
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 1267-1274.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220265
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Pingping1,2( ), ZHONG Xin1(
), ZHONG Xin1( ), ZHANG Le3, LI Hong2(
), ZHANG Le3, LI Hong2( ), NIU Yaran1, ZHANG Xiangyu1, LI Qilian3, ZHENG Xuebin1
), NIU Yaran1, ZHANG Xiangyu1, LI Qilian3, ZHENG Xuebin1
Received:2022-05-06
Revised:2022-05-29
Published:2022-12-20
Online:2022-06-16
Contact:
ZHONG Xin, assistant professor. E-mail: zhongxin@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:LIU Pingping (1995-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: ppliu1234@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LIU Pingping, ZHONG Xin, ZHANG Le, LI Hong, NIU Yaran, ZHANG Xiangyu, LI Qilian, ZHENG Xuebin. Molten Salt Corrosion Behaviors and Mechanisms of Ytterbium Silicate Environmental Barrier Coating[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1267-1274.
| Yb2SiO5 | Yb2Si2O7 | Si | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Ar/(L·min-1) | 46 | 53 | 52 |
| Secondary H2/(L·min-1) | 14 | 10 | 13 |
| Carrier Ar/(L·min-1) | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.0 |
| Spray distance/mm | 220 | 220 | 290 |
Table 1 Operating parameters used for vacuum plasma spraying
| Yb2SiO5 | Yb2Si2O7 | Si | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Ar/(L·min-1) | 46 | 53 | 52 |
| Secondary H2/(L·min-1) | 14 | 10 | 13 |
| Carrier Ar/(L·min-1) | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.0 |
| Spray distance/mm | 220 | 220 | 290 |
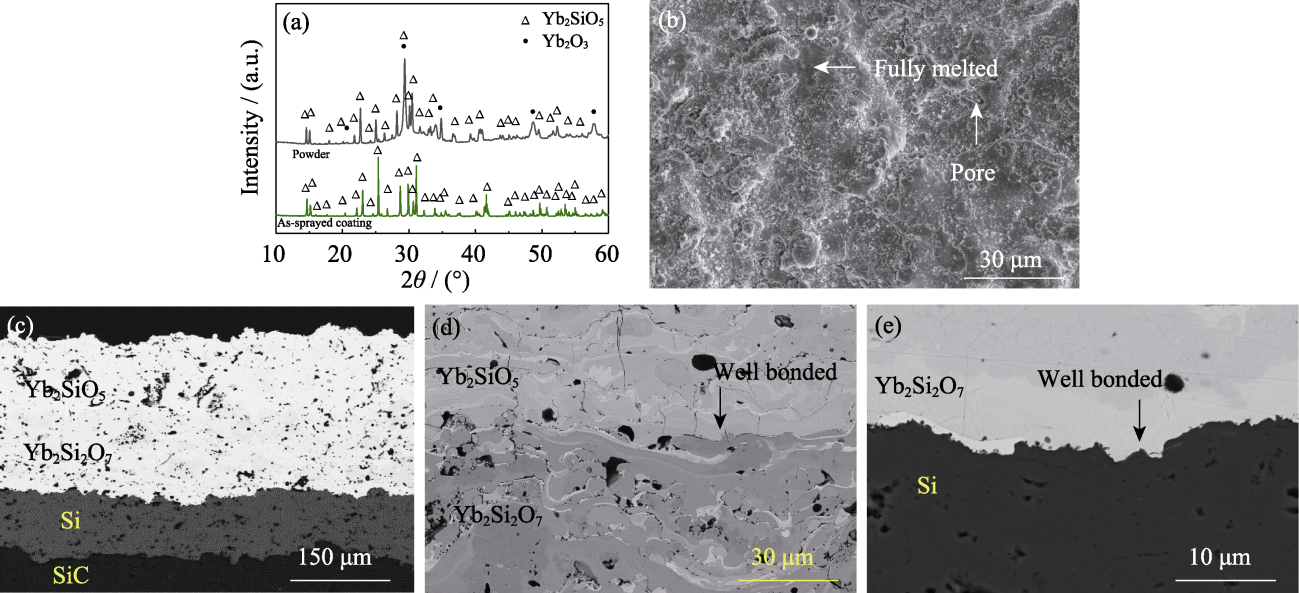
Fig. 1 XRD patterns and SEM morphologies of as-sprayed Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si coating (a) XRD patterns; (b) Surface morphology; (c-e) Cross-sectional morphologies
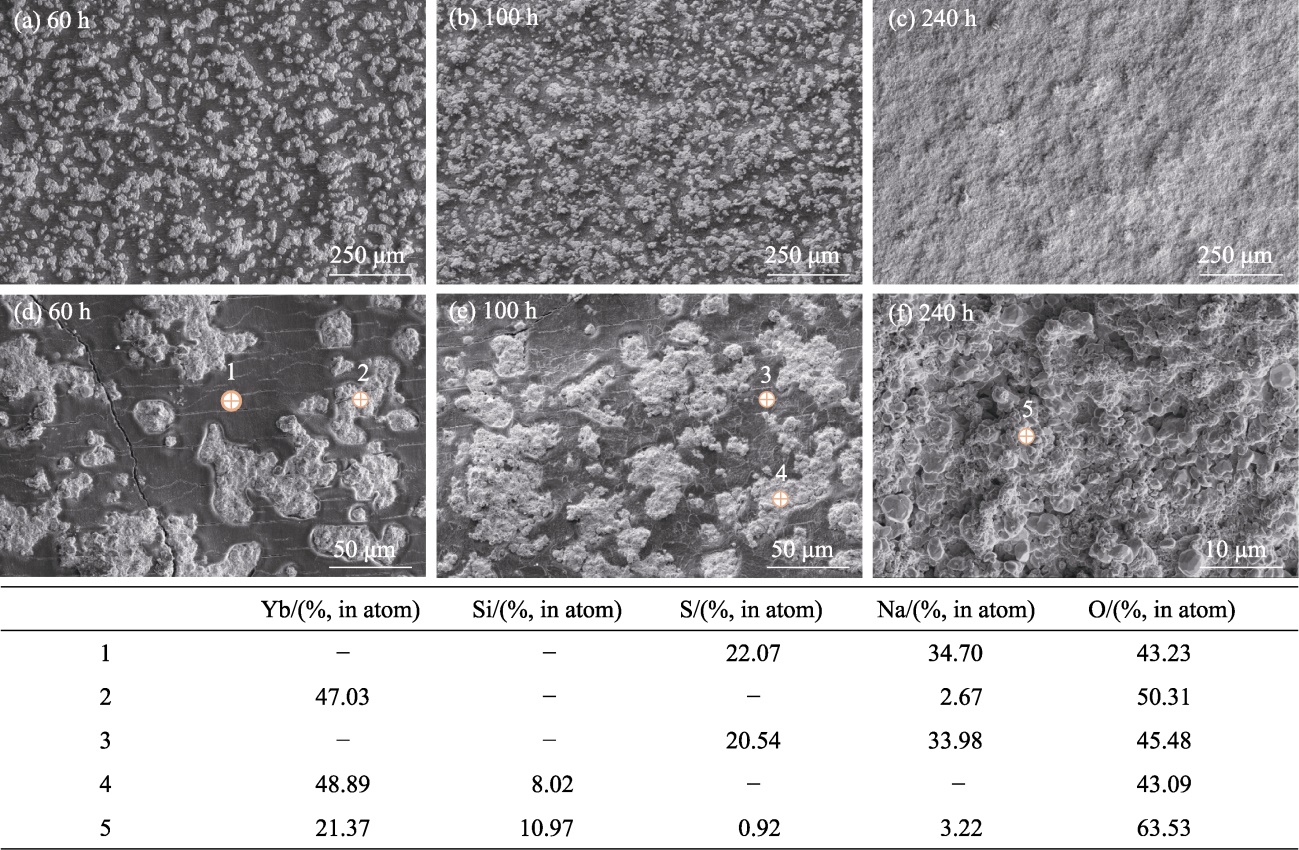
Fig. 4 Surface morphologies of Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si coating after molten salt corrosion for different time and correponding EDS analyses of different areas (a-c) Low magnification; (d-f) High magnification
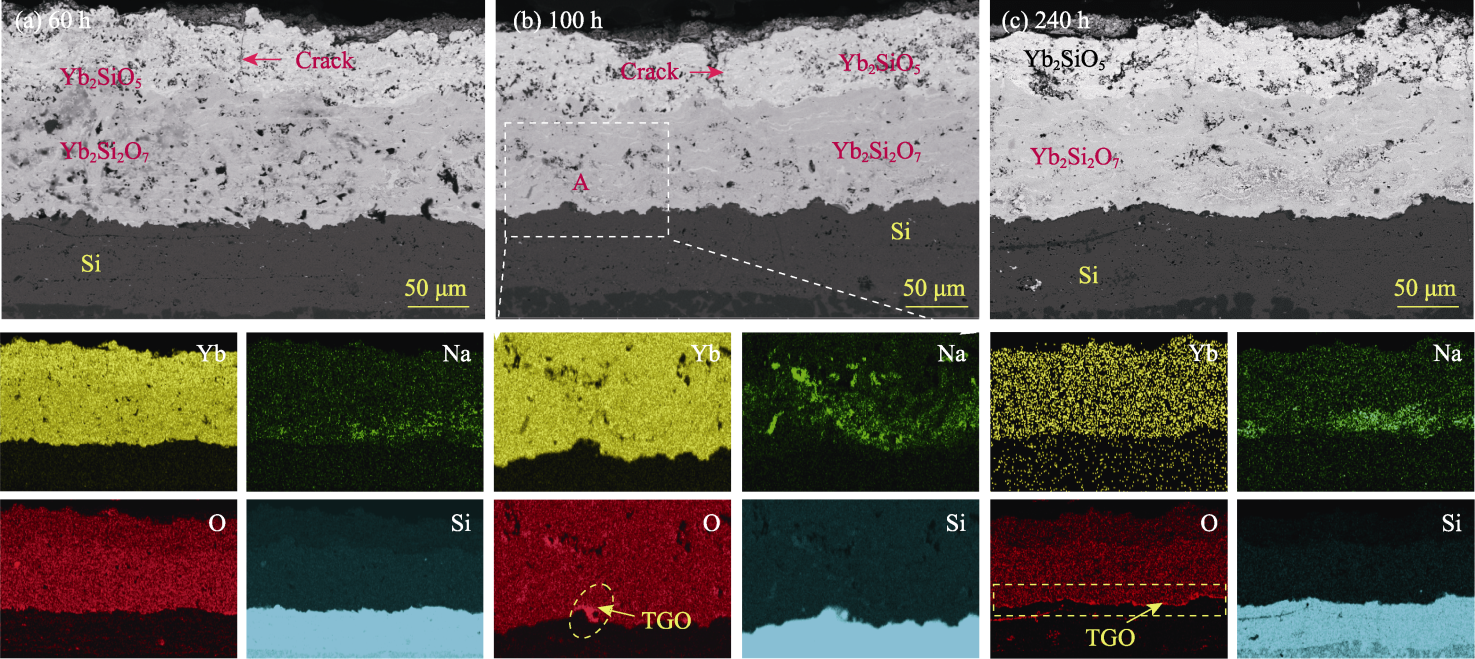
Fig. 6 Cross-sectional morphologies and corresponding EDS element mappings of Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si EBCs after molten salt corrosion for different time Colorful figures are available on website
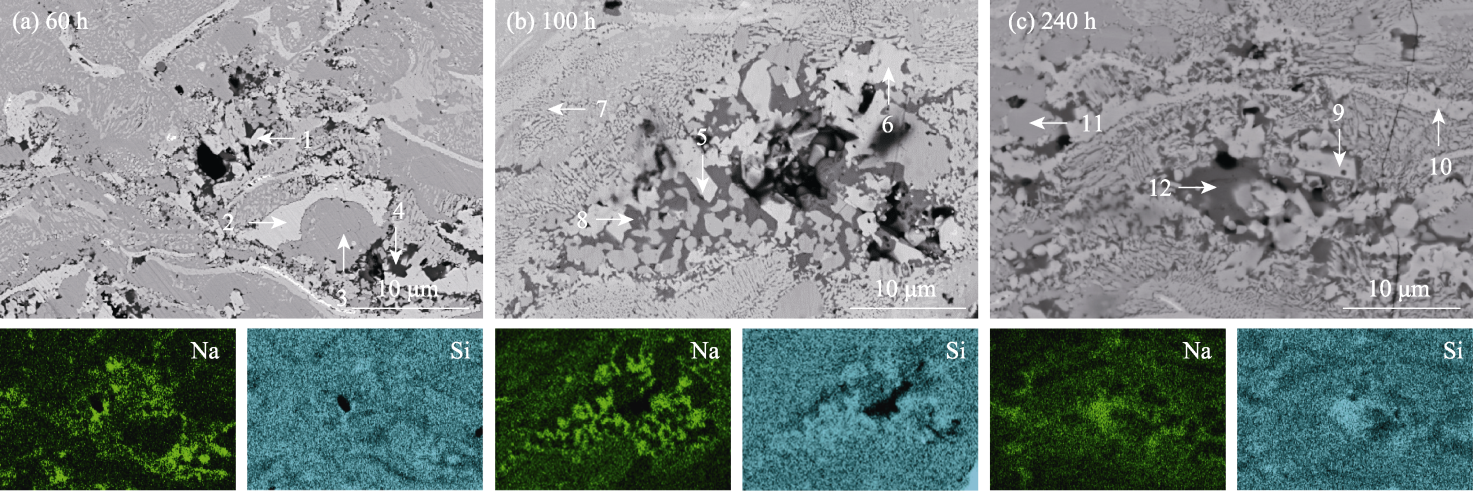
Fig. 7 High-magnification cross-sectional morphologies and corresponding EDS mappings of infiltration zone in Yb2Si2O7 interlayer after molten salt corrosion for different time Colorful figures are available on website
| Position | Yb | Si | Na | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21.69 | 14.27 | 1.98 | 62.06 |
| 2 | 24.91 | 12.57 | - | 62.52 |
| 3 | 18.29 | 18.09 | - | 63.62 |
| 4 | 10.15 | 18.67 | 2.41 | 58.77 |
| 5 | 22.50 | 13.75 | 1.67 | 62.08 |
| 6 | 24.92 | 12.57 | - | 62.51 |
| 7 | 18.03 | 18.31 | - | 63.66 |
| 8 | 8.95 | 19.25 | 13.25 | 58.55 |
| 9 | 22.93 | 13.20 | 2.04 | 61.82 |
| 10 | 24.45 | 12.96 | - | 62.59 |
| 11 | 17.82 | 18.04 | - | 63.25 |
| 12 | 8.91 | 19.21 | 13.39 | 58.49 |
Table 2 EDS elemental compositions of the marked regions in Fig. 7/%(in atom)
| Position | Yb | Si | Na | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21.69 | 14.27 | 1.98 | 62.06 |
| 2 | 24.91 | 12.57 | - | 62.52 |
| 3 | 18.29 | 18.09 | - | 63.62 |
| 4 | 10.15 | 18.67 | 2.41 | 58.77 |
| 5 | 22.50 | 13.75 | 1.67 | 62.08 |
| 6 | 24.92 | 12.57 | - | 62.51 |
| 7 | 18.03 | 18.31 | - | 63.66 |
| 8 | 8.95 | 19.25 | 13.25 | 58.55 |
| 9 | 22.93 | 13.20 | 2.04 | 61.82 |
| 10 | 24.45 | 12.96 | - | 62.59 |
| 11 | 17.82 | 18.04 | - | 63.25 |
| 12 | 8.91 | 19.21 | 13.39 | 58.49 |
| [1] |
PADTURE N P. Advanced structural ceramics in aerospace propulsion. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(8): 804-809.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | LEE K N, FOX D S, ELDRIDGE J I, et al. Advanced environmental barrier coatings developed for SiC/SiC composite vanes (2022-06-01). https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?R=20050214693. |
| [3] |
EATON H E, LINSEY G D. Accelerated oxidation of SiC CMC's by water vapor and protection via environmental barrier coating approach. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2002, 22(14/15): 2741-2747.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
RICHARDS B T, WADLEY H N G. Plasma spray deposition of tri-layer environmental barrier coatings. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(12): 3069-3083.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
TIAN Z L, ZHENG L Y, WANG J M, et al. Theoretical and experimental determination of the major thermo-mechanical properties of RE2SiO5 (RE=Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu, and Y) for environmental and thermal barrier coating applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(1): 189-202.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LIU J, ZHANG L T, LIU Q M, et al. Calcium-magnesium- aluminosilicate corrosion behaviors of rare-earth disilicates at 1400 ℃. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2013, 33(15/16): 3419-3428.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
JIANG F R, CHENG L F, WANG Y G. Hot corrosion of RE2SiO5 with different cation substitution under calcium-magnesium- aluminosilicate attack. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(12): 9019-9023.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
DONG Y, REN K, LU Y H, et al. High-entropy environmental barrier coating for the ceramic matrix composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(7): 2574-2579.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
SUN L C, REN X M, DU T F, et al. High entropy engineering: new strategy for the critical property optimizations of rare earth silicates. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 339-346.
DOI |
| [10] |
ZHONG X, NIU Y R, LI H, et al. Thermal shock resistance of tri-layer Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si coating for SiC and SiC-matrix composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(10): 4743-4752.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHU T, NIU Y R, ZHONG X, et al. Influence of phase composition on microstructure and thermal properties of ytterbium silicate coatings deposited by atmospheric plasma spray. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(11): 3974-3985.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHONG X, NIU Y R, LI HONG, et al. Microstructure evolution and thermomechanical properties of plasma-sprayed Yb2SiO5 coating during thermal aging. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(5): 1896-1906.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHONG X, WANG Y W, NIU Y R, et al. Corrosion behaviors and mechanisms of ytterbium silicate environmental barrier coatings by molten calcium-magnesium-alumino-silicate melts. Corrosion Science, 2021, 191: 109718.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG Y W, NIU Y R, ZHONG X, et al. Water vapor corrosion behaviors of plasma sprayed RE2SiO5 (RE=Gd, Y, Er) coatings. Corrosion Science, 2020, 167: 108529.
DOI URL |
| [15] | ZHONG X, ZHU T, NIU Y R, et al. Effect of microstructure evolution and crystal structure on thermal properties for plasma- sprayed RE2SiO5 (RE=Gd, Y, Er) environmental barrier coatings. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 85: 141-151. |
| [16] |
LI G, QIN L, CAO X Q, et al. Water vapor corrosion resistance and failure mechanism of SiCf/SiC composites completely coated with plasma sprayed tri-layer EBCs. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(5): 7082-7092.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LEE K N, FOX D S, BANSAL N P. Rare earth silicate environmental barrier coatings for SiC/SiC composites and Si3N4 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2005, 25(10): 1705-1715.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZHANG X F, ZHOU K S, LIU M, et al. Preparation of Si/mullite/ Yb2SiO5 environment barrier coating (EBC) by plasma spray- physical vapor deposition (PS-PVD). Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(3): 325-330.
DOI URL |
| [19] | WANG C, ZHANG X F, ZHOU K S, et al. Nano-composite structured environmental barrier coat-ings prepared by plasma spray- physical vapor deposition and their thermal cycle performance. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2019, 48(11): 3455-3462 |
| [20] |
ZHANG X F, SONG J B, DENG Z Q, et al. Interface evolution of Si/Mullite/Yb2SiO5 PS-PVD environmental barrier coatings under high temperature. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(4): 1478-1487.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG X F, ZHOU K S, LIU M, et al. Oxidation and thermal shock resistant properties of Al-modified environmental barrier coating on SiCf/SiC composites. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(16): 13075-13082.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
HU X X, XU F F, LI K W, et al. Water vapor corrosion behavior and failure mechanism of plasma sprayed mullite/Lu2Si2O7-Lu2SiO5 coatings. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(12): 14177-14185.
DOI URL |
| [23] | LIU P P, ZHONG X, NIU Y R, et al. Reaction behaviors and mechanisms of tri-layer Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si environmental barrier coatings with molten calcium-magnesium-alumino-silicate. Corrosion Science, 2022: 110069. |
| [24] |
WU S J, CHENG L F, ZHANG L T, et al. Corrosion of SiC/SiC composite in Na2SO4 vapor environments from 1000 ℃ to 1500 ℃. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2006, 37(9): 1396-1401.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
KOSIENIAK E, BIESIADA K, KACZOROWSKI J, et al. Corrosion failures in gas turbine hot components. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2012, 12(3): 330-337.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
JACOBSON N S. Kinetics and mechanism of corrosion of SiC by molten salts. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1986, 69(1): 74-82.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
HERWEYER L A, OPILA E J. High-temperature Na2SO4 interaction with air plasma sprayed Yb2Si2O7+Si EBC system: Topcoat behavior. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2021, 104(12): 6496-6507.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LI L, LU J, LIU X Z, et al. AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys with superior hot corrosion resistance to Na2SO4+25% NaCl at 900 ℃. Corrosion Science, 2021, 187: 109479.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
HAGAN J M, OPILA E J. High-temperature Na2SO4 deposit- assisted corrosion of silicon carbide-I: temperature and time dependence. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2015, 98(4): 1275-1284.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
SUN Z Q, LI M S, ZHOU Y C. Kinetics and mechanism of hot corrosion of γ-Y2Si2O7 in thin-film Na2SO4 molten salt. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(7): 2236-2242.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
FAN X Y, SUN R J, DONG J, et al. Effects of sintering additives on hot corrosion behavior of γ-Y2Si2O7 ceramics in Na2SO4+V2O5 molten salt. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(1): 517-525.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
LATSHAW A M, YEON J, SMITH M D, et al. Synthesis, structure, and polymorphism of A3LnSi2O7 (A=Na, K; Ln=Sm, Ho, Yb). Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2016, 235: 100-106.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LATSHAW A M, WILKINS B O, CHANCE W M, et al. Influence of rare earth cation size on the crystal structure in rare earth silicates, Na2RESiO4 (OH) (RE=Sc, Yb) and NaRESiO4 (RE=La, Yb). Solid State Sciences, 2016, 51: 59-65.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
JONNALAGADDA K P, MAHADE S, KRAMER S, et al. Failure of multilayer suspension plasma sprayed thermal barrier coatings in the presence of Na2SO4 and NaCl at 900 ℃. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2019, 28(1): 212-222.
DOI URL |
| [35] | 蒋凤瑞. B1-xSxAS及稀土硅酸盐环境障碍涂层热腐蚀性能研究. 西安: 西北工业大学博士学位论文, 2017. |
| [1] | FAN Dong, ZHONG Xin, WANG Yawen, ZHANG Zhenzhong, NIU Yaran, LI Qilian, ZHANG Le, ZHENG Xuebin. Corrosion Behavior and Mechanism of Aluminum-rich CMAS on Rare-earth Silicate Environmental Barrier Coatings: [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 544-552. |
| [2] | LUO Shuwen, MA Mingsheng, LIU Feng, LIU Zhifu. Corrosion Behavior and Mechanism of LTCC Materials in Ca-B-Si System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 553-560. |
| [3] | SUN Luchao, REN Xiaomin, DU Tiefeng, LUO Yixiu, ZHANG Jie, WANG Jingyang. High Entropy Engineering: New Strategy for the Critical Property Optimizations of Rare Earth Silicates [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 339-346. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xiao-Feng, ZHOU Ke-Song, LIU Min, DENG Chun-Ming, NIU Shao-Peng, XU Shi-Ming. Preparation of Si/Mullite/Yb2SiO5 Environment Barrier Coating (EBC) by Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition (PS-PVD) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(3): 325-330. |
| [5] | ZHANG Xiao-Feng, ZHOU Ke-Song, SONG Jin-Bing, DENG Chun-Ming, NIU Shao-Peng, DENG Zi-Qian. Deposition and CMAS Corrosion Mechanism of 7YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings Prepared by Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 287-293. |
| [6] | LU Lin-Jing, CHENG Lai-Fei, HONG Zhi-Liang, WANG Yi-Guang, ZHANG Li-Tong. Fabrication and Water-vapor Corrosion Resistance of Ba0.25Sr0.75Al2Si2O8 Environmental Barrier Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(7): 701-706. |
| [7] | WU Jiang,LIN Hong,LI Jian-Bao,LI Jun-Feng. Corrosion Behavior of AlNbO4/Mullite Composite as Environmental Barrier Coating in Water Vapor Environment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(4): 445-448. |
| [8] | HONG Zhi-Liang,CHENG Lai-Fei,LU Lin-Jing,ZHANG Li-Tong,WANG Yi-Guang. Corrosion Behavior of Lu-Si-O System in Water Vapor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 15(2): 186-190. |
| [9] | CHEN Xian-Hong,CHENG Lai-Fei,WANG Yi-Guang,ZHANG Li-Tong,HONG Zhi-Liang,WU Ya-Hui. Corrosion Behavior of AlPO4 as Environmental Barrier Coating in Water Vapor Enviroment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(2): 397-401. |
| [10] |
GUAN Yong-Jun,XIA Yuan.
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy of PEO Coating on Aluminum Alloy in NaCl Solution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(4): 784-788. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||