
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 1245-1258.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220114
Special Issue: 【生物材料】肿瘤治疗; 【生物材料】骨骼与齿类组织修复
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles
CHEN Cheng1( ), DING Jingxin1, WANG Hui2(
), DING Jingxin1, WANG Hui2( ), WANG Deping1(
), WANG Deping1( )
)
Received:2022-03-02
Revised:2022-04-03
Published:2022-05-07
Online:2022-05-07
Contact:
WANG Hui, associate professor. E-mail: WHIL86@shutcm.edu.cn;About author:CHEN Cheng (1997-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 1930642@tongji.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
CHEN Cheng, DING Jingxin, WANG Hui, WANG Deping. Nd-doped Mesoporous Borosilicate Bioactive Glass-ceramic Bone Cement[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1245-1258.

Scheme 1 Schematic diagram of preparation and properties of MBGC-xNd microspheres and MBGC-xNd/SA bone cement The color figure can be obtained from online edition
| Sample | SiO2 | B2O3 | P2O5 | CaO | NdO3/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBGC-0Nd | 50 | 10 | 4 | 36 | 0 |
| MBGC-1Nd | 50 | 10 | 4 | 35 | 1 |
| MBGC-3Nd | 50 | 10 | 4 | 33 | 3 |
| MBGC-5Nd | 50 | 10 | 4 | 31 | 5 |
Table 1 Composition in molar percent of MBGC-xNd microspheres
| Sample | SiO2 | B2O3 | P2O5 | CaO | NdO3/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBGC-0Nd | 50 | 10 | 4 | 36 | 0 |
| MBGC-1Nd | 50 | 10 | 4 | 35 | 1 |
| MBGC-3Nd | 50 | 10 | 4 | 33 | 3 |
| MBGC-5Nd | 50 | 10 | 4 | 31 | 5 |
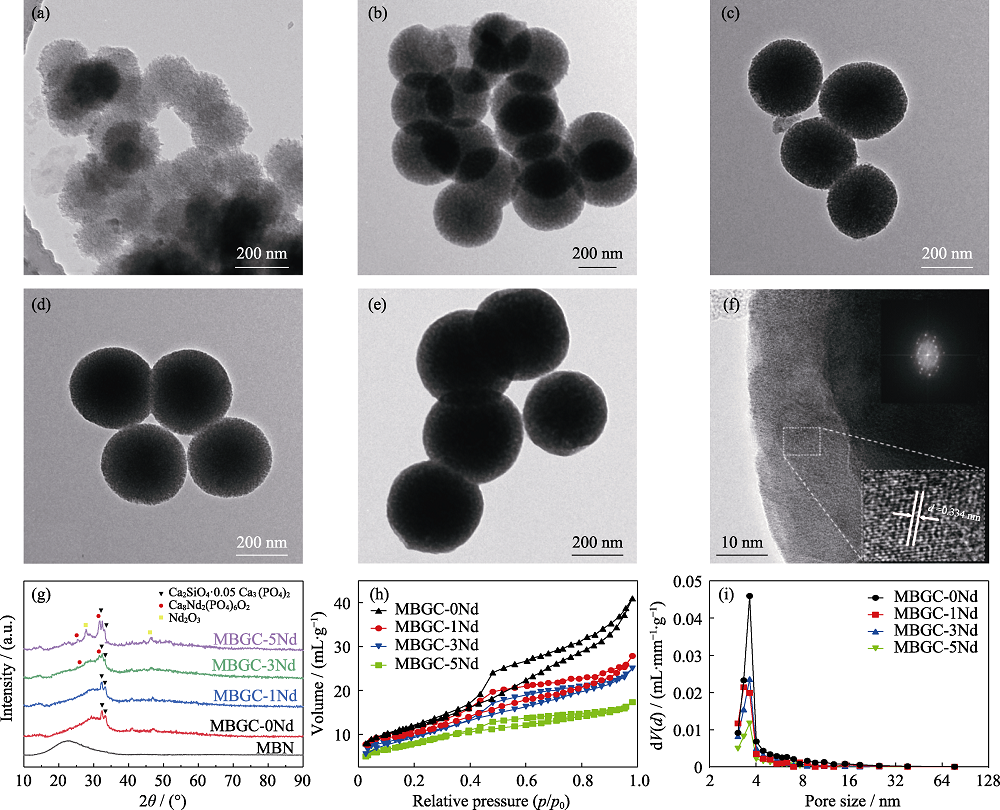
Fig. 1 Characterization of MBGC-xNd microspheres (a-e) TEM images of (a) MBN, (b) MBGC-0Nd microspheres, (c) MBGC-1Nd microspheres, (d) MBGC-3Nd microspheres, and (e) MBGC-5Nd microspheres; (f) High-resolution TEM image of MBGC-3Nd microspheres with insert showing the interplanar crystal spacing at about 0.334 nm; (g) XRD patterns of MBN and MBGC-xNd microspheres; (h) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherm and (i) pore size distribution curve of MBGC-xNd microsphere The color figures can be obtained from online edition
| Sample | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore size /nm | Pore volume /(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MBN | 329.261 | 12.506 | 0.4498 |
| MBGC-0Nd | 42.092 | 6.024 | 0.0634 |
| MBGC-1Nd | 36.065 | 4.776 | 0.0431 |
| MBGC-3Nd | 34.424 | 4.496 | 0.0387 |
| MBGC-5Nd | 28.818 | 3.710 | 0.0268 |
Table 2 Pore structure of MBN and MBGC-xNd microspheres
| Sample | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore size /nm | Pore volume /(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MBN | 329.261 | 12.506 | 0.4498 |
| MBGC-0Nd | 42.092 | 6.024 | 0.0634 |
| MBGC-1Nd | 36.065 | 4.776 | 0.0431 |
| MBGC-3Nd | 34.424 | 4.496 | 0.0387 |
| MBGC-5Nd | 28.818 | 3.710 | 0.0268 |
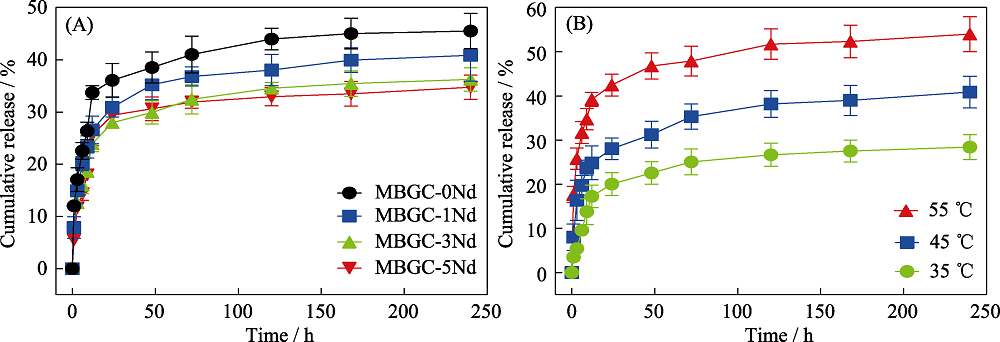
Fig. 3 Cumulative release curves of DOX from (A) MBGC-xNd@DOX microspheres in PBS at pH 4.7 and (B) MBGC-3Nd/SA@DOX in PBS at pH 4.7 under different ambient temperatures The color figures can be obtained from online edition
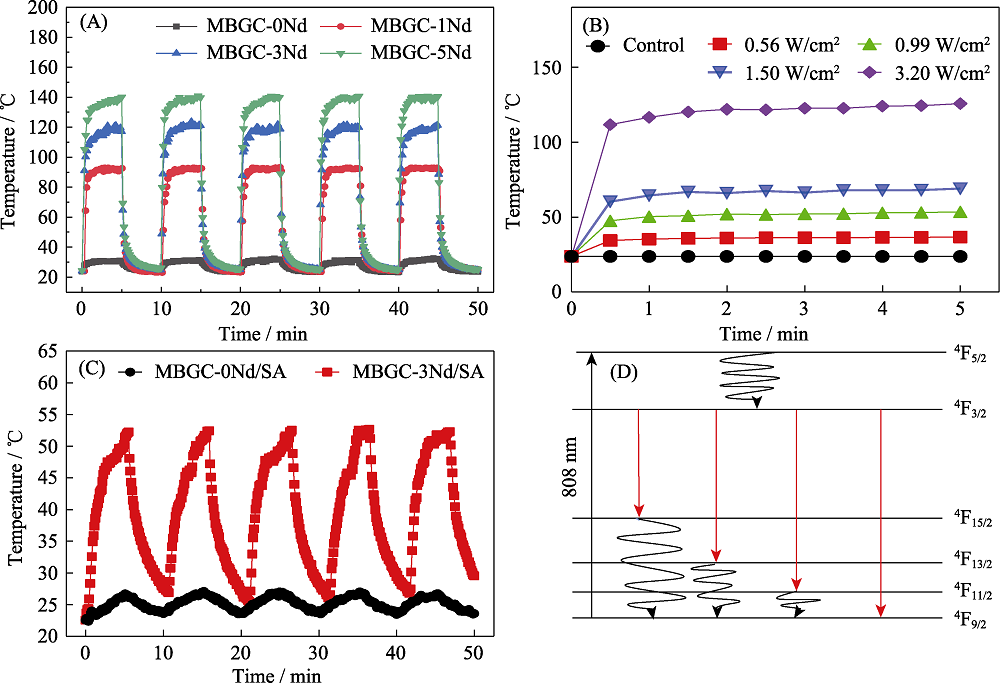
Fig. 4 Photothermal properties of MBGC-xNd microspheres (A) Heating curves of MBGC-xNd microspheres under 808 nm laser irradiation (3.2 W/cm2); (B) Heating curves of MBGC-3Nd microspheres under 808 nm laser irradiation at different power densities; (C) Heating curves of MBGC-3Nd/SA immersed in SBF under 808 nm laser irradiation (2.4 W/cm2); (D) Energy level diagram of Nd3+ The color figures can be obtained from online edition
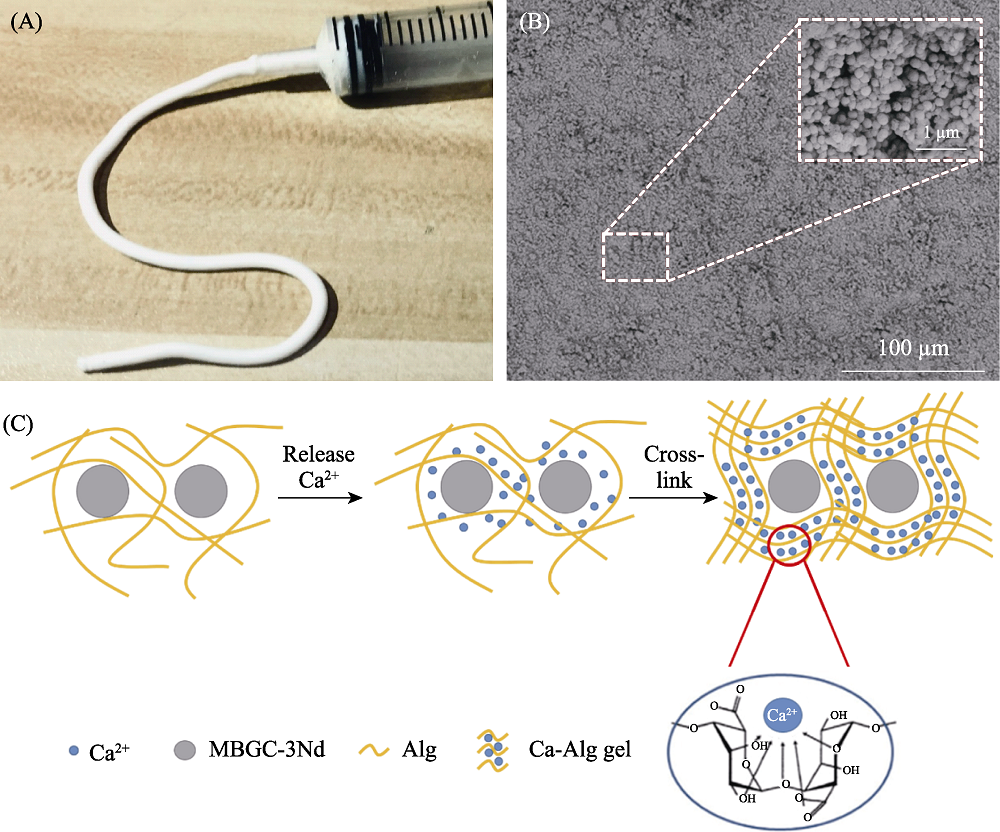
Fig. 5 Characterization of MBGC-3Nd/SA bone cement (A) Photo of extruded bone cement; (B) SEM image of MBGC-3Nd/SA; (C) Schematic illustration of the setting process of MBGC-3Nd/SA The color figures can be obtained from online edition
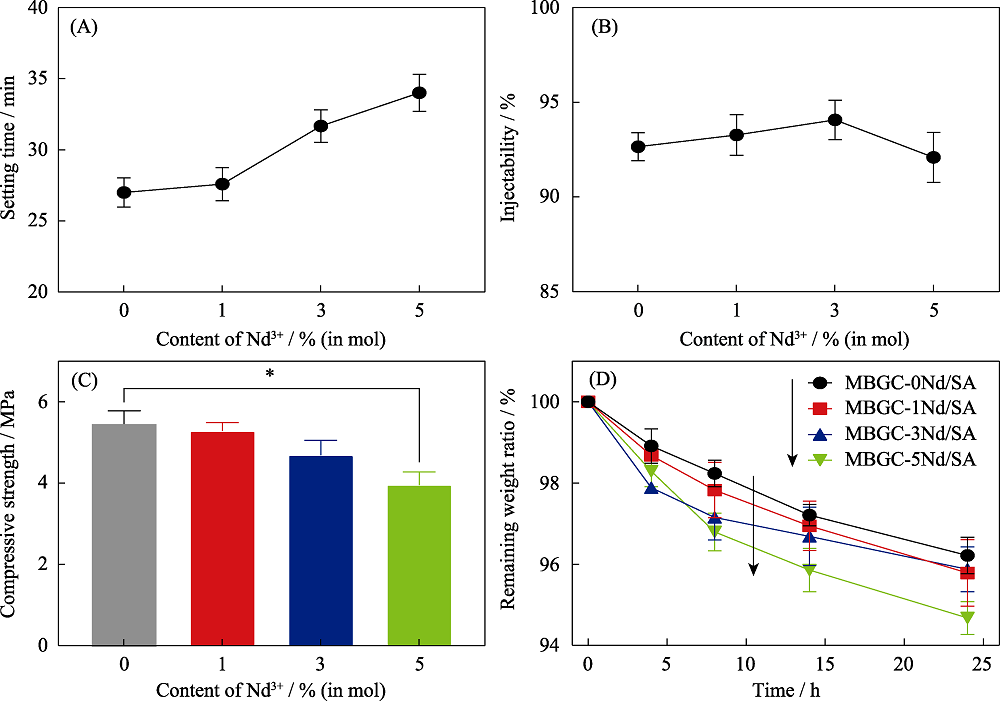
Fig. 6 Setting properties of MBGC-xNd/SA (A) Setting time; (B) Injectability; (C) Compressive strength; (D) Anti-washout property. *: p<0.05 (n=5) The color figures can be obtained from online edition
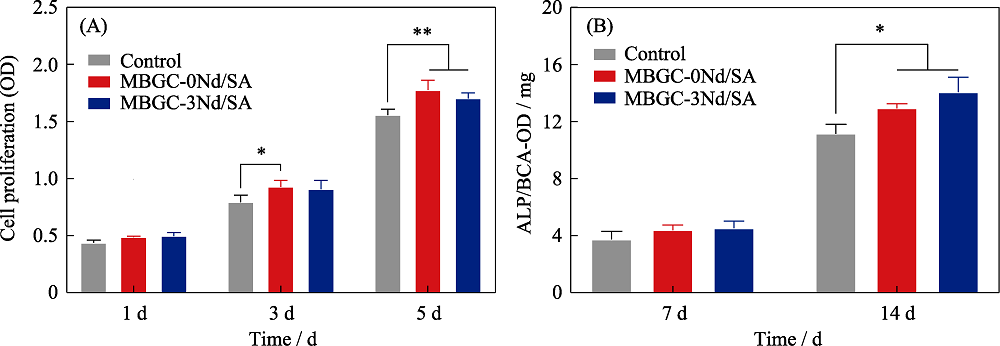
Fig. 7 (A) Proliferation results and (B) alkaline phosphate activity of rBMSCs cultured in the bone cement extract *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01. (n = 5). The color figure can be obtained from online edition
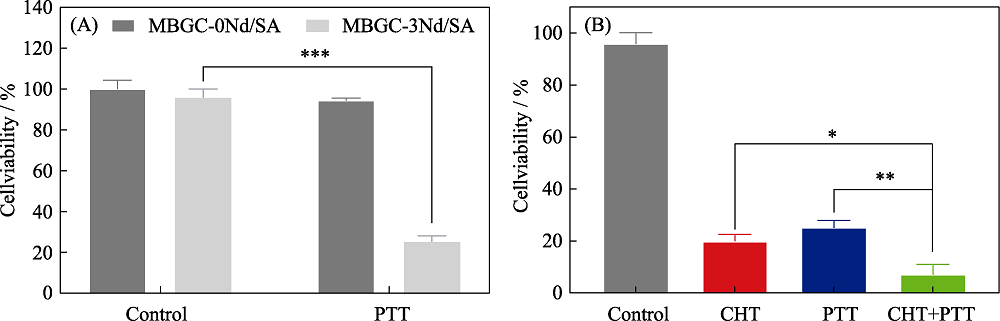
Fig. 8 Relative survival of MG-63 cells co-cultured with (A) bone cement under 808 nm laser irradiation at a power density of 2.4 W/cm2 for 5 min and (B) MBGC-3Nd/SA under PTT, CHT or combination therapy. *: p<0.05; **: p<0.01, ***: p<0.001 (n=5) The color figures can be obtained from online edition
| [1] | RAINUSSO N, WANG L L, YUSTEIN J T. The adolescent and young adult with cancer: state of the art-bone tumors. Current Oncolology Reports, 2013, 15(4): 296-307. |
| [2] | BALLATORI S E, HINDS P W. Osteosarcoma: prognosis plateau warrants retinoblastoma pathway targeted therapy. Signal Transduction Target Therapy, 2016, 1: 16001-12. |
| [3] |
LIAO J F, SHI K, JIA Y P, et al. Gold nanorods and nanohydroxyapatite hybrid hydrogel for preventing bone tumor recurrence via postoperative photothermal therapy and bone regeneration promotion. Bioactive Materials, 2021, 6(8): 2221-2230.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
WANG W H, YEUNG K W K. Bone grafts and biomaterials substitutes for bone defect repair: a review. Bioactive Materials, 2017, 2(4): 224-247.
DOI URL |
| [5] | CUI X, ZHANG Y D, WANG H, et al. An injectable borate bioactive glass cement for bone repair: preparation, bioactivity and setting mechanism. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2016, 432: 150-157. |
| [6] | CUI X, ZHAO C J, GU Y F, et al. A novel injectable borate bioactive glass cement for local delivery of vancomycin to cure osteomyelitis and regenerate bone. Journal of Material Science: Mater ials in Medicine, 2014, 25(3): 733-745. |
| [7] | XIE X, PANG L B, YAO A H, et al. Nanocement produced from borosilicate bioactive glass nanoparticles composited with alginate. Australian Journals of Chemistry, 2019, 72(5): 354-361. |
| [8] | CHANG Y C, ZHAO R L, WANG H, et al. A novel injectable whitlockite-containing borosilicate bioactive glass cement for bone repair. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2020, 547: 120291-11. |
| [9] | WU Z F, LIN Z Y, YAO A H, et al. Influence of particle size distribution on the rheological properties and mathematical model fitting of injectable borosilicate bioactive glass bone cement. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(15):24395-24406. |
| [10] |
PANG L B, WANG D P. Drug carrier based on mesoporous borosilicate glass microspheres. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 780-786.
DOI URL |
| [11] | LI J, ZHANG C T, GONG S M, et al. A nanoscale photothermal agent based on a metal-organic coordination polymer as a drug-loading framework for effective combination therapy. Acta Biomaterialia, 2019, 94: 435-446. |
| [12] | ZHAO Q F, WANG X D, YANG M, et al. Multi-stimuli responsive mesoporous carbon nano-platform gated by human serum albumin for cancer thermo-chemotherapy. Colloids Surface B Biointerfaces, 2019, 184: 110532-11. |
| [13] |
ZHANG T, JIANG Z Q, XVE T, et al. One-pot synthesis of hollow PDA@DOX nanoparticles for ultrasound imaging and chemo-thermal therapy in breast cancer. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(45): 21759-21766.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
WANG L L, HERVAULT A, SOUTHERN P, et al. In vitro exploration of the synergistic effect of alternating magnetic field mediated thermo-chemotherapy with doxorubicin loaded dual pH- and thermo-responsive magnetic nanocomposite carriers. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2020, 8(46): 10527-10539.
DOI URL |
| [15] | YANG Y, LIN Y Z, DI D H, et al. Gold nanoparticle-gated mesoporous silica as redox-triggered drug delivery for chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy. Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 2017, 508: 323-331. |
| [16] |
ZHAO L Z, YUAN W, THAM H P, et al. Fast-clearable nanocarriers conducting chemo/photothermal combination therapy to inhibit recurrence of malignant tumors. Small, 2017, 13(29): 1700963-9.
DOI URL |
| [17] | ROSAL B D, ROCHA U, XIMENDES E C, et al. Nd3+ ions in nanomedicine: perspectives and applications. Optical Materials, 2017, 63: 185-196. |
| [18] |
ROSAL B D, DELGADO A P, CARRASCO E, et al. Neodymium-based stoichiometric ultrasmall nanoparticles for multifunctional deep-tissue photothermal therapy. Advanced Optical Materials, 2016, 4(5): 782-789.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ROCHA U, CARLOS J, SILVA W F, et al. Sub-tissue thermal sensing based on neodymium-doped LaF3 nanoparticles. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(2): 1188-1199.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
MA L L, ZHOU Y L, ZHANG Z W B, et al. Multifunctional bioactive Nd-Ca-Si glasses for fluorescence thermometry, photothermal therapy, and burn tissue repair. Science Advances, 2020, 6(32): eabb1311-12.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ROCHA U, KUMAR K U, JACINTO C, et al. Neodymium-doped LaF3 nanoparticles for fluorescence bioimaging in the second biological window. Small, 2014, 10(6): 1141-1154.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
XIE W H, CHEN X Y, LI Y L, et al. Facile synthesis and in vitro bioactivity of radial mesoporous bioactive glass with high phosphorus and calcium content. Advanced Powder Technology, 2020, 31(8): 3307-3317.
DOI URL |
| [23] | WANG X, WANG G, ZHANG Y. Research on the biological activity and doxorubicin release behavior in vitro of mesoporous bioactive SiO2-CaO-P2O5 glass nanospheres. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 419: 531-539. |
| [24] | ZHU Y F, KOCKRICK E, IKOMA T, et al. An efficient route to rattle-type Fe3O4@SiO2 hollow mesoporous spheres using colloidal carbon spheres templates. Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 21: 2547-2553 |
| [25] |
TIAN T, HAN Y, MA B, et al. Novel Co-akermanite (Ca2CoSi2O7) bioceramics with the activity to stimulate osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2015, 3(33): 6773-6782.
DOI URL |
| [26] | WARREN B E, PINCUS A G. Atomic consideration of immiscibility in glass systems. Journal of American Ceramics Society, 1940, 23: 301-304. |
| [27] | ANAND V, SINGH K J, KAUR K. Evaluation of zinc and magnesium doped 45S5 mesoporous bioactive glass system for the growth of hydroxyl apatite layer. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2014, 406: 88-94. |
| [28] |
SANCHEZ-SALCEDO S, MALAVASI G, SALINAS A J, et al. Highly-bioreactive silica-based mesoporous bioactive glasses enriched with gallium(III). Materials (Basel), 2018, 11(3): 367-17.
DOI URL |
| [29] | ZHOU J, WANG H, ZHAO S C, et al. In vivo and in vitro studies of borate based glass micro-fibers for dermal repairing. Material Science Engineering C: Materials for Biological Application, 2016, 60: 437-445. |
| [30] |
STOUWDAM J W, VEGGEL F. Near-infrared emission of redispersible Er3+, Nd3+, and Ho3+ doped LaF3 nanoparticles. Nano Letters, 2002, 2(7): 733-737.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
WANG X F, LIU Q, BU Y Y, et al. Optical temperature sensing of rare-earth ion doped phosphors. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(105): 86219-86236.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
HEMMER E, ACOSTA-MORA P, MENDEZ-RAMOS J, et al. Optical nanoprobes for biomedical applications: shining a light on upconverting and near-infrared emitting nanoparticles for imaging, thermal sensing, and photodynamic therapy. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2017, 5(23): 4365-4392.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
BALAKRISHNAN B, JAYAKRISHNAN A. Self-cross-linking biopolymers as injectable in situ forming biodegradable scaffolds. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(18): 3941-3951.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
BALAKRISHNAN B, JOSHI N, JAYAKRISHNAN A, et al. Self- crosslinked oxidized alginate/gelatin hydrogel as injectable, adhesive biomimetic scaffolds for cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomaterialia, 2014, 10(8): 3650-3663.
DOI URL |
| [35] | QU Y, ZHUANG H, ZHANG M, et al. Bone cements for therapy and regeneration for minimally invasive treatment of neoplastic bone defects. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2021, 9: 4355-4364. |
| [36] | LIN S W, LI X Q, LIU S Y, et al. Inhibition of combination of icaritin and doxorubicin on human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells in vitro. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional & Western Medicine, 2016, 36(6): 729-734. |
| [37] | ZHAO Y K, TANG S S, GUO J M, et al. Targeted delivery of doxorubicin by nano-loaded mesenchymal stem cells for lung melanoma metastases therapy. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 44758. |
| [38] |
CUI X, ZHANG Y D, WANG J Y, et al. Strontium modulates osteogenic activity of bone cement composed of bioactive borosilicate glass particles by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Bioactive Materials, 2020, 5(2): 334-347.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | PANG L B, SHEN Y F, HU H R, et al. Chemically and physically cross-linked polyvinyl alcohol-borosilicate gel hybrid scaffolds for bone regeneration. Material Science Engineering C: Materials in Biological Application, 2019, 105: 110076-12. |
| [40] |
BI L X, RAHAMAN M N, DAY D E, et al. Effect of bioactive borate glass microstructure on bone regeneration, angiogenesis, and hydroxyapatite conversion in a rat calvarial defect model. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(8): 8015-8026.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
GU Y F, HUANG W H, RAHAMAN M N, et al. Bone regeneration in rat calvarial defects implanted with fibrous scaffolds composed of a mixture of silicate and borate bioactive glasses. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(11): 9126-9136.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
RAHAMAN M N, DAY D E, BAL B S, et al. Bioactive glass in tissue engineering. Acta Biomaterialia, 2011, 7(6): 2355-2373.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | PARK M, LI Q, SHCHEYNIKOV N, et al. NaBCl is a ubiquitous electrogenic Na+-coupled borate transporter essential for cellular boron homeostasis and cell growth and proliferation. Mollecular Cell, 2004, 16(3): 331-341. |
| [44] | NIKFARJAM M, MURALIDHARAN V, CHRISTOPHI C. Mechanisms of focal heat destruction of liver tumors. Journal of Surgical Research, 2005, 127: 208-223. |
| [45] |
CHU K F, DUPUY D E. Thermal ablation of tumours: biological mechanisms and advances in therapy. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2014, 14(3): 199-208.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
MONFOULRT L E, BECQUART P, MARCHAT D, et al. The pH in the microenvironment of human mesenchymal stem cells is a critical factor for optimal osteogenesis in tissue-engineered constructs. Tissue Engineering Part A, 2014, 20(13): 1827-1840.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
MA H S, JIANG C, ZHAI D, et al. A bifunctional biomaterial with photothermal effect for tumor therapy and bone regeneration. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(8): 1197-1208.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
XU C, MA B, PENG J L, et al. Tricalcium silicate/graphene oxide bone cement with photothermal properties for tumor ablation. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2019, 7(17): 2808-2818.
DOI PMID |
| [49] | LIU Y Q, LIN R C, MA L L, et al. Mesoporous bioactive glass for synergistic therapy of tumor and regeneration of bone tissue. Applied Materials Today, 2020, 19: 100578-14. |
| [50] | ZHU X J, FENG W, CHANG J, et al. Temperature-feedback upconversion nanocomposite for accurate photothermal therapy at facile temperature. Nature Communication, 2016, 7: 10437-10. |
| [51] |
ZHENG M B, YUE C X, MA Y F, et al. Single- step assembly of DOX/ICG loaded lipid-polymer nanoparticles for highly effective chemo-photothermal combination therapy. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(3): 2056-2067.
DOI URL |
| [52] | SHUKLA N, SINGH B, KIM H J, et al. Combinational chemotherapy and photothermal therapy using a gold nanorod platform for cancer treatment. Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 2020, 37(8): 2000099-15. |
| [53] |
MENG Z Q, WEI F, WANG R H, et al. NIR- laser-switched in vivo smart nanocapsules for synergic photothermal and chemotherapy of tumors. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(2): 245-253.
DOI URL |
| [1] | LIN Ziyang, CHANG Yuchen, WU Zhangfan, BAO Rong, LIN Wenqing, WANG Deping. Different Simulated Body Fluid on Mineralization of Borosilicate Bioactive Glass-based Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 745-752. |
| [2] | CHANG Yuchen, LIN Ziyang, XIE Xin, WU Zhangfan, YAO Aihua, YE Song, LIN Jian, WANG Deping, CUI Xu. An Injectable Composite Bone Cement Based on Mesoporous Borosilicate Bioactive Glass Spheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12): 1398-1406. |
| [3] | LI Hai-Bin, WANG De-Ping, WU Ying-Ying, YAO Ai-Hua, YE Song. Effect of Citric Acid Concentration on the Properties of Borate Glass Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 831-836. |
| [4] | YU Su-Chun, YU Ying, DAI Hong-Lian. Construction of Gelatin Microsphere / Magnesium Phosphate Bone Cement Composite Drug Sustained Delivery System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(6): 655-660. |
| [5] | LI Bo, XU Wen-Feng, LIAO Xiao-Ling. Research Progress in Calcium Phosphate Microspheres for Bone Defect Repair [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10): 1009-1017. |
| [6] | YANG Guo-Jing, LIN Mian, ZHANG Lei, GOU Zhong-Ru. Progress of Calcium Sulfate and Inorganic Composites for Bone Defect Repair [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(8): 795-803. |
| [7] | WANG Ying,WEI Jie,GUO Han,LIU Chang-Sheng. Bioactive Calcium Phosphate Cement with Anti-washout for Bone Replacement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(6): 1435-1442. |
| [8] | ZHANG Li,LI Yu-Bao,ZHOU Gang,LU Guo-Yu,ZUO Yi. Setting Mechanism of Nano-hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(5): 1197-1202. |
| [9] | YANG Wei-Zhong,ZHOU Da-Li,YIN Guang-Fu,YIN Shao-Ya,ZHENG Chang-Qiong. Hydraulic Characteristic and Osteoinduction Capacity of Calcium Phosphate/BMP Bioactive Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2005, 20(5): 1174-1180. |
| [10] | YANG Wei-Zhong,ZHOU Da-Li,YIN Guang-Fu,YIN Shao-Ya,ZHENG Chang-Qiong,GAO Li-Da. BMP Releasing Kinetics and Osteogenesis Capacity of BMP/α-Tricalcium Phosphate Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2004, 19(6): 1359-1366. |
| [11] | DAI Hong-Lian,LI Shi-Pu,HE Jian-Hua,YAN Yu-Hua. Carbon Fiber Reinforced α-TCP/TTCP Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2004, 19(5): 1025-1030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||