
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 537-543.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220449
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Xiaosen( ), ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun(
), ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun( ), LI Ruifeng
), LI Ruifeng
Received:2022-08-01
Revised:2022-11-02
Published:2022-11-16
Online:2022-11-16
Contact:
ZHENG Jiajun, professor. E-mail: zhengjiajun@tyut.edu.cnAbout author:MA Xiaosen (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 294945674@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543.
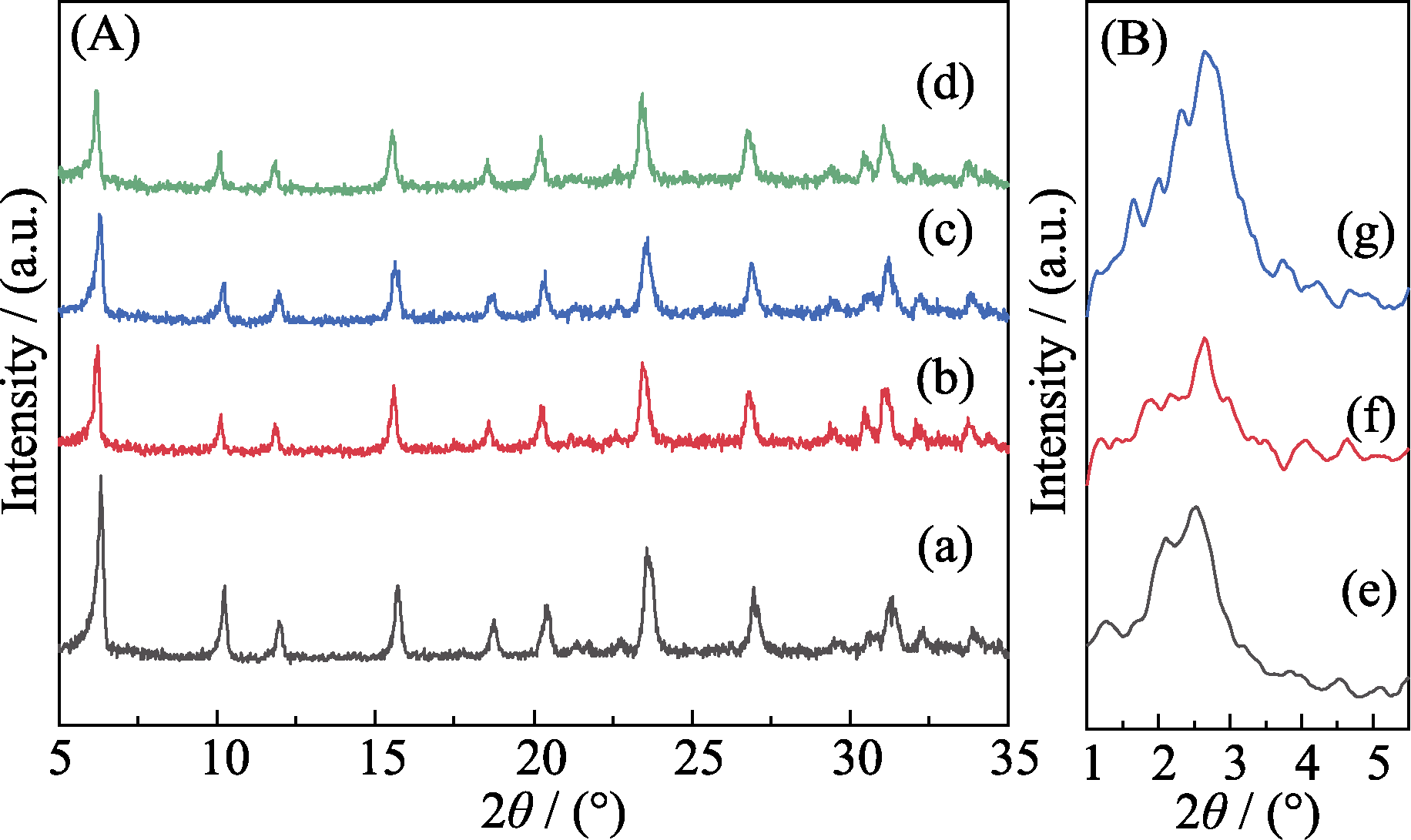
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of the samples of (a) 13X, (b, e) 13X@SiO2-2.2,(c, f) 13X@SiO2-2.6, and (d, g) 13X@SiO2-3.5 (A) Large angle XRD patterns; (B) Small angle XRD patterns
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Sext/(m2·g-1) | Smic/(m2·g-1) | Vmic/(cm3·g-1) | Vmes/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13X | 314 | 14 | 299 | 0.11 | 0.02 |
| 13X@SiO2-2.2 | 324 | 95 | 229 | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| 13X@SiO2-2.6 | 337 | 130 | 207 | 0.08 | 0.09 |
| 13X@SiO2-3.5 | 444 | 259 | 184 | 0.07 | 0.18 |
Table 1 Textural properties of the samples
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Sext/(m2·g-1) | Smic/(m2·g-1) | Vmic/(cm3·g-1) | Vmes/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13X | 314 | 14 | 299 | 0.11 | 0.02 |
| 13X@SiO2-2.2 | 324 | 95 | 229 | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| 13X@SiO2-2.6 | 337 | 130 | 207 | 0.08 | 0.09 |
| 13X@SiO2-3.5 | 444 | 259 | 184 | 0.07 | 0.18 |
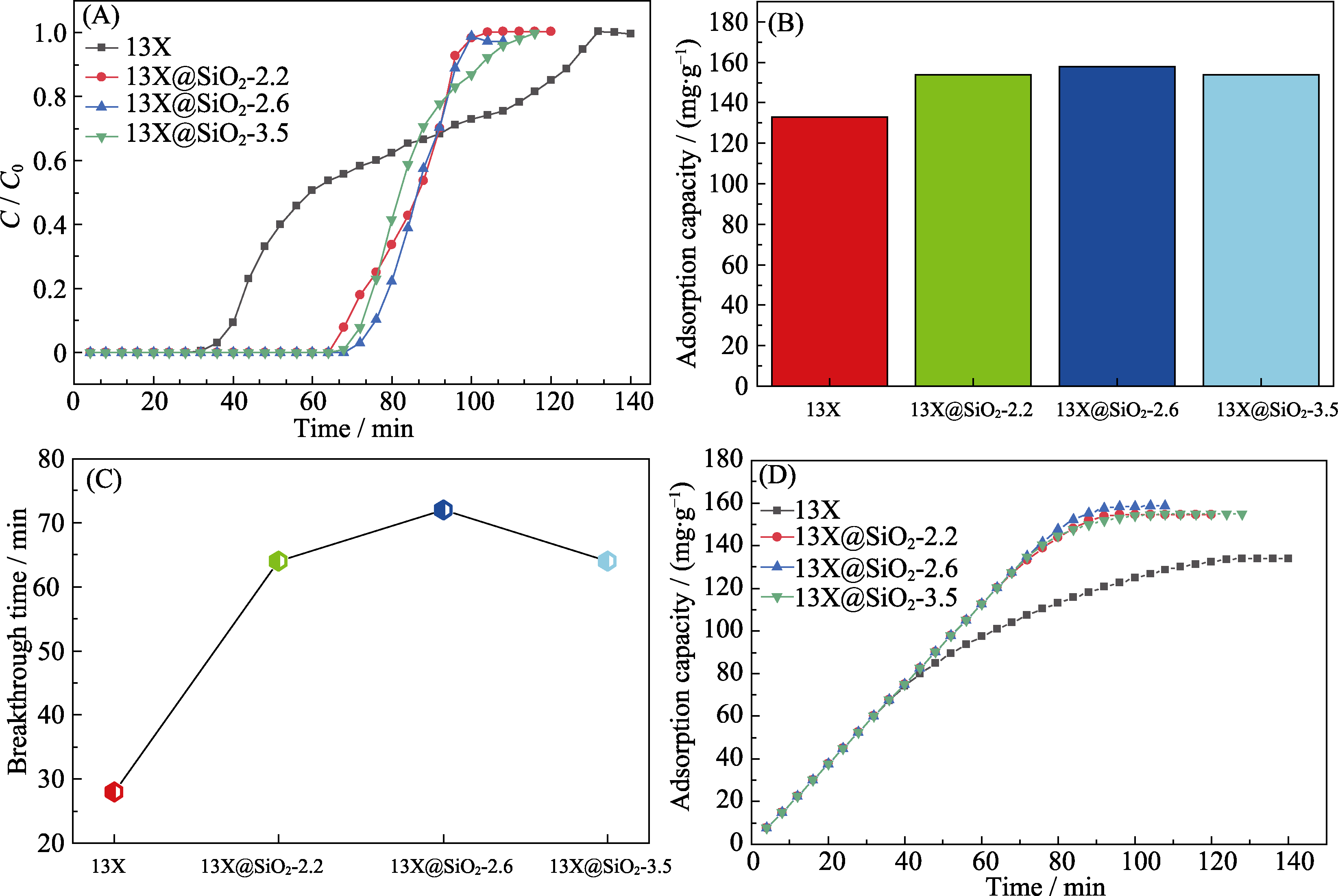
Fig. 4 Adsorption of toluene on the different adsorbents under dry condition (A) Adsorption breakthrough curves; (B) Saturated adsorption capacity; (C) Comparison of the breakthrough times; (D) Cumulative adsorption capacity of different adsorbents
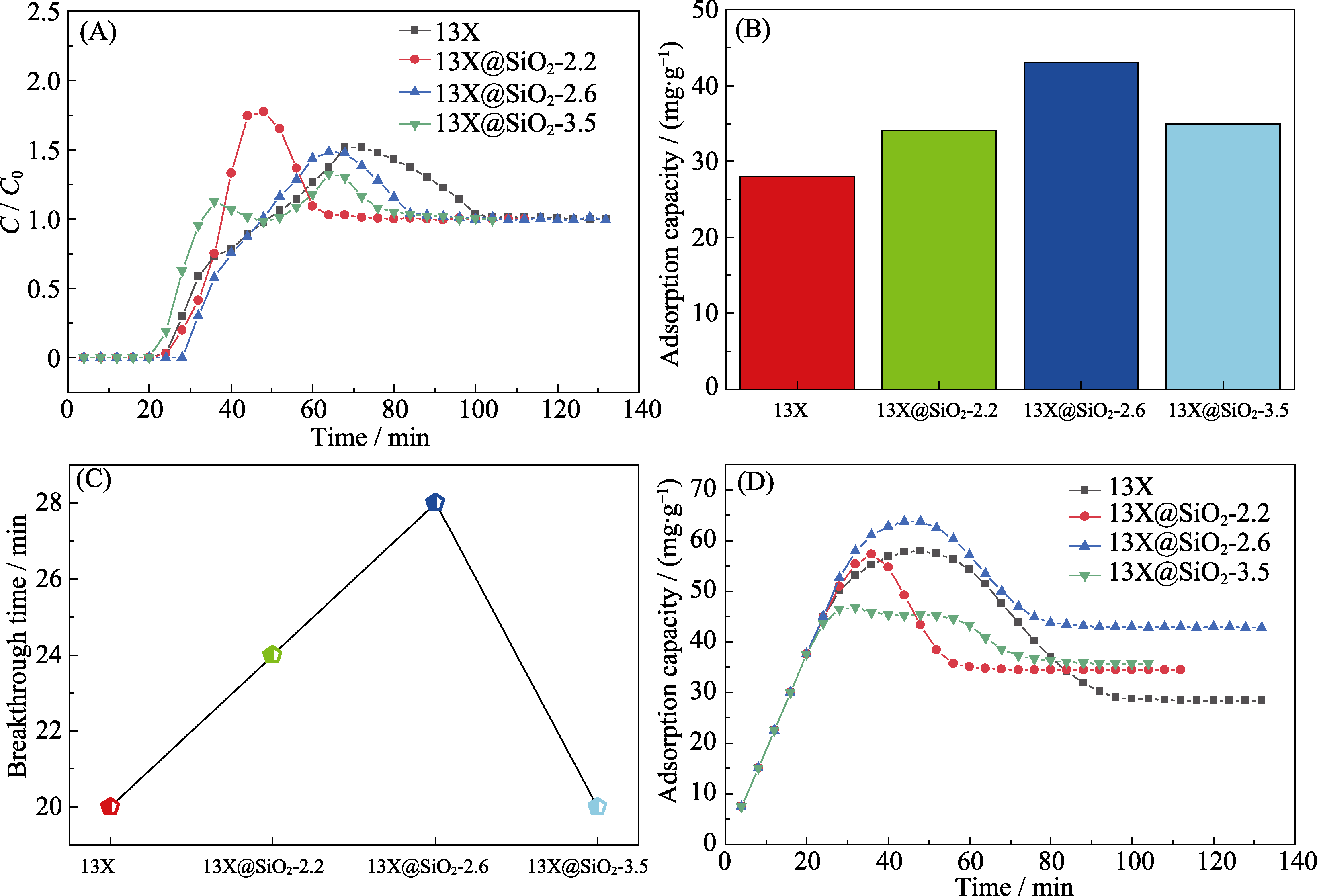
Fig. 5 Adsorption of toluene on the different adsorbents under 30% relative humid conditions (A) Adsorption breakthrough curves; (B) Saturated adsorption capacity; (C) Comparison of the breakthrough time; (D) Cumulative adsorption capacities of different adsorbents of toluene

Fig. 6 Adsorption of toluene on the different adsorbents under 50% relative humid conditions (A) Adsorption breakthrough curves; (B) Saturated adsorption capacity; (C) Comparison of the breakthrough time; (D) Cumulative adsorption capacity of different adsorbents of toluene
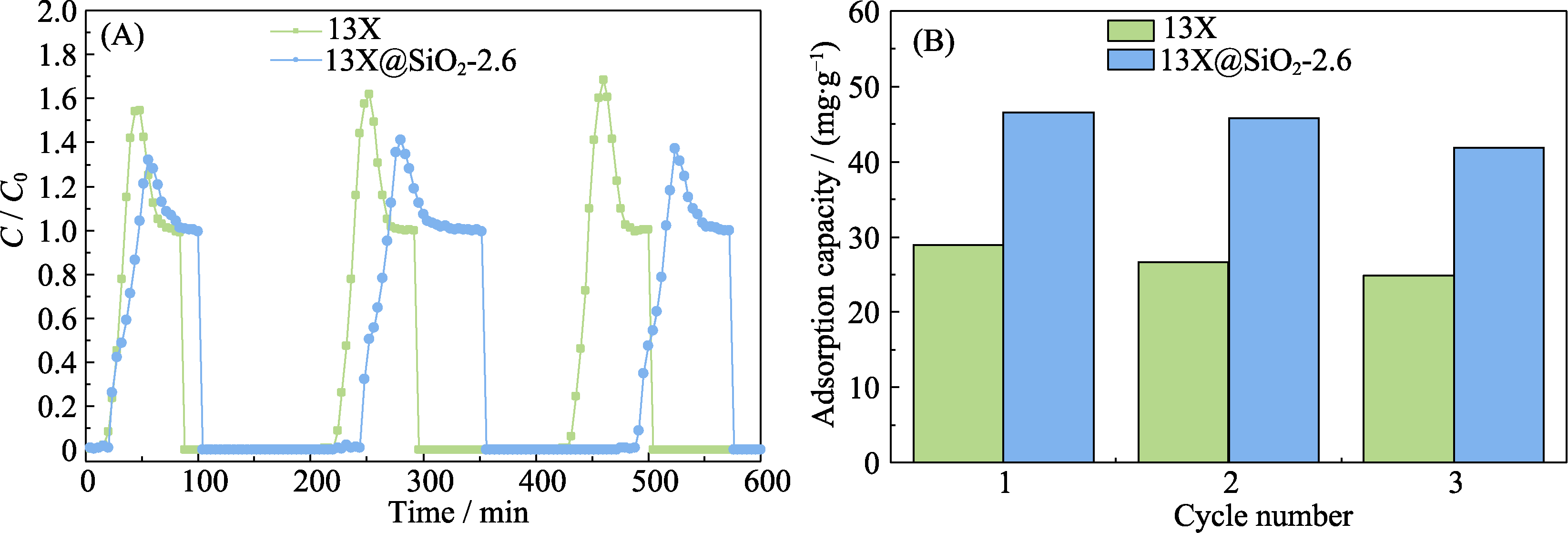
Fig. S7 (A) Adsorption of toluene on different adsorbents with triple adsorption-desorption cycle. Adsorption penetration curve and (B) saturated adsorption capacity under 50% relative humid conditions
| [1] |
KAMAL M S, RAZZAK S A, HOSSAIN M M. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)-a review. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 140: 117.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LI W B, WANG J X, GONG H. Catalytic combustion of VOCs on non-noble metal catalysts. Catalysis Today, 2009, 148(1/2): 81.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DENG H, PAN T T, ZHANG Y, et al. Adsorptive removal of toluene and dichloromethane from humid exhaust on MFI, BEA and FAU zeolites: an experimental and theoretical study. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 394: 124986.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHANG X D, LV X T, SHI X Y, et al. Enhanced hydrophobic UiO-66 (University of Oslo 66) metal-organic framework with high capacity and selectivity for toluene capture from high humid air. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 539: 152.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
BAEK S, KIM J, IHM S. Design of dual functional adsorbent/ catalyst system for the control of VOC’s by using metal-loaded hydrophobic Y-zeolites. Catalysis Today, 2004, 93-95: 575.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
BENKHEDDA J, JAUBERT J N, BARTH D, et al. Experimental and modeled results describing the adsorption of toluene onto activated carbon. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2000, 45(4): 650.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
KARKA S, KODUKULA S, NANDURY S V, et al. Polyethylenimine- modified zeolite 13X for CO2 capture: adsorption and kinetic studies. ACS OMEGA, 2019, 4(15): 16441.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HARLICK P J E, TEZEL F H. An experimental adsorbent screening study for CO2 removal from N2. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2004, 76(1/2/3): 71.
DOI URL |
| [9] | SHEN C M, WOREK W M. Cosorption characteristics of solid adsorbents. International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 1994, 37(14): 2123. |
| [10] |
LIU S, PENG Y, CHEN J J, et al. Engineering surface functional groups on mesoporous silica: towards a humidity-resistant hydrophobic adsorbent. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(28): 13769.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GUILLEMOT M, MIJOIN J, MIGNARD S, et al. Adsorption of tetrachloroethylene (PCE) in gas phase on zeolites of faujasite type: Influence of water vapour and of Si/Al ratio. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2008, 111(1/2/3): 334.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
YIN T, MENG X, JIN L P, et al. Prepared hydrophobic Y zeolite for adsorbing toluene in humid environment. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 305: 110327.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
JIA L X, SUN X Y, YE X Q, et al. Core-shell composites of USY@mesosilica: synthesis and application in cracking heavy molecules with high liquid yield. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2013, 176: 16-24.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LI R N, XUE T S, LI Z, et al. Hierarchical structure ZSM-5/ SBA-15 composite with improved hydrophobicity for adsorption- desorption behavior of toluene. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 392: 124861.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LI R N, CHONG S J, ALTAF N, et al. Synthesis of ZSM-5/siliceous zeolite composites for improvement of hydrophobic adsorption of volatile organic compounds. Frontiers in chemistry, 2019, 7: 505.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
LIU H J, WEI K Y, LONG C. Enhancing adsorption capacities of low-concentration VOCs under humid conditions using NaY@meso-SiO2 core-shell composite. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 442: 136108.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
MIYAMOTO M, ONO S, KUSUKAMI K, et al. High water tolerance of a core-shell-structured Zeolite for CO2adsorptive separation under wet conditions. ChemSusChem, 2018, 11(11): 1756.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIU L Y, DU T, FANG X, et al. Preparation of hydrophobic zeolite 13X@SiO2and their adsorption properties of CO2and H2O. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 1053: 311.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LIU L Y, SINGH R, LI G, et al. Synthesis of hydrophobic zeolite X@SiO2 core-shell composites. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 133(2/3): 1144.
DOI URL |
| [20] | LI R N, XUE T S, BINGRE R, et al. Microporous zeolite@vertically aligned Mg-Al layered double hydroxide core@shell structures with improved hydrophobicity and toluene adsorption capacity under wet conditions. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(41): 34834. |
| [21] | YI H, LI Z Y, REN C Q. Introduction to the standard relative humidity table for saturated salt solutions (international recommendation). The 7th National Conference on Humidity and Moisture and the 5th Conference on Gas-Humidity Sensitivity, Huhehaote, 1998: 70-72. |
| [22] |
LU S, LIU Q, HAN R, et al. Core-shell structured Y zeolite/ hydrophobic organic polymer with improved toluene adsorption capacity under dry and wet conditions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 409: 128194.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LUO X, GUO J, CHANG P, et al. ZSM-5@MCM-41 composite porous materials with a core-shell structure: Adjustment of mesoporous orientation basing on interfacial electrostatic interactions and their application in selective aromatics transport. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 239: 116516.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
XIA H J, WANG J, CHEN G, et al. One-pot synthesis of SiO2@SiO2 core-shell microspheres with controllable mesopore size as a new stationary phase for fast HPLC separation of alkyl benzenes and β-agonists. Microchimica Acta, 2019, 186(2): 125.
DOI |
| [25] | 罗智恒. 疏水性13X沸石的制备及其在H2O/CO2吸附分离中的应用研究. 沈阳: 东北大学硕士学位论文, 2017. |
| [26] |
VELLINGIRI K, KUMAR P, DEEP A, et al. Metal-organic frameworks for the adsorption of gaseous toluene under ambient temperature and pressure. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 307: 1116.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
KRAUS M, TROMMLER U, HOLZER F, et al. Competing adsorption of toluene and water on various zeolites. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 351: 356.
DOI URL |
| [28] | LEE K M, KIM N S, NUMAN M, et al. Post synthetic modification of zeolite internal surface for sustainable capture of volatile organic compounds under humid conditions. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(45): 53925. |
| [29] |
JACOBS J H, DEERING C E, LESAGE K L, et al. Rapid cycling thermal swing adsorption apparatus: commissioning and data analyses for water adsorption of zeolites 4A and 13X over 2000 cycles. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(19): 7487.
DOI URL |
| [30] | FISCHER F, LUTZ W, BUHL J C, et al. Insights into the hydrothermal stability of zeolite 13X. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018, 262: 258 |
| [1] | DING Ling, JIANG Rui, TANG Zilong, YANG Yunqiong. MXene: Nanoengineering and Application as Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | WU Rui, ZHANG Minhui, JIN Chenyun, LIN Jian, WANG Deping. Photothermal Core-Shell TiN@Borosilicate Bioglass Nanoparticles: Degradation and Mineralization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [3] | GUO Chunxia, CHEN Weidong, YAN Shufang, ZHAO Xueping, YANG Ao, MA Wen. Adsorption of Arsenate in Water by Zirconia-halloysite Nanotube Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 529-536. |
| [4] | WANG Shiyi, FENG Aihu, LI Xiaoyan, YU Yun. Pb (II) Adsorption Process of Fe3O4 Supported Ti3C2Tx [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [5] | CHEN Lei, HU Hailong. Evolution of Electric Field and Breakdown Damage Morphology for Flexible PDMS Based Dielectric Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 155-162. |
| [6] | YU Yefan, XU Ling, NI Zhongbing, SHI Dongjian, CHEN Mingqing. Prussian Blue Modified Biochar: Preparation and Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen from Sewage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 205-212. |
| [7] | TANG Ya, SUN Shengrui, FAN Jia, YANG Qingfeng, DONG Manjiang, KOU Jiahui, LIU Yangqiao. PEI Modified Hydrated Calcium Silicate Derived from Fly Ash and Its adsorption for Removal of Cu (II) and Catalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1281-1291. |
| [8] | DAI Jieyan, FENG Aihu, MI Le, YU Yang, CUI Yuanyuan, YU Yun. Adsorption Mechanism of NaY Zeolite Molecular Adsorber Coating on Typical Space Contaminations [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1237-1244. |
| [9] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Mesoporous Organic-inorganic Hybrid Siliceous Hollow Spheres: Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [10] | OUYANG Qin, WANG Yanfei, XU Jian, LI Yinsheng, PEI Xueliang, MO Gaoming, LI Mian, LI Peng, ZHOU Xiaobing, GE Fangfang, ZHANG Chonghong, HE Liu, YANG Lei, HUANG Zhengren, CHAI Zhifang, ZHAN Wenlong, HUANG Qing. Research Progress of SiC Fiber Reinforced SiC Composites for Nuclear Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 821-840. |
| [11] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [12] | LIU Cheng, ZHAO Qian, MOU Zhiwei, LEI Jiehong, DUAN Tao. Adsorption Properties of Novel Bismuth-based SiOCNF Composite Membrane for Radioactive Gaseous Iodine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1043-1050. |
| [13] | CHEN Xiaomei, CHEN Ying, YUAN Xia. Decomposition of Cyclohexyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Core-shell Material Co3O4@SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 65-71. |
| [14] | CHU Yuxing, LIU Hairui, YAN Shuang. Preparation and Gas Sensing Properties of SnO2/NiO Composite Semiconductor Nanofibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 950-958. |
| [15] | YU Xiangkun, LIU Kun, LI Zhipeng, ZHAO Yulu, SHEN Jinyou, MAO Ping, SUN Aiwu, JIANG Jinlong. Efficient Adsorption of Radioactive Iodide by Copper/Palygorskite Composite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 856-864. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||