
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (8): 873-882.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210798
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
HU Yue1( ), AN Lin1, HAN Xin2(
), AN Lin1, HAN Xin2( ), HOU Chengyi1, WANG Hongzhi1, LI Yaogang3, ZHANG Qinghong3(
), HOU Chengyi1, WANG Hongzhi1, LI Yaogang3, ZHANG Qinghong3( )
)
Received:2022-12-29
Revised:2022-03-09
Published:2022-08-20
Online:2022-03-10
Contact:
ZHANG Qinghong, professor. E-mail: zhangqh@dhu.edu.cn;About author:HU Yue (1998-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: yue_hamish@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
HU Yue, AN Lin, HAN Xin, HOU Chengyi, WANG Hongzhi, LI Yaogang, ZHANG Qinghong. RhO2 Modified BiVO4 Thin Film Photoanodes: Preparation and Photoelectrocatalytic Water Splitting Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 873-882.
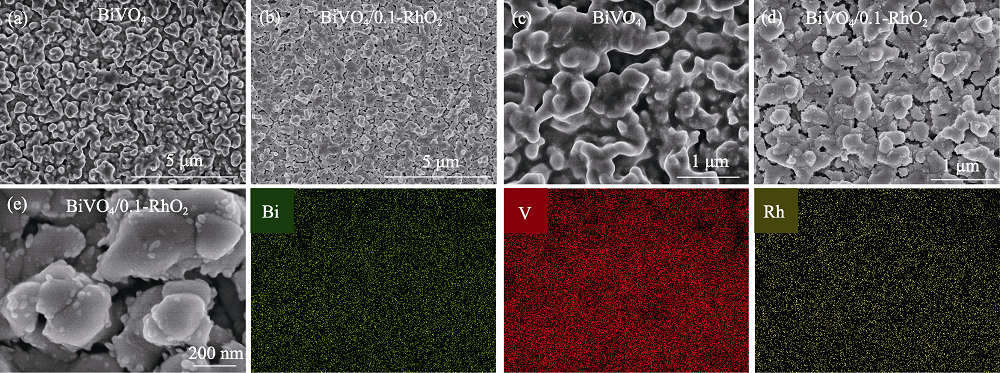
Fig. 2 (a, b) Low-magnification and (c, d) high-magnification FESEM images of bare BiVO4 surface and BiVO4/0.1-RhO2 photoanodes, and (e) high-magnification SEM image with elemental mappings of the BiVO4/0.1-RhO2 photoanode
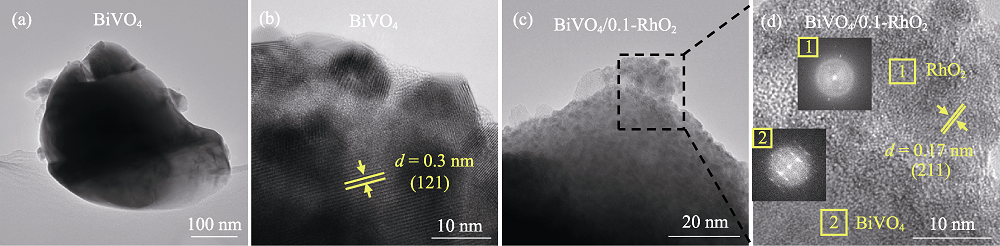
Fig. 3 (a, c) TEM and (b, d) HRTEM images of (a, b) bare BiVO4 and (c, d) BiVO4/0.1-RhO2 photoanodes The inset in (d) is the SAED patterns of the selected area
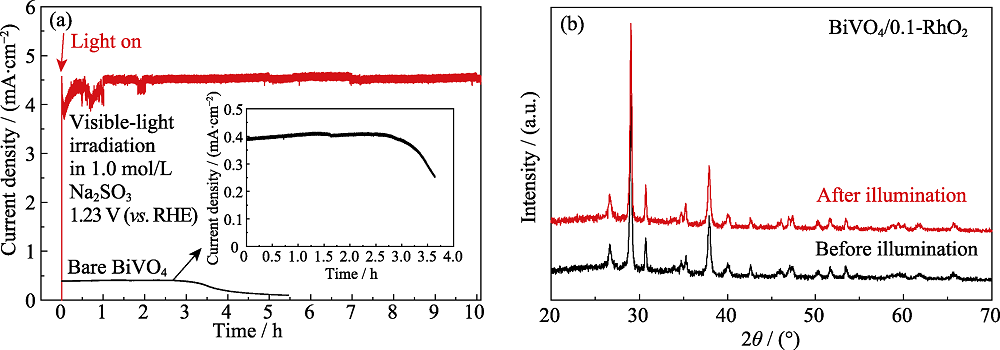
Fig. 8 (a) Photocurrent stability of the BiVO4/0.1-RhO2 photoanode in 1.0 mol/L Na2SO3 (pH8.5) under visible-light illumination, and (b) XRD patterns of the BiVO4/0.1-RhO2 photoanodes before and after illumination, respectively
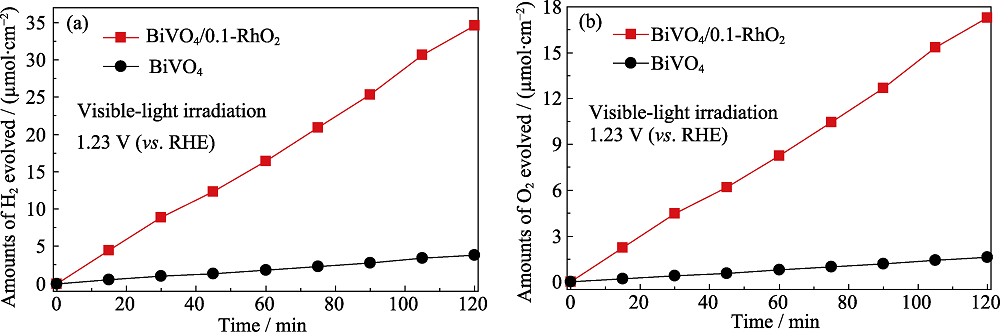
Fig. 9 (a) Hydrogen and (b) oxygen evolution vs. reaction time per illuminated area for bare BiVO4 and BiVO4/RhO2 photoanodes under visible-light irradiation with the electrolyte of 1.0 mol/L Na2SO3 (pH8.5) as hole scavenger
| [1] | FANG M, CAI Q, QIN Q, et al. Mo-doping induced crystal orientation reconstruction and oxygen vacancy on BiVO4 homojunction for enhanced solar-driven water splitting. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 421: 127796. |
| [2] |
ZHANG W, SHEN Q, XUE J, et al. Preparation and photoelectrochemical water oxidation of hematite nanobelts containing highly ordered oxygen vacancies. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1290-1296.
DOI URL |
| [3] | HAN X, SI T, LIU Q, et al. 2D bimetallic RuNi alloy co-catalysts remarkably enhanced the photocatalytic H2 evolution performance of g-C3N4 nanosheets. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 426: 130824. |
| [4] | SU K, ZHANG Y, LU F, et al. Platinum decorated titanium dioxide nanosheets for efficient photoelectrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1200-1204. |
| [5] |
KIM J H, LEE J S. Elaborately modified BiVO4 photoanodes for solar water splitting. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(20): 1806938.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HE Y M, HAMANN T, WANG D W. Thin film photoelectrodes for solar water splitting. Chemical Society Reviews, 2019, 48(7): 2182-2215.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
BAE D, SEGER B, VESBORG P C K, et al. Strategies for stable water splitting via protected photoelectrodes. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(7): 1933-1954.
DOI URL |
| [8] | LU X, YE K H, ZHANG S, et al. Amorphous type FeOOH modified defective BiVO4 photoanodes for photoelectrochemical water oxidation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 428: 131027. |
| [9] |
JIAN J, JIANG G S, VAN DE KROL R, et al. Recent advances in rational engineering of multinary semiconductors for photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation. Nano Energy, 2018, 51: 457-480.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GAO Y, FAN W, QU K, et al. Confined growth of Co-Pi co- catalyst by organic semiconductor polymer for boosting the photoelectrochemical performance of BiVO4. New Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 43(21): 8160-8167.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
PENG B, XIA M, LI C, et al. Network structured CuWO4/BiVO4/ Co-Pi nanocomposite for solar water splitting. Catalysts, 2018, 8(12): 663-672.
DOI URL |
| [12] | YE K H, WANG Z L, GU J W, et al. Carbon quantum dots as a visible light sensitizer to significantly increase the solar water splitting performance of bismuth vanadate photoanodes. Energy & Environmental Science, 2017, 10(3): 772-779. |
| [13] |
ZENG Q Y, LI J H, LI L S, et al. Synthesis of WO3/BiVO4 photoanode using a reaction of bismuth nitrate with peroxovanadate on WO3 film for efficient photoelectrocatalytic water splitting and organic pollutant degradation. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2017, 217: 21-29.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZHONG D K, CHOI S, GAMELIN D R. Near-complete suppression of surface recombination in solar photoelectrolysis by "Co-Pi" catalyst-modified W: BiVO4. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(45): 18370-18377.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
RITLENG V, SIRLIN C, PFEFFER M. Ru-, Rh-, and Pd-catalyzed C-C bond formation involving C-H activation and addition on unsaturated substrates: reactions and mechanistic aspects. Chemical Reviews, 2002, 102(5): 1731-1769.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
SONG G, WANG F, LI X. C-C, C-O and C-N bond formation via rhodium (III)-catalyzed oxidative C-H activation. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(9): 3651-3678.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
CAMPBELL C T. Ultrathin metal films and particles on oxide surfaces: structural, electronic and chemisorptive properties. Surface Science Reports, 1997, 27(1/2/3): 1-111.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
COLBY D A, TSAI A S, BERGMAN R G, et al. Rhodium catalyzed chelation-assisted C-H bond functionalization reactions. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2012, 45(6): 814-825.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
OHNO T, BAI L, HISATOMI T, et al. Photocatalytic water splitting using modified GaN:ZnO solid solution under visible light: long-time operation and regeneration of activity. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(19): 8254-8259.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WANG S, CHEN P, YUN J H, et al. An electrochemically treated BiVO4 photoanode for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(29): 8500-8504.
DOI URL |
| [21] | MIAO Y, LIU J, CHEN L, et al. Single-atomic-Co cocatalyst on (040) facet of BiVO4 toward efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 427: 131011. |
| [22] |
PERRY S C, PANGOTRA D, VIEIRA L, et al. Electrochemical synthesis of hydrogen peroxide from water and oxygen. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2019, 3(7): 442-458.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHANG Y P, LI Y, NI D Q, et al. Improvement of BiVO4 photoanode performance during water photo-oxidation using Rh-doped SrTiO3 perovskite as a co-catalyst. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(32): 1902101.
DOI URL |
| [24] | FEI H, SHAO J, LI H, et al. Construction of ultra-thin 2D CN-Br- 0.12/2% RhOx photo-catalyst with rapid electron and hole separation for efficient bisphenol A degradation. Applied Catalysis B- Environmental, 2021, 299: 120623. |
| [25] |
LEITE E R, MACIEL A P, WEBER I T, et al. Development of metal oxide nanoparticles with high stability against particle growth using a metastable solid solution. Advanced Materials, 2002, 14(12): 905-908.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
FOUNTAINE K T, LEWERENZ H J, ATWATER H A. Interplay of light transmission and catalytic exchange current in photoelectrochemical systems. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 105(17): 173901.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
TOLOD K R, HERNANDEZ S, RUSSO N. Recent advances in the BiVO4 photocatalyst for sun-driven water oxidation: top-performing photoanodes and scale-up challenges. Catalysts, 2017, 7(1): 13-23.
DOI URL |
| [28] | SHE H, YUE P, HUANG J, et al. One-step hydrothermal deposition of F:FeOOH onto BiVO4 photoanode for enhanced water oxidation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 392: 123703. |
| [29] | JU S, JUN J, HUH D, et al. Simultaneous improvement of absorption and separation efficiencies of Mo:BiVO4 photoanodes via nanopatterned SnO2/Au hybrid layers. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(20): 17000-17007. |
| [30] |
QI J, KONG D, LIU D, et al. Bimetallic phosphide decorated Mo-BiVO4 for significantly improved photoelectrochemical activity and stability. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(27): 15629-15634.
DOI URL |
| [31] | YIN X, QIU W, LI W, et al. High porosity Mo doped BiVO4 film by vanadium re-substitution for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 389: 124365. |
| [32] |
JIAN J, XU Y, YANG X, et al. Embedding laser generated nanocrystals in BiVO4 photoanode for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 2609.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
COSTANTINO F, KAMAT P V. Do sacrificial donors donate H2 in photocatalysis? ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 7: 242-246.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
MAEDA K, XIONG A, YOSHINAGA T, et al. Photocatalytic overall water splitting promoted by two different cocatalysts for hydrogen and oxygen evolution under visible light. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(24): 4096-4099.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
WANG D, LI R, ZHU J, et al. Photocatalytic water oxidation on BiVO4 with the electrocatalyst as an oxidation cocatalyst: essential relations between electrocatalyst and photocatalyst. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(8): 5082-5089.
DOI URL |
| [1] | WANG Ruyi, XU Guoliang, YANG Lei, DENG Chonghai, CHU Delin, ZHANG Miao, SUN Zhaoqi. p-n Heterostructured BiVO4/g-C3N4 Photoanode: Construction and Its Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 87-96. |
| [2] | CHEN Hanxiang, ZHOU Min, MO Zhao, YI Jianjian, LI Huaming, XU Hui. 0D/2D CoN/g-C3N4 Composites: Structure and Photocatalytic Performance for Hydrogen Production [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [3] | MA Hui, TAO Jianghui, WANG Yanni, HAN Yu, WANG Yabin, DING Xiuping. Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Silica & Titania Hybrid Mesoporous Spheres and Their Catalytic Performance Regulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 404-412. |
| [4] | GAO Wa, XIONG Yujie, WU Congping, ZHOU Yong, ZOU Zhigang. Recent Progress on Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction with Ultrathin Nanostructures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 3-14. |
| [5] | ZHANG Yaping,LEI Yuxuan,DING Wenming,YU Lianqing,ZHU Shuaifei. Preparation and Photoelectrochemical Property of the Dual-ferroelectric Composited Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 987-992. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yiqing,ZHANG Shujuan,WAN Zhengrui,MO Han,WANG Niangui,ZHOU Liqun. RuFe Nanoparticles Modified Sheet-like BiVO4 : High-efficient Synergistic Catalyst for Ammonia Borane Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 809-816. |
| [7] | XU Shichao,ZHU Tianzhe,QIAO Yang,BAI Xuejian,TANG Nan,ZHENG Chunming. Fabrication of Z-scheme BiVO4/GO/g-C3N4 Photocatalyst with Efficient Visble-light Photocatalytic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 839-846. |
| [8] | XU Jingwei,LI Zheng,WANG Zepu,YU Han,HE Qi,FU Nian,DING Bangfu,ZHENG Shukai,YAN Xiaobing. Morphology and Photocatalytic Performance Regulation of Nd3+-doped BiVO4 with Staggered Band Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 789-795. |
| [9] | WANG Ping,LI Xinyu,SHI Zhanling,LI Haitao. Synergistic Effect of Ag and Ag2O on Photocatalytic H2-evolution Performance of TiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 781-788. |
| [10] | ZHENG Yun,CHEN Yilin,GAO Bifen,LIN Bizhou. Progress on Phosphorene for Photocatalytic Water Splitting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(6): 647-653. |
| [11] | LI Jie, SONG Chen-Fei, PANG Xian-Juan. Controllable Synthesis and Photocatalytic Performance of BiVO4 under Visible-light Irradiation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 164-172. |
| [12] | SU Kun, ZHANG Ya-Ru, LU Fei, ZHANG Jun, WANG Xi. Platinum Decorated Titanium Dioxide Nanosheets for Efficient Photoelectrocatalytic Hydrogeu Evolution Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1200-1204. |
| [13] | WANG Song-Can, TANG Feng-Qiu, WANG Lian-Zhou. Visible Light Responsive Metal Oxide Photoanodes for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting: a Comprehensive Review on Rational Materials Design [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(2): 173-197. |
| [14] | SONG Jia, XU Ying, MO Yan-Ping, LI Yong-An. Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Bi2WO6 by the Synergistic Action of Ti(IV) and Graphene Bi-cocatalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(3): 269-274. |
| [15] | GUO Dong-Xue, ZHANG Qing-Hong, WANG Hong-Zhi, LI Yao-Gang, CAO Guang-Xiu. Preparation of RuO2/ZrO2/TaON Composite Photocatalyst and Its Photocatalytic Properties for Water Splitting Hydrogen Evolution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(10): 1025-1030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||