
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 267-277.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210705
Special Issue: 增材制造专题(2022); 【虚拟专辑】增材制造及3D打印(2021-2022)
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Yong1,2( ), GUO Xiaotian1,3, TANG Jie1,2, CHANG Haotian1,3, HUANG Zhengren1,2, HU Xiulan3(
), GUO Xiaotian1,3, TANG Jie1,2, CHANG Haotian1,3, HUANG Zhengren1,2, HU Xiulan3( )
)
Received:2021-11-15
Revised:2021-12-23
Published:2022-03-20
Online:2022-01-06
Contact:
HU Xiulan, professor. E-mail: whoxiulan@163.com
About author:YANG Yong (1974-), male, professor. E-mail: yangyong@mail.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
YANG Yong, GUO Xiaotian, TANG Jie, CHANG Haotian, HUANG Zhengren, HU Xiulan. Research Progress and Prospects of Non-oxide Ceramic in Stereolithography Additive Manufacturing[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(3): 267-277.
| Material | Absorbance (d/μm, λ/nm) | Refractive index (d/μm, λ/nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Al2O3[ | 0.044 (10, 405) | 1.787 (2.3, 365) |
| ZrO2[ | 0.003 (10, 405) | Low |
| ZTA[ | Low | Low |
| SiO2[ | Low | 1.564 (2.25, 365) |
| SiC[ | 0.479 (10, 405) | 2.553 (12.25, 467-691) |
| Si3N4[ | 0.180 (5, 405) | 2.023 (-, 632.8) |
| TiO2[ | Low | 2.493 (-, 632.8) |
| BN[ | High | High |
Table 1 Refractive index and absorbance of ceramic materials
| Material | Absorbance (d/μm, λ/nm) | Refractive index (d/μm, λ/nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Al2O3[ | 0.044 (10, 405) | 1.787 (2.3, 365) |
| ZrO2[ | 0.003 (10, 405) | Low |
| ZTA[ | Low | Low |
| SiO2[ | Low | 1.564 (2.25, 365) |
| SiC[ | 0.479 (10, 405) | 2.553 (12.25, 467-691) |
| Si3N4[ | 0.180 (5, 405) | 2.023 (-, 632.8) |
| TiO2[ | Low | 2.493 (-, 632.8) |
| BN[ | High | High |
| Material | Flexural strength/MPa | Elasticity modulus/GPa | Fracture toughness/ (MPa·m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RB-SiC[ | ≥330 | ≥340 | ≥4.1 |
| S-SiC[ | 349-431 | 308-342 | 3.77 |
| RB-SiC[ | (305±15) | - | - |
| RB-SiC*[ | 210.4 | - | - |
| (Cf)/SiC*[ | 262.6 | - | - |
Table 2 Structure and properties of SiC ceramics obtained by different manufacturing methods
| Material | Flexural strength/MPa | Elasticity modulus/GPa | Fracture toughness/ (MPa·m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RB-SiC[ | ≥330 | ≥340 | ≥4.1 |
| S-SiC[ | 349-431 | 308-342 | 3.77 |
| RB-SiC[ | (305±15) | - | - |
| RB-SiC*[ | 210.4 | - | - |
| (Cf)/SiC*[ | 262.6 | - | - |
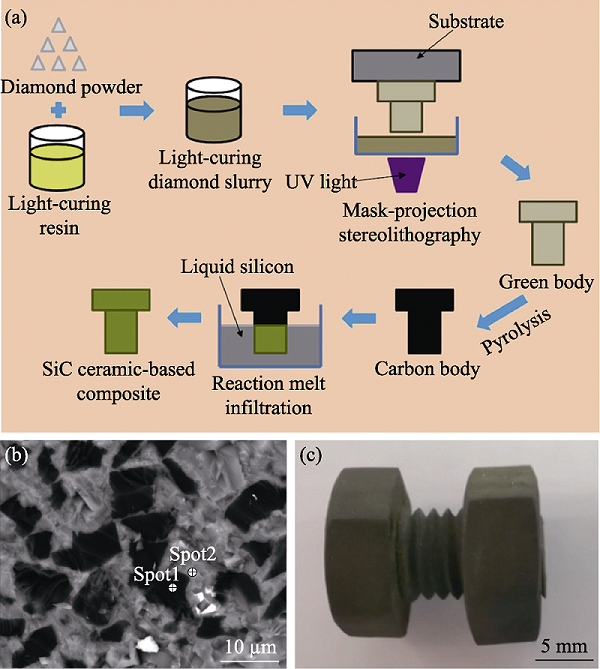
Fig. 4 Preparation of SiC ceramic-based composite by stereolithography[52] (a) Prepared schematic of SiC ceramic-based composite by stereolithography; (b) SEM image of SiC ceramic-based composite with a diamond volume fraction of 15%; (c) SiC ceramic-based composite
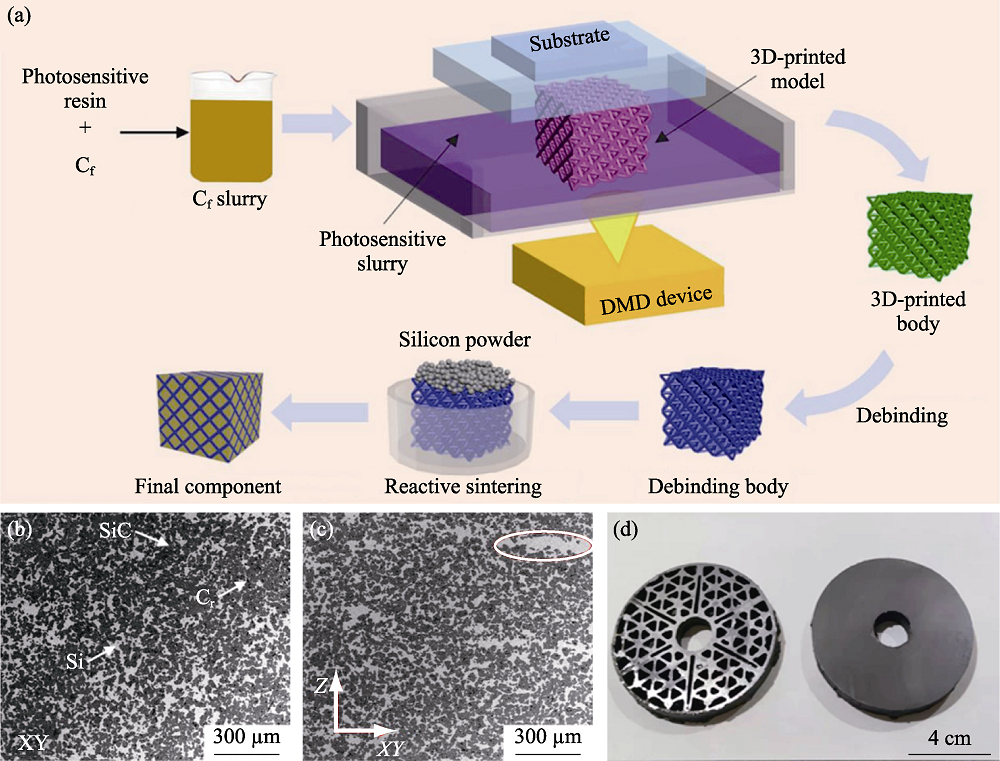
Fig. 5 Preparation of Cf/SiC ceramic composites by digital light processing technology and liquid silicon infiltration process[46] (a) Prepared schematic of SiC composites; (b, c) SEM images of cross section and horizontal plane of Cf/SiC composite; (d) Sintered Cf/SiC composites
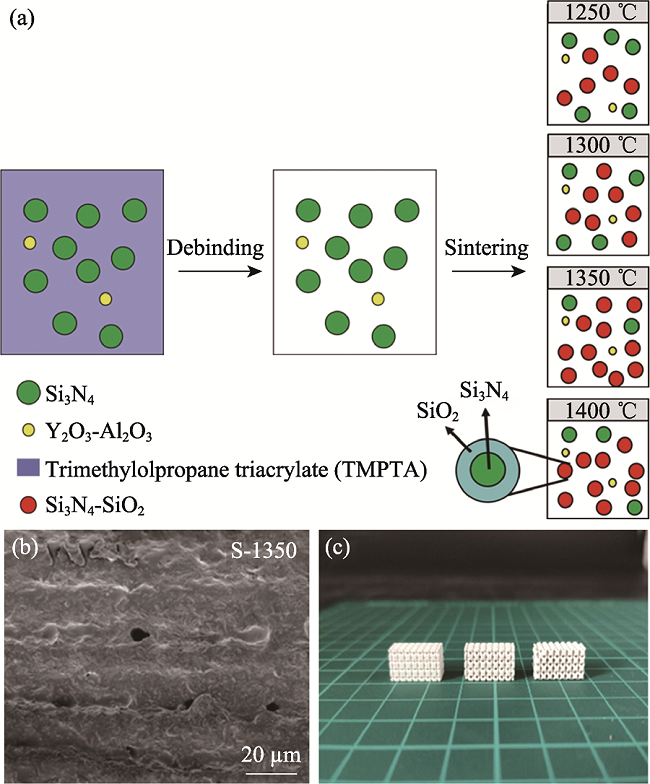
Fig. 6 Preparation of Si3N4-SiO2 ceramics by digital light processing (DLP) technology[58] (a) Schematic synthetic reaction process of oxidation of silicon nitride at high temperature; (b) SEM image of fracture surface of Si3N4-SiO2 ceramics sintered at 1350 ℃; (c) Si3N4-SiO2 ceramics with lattice structure
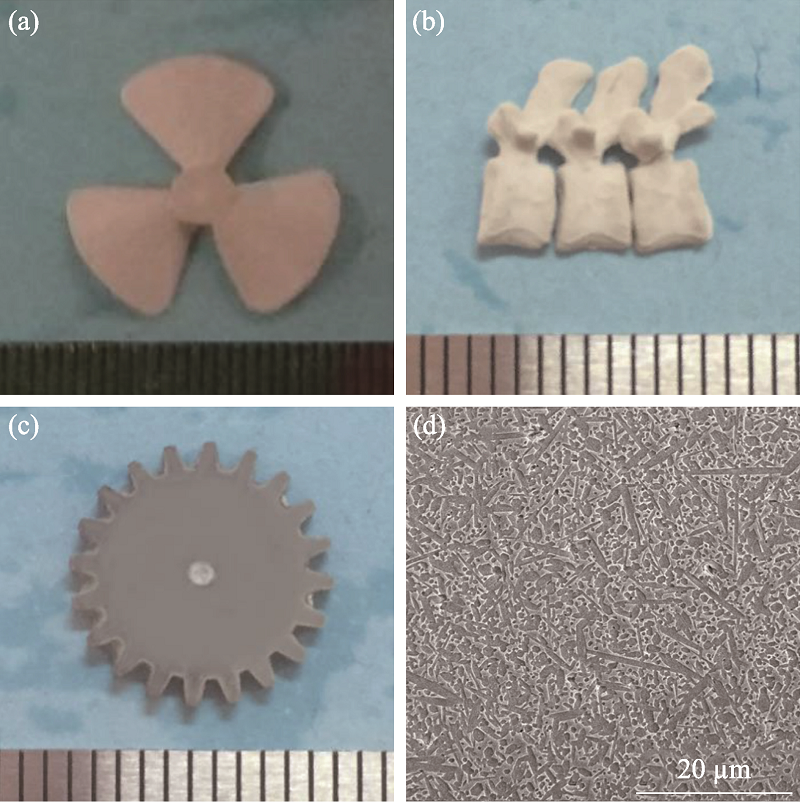
Fig. 7 Fabrication of complex shaped ceramic parts with surface- oxidized Si3N4 powder via digital light processing based stereolithography method[60] (a) Green Si3N4 body of a blade; (b) Green Si3N4 body of a vertebrae; (c) Sintered body of a Si3N4 gear; (d) SEM image of sintered body of a Si3N4 gear
| Material | Technology | Resin+photoinitiator | Dispersant | Powder | Cured thickness /μm | Solid content/% (in volume) | Bending strength /MPa | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiC | DLP | HDDA+DVE-3+ TPO | KOS110 | 15 μm SiC | 78 | 30 | - | [ |
| SiC | DLP | HDDA+TMPTA+TPO | KOS110+ 17000 | 15 μm SiC+ ~40 nm SiC | - | 45 | 165.2 | [ |
| SiC | DLP | ACMO+HDDA+ TMPTA+BAPO | 4200 | 10 μm SiC | ≈60 | 40 | 50.18 | [ |
| Al2O3-Si3N4 | SLA | TMPTA+HDDA+ Irgacure 184 | PEG200+ glycerol | 1 μm Al2O3+ 200 nm Si3N4 | 40 | 47 | - | [ |
| SiO2-Si3N4 | DLP | TMPTA+Irgacure 184 | - | 3.45 μm Si3N4+ Y2O3+Al2O3 | 50-60 | 50 | (77±5) | [ |
| Si3N4 | DLP | HDDA+TMPTA+819 | Copolymer | 200 nm oxidized Si3N4 | 51 | - | - | [ |
| Si3N4 | DLP | EA+819+HDDA+184 | Darvan | 800 nm (KH-560)Si3N4 | 50 | 45 | - | [ |
Table 3 Comparison of molding and sintering performances in stereolithography of high refractive index and high absorbance ceramics
| Material | Technology | Resin+photoinitiator | Dispersant | Powder | Cured thickness /μm | Solid content/% (in volume) | Bending strength /MPa | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiC | DLP | HDDA+DVE-3+ TPO | KOS110 | 15 μm SiC | 78 | 30 | - | [ |
| SiC | DLP | HDDA+TMPTA+TPO | KOS110+ 17000 | 15 μm SiC+ ~40 nm SiC | - | 45 | 165.2 | [ |
| SiC | DLP | ACMO+HDDA+ TMPTA+BAPO | 4200 | 10 μm SiC | ≈60 | 40 | 50.18 | [ |
| Al2O3-Si3N4 | SLA | TMPTA+HDDA+ Irgacure 184 | PEG200+ glycerol | 1 μm Al2O3+ 200 nm Si3N4 | 40 | 47 | - | [ |
| SiO2-Si3N4 | DLP | TMPTA+Irgacure 184 | - | 3.45 μm Si3N4+ Y2O3+Al2O3 | 50-60 | 50 | (77±5) | [ |
| Si3N4 | DLP | HDDA+TMPTA+819 | Copolymer | 200 nm oxidized Si3N4 | 51 | - | - | [ |
| Si3N4 | DLP | EA+819+HDDA+184 | Darvan | 800 nm (KH-560)Si3N4 | 50 | 45 | - | [ |
| [1] |
HALLORAN J W. Ceramic stereolithography: additive manufacturing for ceramics by photopolymerization. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2016, 46(1): 19-40.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DUFAUD O, CORBEL S. Oxygen diffusion in ceramic suspensions for stereolithography. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2003, 92(1): 55-62.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
WU H D, CHENG Y L, LIU W, et al. Effect of the particle size and the debinding process on the density of alumina ceramics fabricated by 3D printing based on stereolithography. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(15): 17290-17294.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LI W L, LIU W W, QI F, et al. Determination of micro-mechanical properties of additive manufactured alumina ceramics by nanoindentation and scratching. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(8): 10612-10618.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
SCHWENTENWEIN M, HOMA J. Additive manufacturing of dense alumina ceramics. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2015, 12(1): 1-7.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZHANG K Q, XIE C, WANG G, et al. High solid loading, low viscosity photosensitive Al2O3 slurry for stereolithography based additive manufacturing. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(1): 203-208.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WU X Q, LIAN Q, LI D C, et al. Effects of soft-start exposure on the curing characteristics and flexural strength in ceramic projection stereolithography process. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(13): 3788-3796.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
XU X H, ZHOU S X, WU J F, et al. Preparation of highly dispersive solid microspherical α-Al2O3 powder with a hydrophobic surface for stereolithography-based 3d printing technology. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(2): 1895-1906.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI X B, ZHONG H, ZHANG J X, et al. Fabrication of zirconia all-ceramic crown via DLP-based stereolithography. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2020, 17(3): 844-853.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
FU X S, ZOU B, XING H Y, et al. Effect of printing strategies on forming accuracy and mechanical properties of ZrO2 parts fabricated by SLA technology. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(14): 17630-17637.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HE R X, LIU W, WU Z W, et al. Fabrication of complex-shaped zirconia ceramic parts via a DLP-stereolithography-based 3D printing method. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(3): 3412-3416.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LI X B, ZHONG H, ZHANG J X, et al. Dispersion and properties of zirconia suspensions for stereolithography. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2020, 17(1): 239-247.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SUN J X, BINNER J, BAI J M. Effect of surface treatment on the dispersion of nano zirconia particles in non-aqueous suspensions for stereolithography. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(4): 1660-1667.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WU H D, LIU W, HE R X, et al. Fabrication of dense zirconia- toughened alumina ceramics through a stereolithography-based additive manufacturing. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(1): 968-972.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LIU X Y, ZOU B, XING H Y, et al. The preparation of ZrO2-Al2O3 composite ceramic by SLA-3D printing and sintering processing. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(1): 937-944.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
XING H Y, ZOU B, LIU X Y, et al. Effect of particle size distribution on the preparation of ZTA ceramic paste applying for stereolithography 3D printing. Powder Technology, 2020, 359: 314-322.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG Y Y, WANG Z Y, LIU S H, et al. Additive manufacturing of silica ceramics from aqueous acrylamide based suspension. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(17): 21328-21332.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CHARTIER T, BADEV A, ABOULIATIM Y, et al. Stereolithography process: influence of the rheology of silica suspensions and of the medium on polymerization kinetics-cured depth and width. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2012, 32(8): 1625-1634.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
BAE C J, KIM D, HALLORAN J W. Mechanical and kinetic studies on the refractory fused silica of integrally cored ceramic mold fabricated by additive manufacturing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(2): 618-623.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LASGORCEIX M, CHAMPION E, CHARTIER T. Shaping by microstereolithography and sintering of macro-micro-porous silicon substituted hydroxyapatite. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(4): 1091-1101.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WANG Z, HUANG C Z, WANG J, et al. Development of a novel aqueous hydroxyapatite suspension for stereolithography applied to bone tissue engineering. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(3): 3902-3909.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
PFAFFINGER M, HARTMANN M, SCHWENTENWEIN M, et al. Stabilization of tricalcium phosphate slurries against sedimentation for stereolithographic additive manufacturing and influence on the final mechanical properties. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2017, 14(4): 499-506.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
CHEN Z W, LIU C B, LI J J, et al. Mechanical properties and microstructures of 3D printed bulk cordierite parts. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(15): 19257-19267.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
HE R J, ZHOU N P, ZHANG K Q, et al. Progress and challenges towards additive manufacturing of SiC ceramic. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(4): 637-674.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SEFIU A R, DING Y X, SHU F X, et al. Photopolymerization- based additive manufacturing of ceramics: a systematic review. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(3): 442-471.
DOI URL |
| [26] | LIU Y, CHEN Z W. Research progress in photopolymerization- based 3D printing technology of ceramics. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2020(9): 1-12. |
| [27] | TANG J, YANG Y, HUANG Z R. Research progress of silicon carbide ceramic slurry based 3D printing. Materials Reports, 35(S01): 8. |
| [28] |
GRIFFITH M L, HALLORAN J W. Scattering of ultraviolet radiation in turbid suspensions. Journal of Applied Physics, 1997, 81(6): 2538-2546.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
DING G J, HE R J, ZHANG K Q, et al. Stereolithography-based additive manufacturing of gray-colored SiC ceramic green body. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(12): 7198-7209.
DOI URL |
| [30] | WU K C, SEEFELDT K F, SOLOMON M J, et al. Prediction of ceramic stereolithography resin sensitivity from theory and measurement of diffusive photon transport. Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 98(2): 10. |
| [31] |
BURGER R, WENDLAND W L. Sedimentation and suspension flows: historical perspective and some recent developments. Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 2001, 41(2/3): 101-116.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
CHEN Z W, LI Z Y, LI J J, et al. 3D printing of ceramics: a review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(4): 661-687.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
WANG M, XIE C, HE R J, et al. Polymer-derived silicon nitride ceramics by digital light processing based additive manufacturing. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(9): 5117-5126.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
DE HAZAN Y, PENNER D. SiC and SiOC ceramic articles produced by stereolithography of acrylate modified polycarbosilane systems. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(16): 5205-5212.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
TANG J, GUO X T, CHANG H T, et al. The preparation of SiC ceramic photosensitive slurry for rapid stereolithography. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(15): 7516-7524.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
VRANCKENAND K C, POSSEMIERS K, VAN DER VOORT P, et al. Surface modification of silica gels with aminoorganosilanes. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 1995, 98(3): 235-241.
DOI URL |
| [37] | LIU D, MALGHAN S G. Role of polyacrylate in modifying interfacial properties and stability of silicon nitride particles in aqueous suspensions. Colloids & Surfaces A Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects, 1996, 110(1): 37-45. |
| [38] |
XIAO C X, NI Q, CHEN HAN, et al. Effect of polyvinylpyrrolidone on rheology of aqueous SiC suspensions dispersed with poly(aspartic acid). Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2012, 399: 108-111.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
LIU G W, ZHANG X Z, YANG J, et al. Recent advances in joining of SiC-based materials (monolithic SiC and SiCf/SiC composites): joining processes, joint strength, and interfacial behavior. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2019, 8(1): 19-38.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
CHEN X W, CHENG G F, ZHANG J M, et al. Residual stress variation in SiCf/SiC composite during heat treatment and its effects on mechanical behavior. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2020, 9(5): 567-575.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
EOM J H, KIM Y W, RAJU S. Processing and properties of macroporous silicon carbide ceramics: a review. Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies, 2013, 1(3): 220-242.
DOI URL |
| [42] | ZHAO R C, BAO J X. Lightweight structure and mirror blank formation of the SiC ceramic mirror with large caliber. Optics & Optoelectronic Technology, 2014, 12(6): 65-69. |
| [43] |
WU H B, YAN Y J, LIU G L, et al. Effects of grain grading on microstructures and mechanical behaviors of pressureless solid-state-sintered SiC. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2015, 12(5): 976-984.
DOI URL |
| [44] | LI Y, GAO J Q, YANG J F. Preparation of complicated SiC green bodies via aqueous slip casting. Key Engineering Materials, 2010, 434-435: 88-91. |
| [45] |
BAI X J, DING G J, ZHANG K Q, et al. Stereolithography additive manufacturing and sintering approaches of SiC ceramics. Open Ceramics, 2021, 5: 100046.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
ZHANG H, YANG Y, HU K H, et al. Stereolithography-based additive manufacturing of lightweight and high-strength Cf/SiC ceramics. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 34: 101199.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
DING G J, HE R J, ZHANG K Q, et al. Dispersion and stability of SiC ceramic slurry for stereolithography. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(4): 4720-4729.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
DING G J, HE R J, ZHANG K Q, et al. Stereolithography 3D printing of SiC ceramic with potential for lightweight optical mirror. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(11, Part B): 18785-18790.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
HU C Q, CHEN Y F, YANG T S, et al. Effect of SiC powder on the properties of SiC slurry for stereolithography. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(9): 12442-12449.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
CAO J W, IDREES M, TIAN G Q, et al. Complex SiC-based structures with high specific strength fabricated by vat photopolymerization and one-step pyrolysis. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 48: 102430.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
TIAN X Y, ZHANG W G, LI D C, et al. Reaction-bonded SiC derived from resin precursors by stereolithography. Ceramics International, 2012, 38(1): 589-597.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
CHEN R G, LIAN Q, HE X N, et al. A stereolithographic diamond-mixed resin slurry for complex SiC ceramic structures. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(7): 3991-3999.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
XING H Y, ZOU B, WANG X F, et al. Fabrication and characterization of SiC whiskers toughened Al2O3 paste for stereolithography 3D printing applications. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 828(5): 154347.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
ZORAN K, VLADIMIR D K. Silicon nitride: the engineering material of the future. Journal of Materials Science, 2012, 47(2): 535-552.
DOI URL |
| [55] | HAMPSHIRE S. Silicon nitride ceramics-review of structure, processing and properties. Journal of Achievements of Materials and Manufacturing Engineering, 2007, 24(1): 2685-2689. |
| [56] |
RILEY F L. Silicon nitride and related materials. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2000, 83(2): 245-265.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
XING H Y, ZOU B, LIU X Y, et al. Fabrication strategy of complicated Al2O3-Si3N4 functionally graded materials by stereolithography 3D printing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(15): 5797-5809.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
CHEN R F, DUAN W Y, WANG G, et al. Preparation of broadband transparent Si3N4-SiO2 ceramics by digital light processing (DLP) 3D printing technology. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(11): 5495-5504.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
LI X B, ZHANG J X, DUAN Y S, et al. Rheology and curability characterization of photosensitive slurries for 3D printing of Si3N4 ceramics. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10: 6438.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
HUANG R J, JIANG Q G, WU H D, et al. Fabrication of complex shaped ceramic parts with surface-oxidized Si3N4 powder via digital light processing based stereolithography method. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(4): 5158-5162.
DOI URL |
| [61] | SHEN X, GAO Y A, XU Z. Research and application of silane coupling agents. Shanghai Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2006, 27(1): 14-17. |
| [62] |
LIU Y, ZHAN L N, HE Y, et al. Stereolithographical fabrication of dense Si3N4 ceramics by slurry optimization and pressure sintering. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(2): 2063-2071.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
TIAN Z, YANG Y P, WANG Y, et al. Fabrication and properties of a high porosity H-BN-SiO2 ceramics fabricated by stereolithography- based 3D printing. Materials Letters, 2019, 236: 144-147.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
SHI B H, SHANG Y Y, ZHANG P, et al. Dynamic capillary-driven additive manufacturing of continuous carbon fiber composite. Matter, 2020, 2(6): 1594-1604.
DOI URL |
| [1] | DING Ling, JIANG Rui, TANG Zilong, YANG Yunqiong. MXene: Nanoengineering and Application as Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | YANG Zhuo, LU Yong, ZHAO Qing, CHEN Jun. X-ray Diffraction Rietveld Refinement and Its Application in Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | CHEN Qiang, BAI Shuxin, YE Yicong. Highly Thermal Conductive Silicon Carbide Ceramics Matrix Composites for Thermal Management: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | LIN Junliang, WANG Zhanjie. Research Progress on Ferroelectric Superlattices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [5] | NIU Jiaxue, SUN Si, LIU Pengfei, ZHANG Xiaodong, MU Xiaoyu. Copper-based Nanozymes: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [6] | YUAN Jingkun, XIONG Shufeng, CHEN Zhangwei. Research Trends and Challenges of Additive Manufacturing of Polymer-derived Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [7] | DU Jianyu, GE Chen. Recent Progress in Optoelectronic Artificial Synapse Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [8] | YANG Yang, CUI Hangyuan, ZHU Ying, WAN Changjin, WAN Qing. Research Progress of Flexible Neuromorphic Transistors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [9] | YOU Junqi, LI Ce, YANG Dongliang, SUN Linfeng. Double Dielectric Layer Metal-oxide Memristor: Design and Applications [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [10] | ZHANG Chaoyi, TANG Huili, LI Xianke, WANG Qingguo, LUO Ping, WU Feng, ZHANG Chenbo, XUE Yanyan, XU Jun, HAN Jianfeng, LU Zhanwen. Research Progress of ScAlMgO4 Crystal: a Novel GaN and ZnO Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [11] | CHEN Kunfeng, HU Qianyu, LIU Feng, XUE Dongfeng. Multi-scale Crystallization Materials: Advances in in-situ Characterization Techniques and Computational Simulations [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [12] | QI Zhanguo, LIU Lei, WANG Shouzhi, WANG Guogong, YU Jiaoxian, WANG Zhongxin, DUAN Xiulan, XU Xiangang, ZHANG Lei. Progress in GaN Single Crystals: HVPE Growth and Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [13] | LIN Siqi, LI Airan, FU Chenguang, LI Rongbing, JIN Min. Crystal Growth and Thermoelectric Properties of Zintl Phase Mg3X2 (X=Sb, Bi) Based Materials: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [14] | LIU Yan, ZHANG Keying, LI Tianyu, ZHOU Bo, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Electric-field Assisted Joining Technology for the Ceramics Materials: Current Status and Development Trend [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 113-124. |
| [15] | XIE Bing, CAI Jinxia, WANG Tongtong, LIU Zhiyong, JIANG Shenglin, ZHANG Haibo. Research Progress of Polymer-based Multilayer Composite Dielectrics with High Energy Storage Density [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||