
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 278-288.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210599
Special Issue: 2022年度中国知网高下载论文
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Kai1,2( ), SUN Ce2, SHI Yusheng3, HU Jiaming2, ZHANG Qingqing2, SUN Yunfei2, ZHANG Song4, TU Rong4, YAN Chunze3, CHEN Zhangwei5, HUANG Shangyu2, SUN Huajun1(
), SUN Ce2, SHI Yusheng3, HU Jiaming2, ZHANG Qingqing2, SUN Yunfei2, ZHANG Song4, TU Rong4, YAN Chunze3, CHEN Zhangwei5, HUANG Shangyu2, SUN Huajun1( )
)
Received:2021-09-28
Revised:2021-11-21
Published:2022-03-20
Online:2021-12-24
Contact:
SUN Huajun, professor. E-mail: huajunsun@whut.edu.cn
About author:LIU Kai (1987-), male, associate professor. E-mail: victor_liu@whut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
LIU Kai, SUN Ce, SHI Yusheng, HU Jiaming, ZHANG Qingqing, SUN Yunfei, ZHANG Song, TU Rong, YAN Chunze, CHEN Zhangwei, HUANG Shangyu, SUN Huajun. Current Status and Prospect of Additive Manufacturing Piezoceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(3): 278-288.
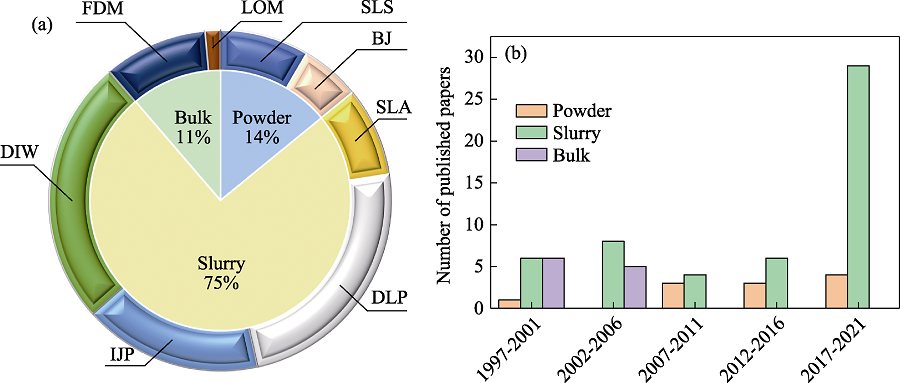
Fig. 1 Papers published on additive manufacturing of piezoceramics (data from Web of Science) (a) Proportion of published literature of each process; (b) Number of papers published at each stage SLS: Selective laser sintering; BJ: Binder jetting; SLA: Stereolithography apparatus; IJP: Ink-jet printing; DLP: Digital light processing; DIW: Direct ink writing; FDM: Fused deposition modeling; LOM: Laminated object manufacturing
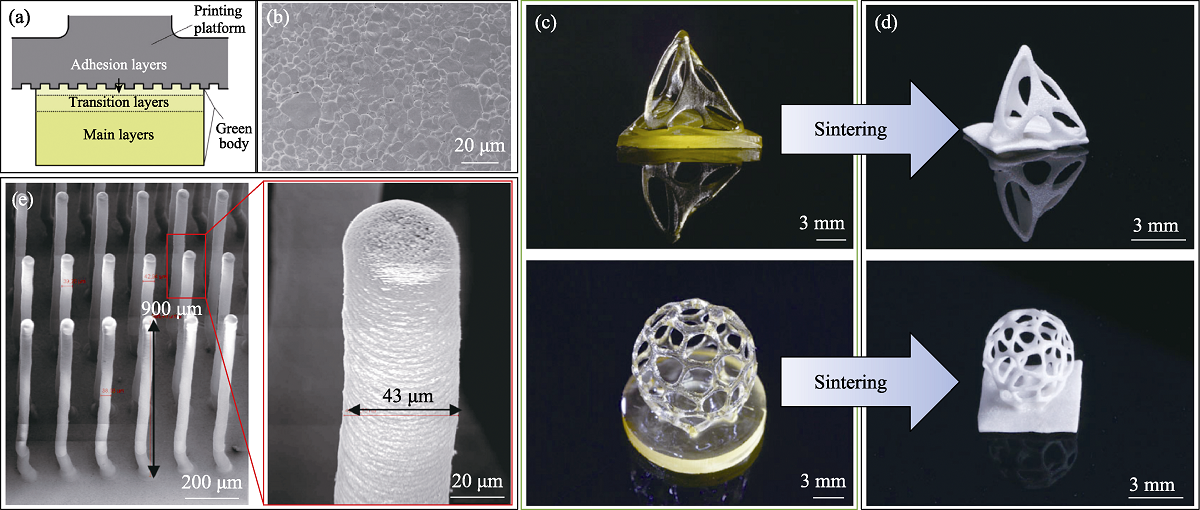
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of layered exposure strategy (a) and micro-topography photo of sintered part[32] (b), photo of precursor body fabricated by Digital Light Processing (c), photos of BTO sample after sintering[35] (d), photos of PZT ceramic microarrays fabricated by Binder Jetting[37] (e)
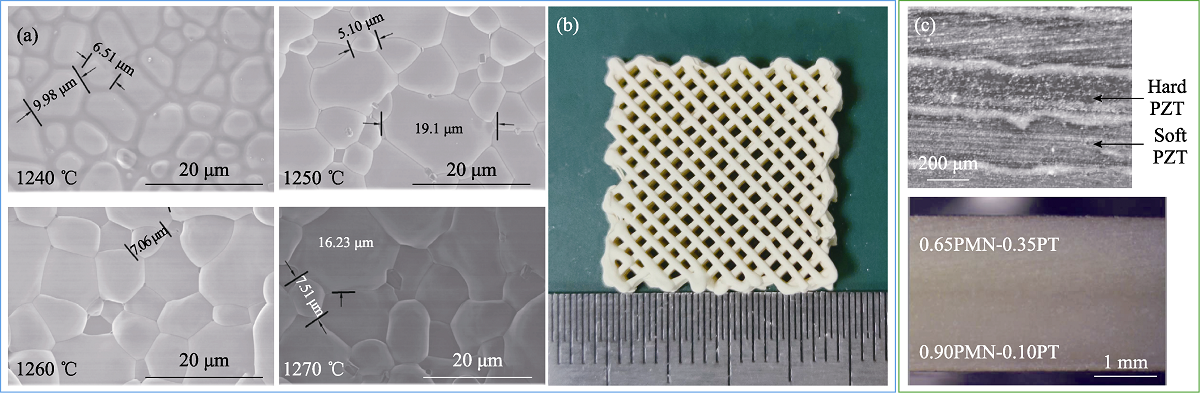
Fig. 4 Micro-morphology photos of the PZT ceramics sintered at different temperatures (a) and photos of sintered PZT ceramics fabricated by Direct Ink Writing (b)[41], and cross-section photo of gradient piezoelectric ceramics fabricated by Fused Deposition Modeling (c)[51,52]
| Materials | Process | Density/(g·cm-3) | Relative density/% | d33/(pC·N-1) | Relative dielectric constant (εr) | Dielectric loss (tan δ) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTO | SLS | - | 97 | - | 1800 | - | [ |
| PZT | SLS | 4 | 50.6 | - | - | - | [ |
| PZT | LENS | - | 90 | - | 430 | 0.05 | [ |
| BTO | BJ | - | 93-94 | 183 | - | - | [ |
| BTO | SLA | 5.69 | 95 | 163 | 2762 | 0.016 | [ |
| BTO | DIW | 5.13 | 85.24 | 204.61 | 2551 | - | [ |
| PZT | DIW | (7.21±0.06) | 94.9 | 678 | (4132±575) | (3.4±1%) | [ |
| BTO | DIW | 5.42 | 90 | 200 | 2200 | - | [ |
| BTO | DIW | - | 89.97 | 350 | 2576 | - | [ |
| PLZT | DIW | - | 98 | 481 | 1986 | - | [ |
| BCZT | DIW | - | 93 | 100 | 1046 | 0.021 | [ |
| BTO | DIW | - | 96 | 159 | 1900 | - | [ |
| BTO | BJ | 2.21 | 37 | 113(Horizontal) 152.7(Vertical) | 581.6(Horizontal) 698(Vertical) | - | [ |
| KNN | SLA | 4.32 | 96 | - | 1800-1900 | 0.2-0.3 | [ |
| PMN-PT | DLP | 7.98 | 97.8 | 620 | - | - | [ |
| PZT | DLP | 7 | - | 345 | 1390 | 0.021 | [ |
| KNN | DLP | 4.09 | 92 | 170 | 2150 | 0.058 | [ |
| PZT-5H | DLP | 7.35 | 96 | 600 | 2875 | 0.029 | [ |
| BTO | DLP | 5.44 | 90 | 200 | 1965 | 0.017 | [ |
| PZT | IJP | - | (86±3) | - | 190 | 0.05 | [ |
| BTO | DIW | 3.93 | 65.3 | 200 | 4730 | 0.033 | [ |
| BTO | DIW | - | 98 | 195 | - | - | [ |
| BTO | DIW | - | 97.8 | - | 533 | - | [ |
| BTO | DIW | 5.66 | 94 | 420 | 4380 | 0.02 | [ |
| PZT | FDM | 7.7 | - | 664 | 3340 | 0.023 | [ |
Table 1 Comparison of properties of piezoceramics formed by additive manufacturing
| Materials | Process | Density/(g·cm-3) | Relative density/% | d33/(pC·N-1) | Relative dielectric constant (εr) | Dielectric loss (tan δ) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTO | SLS | - | 97 | - | 1800 | - | [ |
| PZT | SLS | 4 | 50.6 | - | - | - | [ |
| PZT | LENS | - | 90 | - | 430 | 0.05 | [ |
| BTO | BJ | - | 93-94 | 183 | - | - | [ |
| BTO | SLA | 5.69 | 95 | 163 | 2762 | 0.016 | [ |
| BTO | DIW | 5.13 | 85.24 | 204.61 | 2551 | - | [ |
| PZT | DIW | (7.21±0.06) | 94.9 | 678 | (4132±575) | (3.4±1%) | [ |
| BTO | DIW | 5.42 | 90 | 200 | 2200 | - | [ |
| BTO | DIW | - | 89.97 | 350 | 2576 | - | [ |
| PLZT | DIW | - | 98 | 481 | 1986 | - | [ |
| BCZT | DIW | - | 93 | 100 | 1046 | 0.021 | [ |
| BTO | DIW | - | 96 | 159 | 1900 | - | [ |
| BTO | BJ | 2.21 | 37 | 113(Horizontal) 152.7(Vertical) | 581.6(Horizontal) 698(Vertical) | - | [ |
| KNN | SLA | 4.32 | 96 | - | 1800-1900 | 0.2-0.3 | [ |
| PMN-PT | DLP | 7.98 | 97.8 | 620 | - | - | [ |
| PZT | DLP | 7 | - | 345 | 1390 | 0.021 | [ |
| KNN | DLP | 4.09 | 92 | 170 | 2150 | 0.058 | [ |
| PZT-5H | DLP | 7.35 | 96 | 600 | 2875 | 0.029 | [ |
| BTO | DLP | 5.44 | 90 | 200 | 1965 | 0.017 | [ |
| PZT | IJP | - | (86±3) | - | 190 | 0.05 | [ |
| BTO | DIW | 3.93 | 65.3 | 200 | 4730 | 0.033 | [ |
| BTO | DIW | - | 98 | 195 | - | - | [ |
| BTO | DIW | - | 97.8 | - | 533 | - | [ |
| BTO | DIW | 5.66 | 94 | 420 | 4380 | 0.02 | [ |
| PZT | FDM | 7.7 | - | 664 | 3340 | 0.023 | [ |
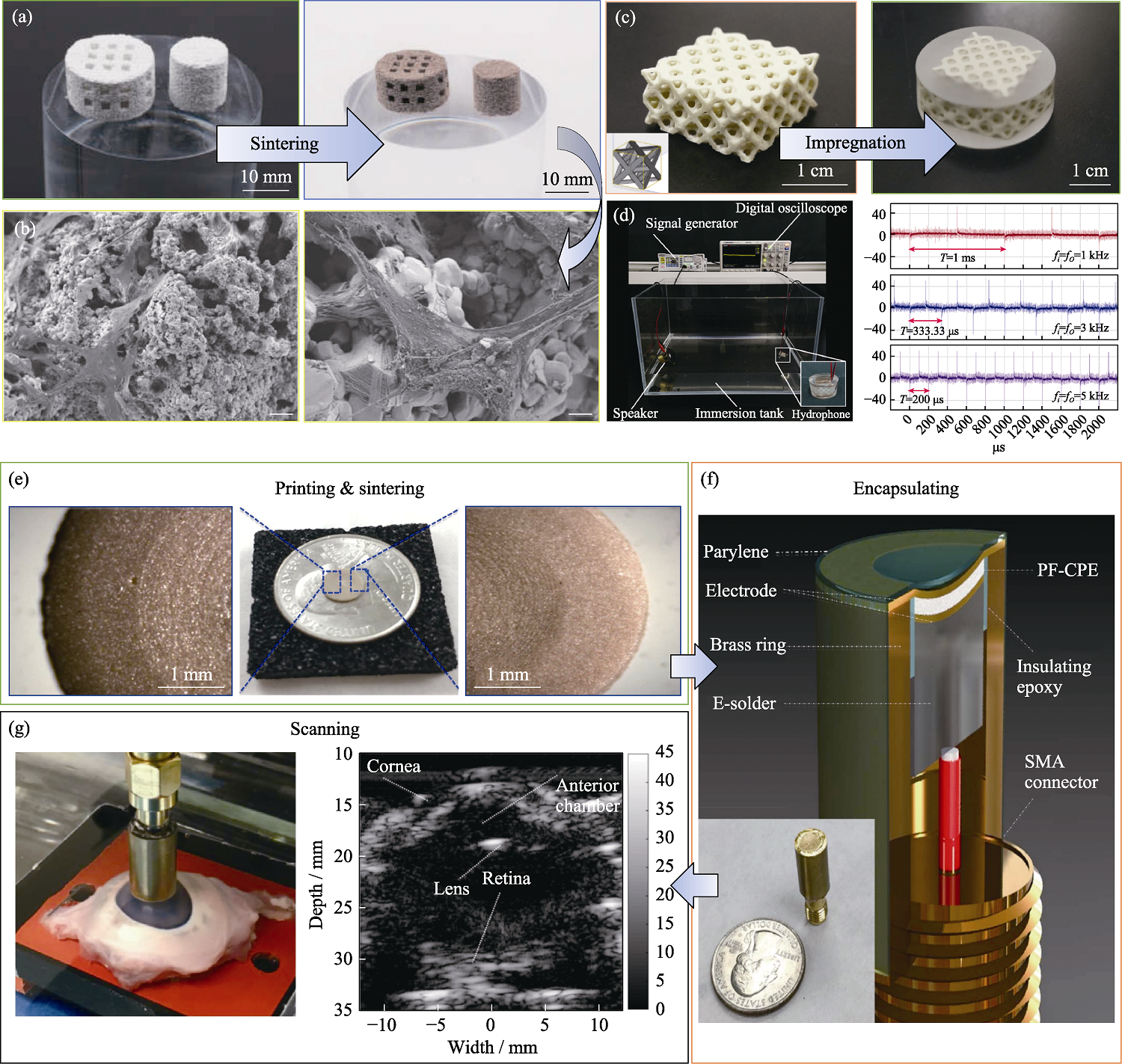
Fig. 5 Photos of BTO/HA piezoelectric ceramics fabricated by Binder Jetting (a) and SEM images of the sample after 24 h MC3T3-E1 cells incubation (b)[70], piezoelectric ceramics and piezoelectric composite materials fabricated by Digital Light Processing (c), the underwater acoustic testing device and the output voltage of the hydrophone under different acoustic excitation frequencies (d) [32], the photo of CPE sample (e) and the packaged ultrasound scanning equipment (f), and pig eye ultrasound imaging results (g)[74]
| [1] |
HOOPER T E, ROSCOW J I, MATHIESON A, et al. High voltage coefficient piezoelectric materials and their applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(13): 6115-6129.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
WASTON B H, BROVA Ml J, FANTON M, et al. Textured Mn- doped PIN-PMN-PT ceramics: harnessing intrinsic piezoelectricity for high-power transducer applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(2): 1270-1279.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
JIA H R, YANG S, ZHU W T, et al. Improved piezoelectric properties of Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 textured ferroelectric ceramics via Sm-doping method. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 881(10): 160666.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LÜ N, ZHONG C, WANG L K. Bending vibration characteristics of the piezoelectric composite double laminated vibrator. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(22): 31259-31267.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CHEN A N, LI M, WU J M, et al. Enhancement mechanism of mechanical performance of highly porous mullite ceramics with bimodal pore structures prepared by selective laser sintering. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 776: 486-494.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DONG Y, JIANG H Y, CHEN A N, et al. Near-zero-shrinkage Al2O3 ceramic foams with coral-like and hollow-sphere structures via selective laser sintering and reaction bonding. Journal of European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(16): 239-246.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHANG X, WANG F, WU Z P, et al. Direct selective laser sintering of hexagonal barium titanate ceramics. Journal of American Ceramic Society, 2021, 104: 1271-1280.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LIU K, SHI Y S, LI C H, et al. Indirect selective laser sintering of epoxy resin-Al2O3 ceramic powders combined with cold isostatic pressing. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(5): 7099-7106.
DOI URL |
| [9] | SHI Y S, LIU K, LI C H, et al. Additive manufacturing of zirconia parts via selective laser sintering combined with cold isostatic pressing. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(21): 118-123. |
| [10] |
LIU K, SUN H J, SHI Y S, et al. Research on selective laser sintering of kaolin-epoxy resin ceramic powders combined with cold isostatic pressing and sintering. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(9): 10711-10718.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LIU K, WU T, BOURELL D L, et al. Laser additive manufacturing and homogeneous densification of complicated shape SiC ceramic parts. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(17): 21067-21075.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KOVSKY I, MOROZOV Y, KUZNETSOV M. Layering fabrication, structure, and electromagnetic properties of perovskite phases by hybrid process: self-propagated high-temperature synthesis and selective laser sintering. Phase Transitions, 2013, 86(11): 1085-1093.
DOI URL |
| [13] | KUZNETSOV M, SHISHKOVSKY I, MOROZOV Y, et al. Design of three-dimensional functional articles via layer-by-layer laser sintering of exothermic powder mixtures. Advanced Manufacturing Processes, 2008, 23(6): 571-578. |
| [14] | BERNARD S A, BALLA V K, BOSE S, et al. Direct laser processing of bulk lead zirconate titanate ceramics. Materials Science & Engineering B, 2010, 172(1): 85-88. |
| [15] |
DINI F, GHAFFARI S A, JAFAR J, et al. A review of binder jet process parameters; powder, binder, printing and sintering condition. Metal Powder Report, 2019, 75(2): 95-100.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LV X Y, YE F, CHENG L F, et al. Binder jetting of ceramics: powders, binders, printing parameters, equipment, and post-treatment. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(10): 12609-12624.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
GAYTAN S M, CADENA M A, KARIM H, et al. Fabrication of barium titanate by binder jetting additive manufacturing technology. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(5): 6610-6619.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SUFIIAROV V, KANTYUKOV A, POPOVICH A, et al. Structure and properties of barium titanate lead-free piezoceramic manufactured by binder jetting process. Materials, 2021, 14(16): 4419.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SCHULT M, BUCKOW E, SEITZ H. Experimental studies on 3D printing of barium titanate ceramics for medical applications. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 2(1): 95-99.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ZHANG X, WU X, SHI J. Additive manufacturing of zirconia ceramics: a state-of-the-art review. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(4): 9029-9048.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LAYANI M, WANG X F, MAGDASSI S. Novel materials for 3D printing by photopolymerization. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(41): 1706344.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZAKERI S, VIPPOLA M, LEVANEN E. A comprehensive review of the photopolymerization of ceramic resins used in stereolithography. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 35: 101177.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
WANG W, SUN J X, GUO B B, et al. Fabrication of piezoelectric nano-ceramics via stereolithography of low viscous and non-aqueous suspensions. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(3): 682-688.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
CHA J M, LEE J W, BAE B, et al. Fabrication and characterization of PZT suspensions for stereolithography based on 3D printing. Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society, 2019, 56(4): 360-364.
DOI URL |
| [25] | DUFAUD O, GALL H L, CORBEL S. Stereolithography of lead zirconate titanate ceramics for MEMS applications. Proceedings of SPIE-the International Society for Optical Engineering, 2003, 5116: 28-37. |
| [26] |
DUFAUD O, MARCHAL P, CORBEL S. Rheological properties of PZT suspensions for stereolithography. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2002, 22(13): 2081-2092.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
DUFAUD O, CORBEL S. Oxygen diffusion in ceramic suspensions for stereolithography. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2003, 92: 55-62.
DOI URL |
| [28] | SUN C, ZHANG X. The influences of the material properties on ceramic micro-stereolithography. Sensors & Actuators A Physical, 2002, 101(3): 364-370. |
| [29] |
SMIRNOV A, CHUGUNOV S, KHOLODKOVA A, et al. Progress and challenges of 3D-printing technologies in the manufacturing of piezoceramics. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(8): 10478-10511.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
LIN L F, WU H D, XU Y R, et al. Fabrication of dense aluminum nitride ceramics via digital light processing-based stereolithography. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 249: 122969.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ZENG Y S, JIANG L M, SUN Y Z, et al. 3D-printing piezoelectric composite with honeycomb structure for ultrasonic devices. Micromachines, 2020, 11(8): 713.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
LIU K, ZHOU C Y, HU J M, et al. Fabrication of barium titanate ceramics via digital light processing 3D printing by using high refractive index monomer. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(12): 5909-5917.
DOI URL |
| [33] | CHEN Z Y, JIANG Q G, SONG X, et al. Piezoelectric Array for Transducer Application Using Additive Manufacturing. 2017 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Washington, 2017. |
| [34] |
SONG X, CHEN Z Y, LEI L W, et al. Piezoelectric component fabrication using projection-based stereolithography of barium titanate ceramic suspensions. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2017, 23(1): 44-53.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
ROSENTAL T, MIZRAHI S, KAMYSHNY A, et al. Particle-free compositions for printing dense 3D ceramic structures by digital light processing. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 2021, 16(3): 255-266.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
NOGUERA R, LEJEUNE M, CHARTIER T. 3D fine scale ceramic components formed by ink-jet prototyping process. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2005, 25(12): 2055-2059.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
LEJEUNE M, CHARTIER T, DOSSOU-YOVO C, et al. Ink-jet printing of ceramic micro-pillar arrays. Journal European Ceramic Society, 2009, 29: 905-911.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
LEE D H, DERBY B. Preparation of PZT suspensions for direct ink jet printing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2004, 24(6): 1069-1072.
DOI URL |
| [39] | DERBY B, LEE D H, WANG T, et al. Development of PZT suspensions for ceramic ink-jet printing. Materials Research Society Symposium Proceeding, 2003, 758: 113-118. |
| [40] |
WANG T M, DERBY B. Ink-jet printing and sintering of PZT. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2005, 88(8): 2053-2058.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
LIU K, ZHANG Q Q, ZHOU C Y, et al. 4D printing of lead zirconate titanate piezoelectric composites transducer based on direct ink writing. Frontiers in Materials, 2021, 8: 659441.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
WALTON R L, BROVA M J, WASTON B H, et al. Direct writing of textured ceramics using anisotropic nozzles. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 41(3): 1945-1953.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
WALTON R L, FANTON M A, MEYER R J, et al. Dispersion and rheology for direct writing lead-based piezoelectric ceramic pastes with anisotropic template particles. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(11): 6157-6168.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
RENTERIA A, DIAZ J A, HE B T, et al. Particle size influence on material properties of BaTiO3 ceramics fabricated using freeze- form extrusion 3D printing. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(11): 115211.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
HALL S E, REGIS J E, RENTERIA A, et al. Paste extrusion 3D printing and characterization of lead zirconate titanate piezoelectric ceramics. Ceramics International, 2021, 47: 22042-22048.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
RENTERIA A, FONTES H, DIAZ J A, et al. Optimization of 3D printing parameters for BaTiO3 piezoelectric ceramics through design of experiments. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(8): 085706.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
RENTERIA A, GARCIA L F, BALCORTA V H, et al. Influence of bimodal particle distribution on material properties of BaTiO3 fabricated by paste extrusion 3D printing. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(13): 18477-18486.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
LI Y Y, LI L T, LI B. Direct ink writing of 3-3 piezoelectric composite. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 620: 125-128.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
NAN B, OLHERO S, PINHO R, et al. Direct ink writing of macro- porous lead-free piezoelectric Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(6): 3191-3203.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
GADEA C, SPELTA T, SIMONSEN S B, et al. Hybrid inks for 3D printing of tall BaTiO3-based ceramics. Open Ceramics, 2021, 6: 100110.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
JAFARI M A, HAN W, MOHAMMADI F, et al. A novel system for fused deposition of advanced multiple ceramics. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2000, 6(3): 161-175.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
HALL A, ALLAHVERDI M, AKDOGAN E K, et al. Piezoelectric/ electrostrictive multimaterial PMN-PT monomorph actuators. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2005, 25(12): 2991-2997.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
CHEN Z W, LI Z Y, LI J J, et al. 3D printing of ceramics: a review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(4): 661-687.
DOI URL |
| [54] | MIAO K, ZHOU H, GAO Y P, et al. Laser powder-bed-fusion of Si3N4 reinforced AlSi10Mg composites: processing, mechanical properties and strengthening mechanisms. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2021, 825: 141874. |
| [55] |
LU Z L, CAO J W, SONG Z Q, et al. Research progress of ceramic matrix composite parts based on additive manufacturing technology. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 2019, 14(4): 333-348.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
CHAVEZ L A, WILBURN B R, LBAVE P, et al. Fabrication and characterization of 3D printing induced orthotropic functional ceramics. Smart Materials and Structures, 2019, 28(12): 125007.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
ZHANG L, WANG T, SUN J X, et al. A study of lead-free (K0.5N0.5)NbO3 piezoelectric ceramics processed by additive manufacturing. Journal of Micromechanics and Molecular Physics, 2020, 5(4): 2050011.
DOI URL |
| [58] | WOODWARD D I, PURSSELL C P, BILLSON D R, et al. Additively-manufactured piezoelectric devices. Physica Status Solidi (A) Applications and Materials, 2015, 212(10): 2017-2113. |
| [59] |
CHEN Y, BAO X L, WONG C M, et al. PZT ceramics fabricated based on stereolithography for an ultrasound transducer array application. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(18): 22725-22730.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
CHEN W C, WANG F F, YAN K, et al. Micro-stereolithography of KNN-based lead-free piezoceramics. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(4): 4880-4885.
DOI URL |
| [61] | ZHANG Y H, CHEN W C, WU D W. Geometric deformation prediction and compensation for micro-stereolithography of piezoceramic. Electronic Components and Materials, 2019, 38(4): 77-82. |
| [62] |
SOTOV A, KANTYUKOV A, POPOVICH A, et al. LCD-SLA 3D printing of BaTiO3 piezoelectric ceramics. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(21): 30358-30366.
DOI URL |
| [63] | KUSCER D, DRNOVSEK S, LEVASSORT F. Inkjet-printing- derived lead-zirconate-titanate-based thick films for printed electronics. Materials & Design, 2021, 198(8): 109324. |
| [64] |
KIM H, RENTERIA-MARQUEZ A, ISLAM M D, et al. Fabrication of bulk piezoelectric and dielectric BaTiO3 ceramics using paste extrusion 3D printing technique. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(6): 3685-3694.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
LORENZ M, MARTIN A, WEBBER K G, et al. Electromechanical properties of robocasted barium titanate ceramics. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2020, 22(9): 2000325.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
RSOENTAL T, MAGDASSI S. A new approach to 3D printing dense ceramics by ceramic precursor binders. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2019, 21(10): 1900604.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
WEI X X, LIU Y H, ZHAO D J, et al. 3D printing of piezoelectric barium titanate with high density from milled powders. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(15): 5423-5430.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
LOUS G M, CORNEJO I A, MCNULTY T F, et al. Fabrication of piezoelectric ceramic/polymer composite transducers using fused deposition of ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2000, 83(1): 124-128.
DOI URL |
| [69] | CHABOK H, ZHOU C, CHEN Y, et al. Ultrasound Transducer Array Fabrication Based on Additive Manufacturing of Piezocomposites. Proceedings of the ASME/ISCIE 2012 International Symposium on Flexible Automation, St. Louis, 2012: 433. |
| [70] |
POLLEY C, DISTLER T, DETSCH R, et al. 3D printing of piezoelectric barium titanate-hydroxyapatite scaffolds with interconnected porosity for bone tissue engineering. Materials, 2020, 13(7): 1773.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
XU H, XIE Y M, ZHOU S W, et al. Piezoelectric properties of triply periodic minimum surface structures. Composites Science and Technology, 2020, 200: 108417.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
SONG X, HE L, YANG W H, et al. Additive manufacturing of bi-continuous piezocomposites with triply periodic phase interfaces for combined flexibility and piezoelectricity. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 2019, 141: 111004.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
CHENG J, CHEN Y, WU J W, et al. 3D printing of BaTiO3 piezoelectric ceramics for a focused ultrasonic array. Sensors, 2019, 19(19): 4078.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
CHEN Z Y, SONG X, LEI L W, et al. 3D printing of piezoelectric element for energy focusing and ultrasonic sensing. Nano Energy, 2016, 27: 78-86.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
ANDEREGG D A, BRYANT H A, RUFFIN D C, et al. In-situ monitoring of polymer flow temperature and pressure in extrusion based additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing, 2019, 26: 76-83.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
CLIJSTERS S, CRAEGHS T, BULS S, et al. In situ quality control of the selective laser melting process using a high-speed, real-time melt pool monitoring system. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2014, 75: 1089-1101.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
FANG T, JAFARI M A, DANFORTH S C, et al. Signature analysis and defect detection in layered manufacturing of ceramic sensors and actuators. Machine Vision and Applications, 2003, 15: 63-75.
DOI URL |
| [1] | DING Ling, JIANG Rui, TANG Zilong, YANG Yunqiong. MXene: Nanoengineering and Application as Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | SUN Qiangqiang, CHEN Zixuan, YANG Ziyue, WANG Yimeng, CAO Baoyue. Amorphous Vanadium Oxide Loaded by Metallic Nickel-copper towards High-efficiency Electrocatalyzing Hydrogen Production [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 647-655. |
| [3] | YANG Zhuo, LU Yong, ZHAO Qing, CHEN Jun. X-ray Diffraction Rietveld Refinement and Its Application in Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [4] | CHEN Qiang, BAI Shuxin, YE Yicong. Highly Thermal Conductive Silicon Carbide Ceramics Matrix Composites for Thermal Management: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [5] | WU Rui, ZHANG Minhui, JIN Chenyun, LIN Jian, WANG Deping. Photothermal Core-Shell TiN@Borosilicate Bioglass Nanoparticles: Degradation and Mineralization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [6] | LIN Junliang, WANG Zhanjie. Research Progress on Ferroelectric Superlattices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [7] | NIU Jiaxue, SUN Si, LIU Pengfei, ZHANG Xiaodong, MU Xiaoyu. Copper-based Nanozymes: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [8] | MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [9] | WU Shuang, GOU Yanzi, WANG Yongshou, SONG Quzhi, ZHANG Qingyu, WANG Yingde. Effect of Heat Treatment on Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Domestic KD-SA SiC Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 569-576. |
| [10] | HE Danqi, WEI Mingxu, LIU Ruizhi, TANG Zhixin, ZHAI Pengcheng, ZHAO Wenyu. Heavy-Fermion YbAl3 Materials: One-step Synthesis and Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [11] | YUAN Jingkun, XIONG Shufeng, CHEN Zhangwei. Research Trends and Challenges of Additive Manufacturing of Polymer-derived Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [12] | DU Jianyu, GE Chen. Recent Progress in Optoelectronic Artificial Synapse Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [13] | YANG Yang, CUI Hangyuan, ZHU Ying, WAN Changjin, WAN Qing. Research Progress of Flexible Neuromorphic Transistors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [14] | YOU Junqi, LI Ce, YANG Dongliang, SUN Linfeng. Double Dielectric Layer Metal-oxide Memristor: Design and Applications [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [15] | LIN Siqi, LI Airan, FU Chenguang, LI Rongbing, JIN Min. Crystal Growth and Thermoelectric Properties of Zintl Phase Mg3X2 (X=Sb, Bi) Based Materials: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||