
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 343-349.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220481
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles Next Articles
YU Ruixian( ), WANG Guodong, WANG Shouzhi, HU Xiaobo(
), WANG Guodong, WANG Shouzhi, HU Xiaobo( ), XU Xiangang, ZHANG Lei(
), XU Xiangang, ZHANG Lei( )
)
Received:2022-08-13
Revised:2022-10-09
Published:2022-11-20
Online:2022-11-20
Contact:
HU Xiaobo, professor. E-mail: xbhu@sdu.edu.cn;About author:YU Ruixian (1987-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: yuruixian0001@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
YU Ruixian, WANG Guodong, WANG Shouzhi, HU Xiaobo, XU Xiangang, ZHANG Lei. Effect of High-temperature Annealing on AlN Crystal Grown by PVT Method[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 343-349.
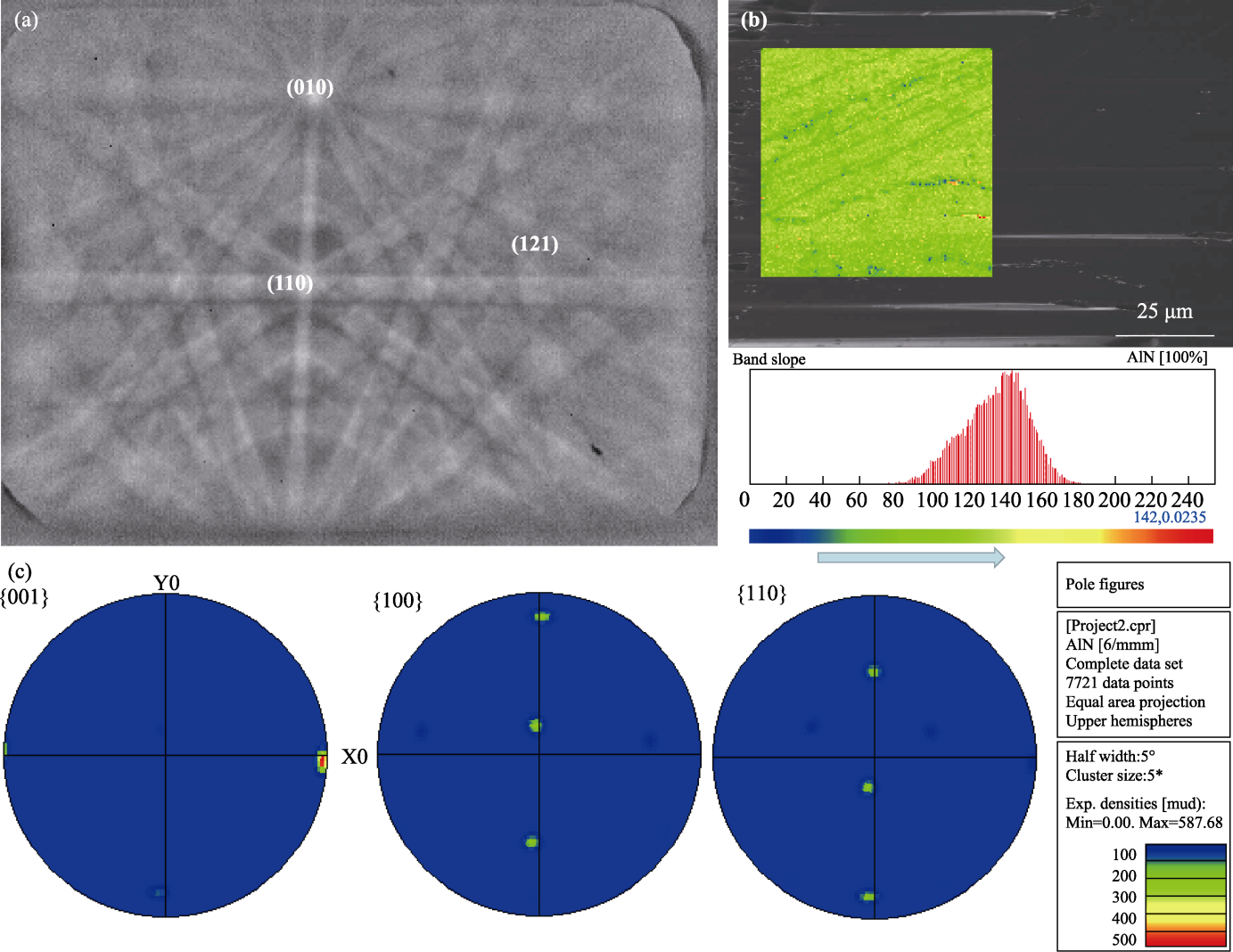
Fig. 3 EBSD of AlN crystal sample (a) EBSD Kikuchi patterns of AlN crystal without annealing; (b) Band slop obtained from EBSD mapping date; (c) Pole figures of AlN without annealing
| Sample | (10¯12) FWHM/arcsec* | Edge dislocations density, ρe/(×107, cm-2) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw | 104.04 | 5.80 |
| AlN-1400 | 79.92 | 3.42 |
| AlN-1600 | 78.92 | 3.34 |
| AlN-1800 | 97.2 | 5.06 |
Table 1 Calculated edge dislocations density(ρe) of AlN samples
| Sample | (10¯12) FWHM/arcsec* | Edge dislocations density, ρe/(×107, cm-2) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw | 104.04 | 5.80 |
| AlN-1400 | 79.92 | 3.42 |
| AlN-1600 | 78.92 | 3.34 |
| AlN-1800 | 97.2 | 5.06 |
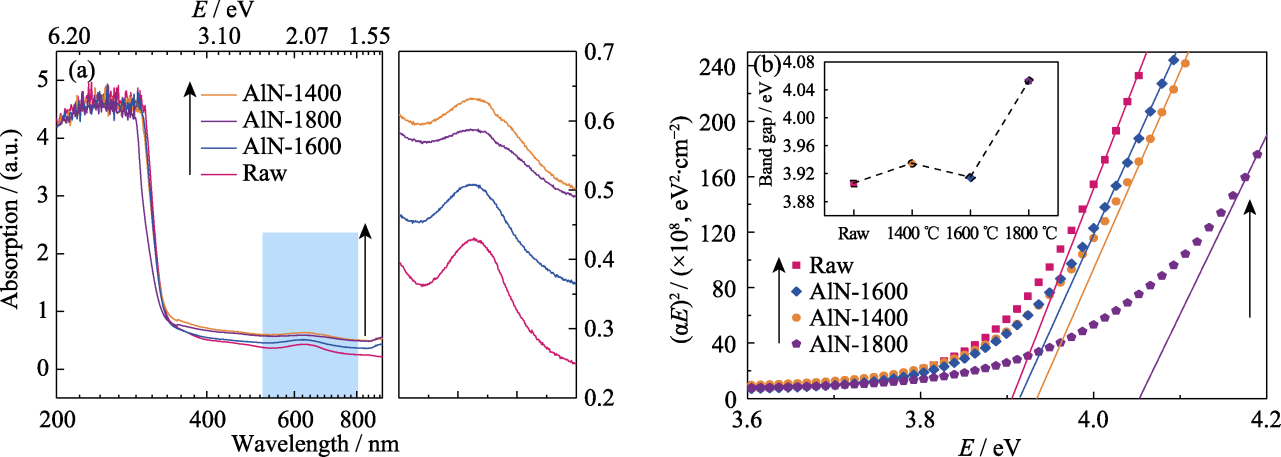
Fig. 6 Optical absorption spectra of the AlN crystals with and without annealing (a) Absorption spectra of the AlN without and with annealing at different temperatures with right enlarged spectra showing an absorption peak at 634 nm; (b) Correlation curves of (αE)2 on E with inset showing the band gap of AlN without and with annealing at different temperatures
| [1] |
SUN M S, LI J F, ZHANG J C et al. The fabrication of AlN by hydride vapor phase epitaxy. Journal of Semiconductors, 2019, 40: 121803.
DOI |
| [2] |
YU R X, LIU G X, WANG G D et al. Ultrawide-bandgap semiconductor AlN crystals: growth and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2021, 9: 1852.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
YU R X, CHEN C M, ZHANG L et al. Influence of different heater structures on the temperature field of AlN crystal growth by resistance heating. Materials, 2021, 14: 7441.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHENG W, HUANG F, ZHENG R S, et al. Low-dimensional structure vacuum-ultraviolet-sensitive (λ<200 nm) photodetector with fast-response speed based on high-quality AlN micro/ nanowire. Adv. Mater., 2015, 27: 3921.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CHEN Z L, LIU Z Q, WEI T B, et al. Improved epitaxy of AlN film for deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes enabled by graphene. Adv. Mater., 2019, 31: 1807345.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LU T J, LIENHARD B, JEONG K Y, et al. Bright high-purity quantum emitters in aluminum nitride integrated photonics. ACS Photonics, 2020, 7: 2650.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LIU X H, ZHANG J C, SU X J, et al. Fabrication of crack-free AlN film on sapphire by hydride vapor phase epitaxy using an in situ etching method. Appl. Phys. Exp., 2016, 9: 045501.
DOI |
| [8] |
KATAGIRI Y, KISHINO S, OKUURA K, et al. Low-pressure HVPE growth of crack-free thick AlN on a trench-patterned AlN template. J. Cryst. Growth, 2009, 311: 2831.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HARTMANN C, DITTMAR A, WOLLWEBER J, et al. Bulk AlN growth by physical vapor transport. Semicond. Sci. Technol., 2014, 29: 084002.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ZHUANG D, HERRO Z G, SCHLEAAER R, et al. Seeded growth of AlN single crystals by physical vapor transport. J. Cryst. Growth, 2006, 287: 372.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GUGUSCHEV C, DITTMAR A, MOUKHINA E, et al. Growth of bulk AlN single crystals with low oxygen content taking into account thermal and kinetic effects of oxygen-related gaseous species. J. Cryst. Growth, 2012, 360: 185.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
TANIYASU Y, KASU M, MAKIMOTO T. Electrical conduction properties of n-type Si-doped AlN with high electron mobility (>100 cm2·V-1·s-1). Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 85: 4672.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
STRASSBURG M, SENAWIRATNE J, DIETZ N. The growth and optical properties of large, high-quality AlN single crystals. J. Appl. Phys., 2004, 96: 5870.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HARTMANN C, WOLLWEBER J, DITTMAR A, et al. Preparation of bulk AlN seeds by spontaneous nucleation of freestanding crystals. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2013, 52: 08JA06.
DOI |
| [15] |
WANG G D, ZHANG L, WANG Y, et al. Effect of temperature gradient on AlN crystal growth by physical vapor transport method. Cryst. Growth Des., 2019, 19: 6736.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MOTAMEDI P, CADIEN K. Structural and optical characterization of low-temperature ALD crystalline AlN. J. Cryst. Growth, 2015, 421: 45.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
HARTMANN C, MATIWE L, WOLLWEBER J, et al. Favorable growth conditions for the preparation of bulk AlN single crystals by PVT. CrystEngComm, 2020, 22: 1762.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
COLLAZO R, XIE J, GADDY B, et al. On the origin of the 265 nm absorption band in AlN bulk crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, 100: 191914.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
GADDY B E, BRYAN Z, BRYAN I, et al. The role of the carbon- silicon complex in eliminating deep ultraviolet absorption in AlN. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 104: 202106.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ZHAO L, YANG K, AI Y J, et al. Crystal quality improvement of sputtered AlN film on sapphire substrate by high-temperature annealing. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2018, 29: 13766.
DOI |
| [1] | AO Wei-Dong, LIU Yan, MA Qing-Shan, LIU Huan, ZHOU Bin, ZHENG Xiao-Jia, YU Dong-Qi, ZHANG Wen-Hua. Controllable Synthesis of Vertically Aligned ReS2(1-x)Se2x Nanosheets with Tunable Chemical Compositions and Bandgaps [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1083-1088. |
| [2] | XIAO Hai-Lin, SHAO Gang-Qin, SAI Qing-Lin, XIA Chang-Tai, ZHOU Sheng-Ming, YI Xue-Zhuan. Wide Bandgap Engineering of β-(Al, Ga)2O3 Mixed Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(11): 1258-1262. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||