
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (8): 891-896.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220074
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
DENG Taoli1,2( ), CHEN Hexin1, HEI Lingli1, LI Shuxing1(
), CHEN Hexin1, HEI Lingli1, LI Shuxing1( ), XIE Rongjun1(
), XIE Rongjun1( )
)
Received:2022-02-15
Revised:2022-04-07
Published:2022-08-20
Online:2022-04-07
Contact:
LI Shuxing, PhD. E-mail: lishuxing@xmu.edu.cn;About author:DENG Taoli (1989-), female, PhD candidate. E-mail: dengtaoli77@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
DENG Taoli, CHEN Hexin, HEI Lingli, LI Shuxing, XIE Rongjun. Achieving High Light Uniformity Laser-driven White Lighting Source by Introducing Secondary Phases in Phosphor Converters[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 891-896.

Fig. S1 CCT (a) and illuminance (b) distribution curves at different angles (10°~170°) of YAG PiG films with different TiO2, BN, Al2O3, or SiO2 contents
| UniCCT/% | 0 | 10% | 15% | 20% | 25% | 30% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 10.4 | 91.5 | 94.3 | 94.8 | 91 | 91 |
| BN | 10.4 | 73.6 | 86.9 | 88.4 | 94.1 | 90.9 |
| Al2O3 | 10.4 | 18.1 | - | 84.2 | - | 89.3 |
| SiO2 | 10.4 | 12.1 | 13.7 | 19.4 | 16.2 | 48.3 |
Table S1 CCT uniformity of YAG PiG films with different TiO2, BN, Al2O3, or SiO2 contents under blue laser excitation
| UniCCT/% | 0 | 10% | 15% | 20% | 25% | 30% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 10.4 | 91.5 | 94.3 | 94.8 | 91 | 91 |
| BN | 10.4 | 73.6 | 86.9 | 88.4 | 94.1 | 90.9 |
| Al2O3 | 10.4 | 18.1 | - | 84.2 | - | 89.3 |
| SiO2 | 10.4 | 12.1 | 13.7 | 19.4 | 16.2 | 48.3 |
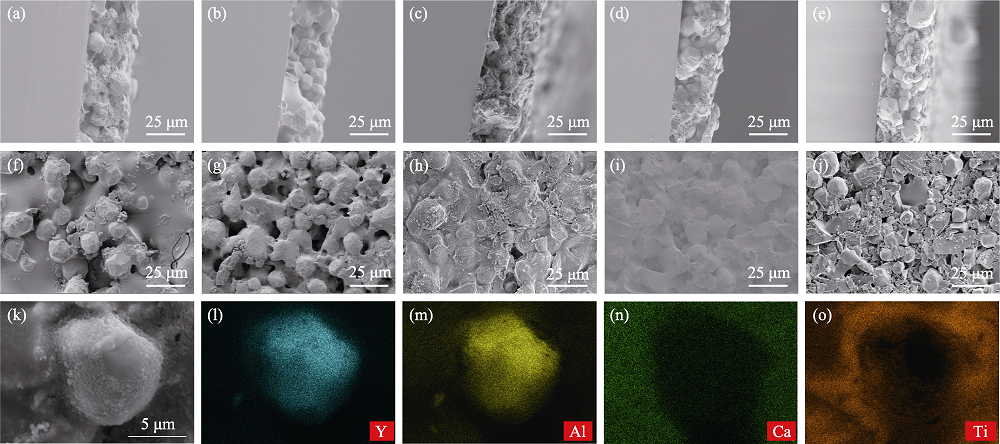
Fig. 1 (a-e) Cross-section and (f-j) top-view SEM images of (a, f) YAG, (b, g)YAG-TiO2, (c, h) YAG-BN, (d, i) YAG-Al2O3, (e, j) YAG-SiO2 PiG films; (k-o) SEM image of the selected area of the YAG-TiO2 PiG film and corresponding EDS mappings of Y, Al, Ca and Ti
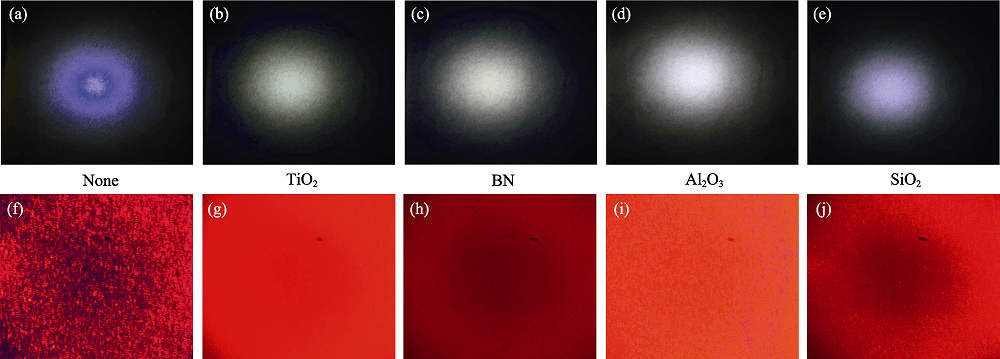
Fig. 2 (a-e) Illumination images of laser-driven white light sources from YAG, YAG-TiO2, YAG-BN, YAG-Al2O3, and YAG-SiO2 PiG films under excitation of a laser power density of 1.72 W/mm2, and (f-j) Speckle images of YAG, YAG-TiO2, YAG-BN, YAG-Al2O3, and YAG-SiO2 PiG films under 445 nm laser excitation
| Sample | None | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | BN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\bar{x}$/(Mcd·m–2) | 0.51 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.11 |
| σ | 1260 | 554 | 461 | 248 | 205 |
Table 1 Luminance uniformity of YAG-based PiG films with different scattering media
| Sample | None | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | BN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\bar{x}$/(Mcd·m–2) | 0.51 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.11 |
| σ | 1260 | 554 | 461 | 248 | 205 |
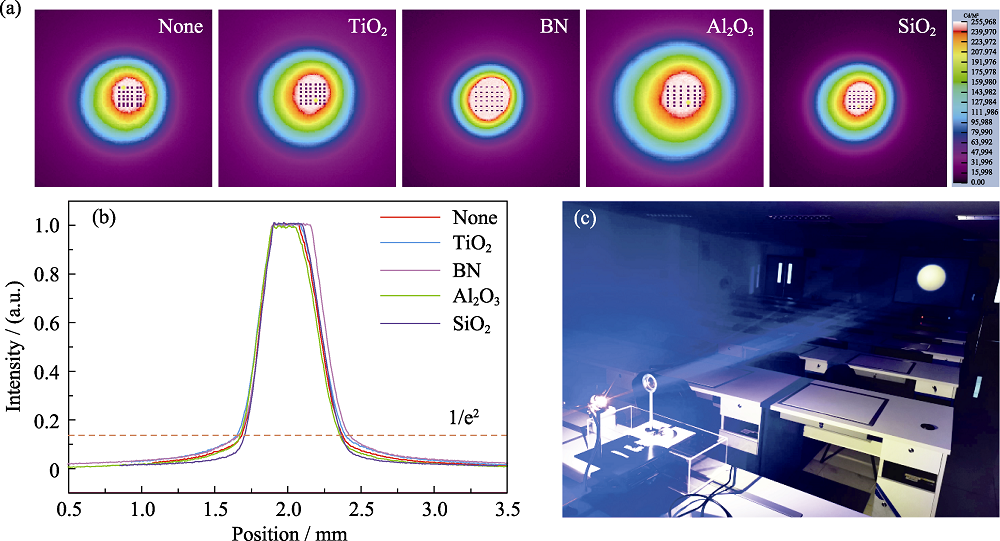
Fig. 3 (a) Luminance of light spots in YAG, YAG-TiO2, YAG-BN, YAG-Al2O3, and YAG-SiO2 PiG films under excitation with a laser power of 0.015 W, respectively, (b) luminance distribution curves along the light spot diameter, and (c) photograph of the light spot at a distance of 10 m when the YAG-BN PiG film pumped by a blue LD
| Sample | None | SiO2 | Al2O3 | BN | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max/K | 100000 | 50780 | 6720 | 7124 | 6620 |
| Min/K | 4745 | 6798 | 5193 | 5287 | 5073 |
| Ave/K | 45565 | 14080 | 5815 | 5621 | 5353 |
| Uni/% | 10.4 | 48.3 | 89.3 | 94.1 | 94.8 |
Table 2 CCT uniformity of YAG, YAG-TiO2, YAG-BN, YAG-Al2O3, YAG-SiO2 PiG films under blue laser excitation
| Sample | None | SiO2 | Al2O3 | BN | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max/K | 100000 | 50780 | 6720 | 7124 | 6620 |
| Min/K | 4745 | 6798 | 5193 | 5287 | 5073 |
| Ave/K | 45565 | 14080 | 5815 | 5621 | 5353 |
| Uni/% | 10.4 | 48.3 | 89.3 | 94.1 | 94.8 |
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | BN | TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n2 | 1.48 | 1.76 | 1.73 | 2.61 |
| R | 0.000045 | 0.0064 | 0.0051 | 0.073 |
Table 3 Relative refractive indexes of secondary phases introduced into the YAG-PiG film
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | BN | TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n2 | 1.48 | 1.76 | 1.73 | 2.61 |
| R | 0.000045 | 0.0064 | 0.0051 | 0.073 |
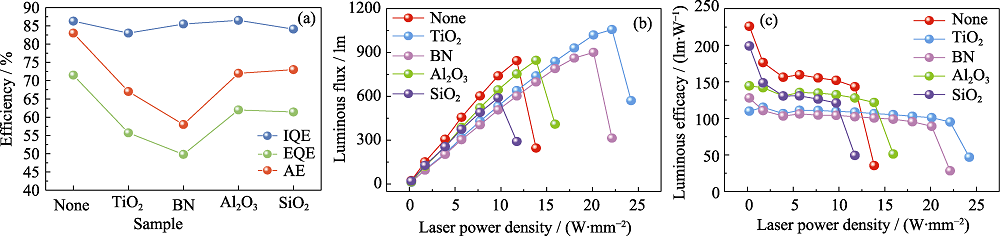
Fig. 5 (a) Quantum efficiency and absorption efficiency, (b) luminous flux, and (c) luminous efficacy of YAG, YAG-TiO2, YAG-BN, YAG-Al2O3, and YAG-SiO2 PiG films
| [1] | WIERER J J, TSAO J Y, SIZOV D S. Comparison between blue lasers and light-emitting diodes for future solid-state lighting. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2013, 7(6): 963-993. |
| [2] | LI S, WANG L, HIROSAKI N, et al. Color conversion materials for high-brightness laser-driven solid-state lighting. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2018, 12(12): 1800173. |
| [3] |
LIANG Y, DING X, YAN C, et al. Phosphor-in-glass (PIG) converter sintered by a fast Joule heating process for high-power laser- driven white lighting. Optics Express, 2021, 29(10): 14218.
DOI URL |
| [4] | ZHENG P, LI S, WANG L, et al. Unique color converter architecture enabling Phosphor-in-Glass (PiG) films suitable for high- power and high-luminance laser-driven white lighting. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(17): 14930-14940. |
| [5] | YOU S, LI S, ZHENG P, et al. A thermally robust La3Si6N11: Ce-in-glass film for high-brightness blue-laser-driven solid state lighting. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2019, 13(2): 1800216. |
| [6] |
YAO Q, HU P, SUN P, et al. YAG:Ce3+transparent ceramic phosphors brighten the next-generation laser-driven lighting. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(19): 1907888.
DOI URL |
| [7] | PENG Y, HUANG Y, LEI Z, et al. Rapid and efficient preparation of phosphor-in-glass converter by induction heating for high-power white LEDs/LDs. Materials Today Communications, 2021, 29: 102839. |
| [8] | AVANAKI A, ESPIG K, KIMPE T, et al. Perceptual uniformity of commonly used color spaces. Proceedings of SPIE-The International. Society for Optical Engineering, 2014: 9041. |
| [9] |
LIU P, GUAN Z, ZHOU T, et al. Laser regulation for variable color temperature lighting with low energy consumption by microlens arrays. Appl. Opt., 2021, 60(19): 5652-5661.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MA Y, LUO X. Small-divergent-angle uniform illumination with enhanced luminance of transmissive phosphor-converted white laser diode by secondary optics design. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2019, 122: 14-22.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
CHEN K, HAN H, CHEN H, et al. White light emitting diodes with enhanced CCT uniformity and luminous flux using ZrO2 nanoparticles. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(10): 5378-5383.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WU B, LUO X, ZHENG H, et al. Effect of gold wire bonding process on angular correlated color temperature uniformity of white light-emitting diode. Opt. Express, 2011, 19(24): 24115-24121.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LIU J, WANG W, LU X, et al. Controlling phosphor particle distribution for high-angular-color-uniformity and low-cost LEDs based on thermalcapillary flow. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2021, 68(2): 592-596.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LAI M, QUOC ANH N D, MA H, et al. Scattering effect of SiO2 particles on correlated color temperature uniformity of multi-chip white light LEDs. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 2016, 39(4): 468-472.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
HOU Y, CHEN C, YING S, et al. The effects of TiO2 diffuser- loaded encapsulation on corrected color temperature uniformity of remote phosphor white leds. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(4): 675.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
NGUYEN A Q D, NGUYEN T T, LEE H. Selection of scattering enhancement particles for improving color homogeneity and luminous flux of phosphor-converted LEDs. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 2017, 40(4): 307-312.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
XU Y, LI S, ZHENG P, et al. A search for extra-high brightness laser-driven color converters by investigating thermally-induced luminance saturation. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(37): 11449-11456.
DOI URL |
| [1] | WEN Zicong, NIU Dechao, LI Yongsheng. Silver Clusters-loaded Silica-based Hybrid Nanoparticles: Synthesis and SERS Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1297-1304. |
| [2] | HU Feng-Xiang, LI Ling, LIN Kui, CUI Lan, SHI Cai-Jing, SAYYAR Ali Shah, CUI Shen. Preparation of N-doped Hollow Carbon Spheres and Investigation of Their Optical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(8): 827-833. |
| [3] | ZHOU Ding, SHI Ying, FAN Ling-Cong, LIN De-Bao, SUN Ze-Qing, XU Jia-Yue. Fabrication and Optical Properties of Ce, Pr Co-doped LuAG Transparent Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(10): 1099-1102. |
| [4] | ZHANG Dong-Mei, TIAN Lei, GUO Hui-Lin. Preparation and Optical Properties of Graphene Quantum Dots Containing Nitrogen [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(10): 1123-1128. |
| [5] | YANG Yu-Jia, WANG Jing, HE Hui-Fen. Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Tb3+ Doped BaZrO3 Powders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(1): 27-33. |
| [6] | YANG Zhi-Huai, ZHANG Yun-Peng, ZHANG Mei-Guang, XU Qiang, ZHANG Ya-Ni, ZHANG Rong. The Electronic and Optical Properties of Tetrahedral Doped Co1-xRexCr2O4 (Re = Li, Na, K, Rb) Spinel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(8): 819-824. |
| [7] | YANG Rui, JIE Wan-Qi, SUN Xiao-Yan, YANG Min, HU Huan, LIN Yun. Characterization of Cr-doped ZnTe Crystals Grown by Temperature Gradient Solution Growth (TGSG) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(4): 401-407. |
| [8] | YIN Cong, XIE Dan, XU Jian-Long, REN Tian-Ling. Magnetic Properties of Proton Irradiated Giant Magnetoresistance Multilayers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(3): 331-336. |
| [9] | WANG Chen-Yang, HU Guan-Qin, WANG Hong, ZHAO Jing-Tai. Preparation of Bi4Si3O12-based Glass-ceramics and Effect of Heat Treatments on Optical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(2): 167-171. |
| [10] | WANG Xiao-Xiao, YANG Lin, LIU Hong, CHEN Qiang, XIAO Ding-Quan, ZHU Jian-Guo. Optical Properties of ZnS:Co+Cr Nanocrystals Synthesized by a Low Temperature Hydrothermal Process [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10): 1049-1054. |
| [11] | ZHENG Chun-Man, WEI Yong-Tao, XIE Kai, HAN Yu. Preparation of Polycrystalline Cu(In,Ga)Se2 Thin Film with Nano-metal Oxide: the Chemical Reaction Process and Its Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(7): 701-706. |
| [12] | ZHANG Yang, HUANG Wan-Xia, SHI Qi-Wu, SONG Lin-Wei, XU Yuan-Jie. Thermal Modulation Behavior inside the Hysteresis Loop of W-Mo Co-doping Vanadium Dioxide Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(5): 497-501. |
| [13] | LIU Guan-Wei, XIE Zhi-Peng, WU Yin. Application of Doping Ceramics via Infiltration on Translucent Alumina Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(4): 375-380. |
| [14] | JIN Teng-Teng, ZHANG Zhi-Jun, ZHANG Hui, ZHAO Jing-Tai. Crystal Structure, Phase Transition and Optical Properties of ν-PrBO3 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(10): 1153-1157. |
| [15] | HUANG Shuai, LI Chen-Hui, SUN Yi-Hua, KE Wen-Ming. Influence of the Substrate Temperature on the Properties of Nb-doped TiO2 Films Deposited by DC Magnetron Sputtering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(1): 64-68. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||