
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 1337-1343.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220208
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
CAI Jia( ), HUANG Gaoxu, JIN Xiaopan, WEI Chi, MAO Jiayi, LI Yongsheng(
), HUANG Gaoxu, JIN Xiaopan, WEI Chi, MAO Jiayi, LI Yongsheng( )
)
Received:2022-04-12
Revised:2022-07-13
Published:2022-12-20
Online:2022-10-19
Contact:
LI Yongsheng, professor. E-mail: ysli@ecust.edu.cnAbout author:CAI Jia (1996-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: caijia0902@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
CAI Jia, HUANG Gaoxu, JIN Xiaopan, WEI Chi, MAO Jiayi, LI Yongsheng. In-situ Modification of Carbon Nanotubes with Metallic Bismuth Nanoparticles for Uniform Lithium Deposition[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1337-1343.
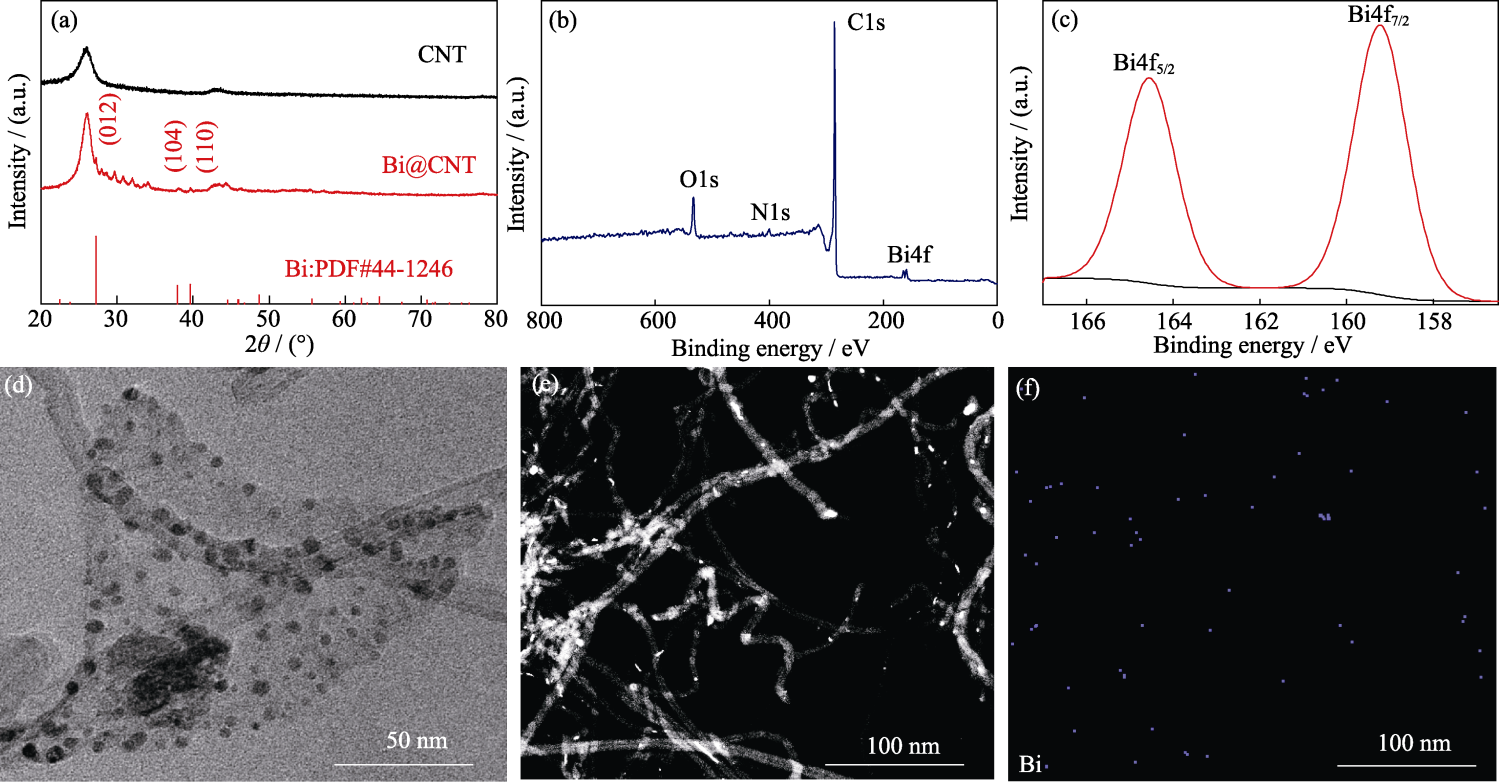
Fig. 2 Microstructure characterization of samples (a) XRD patterns of CNT and Bi@CNT; (b) Total survey and (c) high-resolution Bi4f XPS spectra of Bi@CNT; (d, e) TEM images and (f) EDS elemental mapping of Bi@CNT
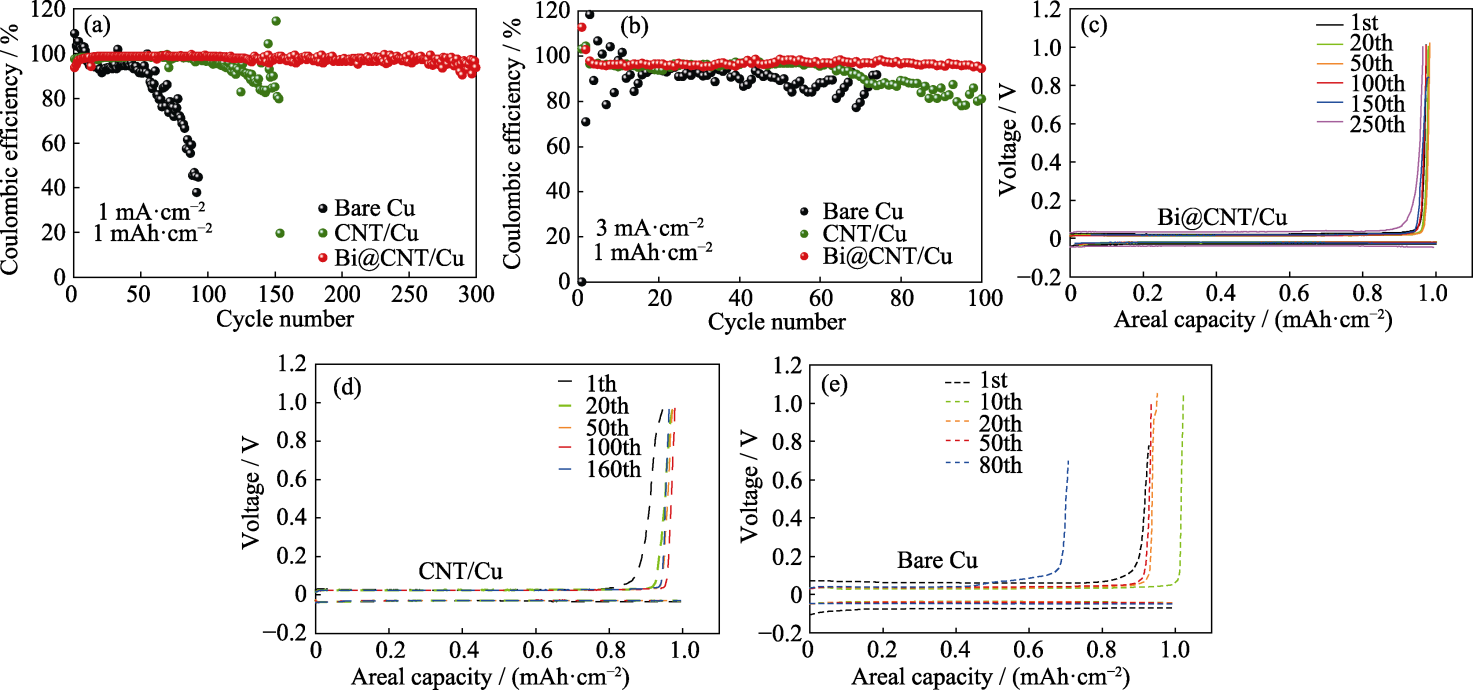
Fig. 3 Coulombic efficiencies of Li|Cu cells based on Bi@CNT/Cu, CNT/Cu and Cu current collectors at (a) 1 mA·cm-2, 1 mAh·cm-2 and (b) 3 mA·cm-2, 1 mAh·cm-2; Capacity-voltage curves of Li|Cu cells based on (c) Bi@CNT/Cu, (d) CNT/Cu, and (e) Cu current collectors at 1 mA·cm-2, 1 mAh·cm-2Colorful figures are available on website
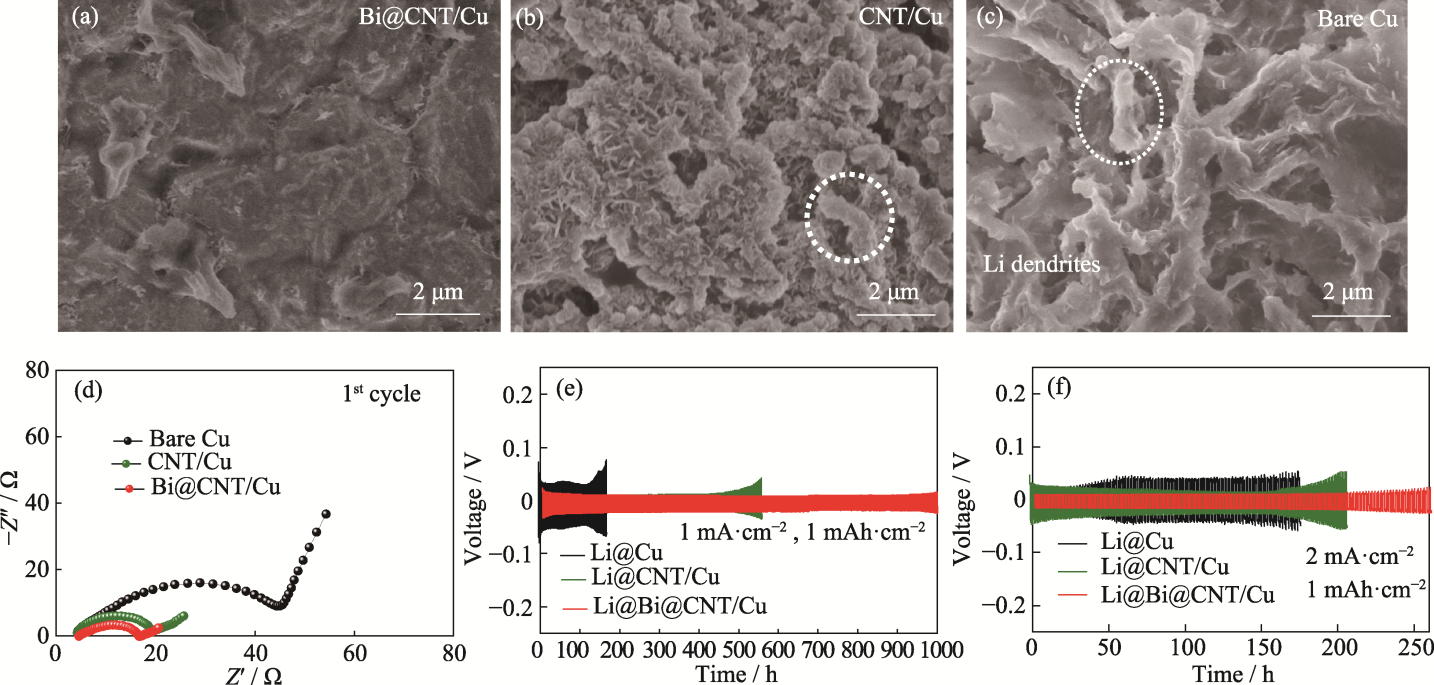
Fig. 4 SEM images of (a) Bi@CNT/Cu, (b) CNT/Cu, and (c) Cu current collectors in Li|Cu cells after 50 cycles; (d) First cyclic EIS plots of Li|Cu cells based on Bi@CNT/Cu, CNT/Cu and Cu current collectors, and voltage-time curves of symmetric cells based on Li@Bi@CNT/Cu, Li@CNT/Cu and Li@Cu anodes at (e) 1 mA·cm-2, 1 mAh·cm-2 and (f) 2 mA·cm-2, 1 mAh·cm-2 Colorful figures are available on website
| Symmetric cell | Li|Cu cell | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current collector | Current density/ (mA·cm-2) | Planting/ strippingcapacity/ (mAh·cm-2) | Cycling time/h | Current density/ (mA·cm-2) | Planting capacity/ (mAh·cm-2) | Cycle number, n | Coulombic efficiency/% | Ref. |
| Bi@CNT | 1 | 1 | 1000 | 1 | 1 | 300 | 98 | This work |
| 2 | 1 | 260 | 3 | 1 | 100 | 96 | ||
| SMC-2 | 1 | 1 | 220 | 0.5 | 1 | 210 | 97 | [21] |
| PDA | 0.1 | 0.2 | 800 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 96 | [22] |
| 3D-CuZn | 1 | 1 | 450 | 1 | 1 | 150 | 95 | [23] |
| Li-MMT | 3 | 1 | 70 | 2 | 0.25 | 100 | 97.9 | [24] |
| LHCE | 1 | 1 | 700 | 1 | 1 | 200 | 99.1 | [25] |
| NMPC | 0.5 | 0.5 | 400 | 1 | 1 | 200 | 98 | [26] |
| Duplex Cu | 1 | 1 | 880 | 1 | 1 | 300 | 97.3 | [27] |
| Ti3C2Tx | 1 | 1 | 500 | 1 | 1 | 250 | 98.4 | [28] |
| q-PET | 3 | 1 | 100 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 98 | [29] |
| SF | 3 | 3 | 350 | 1 | 1 | 200 | 96 | [30] |
Table 1 Comparison of electrochemical properties of copper foils modified by different materials
| Symmetric cell | Li|Cu cell | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current collector | Current density/ (mA·cm-2) | Planting/ strippingcapacity/ (mAh·cm-2) | Cycling time/h | Current density/ (mA·cm-2) | Planting capacity/ (mAh·cm-2) | Cycle number, n | Coulombic efficiency/% | Ref. |
| Bi@CNT | 1 | 1 | 1000 | 1 | 1 | 300 | 98 | This work |
| 2 | 1 | 260 | 3 | 1 | 100 | 96 | ||
| SMC-2 | 1 | 1 | 220 | 0.5 | 1 | 210 | 97 | [21] |
| PDA | 0.1 | 0.2 | 800 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 96 | [22] |
| 3D-CuZn | 1 | 1 | 450 | 1 | 1 | 150 | 95 | [23] |
| Li-MMT | 3 | 1 | 70 | 2 | 0.25 | 100 | 97.9 | [24] |
| LHCE | 1 | 1 | 700 | 1 | 1 | 200 | 99.1 | [25] |
| NMPC | 0.5 | 0.5 | 400 | 1 | 1 | 200 | 98 | [26] |
| Duplex Cu | 1 | 1 | 880 | 1 | 1 | 300 | 97.3 | [27] |
| Ti3C2Tx | 1 | 1 | 500 | 1 | 1 | 250 | 98.4 | [28] |
| q-PET | 3 | 1 | 100 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 98 | [29] |
| SF | 3 | 3 | 350 | 1 | 1 | 200 | 96 | [30] |
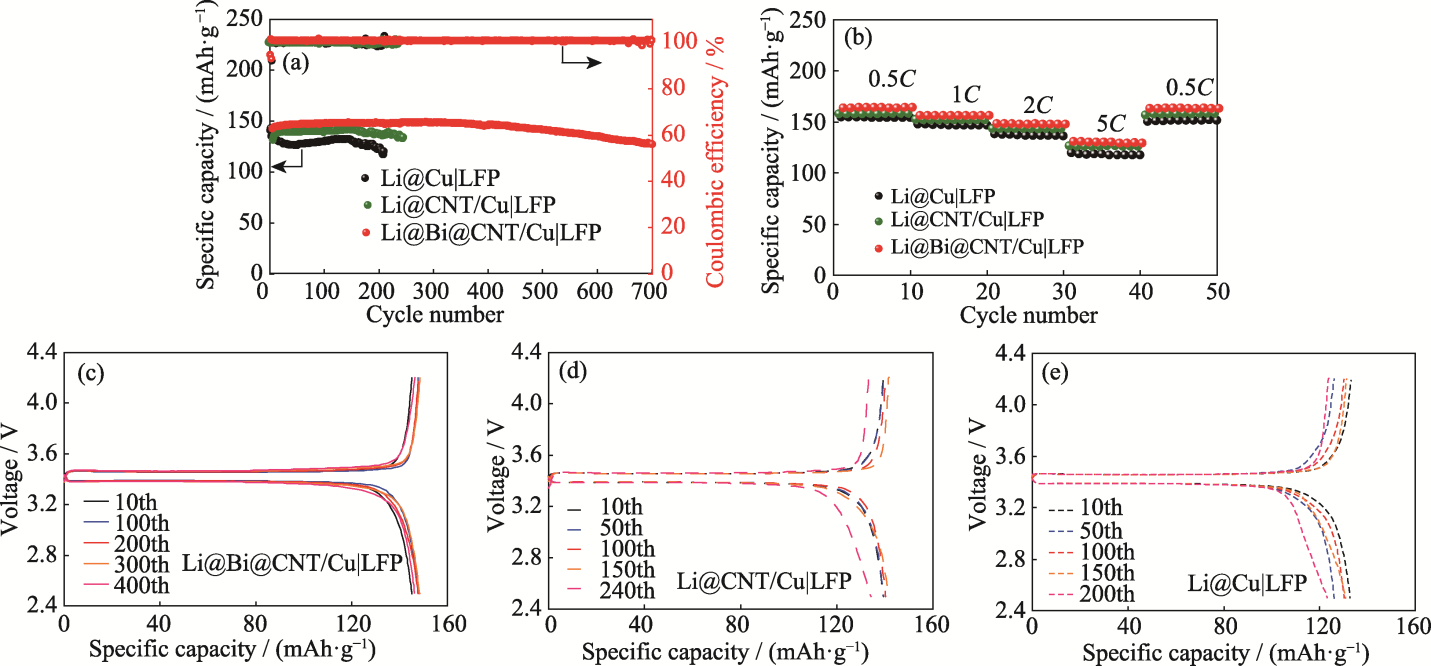
Fig.5 (a) Cycling performances and (b) rate performances of LFP full cells based on Li@Bi@CNT/Cu, Li@CNT/Cu, and Li@Cu anodes, and (c-e) capacity-voltage profiles of LFP full cells based on (c) Li@Bi@CNT/Cu, (d) Li@CNT/Cu, and (e) Li@Cu anodes at 1C Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] |
DUNN B, KAMATH H, TARASCON J M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: a battery of choices. Science, 2011, 334(6058): 928-935.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
QIAN J, HENDERSON W A, XU W, et al. High rate and stable cycling of lithium metal anode. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 6362.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
HE B, RAO Z, CHENG Z, et al. Rationally design a sulfur cathode with solid-phase conversion mechanism for high cycle-stable Li-S batteries. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(14): 2003690.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
JUNG W B, PARK H, JANG J S, et al. Polyelemental nanoparticles as catalysts for a Li-O2 battery. ACS nano, 2021, 15(3): 4235-4244.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
WOOD K N, KAZYAK E, CHADWICK A F, et al. Dendrites and pits: untangling the complex behavior of lithium metal anodes through operando video microscopy. ACS Central Science, 2016, 2(11): 790-801.
PMID |
| [6] |
SANCHEZ A J, KAZYAK E, CHEN Y, et al. Plan-view operando video microscopy of Li metal anodes: identifying the coupled relationships among nucleation, morphology, and reversibility. ACS Energy Letters, 2020, 5(3): 994-1004.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
AURBACH D. Review of selected electrode-solution interactions which determine the performance of Li and Li ion batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2000, 89(2): 206-218.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHENG X B, ZHANG R, ZHAO C Z, et al. A review of solid electrolyte interphases on lithium metal anode. Advanced Science, 2016, 3(3): 1500213.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
SHEN X, LI Y, QIAN T, et al. Lithium anode stable in air for low-cost fabrication of a dendrite-free lithium battery. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 900.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
XU R, ZHANG X Q, CHENG X B, et al. Artificial soft-rigid protective layer for dendrite-free lithium metal anode. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(8): 1705838.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LIU Y, LIU Q, XIN L, et al. Making Li-metal electrodes rechargeable by controlling the dendrite growth direction. Nature Energy, 2017, 2: 17083.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
XU K. Electrolytes and interphases in Li-ion batteries and beyond. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(23): 11503-11618.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
HUANG S, ZHANG W, MING H, et al. Chemical energy release driven lithiophilic layer on 1 m2 commercial brass mesh toward highly stable lithium metal batteries. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(3): 1832-1837.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
PEI F, FU A, YE W, et al. Robust lithium metal anodes realized by lithiophilic 3D porous current collectors for constructing high-energy lithium-sulfur batteries. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(7): 8337-8346.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
YAN K, LU Z, LEE H W, et al. Selective deposition and stable encapsulation of lithium through heterogeneous seeded growth. Nature Energy, 2016, 1: 16010.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
PEI A, ZHENG G, SHI F, et al. Nanoscale nucleation and growth of electrodeposited lithium metal. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(2): 1132-1139.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
ZHANG Y, LUO W, WANG C, et al. High-capacity, low-tortuosity, and channel-guided lithium metal anode. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2017, 114(14): 3584-3589.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
QIU H, TANG T, ASIF M, et al. 3D porous Cu current collectors derived by hydrogen bubble dynamic template for enhanced Li metal anode performance. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(19): 1808468.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
HU Z, LI Z, XIA Z, et al. PECVD-derived graphene nanowall/ lithium composite anodes towards highly stable lithium metal batteries. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 22: 29-39.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
HOU G, SUN Q, AI Q, et al. Growth direction control of lithium dendrites in a heterogeneous lithiophilic host for ultra-safe lithium metal batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 416: 141-147.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG F, LIU X, YANG M, et al. Novel S-doped ordered mesoporous carbon nanospheres toward advanced lithium metal anodes. Nano Energy, 2020, 69: 104443.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
HE Y, XU H, SHI J, et al. Polydopamine coating layer modified current collector for dendrite-free Li metal anode. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 23: 418-426.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHANG D, DAI A, WU M, et al. Lithiophilic 3D porous CuZn current collector for stable lithium metal batteries. ACS Energy Letters, 2019, 5(1): 180-186.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
NAN Y, LI S, HAN C, et al. Interlamellar lithium-ion conductor reformed interface for high performance lithium metal anode. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(25): 2102336.
DOI URL |
| [25] | LIU Y, WU X, NIU C, et al. Systematic evaluation of carbon hosts for high-energy rechargeable lithium-metal batteries. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(4): 1550-1559. |
| [26] |
LIU H, WANG E, ZHANG Q, et al. Unique 3D nanoporous/ macroporous structure Cu current collector for dendrite-free lithium deposition. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 17: 253-259.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LIN K, LI T, CHIANG S W, et al. Facile synthesis of ant-nest-like porous duplex copper as deeply cycling host for lithium metal anodes. Small, 2020, 16(37): 2001784.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
YANG D, ZHAO C, LIAN R, et al. Mechanisms of the planar growth of lithium metal enabled by the 2D lattice confinement from a Ti3C2Tx MXene intermediate layer. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(24): 2010987.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZHANG W, ZHUANG H L, FAN L, et al. A “cation-anion regulation” synergistic anode host for dendrite-free lithium metal batteries. Science Advances, 2018, 4(2): eaar4410.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
FU A, WANG C, PENG J, et al. Lithiophilic and antioxidative copper current collectors for highly stable lithium metal batteries. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(15): 2009805.
DOI URL |
| [1] | LI Rui,WANG Hao,FU Qiang,TIAN Ziyu,WANG Jianxu,MA Xiaojian,YANG Jian,QIAN Yitai. Stable Li-metal Depositon on Lithiophilic 3D CuO Nanosheet-decorated Cu Mesh [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 882-888. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||