
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 219-224.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220300
WANG Huajin1,2( ), KOU Huamin2(
), KOU Huamin2( ), WANG Yongzhe2, JIANG Dapeng2, ZHANG Bo2, QIAN Xiaobo2, WANG Jingya2, ZHU Linling4, ZENG Aijun4, YANG Qiuhong1, SU Liangbi2,3(
), WANG Yongzhe2, JIANG Dapeng2, ZHANG Bo2, QIAN Xiaobo2, WANG Jingya2, ZHU Linling4, ZENG Aijun4, YANG Qiuhong1, SU Liangbi2,3( )
)
Received:2022-05-27
Revised:2022-06-04
Published:2023-02-20
Online:2022-08-26
Contact:
KOU Huamin, associate professor. E-mail: huaminkou@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:WANG Huajin (1996-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: wanghuajin@shu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Huajin, KOU Huamin, WANG Yongzhe, JIANG Dapeng, ZHANG Bo, QIAN Xiaobo, WANG Jingya, ZHU Linling, ZENG Aijun, YANG Qiuhong, SU Liangbi. Irradiation Damage of CaF2 with Different Yttrium Concentrations under 193 nm Laser[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 219-224.
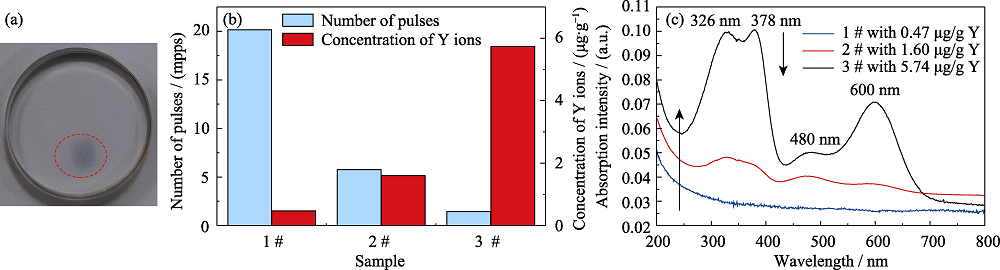
Fig. 2 Radiation damage result (a) Damage morphology; (b) Relationship between Y ions and radiation resistance; (c) Damaged region absorption spectra mpps: million pulsesper second
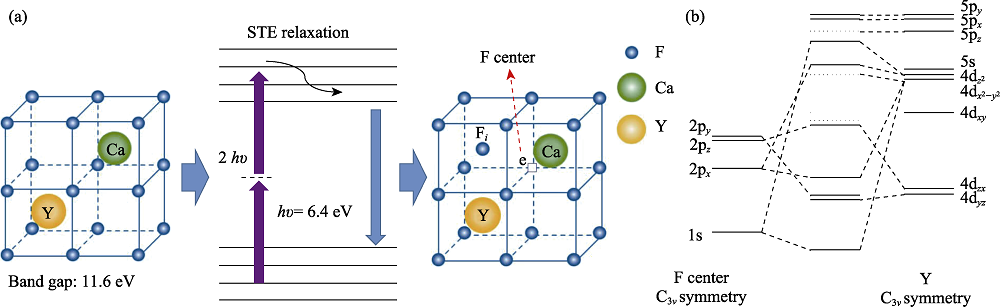
Fig. 3 Schematic diagrams of the formation process of color centers (a) F center generated by self-excited defects formed by two-photon absorption; (b) defect-impurity orbital energy levels of the YFC
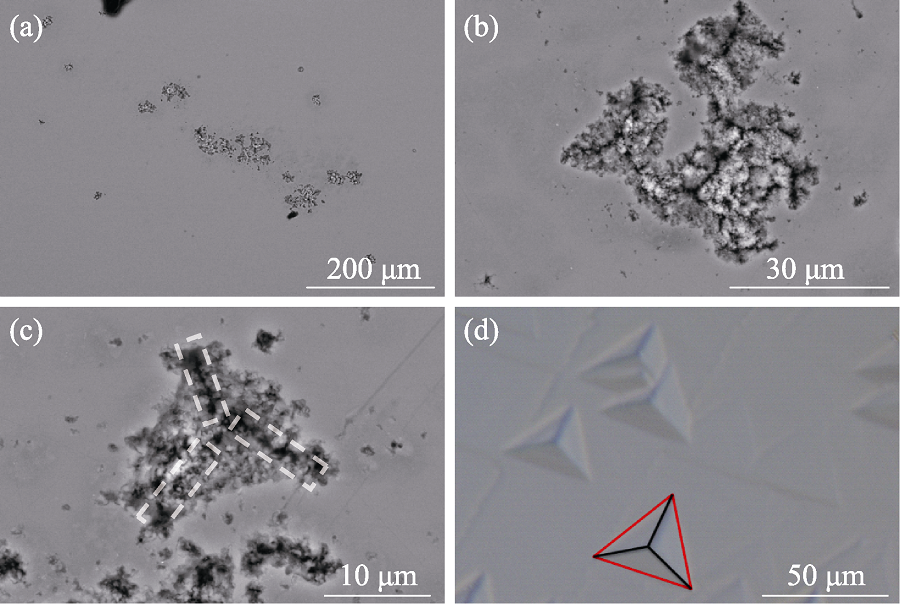
Fig. 5 SEM images of damaged area (a) Complete morphology of the damage pits; (b) Aggregate damage pits; (c) Single damage pit; (d) Etch pits of dislocations (HCl etching)
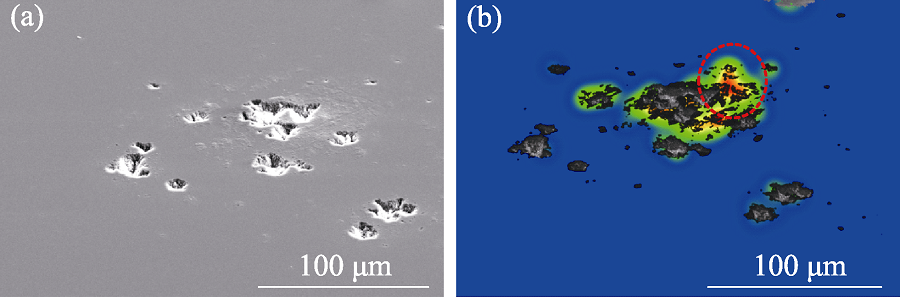
Fig. 6 Damage morphologies of sample 2# under different modes of SEM (a) Secondary electron image; (b) Stress distribution diagram, blue, green and red regions indicate the variation of stress from low to high, respectively
| Crystal | c11/GPa | c12/GPa | Lattice constant/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaF2 | 165 | 46 | 0.546 |
| Ca | 16 | 8 | 0.558 |
Table 1 Elastic stiffness constants cij and lattice constant of Ca and CaF2[28-29]
| Crystal | c11/GPa | c12/GPa | Lattice constant/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaF2 | 165 | 46 | 0.546 |
| Ca | 16 | 8 | 0.558 |
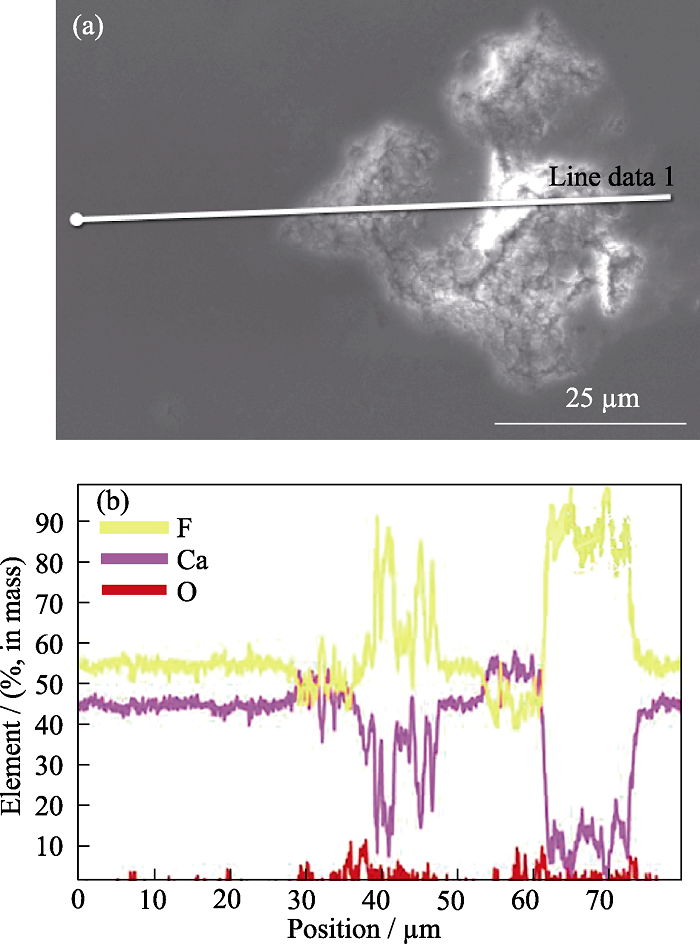
Fig. 7 EDS analysis of sample 2# damage pits (a) EDS sampling location; (b) EDS results of elements at different positions Colorful figure is available on website
| [1] |
KAWAGUCHI Y, DAWES M L, LANGFORD S C, et al. Interaction of wide band gap single crystals with 248 nm excimer laser irradiation. VII. Localized plasma formation on NaCl single crystal surfaces. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(4): 2370.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
REIF J, PETZOLDT S, ELG A P, et al. The role of defects in laser surface damage thresholds of fluoride crystals. Applied Physics A, 1989, 49(2): 199.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
REICHLING M, SILS J, JOHANSEN H, et al. Nanosecond UV laser damage and ablation from fluoride crystals polished by different techniques. Applied Physics A, 1999, 69(1): S743.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
JOHANSEN H, GOGOLL S, STENZEL E, et al. Sem-analysis of fracture features formed in excimer-laser induced surface damage of CaF2. Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids, 1995, 136(1-4): 151.
DOI URL |
| [5] | MUEHLIG C, TRIEBEL W, TOEPFER G, et al. Laser-induced fluorescence of calcium fluoride at 193 and 157 nm excitation. SPIE, 2003, 5188: 123. |
| [6] | RIX S, NATURA U, LETZ M, et al. A microscopic model for long-term laser damage in calcium fluoride. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2009, 7504: 75040J. |
| [7] |
KOMINE N, SAKUMA S, SHIOZAWA M, et al. Influence of sodium impurities on ArF excimer-laser-induced absorption in CaF2 crystals. Applied Optics, 2000, 39(22): 3925.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
BAUER M, BISCHOFF M, JUKRESCH S, et al. Exterior surface damage of calcium fluoride outcoupling mirrors for DUV lasers. Optics Express, 2009, 17(10): 8253.
PMID |
| [9] | AZUMI M, NAKAHATA E. Laser damage of calcium fluoride by ArF excimer laser irradiation. SPIE, 2015, 9632: 199. |
| [10] |
IZERROUKEN M, GUERBOUS L, MEFTAH A. Colour centres formation in CaF2 single crystals by γ-rays and reactor neutrons. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2010, 621(1/2/3): 68.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
SMAKULA A. Color centers in calcium fluoride and barium fluoride crystals. Physical Review, 1950, 77(3): 408.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SCOULER W J, SMAKULA A. Coloration of pure and doped calcium fluoride crystals at 20 ℃ and -190 ℃. Physical Review, 1960, 120(4): 1154.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MIE G. Beiträge zur optik trüber medien, speziell kolloidaler metallösungen. Annalen der physik, 1908, 330(3): 377-445.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
BEUNEU F, FLOREA C, VAJDA P. EPR-study of electron-radiation induced Ca colloids in CaF2 crystals. Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids, 1995, 136(1-4): 175.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
BATOOL A, IZERROUKEN M, AISIDA S O, et al. Effect of Ca colloids on in-situ ionoluminescence of CaF2 single crystals. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2020, 476: 40.
DOI URL |
| [16] | PRZIBRAM K. Absorption bands and electron transitions in coloured fluorites. Nature, 1938, 141(3578): 970. |
| [17] |
BILL H, LACROIX R. EPR of a centre in Y3+ doped artificial CaF2 crystals. Physics Letters, 1966, 22(3): 250.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
BILL H. Endor investigation of Gd3+ in CaF2 crystals. Physics Letters A, 1969, 29(10): 593.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ALIG R C. Theory of photochromic centers in CaF2. Physical Review B, 1971, 3(2): 536.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
STAEBLER D L, SCHNATTERLY S E. Optical studies of a photochromic color center in rare-earth-doped CaF2. Physical Review B, 1971, 3(2): 516.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
MIZUGUCHI M, HOSONO H, KAWAZOE H, et al. Generation of optical absorption bands in CaF2 single crystals by ArF excimer laser irradiation: effect of yttrium impurity. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A: Vacuum, Surfaces, and Films, 1998, 16(5): 3052.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
PARKER S, SONG K S, CATLOW C R A, et al. Geometry and charge distribution of H centres in the fluorite structure. Journal of Physics C: Solid State Physics, 1981, 14(28): 4009.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
KAMIKAWA T, KAZUMATA Y, KIKUCHI A, et al. The F center in calcium fluoride. Physics Letters, 1966, 21(2): 126.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
HAYES W. Point defects in alkaline earth fluorides. Radiation Effects, 1970, 4(2): 239.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
MA Y, ROHLFING M. Optical excitation of deep defect levels in insulators within many-body perturbation theory: the F center in calcium fluoride. Physical Review B, 2008, 77(11): 115118.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
RAUCH R, SCHWOTZER G. Disturbed colour centres in oxygen- and alkali-doped alkaline earth fluoride crystals after X-ray irradiation at 77 and 295 K. Physica Status Solidi (a), 1982, 74(1): 123.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
TANIMURA K. Femtosecond time-resolved spectroscopy of the formation of self-trapped excitons in CaF2. Physical Review B, 2001, 63(18): 184303.
DOI URL |
| [28] | SHANG S L, SAENGDEEJING A, MEI Z G, et al. First-principles calculations of pure elements: equations of state and elastic stiffness constants. Computational Materials Science, 2010, 48(4): 8136. |
| [29] |
GUO Y, FANG Y, LI J. Detailed structural, mechanical, and electronic study of five structures for CaF2 under high pressure. Chinese Physics B, 2021, 30(3): 030502
DOI URL |
| [1] | PANG Si-Yuan, QIAN Xiao-Bo, WU Qing-Hui, YU Hao, XU Jia-Yue, SU Liang-Bi. Structure and Spectral Property of Sc Doped Nd:CaF2 Laser Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(8): 873-876. |
| [2] | HE Yi-Feng, XUE Yan-Yan, LIU Wen-Qing, SU Liang-Bi, TANG Fei, WANG Jing-Ya. Structure and Property of Yb Doped Ca1-xRxF2+x (R=La, Gd) Laser Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 857-862. |
| [3] | WANG Jin, TAO Ke, LI Guo-Feng, LIANG Ke, CAI Hong-Kun. Effect of Hydrogen Annealing on the Property of Low-temperature Epitaxial Growth of Sige Thin Films on Si Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(2): 191-196. |
| [4] | CUI Ying-Xin, XU Ming-Sheng, XU Xian-Gang, HU Xiao-Bo. High Resolution X-ray Diffraction Analysis of Defect Density of Gallium Nitride Epitaxial Layer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(10): 1094-1098. |
| [5] | FU Xin-Jie, SONG Li-Xin, LI Jia-Cheng. Coloration of Ce-doped Multicomponent Silicate Glasses by Electron Irradiation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10): 1018-1022. |
| [6] | XU Ya-Xin, XIONG Jie, XIA Yu-Dong, ZHANG Fei, XUE Yan, TAO Bo-Wan. [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(5): 491-496. |
| [7] | SHENG Yu-Bang, XING Rui-Xian, LUAN Huai-Xun, LIU Zi-Jun, LI Jin-Yan, DAI Neng-Li. Gamma Radiation Effects on the Optical Properties of Yb-doped Silicate Glasses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(8): 860-864. |
| [8] | DU Ji-Shi, ZHANG Tao, ZHAO Li-Li, SONG Li-Xin, HU Xing-Fang. Study on Dynamic of Space Ionizing Radiation Induced Coloration in Glasses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(11): 1197-1204. |
| [9] | QU Xiang-Dong,ZHANG Li-Yuan,ZHU Ren-Yuan,LIAO Jing-Ying,YIN Zhi-Wen. Luminescence Spectra and Radiation Induced Color Centers for Lead Tungstate Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2001, 16(4): 601-608. |
| [10] | LIU Bo,SHI Chao-Shu,ZHOU Dong-Fang. Irradiation Effect of New Scintillators [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2001, 16(1): 1-8. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||