
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 1275-1280.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220294
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Xishi1,2( ), ZHU Yunzhou2(
), ZHU Yunzhou2( ), HUANG Qing1, HUANG Zhengren1,2(
), HUANG Qing1, HUANG Zhengren1,2( )
)
Received:2022-05-25
Revised:2022-06-30
Published:2022-12-20
Online:2022-08-04
Contact:
ZHU Yunzhou, associate professor. E-mail: yunzhouzhu@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:WU Xishi (1991-), male, PhD. E-mail: wuxishi@nimte.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WU Xishi, ZHU Yunzhou, HUANG Qing, HUANG Zhengren. Effect of Pore Structure of Organic Resin-based Porous Carbon on Joining Properties of Cf/SiC Composites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1275-1280.
| Sample | PF/% | EG/% | Pore former* | Residual carbon**/% | Average pore size/nm | Bulk density/(g·cm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | 50 | FeCl2 (1%) | 23+1.1 | 190±15 | 0.73±0.01 |
| 2 | 50 | 50 | H3BO3 (1.5%) | 24.3±0.9 | 642±15 | 0.74±0.01 |
| 3 | 50 | 50 | FeCl2 (1%) + H3BO3 (1.5%) | 24.1±1.7 | 1226±48 | 0.74±0.03 |
| 4 | 50 | 50 | H3BO3 (2.5%) | 25.8±2.1 | 1552±38 | 0.79±0.03 |
| 5 | 50 | 50 | H3BO3 (3.5%) | 26.7±1.5 | 2363±54 | 0.79±0.03 |
Table 1 Composition of resin solution and properties of porous carbons after pyrolysis
| Sample | PF/% | EG/% | Pore former* | Residual carbon**/% | Average pore size/nm | Bulk density/(g·cm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | 50 | FeCl2 (1%) | 23+1.1 | 190±15 | 0.73±0.01 |
| 2 | 50 | 50 | H3BO3 (1.5%) | 24.3±0.9 | 642±15 | 0.74±0.01 |
| 3 | 50 | 50 | FeCl2 (1%) + H3BO3 (1.5%) | 24.1±1.7 | 1226±48 | 0.74±0.03 |
| 4 | 50 | 50 | H3BO3 (2.5%) | 25.8±2.1 | 1552±38 | 0.79±0.03 |
| 5 | 50 | 50 | H3BO3 (3.5%) | 26.7±1.5 | 2363±54 | 0.79±0.03 |
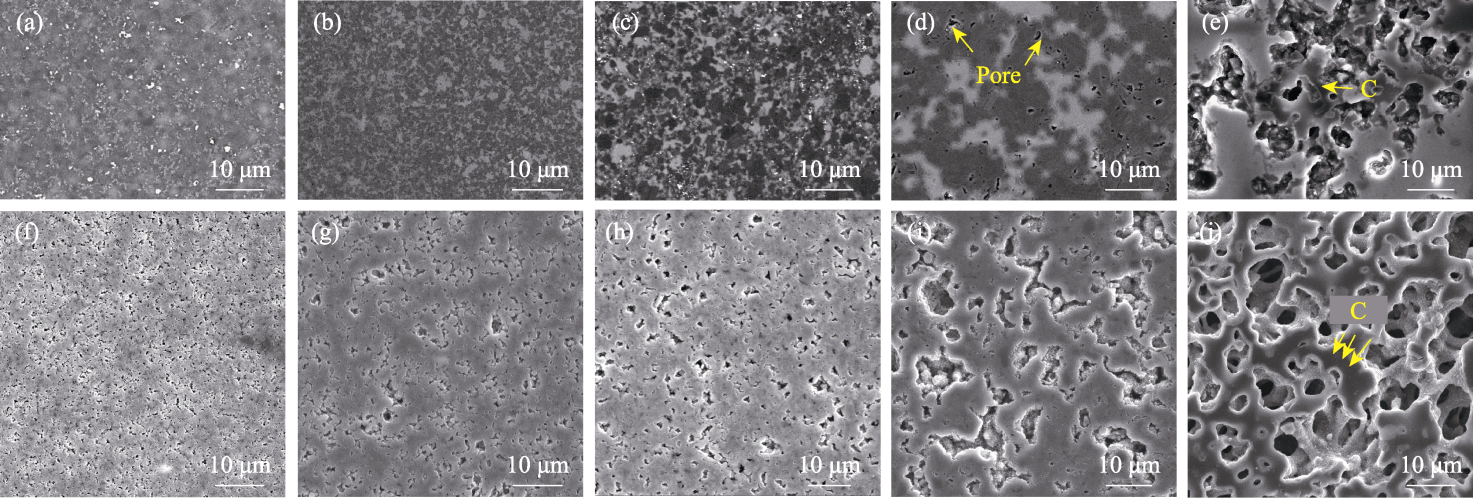
Fig. 2 Morphologies of the polished surfaces before and after HF-HNO3 corrosion of RBSC fabricated from preforms with different pore sizes (a, f) 190 nm; (b, g) 642 nm; (c, h) 1226 nm; (d, i) 1552 nm; (e, j) 2363 nm
| Pore size/nm | Open porosity/% | Density/ (g·cm-3) | Flexural strength/MPa | Residual Si/(%, in volume) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 190 | 0.97 | 2.93 | 296±28 | 16 |
| 642 | 1.26 | 2.91 | 268±46 | 14 |
| 1226 | 1.87 | 2.88 | 248±22 | 16 |
| 1552 | 3.51 | 2.81 | 238±44 | 12 |
| 2363 | 18.76 | 2.10 | 115±32 | 13 |
Table 2 Properties of the RBSC fabricated from preforms with different pore sizes
| Pore size/nm | Open porosity/% | Density/ (g·cm-3) | Flexural strength/MPa | Residual Si/(%, in volume) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 190 | 0.97 | 2.93 | 296±28 | 16 |
| 642 | 1.26 | 2.91 | 268±46 | 14 |
| 1226 | 1.87 | 2.88 | 248±22 | 16 |
| 1552 | 3.51 | 2.81 | 238±44 | 12 |
| 2363 | 18.76 | 2.10 | 115±32 | 13 |
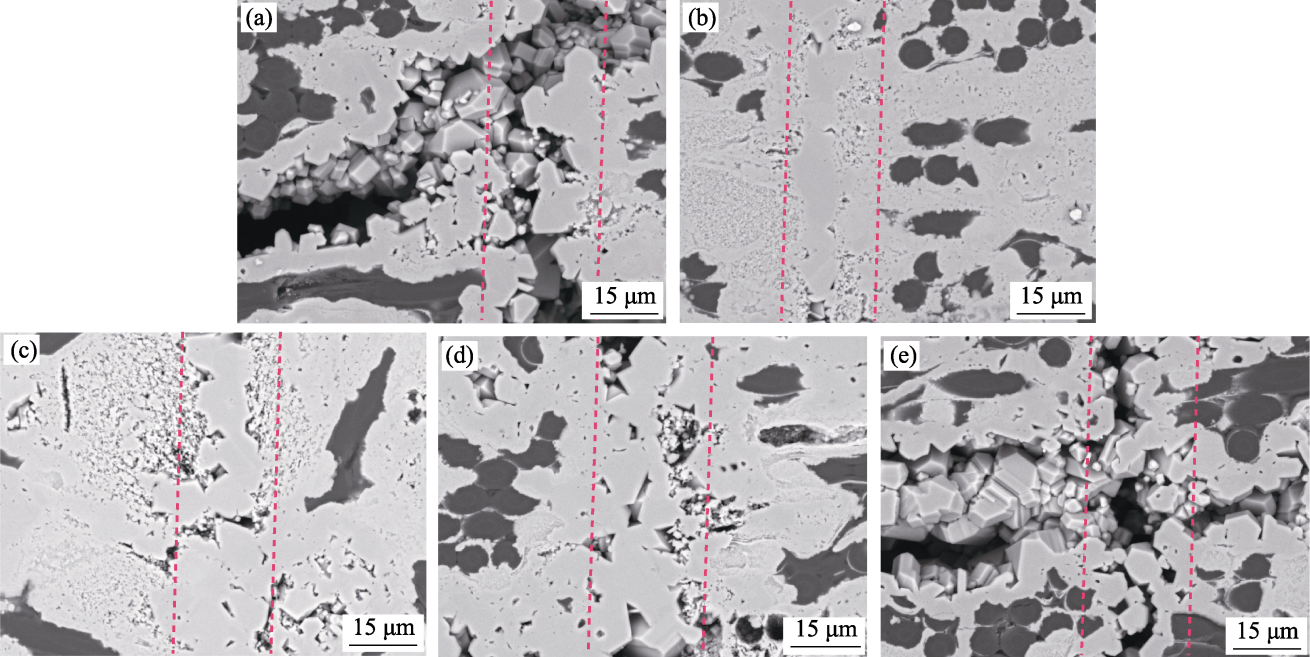
Fig. 4 Surface microstructures after HF-HNO3 corrosion of joining samples with different pore sizes (a) 14 nm; (b) 190 nm; (c) 316 nm; (d) 642 nm; (e) 1226 nm
| Pore size/nm | Flexural strength/MPa | Strength retention/% |
|---|---|---|
| 14 | 90±28 | 61 |
| 190 | 125±12 | 85 |
| 316 | 77±10 | 52 |
| 642 | 107±15 | 73 |
| 1226 | 65±22 | 44 |
Table 3 Properties of joining samples with different pore sizes
| Pore size/nm | Flexural strength/MPa | Strength retention/% |
|---|---|---|
| 14 | 90±28 | 61 |
| 190 | 125±12 | 85 |
| 316 | 77±10 | 52 |
| 642 | 107±15 | 73 |
| 1226 | 65±22 | 44 |
| Sample | PF/ % | EG/ % | Dispersant*/% | Pore former** (FeCl2)/% | α-SiC powder/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 40 | 4 | 1 | 20 |
| 2 | 35 | 35 | 4 | 1 | 30 |
| 3 | 30 | 30 | 4 | 1 | 40 |
| 4 | 25 | 25 | 4 | 1 | 50 |
| 5 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 4 | 1 | 55 |
Table 4 Composition of resin-based slurry
| Sample | PF/ % | EG/ % | Dispersant*/% | Pore former** (FeCl2)/% | α-SiC powder/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 40 | 4 | 1 | 20 |
| 2 | 35 | 35 | 4 | 1 | 30 |
| 3 | 30 | 30 | 4 | 1 | 40 |
| 4 | 25 | 25 | 4 | 1 | 50 |
| 5 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 4 | 1 | 55 |
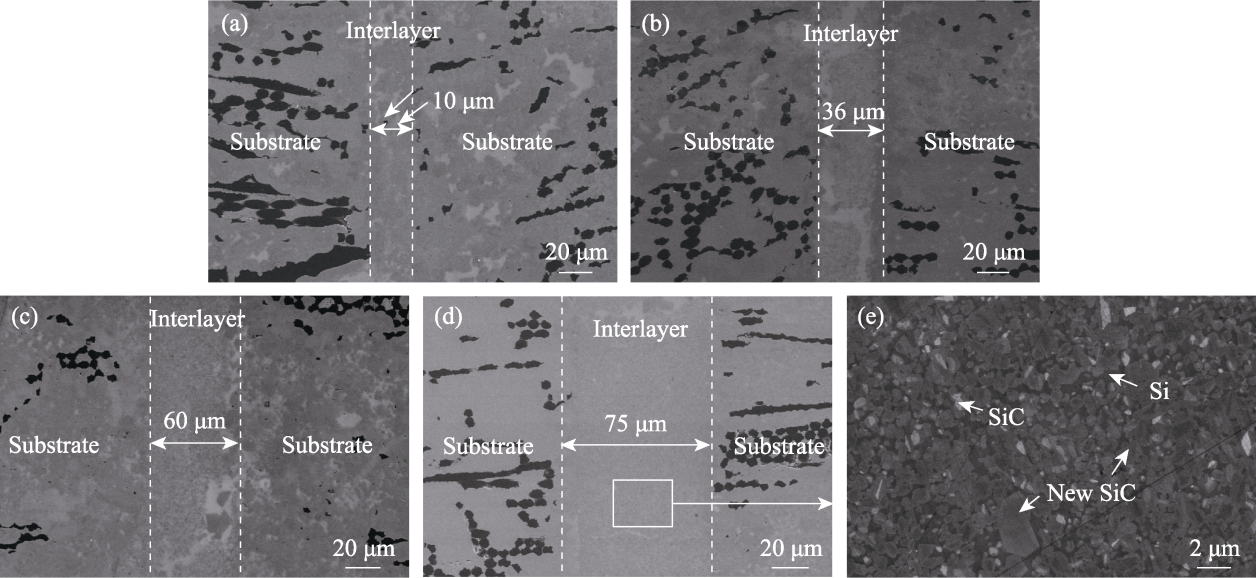
Fig. 6 Microstructures of the joint with different contents of inert filler ((a) 30%; (b) 40%; (c) 50%; (d) 55%, in mass) and (e) partial enlargement of (d)
| [1] |
CHENG T B, WANG X R, ZHANG R B, et al. Tensile properties of two-dimensional carbon fiber reinforced silicon carbide composites at temperatures up to 2300 ℃. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(3): 630-635.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN S, CHEN P, DUAN J, et al. Thermal cycling behavior of bi-layer Yb2Si2O7/SiC EBC coated Cf/SiC composites in burner rig tests. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2022, 5: 2184-2192.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BERBON M Z, DIETRICH D R, MARSHALL D B, et al. Transverse thermal conductivity of thin C/SiC composites fabricated by slurry infiltration and pyrolysis. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001, 84(10): 2229-2234.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CAO X Y, YIN X W, FAN X M, et al. High temperature flexural properties of SiBC modified C/SiC composites. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(4): 6185-6190.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LIU Y, ZHU Y Z, YANG Y, et al. Microstructure of reaction layer and its effect on the joining strength of SiC/SiC joints brazed using Ag-Cu-In-Ti alloy. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2014, 3(1): 71-75.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SAIED M A, LLOYD I K, HALLER W K, et al. Joining dental ceramic layers with glass. Dental Materials, 2011, 27(10): 1011-1016.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
YANG H, ZHOU X B, SHI W, et al. Thickness-dependent phase evolution and bonding strength of SiC ceramics joints with active Ti interlayer. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(4): 1233-1241.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
JEONG D H, SEPTIADI A, FITRIANI P, et al. Joining of SiCf/SiC using polycarbosilane and polysilazane preceramic mixtures. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(9): 10443-10450.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
SINGH M, LARA-CURZIO E. Design, fabrication, and testing of ceramic joints for high temperature SiC/SiC composites. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power-Transactions of the ASME, 2001, 123(2): 288-292.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
SINGH M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of reaction- formed joints in reaction-bonded silicon carbide ceramics. Journal of Materials Science, 1998, 33(24): 5781-5787.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LI S B, MA M L, GAO J Q, et al. Reaction forming of joints in silicon carbide ceramic materials. Materials Science and Engineering A-Structural Materials Properties Microstructure and Processing, 2008, 483-484: 747-750.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LUO Z H, JIANG D L, ZHANG J X, et al. Development of SiC-SiC joint by reaction bonding method using SiC/C tapes as the interlayer. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2012, 32(14): 3819-3824.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHANG Y M, YUAN Z Y, ZHOU Y F. Gelcasting of silicon carbide ceramics using phenolic resin and furfuryl alcohol as the gel former. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(23): 7873-7878.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WU X S, ZHU Y Z, PEI B B, et al. Effect of FeCl2 on the pore structure of porous carbon obtained from phenol formaldehyde resin and ethylene glycol. Materials Letters, 2018, 215: 50-52.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WU X S, SU R H, ZHU Y Z, et al. Pore structure control of porous carbon obtained from phenol formaldehyde resin and ethylene glycol: the effect of H3BO3 on the pore structure. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(8): 4203-4209.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
WU X S, SU R H, PEI B B, et al. Pore structure control of porous carbon via the synergistic effect of boric acid and divalent metal iron salt. Materials Letters, 2019, 255: 126539.
DOI URL |
| [17] | BEHRENDT D, SINGH M. Effect of carbon preform pore volume and infiltrants on the composition of reaction-formed silicon carbide materials. J. Mater. Synth. Process., 1994, 2(2): 117-123. |
| [18] |
WANG Y, TAN S, JIANG D. The effect of porous carbon preform and the infiltration process on the properties of reaction-formed SiC. Carbon, 2004, 42(8/9): 1833-1839.
DOI URL |
| [19] | HILLIG W B. Melt infiltration approach to ceramic matrix composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1988, 71(2): 96-99. |
| [20] |
XU S J, QIAO G J, WANG H J, et al. Microstructure evolution and reaction mechanism of microporous carbon derived SiC ceramic. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(2): 291-296.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SUYAMA S, KAMEDA T, ITOH Y. Development of high-strength reaction-sintered silicon carbide. Diamond and Related Materials, 2003, 12(3-7): 1201-1204.
DOI URL |
| [1] | AN Wenran, HUANG Jingqi, LU Xiangrong, JIANG Jianing, DENG Longhui, CAO Xueqiang. Effect of Heat-treatment Temperature on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of LaMgAl11O19 Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 925-932. |
| [2] | LI Wenjun, WANG Hao, TU Bingtian, CHEN Qiangguo, ZHENG Kaiping, WANG Weiming, FU Zhengyi. Preparation and Property of Mg0.9Al2.08O3.97N0.03 Transparent Ceramic with Broad Optical Transmission Range [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 969-975. |
| [3] | ZHANG Ye, ZENG Yuping. Progress of Porous Silicon Nitride Ceramics Prepared via Self-propagating High Temperature Synthesis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 853-864. |
| [4] | HONG Du, NIU Yaran, LI Hong, ZHONG Xin, ZHENG Xuebin. Tribological Properties of Plasma Sprayed TiC-Graphite Composite Coatings [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 643-650. |
| [5] | XU Puhao, ZHANG Xiangzhao, LIU Guiwu, ZHANG Mingfen, GUI Xinyi, QIAO Guanjun. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SiC Joint Brazed by Al-Ti Alloys as Filler Metal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 683-690. |
| [6] | XIA Qian, SUN Shihao, ZHAO Yiliang, ZHANG Cuiping, RU Hongqiang, WANG Wei, YUE Xinyan. Effect of Boron Carbide Particle Size Distribution on the Microstructure and Properties of Reaction Bonded Boron Carbide Ceramic Composites by Silicon Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 636-642. |
| [7] | DING Jianxiang, ZHANG Kaige, LIU Dongming, ZHENG Wei, ZHANG Peigen, SUN Zhengming. Ag-based Electrical Contact Material Reinforced by Ti3AlC2 Ceramic and Its Derivative Ti3C2Tx [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 567-573. |
| [8] | WEI Tingting, GAO Xiguang, SONG Yingdong. Response of 2D SiC/SiC Composites Resistivity to Service Environments [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 420-426. |
| [9] | SUN Yangshan, YANG Zhihua, CAI Delong, ZHANG Zhengyi, LIU Qi, FANG Shuqing, FENG Liang, SHI Lifen, WANG Youle, JIA Dechang. Crystallization Kinetics, Properties of α-cordierite Based Glass-ceramics Prepared by Glass Powder Sintering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1351-1357. |
| [10] | DONG Kangjia, JIANG Chen, REN Shaobin, LANG Xiaohu, GAO Rui, YE Hui. Anisotropic Calculation of Mechanical Property of GaAs Crystal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 645-651. |
| [11] | SUN Luchao, ZHOU Cui, DU Tiefeng, WU Zhen, LEI Yiming, LI Jialin, SU Haijun, WANG Jingyang. Directionally Solidified Al2O3/Er3Al5O12 and Al2O3/Yb3Al5O12 Eutectic Ceramics Prepared by Optical Floating Zone Melting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 652-658. |
| [12] | LÜ Shasha, ZU Yufei, CHEN Guoqing, ZHAO Bojun, FU Xuesong, ZHOU Wenlong. Preparation and Mechanical Property of the Ceramic-reinforced Cr0.5MoNbWTi Refractory High-entropy Alloy Matrix Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 386-392. |
| [13] | WANG Haoxuan, LIU Qiaomu, WANG Yiguang. Research Progress of High Entropy Transition Metal Carbide Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 355-364. |
| [14] | JIN Min, BAI Xudong, ZHAO Su, ZHANG Rulin, CHEN Yuqi, ZHOU Lina. Mechanical Property of SnSe Single Crystal Prepared via Vertical Bridgman Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 313-318. |
| [15] | ZENG Fanxin, LIU Chuang, CAO Yuliang. Sodium Storage Behavior of Nanoporous Sb/MCNT Anode Material with High Cycle Stability by Dealloying Route [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1137-1144. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||