
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (8): 865-872.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220123
Special Issue: 【能源环境】光催化降解有机分子; 【信息功能】Max层状材料、MXene及其他二维材料
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
XUE Hongyun1,2( ), WANG Congyu1, MAHMOOD Asad1(
), WANG Congyu1, MAHMOOD Asad1( ), YU Jiajun1,2, WANG Yan1, XIE Xiaofeng1, SUN Jing1(
), YU Jiajun1,2, WANG Yan1, XIE Xiaofeng1, SUN Jing1( )
)
Received:2022-03-07
Revised:2022-04-05
Published:2022-08-20
Online:2022-04-26
Contact:
MAHMOOD Asad. E-mail: amkhan036@yahoo.com;About author:XUE Hongyun (1998-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: hyxue0310@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
XUE Hongyun, WANG Congyu, MAHMOOD Asad, YU Jiajun, WANG Yan, XIE Xiaofeng, SUN Jing. Two-dimensional g-C3N4 Compositing with Ag-TiO2 as Deactivation Resistant Photocatalyst for Degradation of Gaseous Acetaldehyde[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 865-872.
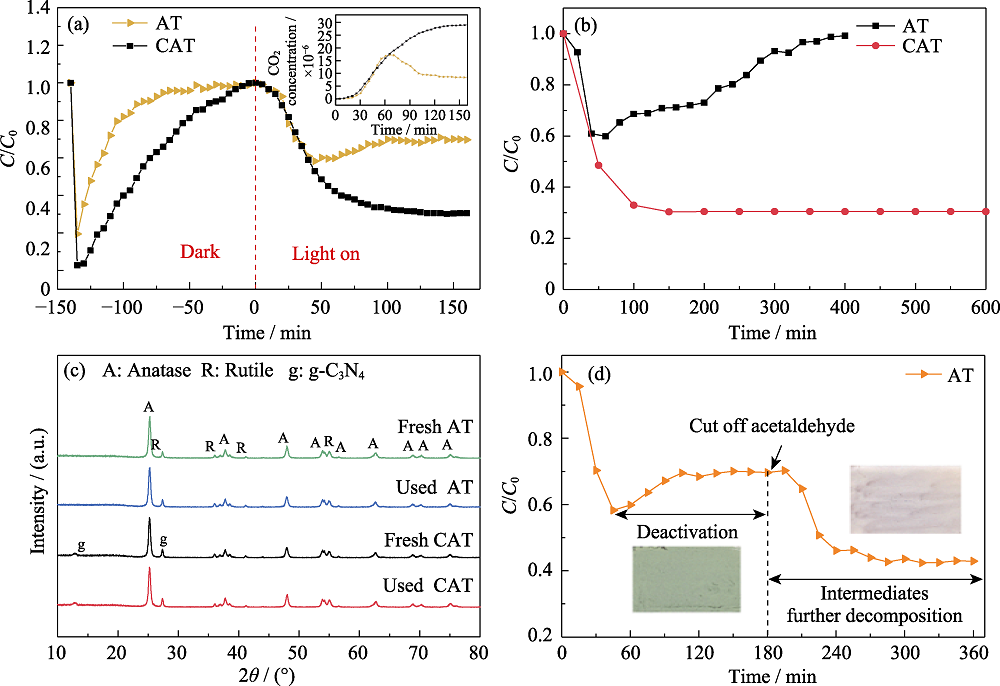
Fig. 1 Activation maintained by CAT for gaseous acetaldehyde (a) Adsorption, photodegradation and CO2 generation curves of acetaldehyde gas by AT and CAT samples; (b) Photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde by AT sample under visible light irradiation for 400 min and CAT sample under visible light irradiation for 600 min; (c) XRD patterns of AT and CAT samples before and after degradation of acetaldehyde gas (160 min) under visible light irradiation; (d) Photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde by AT sample under visible light irradiation for 360 min, and cutting off acetaldehyde inlet at 180 min
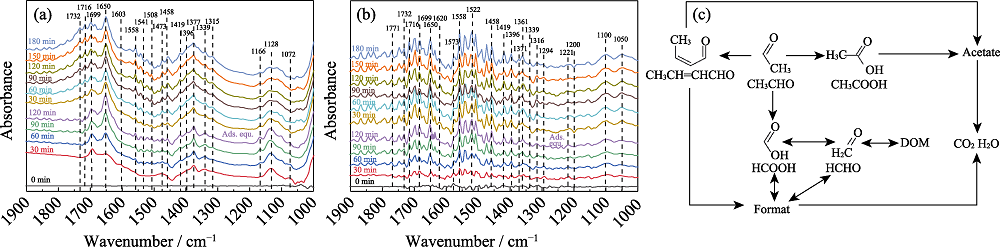
Fig. 2 In-situ DRIFTS spectra of (a) AT and (b) CAT photocatalysts degrading acetaldehyde gas under visible light irradiation, and (c) photocatalytic reaction routes of acetaldehyde
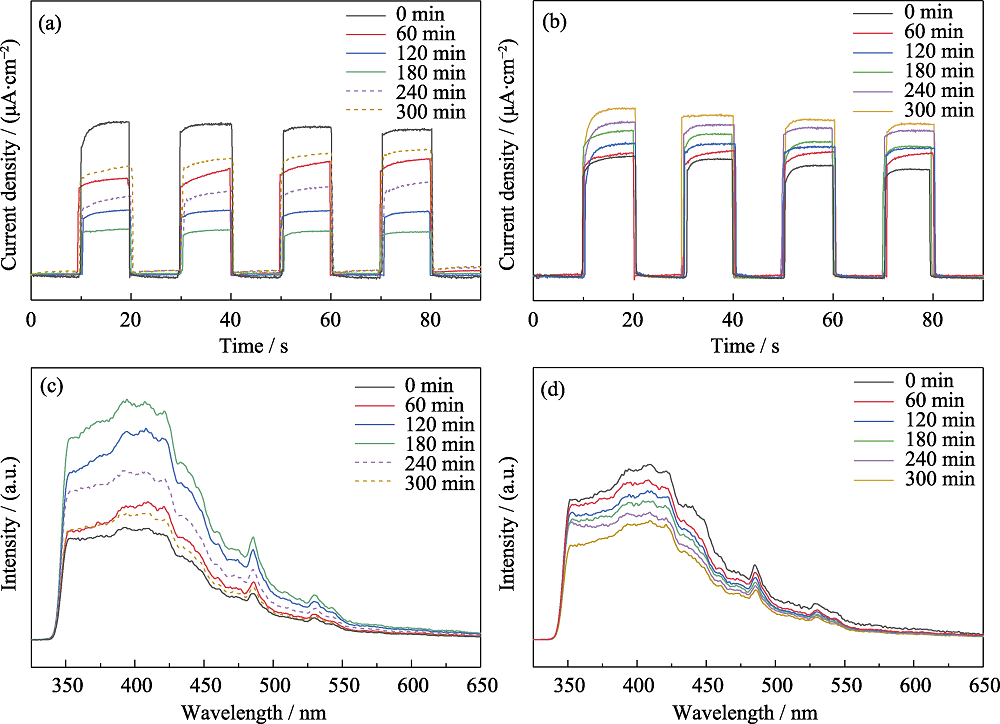
Fig. 3 Photocurrent and PL plots of the photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde (a) Photocurrent and (c) PL plots of AT sample for the photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde under visible light irradiation; (b) Photocurrent and (d) PL plots of the photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde by CAT sample under visible light irradiation for 300 min 0, 60, 120, 180 min represent the photocatalytic reaction time of which the dotted lines of 240 and 300 min represent 1 and 2 h, respectively, when acetaldehyde was stopped but the light was kept on
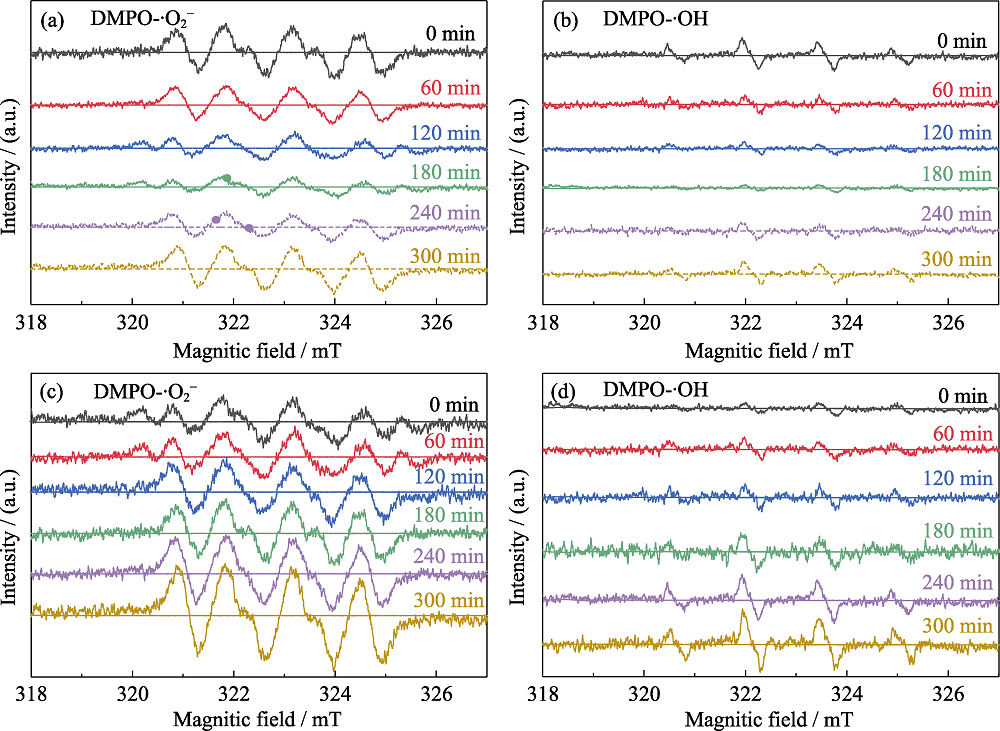
Fig. 4 ESR profiles of (a, c) DMPO-•O2- and (b, d) DMPO-•OH for the photocatalytic degradation of acetaldehyde by AT(a, b) and CAT (c, d) sample Under visible light irradiation for 300 min 0, 60, 120, 180 min represent the photocatalytic reaction time, of which the dotted lines of 240 and 300 min represent 1 and 2 h, respectively, when acetaldehyde was stopped but the light was kept on
| Product | Wavenumber/cm-1 | Mode of vibration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1072 | β(CH3) |
| 2 | 1128, 1166 | v(C-C) |
| 3 | 1315 | δ(CH3) |
| 4 | 1339 | δas(CH3) |
| 5 | 1377 | vs(COO) |
| 6 | 1419 | δs(CH3) |
| 7 | 1458, 1473 | δ(CH2) |
| 8 | 1541, 1558 | vas(COO) |
| 9 | 1603 | v(C=C) |
| 10 | 1732, 1716, 1699, 1650 | v(C=O) |
Table S1 Assignment of FT-IR bands observed for AT sample in the process of dark adsorption and photocatalytic degradation for acetaldehyde
| Product | Wavenumber/cm-1 | Mode of vibration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1072 | β(CH3) |
| 2 | 1128, 1166 | v(C-C) |
| 3 | 1315 | δ(CH3) |
| 4 | 1339 | δas(CH3) |
| 5 | 1377 | vs(COO) |
| 6 | 1419 | δs(CH3) |
| 7 | 1458, 1473 | δ(CH2) |
| 8 | 1541, 1558 | vas(COO) |
| 9 | 1603 | v(C=C) |
| 10 | 1732, 1716, 1699, 1650 | v(C=O) |
| Product | Wavenumber/cm-1 | Mode of vibration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1050, 1100 | β(CH3) |
| 2 | 1200 | r(CH2) |
| 3 | 1221, 1294 | v(C-O) |
| 4 | 1316 | δ(CH3) |
| 5 | 1339, 1371 | vs(COO) |
| 6 | 1361 | δ(CH) |
| 7 | 1419 | δs(CH3) |
| 8 | 1458 | δ(CH2) |
| 9 | 1522, 1558,1573 | vas(COO) |
| 10 | 1620 | v(C=C) |
| 11 | 1771, 1732, 1716, 1699, 1650 | v(C=O) |
Table S2 Assignment of FT-IR bands observed for CAT sample in the process of dark adsorption and photocatalytic degradation for acetaldehyde
| Product | Wavenumber/cm-1 | Mode of vibration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1050, 1100 | β(CH3) |
| 2 | 1200 | r(CH2) |
| 3 | 1221, 1294 | v(C-O) |
| 4 | 1316 | δ(CH3) |
| 5 | 1339, 1371 | vs(COO) |
| 6 | 1361 | δ(CH) |
| 7 | 1419 | δs(CH3) |
| 8 | 1458 | δ(CH2) |
| 9 | 1522, 1558,1573 | vas(COO) |
| 10 | 1620 | v(C=C) |
| 11 | 1771, 1732, 1716, 1699, 1650 | v(C=O) |
| [1] |
WANG S B, ANG H M, TADE M O. Volatile organic compounds in indoor environment and photocatalytic oxidation: state of the art. Environment International, 2007, 33(5): 694-705.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ZHANG X Y, GAO B, CREAMER A E, et al. Adsorption of VOCs onto engineered carbon materials: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 338: 102-123.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
HUANG R J, ZHANG Y L, BOZZETTI C, et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature, 2014, 514: 218-222.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
KAMAL M S, RAZZAK S A, HOSSAIN M M. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)-a review. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 140: 117-134.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GUO Q, ZHOU C Y, MA Z B, et al. Fundamentals of TiO2 photocatalysis: concepts, mechanisms, and challenges. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(50): 1901997.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
FU C, LI M J, LI H J, et al. Fabrication of Au nanoparticle/TiO2 hybrid films for photoelectrocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 692: 727-733.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
DAI Y Q, COBLEY C M, ZENG J, et al. Synthesis of anatase TiO2 nanocrystals with exposed {001} facets. Nano Letters, 2009, 9(6): 2455-2459.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI W, WANG F, LIU Y P, et al. General strategy to synthesize uniform mesoporous TiO2/graphene/mesoporous TiO2 sandwich- like nanosheets for highly reversible lithium storage. Nano letters, 2015, 15(3): 2186-2193.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIU H H, LI Y, XIANG M M, et al. Single-layered MoS2 directly grown on rutile TiO2(110) for enhanced interfacial charge transfer. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(5): 6083-6089.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIANG H J, ZHANG B, GE H B, et al. Porous TiO2/Pt/TiO2 sandwich catalyst for highly selective semihydrogenation of alkyne to olefin. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(10): 6567-6572.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
FORZATTI P, LIETTI L. Catalyst deactivation. Catalysis Today, 1999, 52(2/3): 165-181.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ABBAS N, HUSSAIN M, RUSSO N, et al. Studies on the activity and deactivation of novel optimized TiO2 nanoparticles for the abatement of VOCs. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 175: 330-340.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MO J H, ZHANG Y P, XU Q J, et al. Determination and risk assessment of by-products resulting from photocatalytic oxidation of toluene. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2009, 89(3/4): 570-576.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HE C, CHENG J, ZHANG X, et al. Recent advances in the catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: a review based on pollutant sorts and sources. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(7): 4471-4568.
DOI URL |
| [15] | YANG X J, SUN H W, LI G Y, et al. Fouling of TiO2 induced by natural organic matters during photocatalytic water treatment: mechanisms and regeneration strategy. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 294: 120252. |
| [16] | HUANG H T, FENG J Y, ZHANG S, et al. Molecular-level understanding of the deactivation pathways during methanol photo- reforming on Pt-decorated TiO2. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 272: 118980. |
| [17] |
WEON S, CHOI W. TiO2 nanotubes with open channels as deactivation-resistant photocatalyst for the degradation of volatile organic compounds. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(5): 2556-2563.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WEON S, KIM J, CHOI W. Dual-components modified TiO2 with Pt and fluoride as deactivation-resistant photocatalyst for the degradation of volatile organic compound. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 220: 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
DONG X A, CUI W, WANG H, et al. Promoting ring-opening efficiency for suppressing toxic intermediates during photocatalytic toluene degradation via surface oxygen vacancies. Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(10): 669-678.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ZONG B Y, XU Q K, LI Q J, et al. Novel insights into the unique intrinsic sensing behaviors of 2D nanomaterials for volatile organic compounds: from graphene to MoS2 and black phosphorous. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9: 14411-14421.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
REN Y, DONG Y Z, FENG Y Q, et al. Compositing two- dimensional materials with TiO2 for photocatalysis. Catalysts, 2018, 8(12): 590.
DOI URL |
| [22] | RAO Z P, LU G H, MAHMOOD A, et al. Deactivation and activation mechanism of TiO2 and rGO/Er3+-TiO2 during flowing gaseous VOCs photodegradation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 284: 119813. |
| [23] |
WANG C Y, RAO Z P, MAHMOOD A, et al. Improved photocatalytic oxidation performance of gaseous acetaldehyde by ternary g-C3N4/Ag-TiO2 composites under visible light. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 602: 699-711.
DOI URL |
| [24] | FENG J J, ZHANG D K, ZHOU H P, et al. Coupling P nanostructures with P-doped g-C3N4 as efficient visible light photocatalysts for H2 evolution and RhB degradation. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(5): 6342-6349. |
| [25] |
REN H T, JIA S Y, ZOU J J, et al. A facile preparation of Ag2O/P25 photocatalyst for selective reduction of nitrate. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 176-177: 53-61.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SINGH M, ZHOU N J, DILIP K. PAUL, et al. IR spectral evidence of aldol condensation: acetaldehyde adsorption over TiO2 surface. Journal of Catalysis, 2008, 260(2): 371-379.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
XU B Y, ZHU T, TANG X Y, et al. Heterogeneous reaction of formaldehyde on the surface of TiO2 particles. Science China Chemistry, 2010, 53: 2644-2651.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
BATAULT F, THEVENET F, HEQUET V, et al. Acetaldehyde and acetic acid adsorption on TiO2 under dry and humid conditions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 264: 197-210.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
RASKO´ J, KISS J. Adsorption and surface reactions of acetaldehyde on TiO2, CeO2 and Al2O3. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2005, 287(2): 252-260.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
BIRGER H, DIETER T, SAMMY V, et al. Elucidating the photocatalytic degradation pathway of acetaldehyde: an FTIR in situ study under atmospheric conditions. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2011, 106(3/4): 630-638.
DOI URL |
| [31] | ZHANG W P, LI G Y, LIU H L, et al. Photocatalytic degradation mechanism of gaseous styrene over Au/TiO2@CNTs: relevance of superficial state with deactivation mechanism. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 272: 118969. |
| [1] | WU Lin, HU Minglei, WANG Liping, HUANG Shaomeng, ZHOU Xiangyuan. Preparation of TiHAP@g-C3N4 Heterojunction and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [2] | MA Xinquan, LI Xibao, CHEN Zhi, FENG Zhijun, HUANG Juntong. BiOBr/ZnMoO4 Step-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and Photocatalytic Degradation Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [3] | CHEN Hanxiang, ZHOU Min, MO Zhao, YI Jianjian, LI Huaming, XU Hui. 0D/2D CoN/g-C3N4 Composites: Structure and Photocatalytic Performance for Hydrogen Production [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [4] | HONG Jiahui, MA Ran, WU Yunchao, WEN Tao, AI Yuejie. CoNx/g-C3N4 Nanomaterials Preparation by MOFs Self-sacrificing Template Method for Efficient Photocatalytic Reduction of U(VI) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 741-749. |
| [5] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [6] | WANG Xiaojun, XU Wen, LIU Runlu, PAN Hui, ZHU Shenmin. Preparation and Properties of Ag@C3N4 Photocatalyst Supported by Hydrogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [7] | LIU Xuechen, ZENG Di, ZHOU Yuanyi, WANG Haipeng, ZHANG Ling, WANG Wenzhong. Selective Oxidation of Biomass over Modified Carbon Nitride Photocatalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 38-44. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xian, ZHANG Ce, JIANG Wenjun, FENG Deqiang, YAO Wei. Synthesis, Electronic Structure and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance of Quaternary BiMnVO5 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| [9] | LIU Peng, WU Shimiao, WU Yunfeng, ZHANG Ning. Synthesis of Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS Photocatalyst for CO2 Reduction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 15-21. |
| [10] | WANG Luping, LU Zhanhui, WEI Xin, FANG Ming, WANG Xiangke. Application of Improved Grey Model in Photocatalytic Data Prediction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 871-876. |
| [11] | AN Weijia, LI Jing, WANG Shuyao, HU Jinshan, LIN Zaiyuan, CUI Wenquan, LIU Li, XIE Jun, LIANG Yinghua. Fe(III)/rGO/Bi2MoO6 Composite Photocatalyst Preparation and Phenol Degradation by Photocatalytic Fenton Synergy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 615-622. |
| [12] | XIAO Xiang, GUO Shaoke, DING Cheng, ZHANG Zhijie, HUANG Hairui, XU Jiayue. CsPbBr3@TiO2 Core-shell Structure Nanocomposite as Water Stable and Efficient Visible-light-driven Photocatalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 507-512. |
| [13] | XIONG Jinyan, LUO Qiang, ZHAO Kai, ZHANG Mengmeng, HAN Chao, CHENG Gang. Facilely Anchoring Cu nanoparticles on WO3 Nanocubes for Enhanced Photocatalysis through Efficient Interface Charge Transfer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 325-331. |
| [14] | SHU Mengyang, LU Jialin, ZHANG Zhijie, SHEN Tao, XU Jiayue. CsPbBr3 Perovskite Quantum Dots/Ultrathin C3N4 Nanosheet 0D/2D Composite: Enhanced Stability and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1217-1222. |
| [15] | LIU Yaxin, WANG Min, SHEN Meng, WANG Qiang, ZHANG Lingxia. Bi-doped Ceria with Increased Oxygen Vacancy for Enhanced CO2 Photoreduction Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 88-94. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||