO3/rGO hybrid activation: a comprehensive study. J. the Taiwan Instit. of Chem. Engin., 2022, 133: 104279. |
| [28] |
DUNG N T, THU T V, VAN NGUYEN T, et al. Catalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate with manganese cobaltite nanoparticles for the degradation of organic dyes. RSC Adv., 2020, 10(7):3775.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | CHEN G, NENGZI L C, GAO Y, et al. Degradation of tartrazine by peroxymonosulfate through magnetic Fe2O3/Mn2O3 composites activation. Chine. Chemi. Lett., 2020, 31(10):2730. |
| [30] | XU P, XIE S, LIU X, et al. Electrochemical enhanced heterogenous activation of peroxymonosulfate using CuFe2O4 particle electrodes for the degradation of diclofenac. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 446: 136941. |
| [31] |
ZHANG T, ZHU H, CROUE J P. Production of sulfate radical from peroxymonosulfate induced by a magnetically separable CuFe2O4 spinel in water: efficiency, stability, and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47(6):2784.
DOI URL |
| [32] | LI J, WAN Y, LI Y, et al. Surface Fe(III)/Fe(II) cycle promoted the degradation of atrazine by peroxymonosulfate activation in the presence of hydroxylamine. Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2019, 256: 117782. |
| [33] | WANG Z, NENGZI L C, ZHANG X, et al. Novel NiCo2S4/CS membranes as efficient catalysts for activating persulfate and its high activity for degradation of nimesulide. Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 381: 122517. |
| [34] | WANG S, CHEN Z, YAN P, et al. Enhanced degradation of iohexol in water by CuFe2O4activated peroxymonosulfate: efficiency, mechanism and degradation pathway. Chemosphere, 2022, 289: 133198. |
| [35] |
ZHANG L S, JIANG X H, ZHONG Z A, et al. Carbon nitride supported high-loading Fe single-atom catalyst for activation of peroxymonosulfate to generate 1O2 with 100% selectivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(40):21751.
DOI URL |
| [36] | WANG J, SHEN M, WANG H, et al. Red mud modified sludge biochar for the activation of peroxymonosulfate: singlet oxygen dominated mechanism and toxicity prediction. Sci. Total. Environ., 2020, 740: 140388. |
| [37] | ZHENG Y, ZHUANG W, ZHANG X, et al. Grape-like CNTs/ BaTiO3 nanocatalyst boosted hydraulic-driven piezo-activation of peroxymonosulfate for carbamazepine removal. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 449: 137826. |
| [38] | WANG X, ZHUANG Y, SHI B. Degradation of trichloroacetic acid by MOFs-templated CoFe/graphene aerogels in peroxymonosulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 450: 137799. |
| [39] | XU A, WU D, ZHANG R, et al. Bio-synthesis of Co-doped FeMnOx and its efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate for the degradation of moxifloxacin. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 435: 134695. |
| [40] | ZHAO Y, WANG H, JI J, et al. Degradation of ciprofloxacin by peroxymonosulfate activation using catalyst derived from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Cleaner Produc., 2022, 362: 132442. |
| [1] | CHEN Ying, LUAN Weiling, CHEN Haofeng, ZHU Xuanchen. Multi-scale Failure Behavior of Cathode in Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Stress Field [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 918-924. |
| [2] | CHEN Shikun, WANG Chuchu, CHEN Ye, LI Li, PAN Lu, WEN Guilin. Magnetic Ag2S/Ag/CoFe1.95Sm0.05O4 Z-scheme Heterojunction: Preparation and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1329-1336. |
| [3] | LI Tie, LI Yue, WANG Yingyi, ZHANG Ting. Preparation and Catalytic Properties of Graphene-Bismuth Ferrite Nanocrystal Nanocomposite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 725-732. |
| [4] | AN Weijia, LI Jing, WANG Shuyao, HU Jinshan, LIN Zaiyuan, CUI Wenquan, LIU Li, XIE Jun, LIANG Yinghua. Fe(III)/rGO/Bi2MoO6 Composite Photocatalyst Preparation and Phenol Degradation by Photocatalytic Fenton Synergy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 615-622. |
| [5] | XIONG Jinyan, LUO Qiang, ZHAO Kai, ZHANG Mengmeng, HAN Chao, CHENG Gang. Facilely Anchoring Cu nanoparticles on WO3 Nanocubes for Enhanced Photocatalysis through Efficient Interface Charge Transfer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 325-331. |
| [6] | LAN Qing, SUN Shengrui, WU Ping, YANG Qingfeng, LIU Yangqiao. Co-doped CuO/Visible Light Synergistic Activation of PMS for Degradation of Rhodamine B and Its Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1171-1177. |
| [7] | LIU Cai, LIU Fang, HUANG Fang, WANG Xiaojuan. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Alga-based CDs-Cu-TiO2 Composite Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1154-1162. |
| [8] | BAO Feng, CHANG Jiang. Calcium Silicate Nanowires Based Composite Electrospun Scaffolds: Preparation, Ion Release and Cytocompatibility [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1199-1207. |
| [9] | ZHANG Xincong,GUO Ke,PENG Lianlian,WU Jieyu,ZHANG Fumin,ZHU Weidong,FU Yanghe. Degradation of Dye Wastewater over NH2-UiO-66: Piezoelectrically Induced Mechano-Catalytic Effect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 1023-1028. |
| [10] | ZHU Enquan,MA Yuhua,AINIWA· Munire,SU Zhi. Adsorption-enrichment and Localized-photodegradation of Bentonite-supported Red Phosphorus Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 803-808. |
| [11] | XU Jingwei,LI Zheng,WANG Zepu,YU Han,HE Qi,FU Nian,DING Bangfu,ZHENG Shukai,YAN Xiaobing. Morphology and Photocatalytic Performance Regulation of Nd3+-doped BiVO4 with Staggered Band Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 789-795. |
| [12] | ZHANG Xiaoxu,ZHU Dongbin,LIANG Jinsheng. Progress on Hydrothermal Stability of Dental Zirconia Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 759-768. |
| [13] | JI Bang, ZHAO Wenfeng, DUAN Jieli, MA Lizhe, FU Lanhui, YANG Zhou. Synthesis of TiO2/WO3 on Nickel Foam for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Ethylene [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 581-588. |
| [14] | LIU Ziyang, GENG Zhen, LI Zhaoyang. Preparing Biomedical CaCO3/HA Composite with Oyster Shell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 601-607. |
| [15] | QIANG Xiao-Hu, LI Bin-Bin, HUANG Da-Jian, ZHOU Song-Yi. Boron Oxide on Mechanical and Degradation Property of Calcium Polyphosphate Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 201-206. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||