
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (7): 710-716.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210653
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIANG Yiyi1( ), SHEN Min1, SONG Banxia1, LI Nan1, DING Xianghuan1, GUO Leyi2, MA Guoqiang1,2(
), SHEN Min1, SONG Banxia1, LI Nan1, DING Xianghuan1, GUO Leyi2, MA Guoqiang1,2( )
)
Received:2021-10-22
Revised:2022-01-19
Published:2022-07-20
Online:2022-03-18
Contact:
MA Guoqiang, senior engineer. E-mail: erguo87@163.com; maguoqiang@sinochem.comAbout author:JIANG Yiyi(1988-), female, Master. E-mail: jiangyiyi@sinochem.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
JIANG Yiyi, SHEN Min, SONG Banxia, LI Nan, DING Xianghuan, GUO Leyi, MA Guoqiang. Effect of Dual-functional Electrolyte Additive on High Temperature and High Voltage Performance of Li-ion Battery[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 710-716.
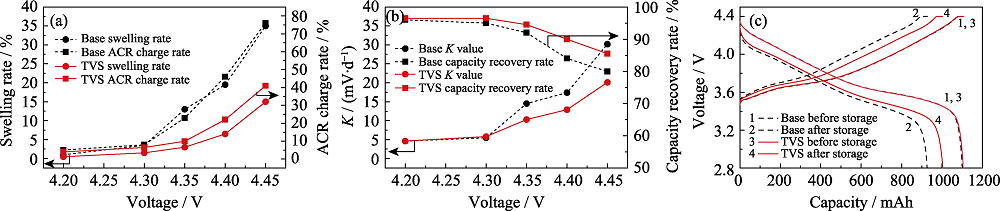
Fig. 3 (a) Gas swelling rates and ACR change rates, (b) K values and capacity recovery rates, (c) charge and discharge curves of pouch cells with and without TVS in electrolytes after storage at 60 ℃ for 14 d
| Sample | Ni/(×10-4, %) | Co/(×10-4, %) | Mn/(×10-4, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base | 90 | 21 | 130 |
| TVS | 35 | 4 | 69 |
Table 1 Uess fractions of Ni, Co and Mn ions deposited on anodes from pouch cell with and without TVS in electrolyte stored at cutoff potential of 4.4 V and temperature of 60 ℃ for 14 d
| Sample | Ni/(×10-4, %) | Co/(×10-4, %) | Mn/(×10-4, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base | 90 | 21 | 130 |
| TVS | 35 | 4 | 69 |
| Sample | CO/µL | CH4/µL | CO2/µL | C2H4/µL | H2/µL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base | 393.3 | 253.2 | 209.3 | 67.0 | 17.6 |
| TVS | 9.2 | 4.8 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 0.2 |
Table S1 Gas composition and contents of pouch cells with and without TVS in electrolytes stored at cutoff potential of 4.4 V and temperature of 60 ℃ for 14 d
| Sample | CO/µL | CH4/µL | CO2/µL | C2H4/µL | H2/µL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base | 393.3 | 253.2 | 209.3 | 67.0 | 17.6 |
| TVS | 9.2 | 4.8 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 0.2 |
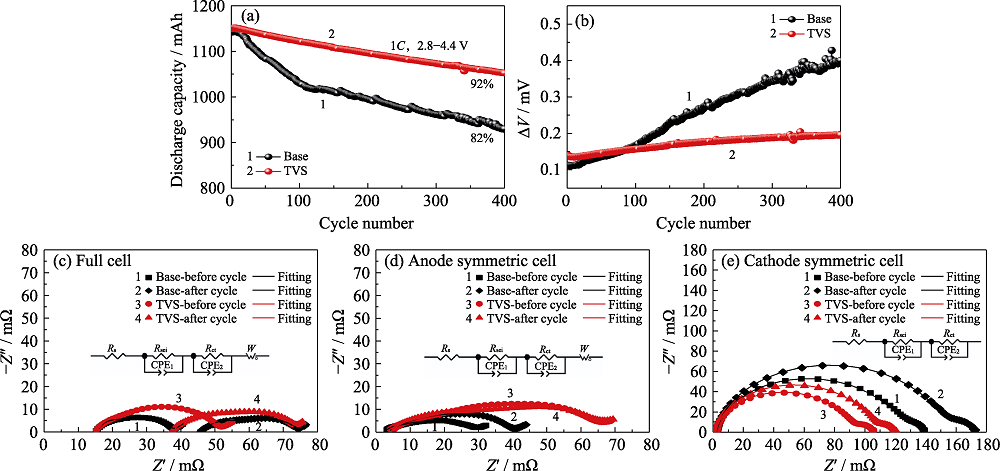
Fig. 4 Cycling performance of pouch cells with and without TVS in electrolytes at 45 ℃ (a) Discharge capacity and (b) ΔV vs cycle number; EIS plots of (c) pouch full cells, (d) graphite/graphite symmetric cells and (e) NCM622/NCM622 symmetric cells before and after 100 cycles
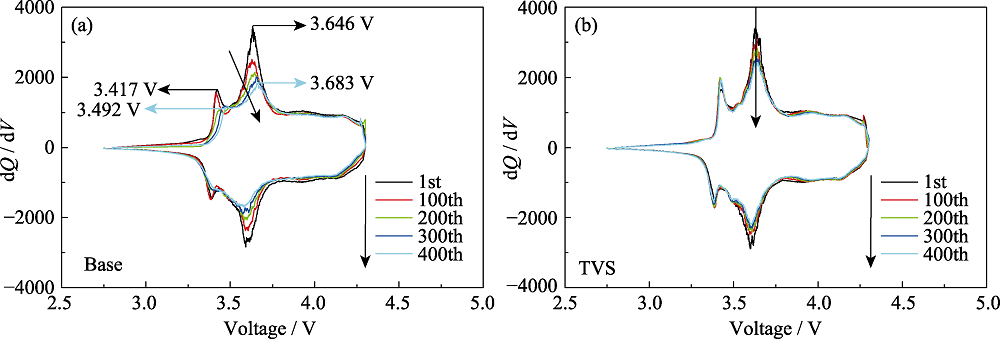
Fig. S2 Cycling performance of pouch cells with and without TVS in electrolytes at 45 ℃ (a) Differential capacity (dQ/dV) versus potential of Base; (b) Differential capacity (dQ/dV) versus potential of TVS
| Sample | Full cell | Anode symmetric cell | Cathode symmetric cell | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs/mΩ | Rsei/mΩ | Rct/mΩ | Rs/mΩ | Rsei/mΩ | Rct/mΩ | Rs/mΩ | Rsei/mΩ | Rct/mΩ | |
| Base-before cycle | 16.2 | 7.5 | 14.2 | 3.4 | 4.7 | 23.2 | 2.6 | 116.1 | 21.2 |
| Base-after cycle | 46.7 | 9.1 | 19.3 | 4.2 | 17.1 | 26.5 | 2.7 | 144.3 | 26.7 |
| TVS-before cycle | 16.4 | 8.9 | 25.8 | 4.5 | 20.5 | 43.3 | 2.1 | 86.1 | 18.2 |
| TVS-after cycle | 38.5 | 10.2 | 25.4 | 4.8 | 22.6 | 43.8 | 2.2 | 100.4 | 18.1 |
Table S2 Fitted EIS results before and after 100 cycles of pouch full cells and corresponding symmetric cells with and without TVS in electrolytes
| Sample | Full cell | Anode symmetric cell | Cathode symmetric cell | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs/mΩ | Rsei/mΩ | Rct/mΩ | Rs/mΩ | Rsei/mΩ | Rct/mΩ | Rs/mΩ | Rsei/mΩ | Rct/mΩ | |
| Base-before cycle | 16.2 | 7.5 | 14.2 | 3.4 | 4.7 | 23.2 | 2.6 | 116.1 | 21.2 |
| Base-after cycle | 46.7 | 9.1 | 19.3 | 4.2 | 17.1 | 26.5 | 2.7 | 144.3 | 26.7 |
| TVS-before cycle | 16.4 | 8.9 | 25.8 | 4.5 | 20.5 | 43.3 | 2.1 | 86.1 | 18.2 |
| TVS-after cycle | 38.5 | 10.2 | 25.4 | 4.8 | 22.6 | 43.8 | 2.2 | 100.4 | 18.1 |
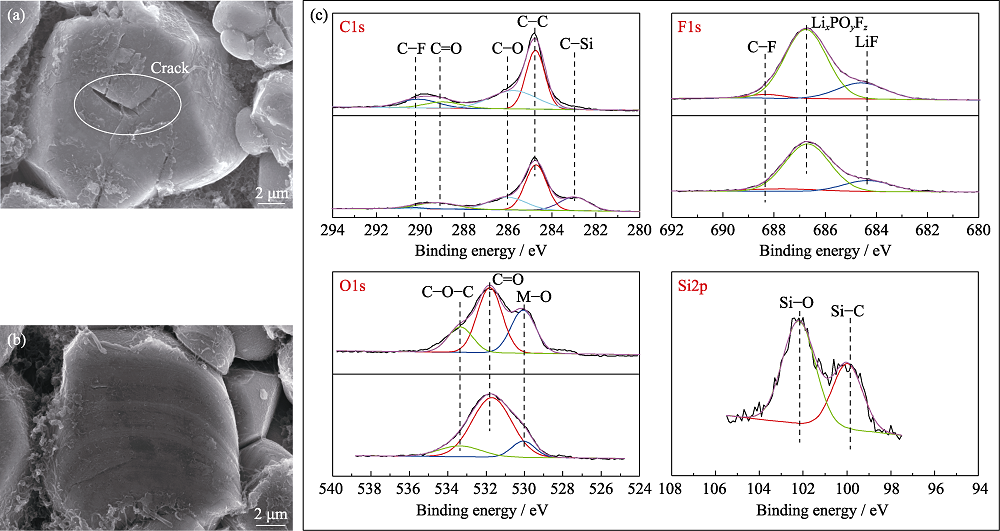
Fig. 5 SEM images of cathodes from pouch cells (a) without and (b) with TVS in electrolytes after 100 cycles; (c) XPS spectra of cathodes from pouch cells without and with TVS in electrolytes after 10 cycles
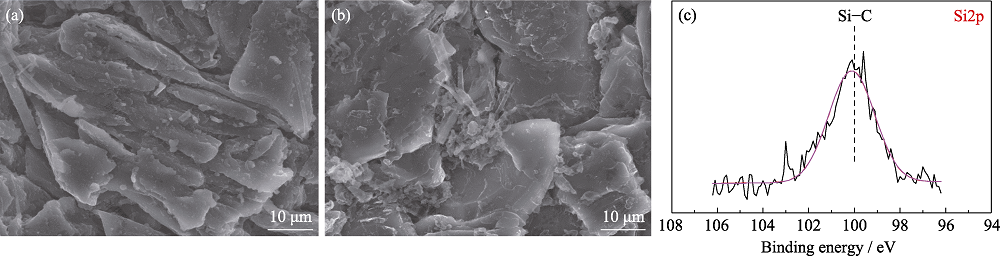
Fig. S3 SEM images of anodes from pouch cells (a) without and (b) with TVS in electrolytes after 100 cycles; (c) Si2p XPS spectra of anode from pouch cell with TVS in electrolyte after 10 cycles
| [1] | ZENG X, LI M, EL-HADY D A, et al. Commercialization of lithium battery technologies for electric vehicles. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(27): 1900161. |
| [2] |
WANG C, OUYANG L, FAN W, et al. Citraconic anhydride as an electrolyte additive to improve the high temperature performance of LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2/graphite pouch batteries. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 805: 757-766.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
WANG C, YU L, FAN W, et al. Lithium difluorophosphate as a promising electrolyte lithium additive for high-voltage lithium-ion batteries. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018, 1(6): 2647-2656.
DOI URL |
| [4] | ZHAO W, ZHENG B, LIU H, et al. Toward a durable solid electrolyte film on the electrodes for Li-ion batteries with high performance. Nano Energy, 2019, 63: 103815. |
| [5] |
JUNG R, METZGER M, MAGLIA F, et al. Chemical versus electrochemical electrolyte oxidation on NMC111, NMC622, NMC811, LNMO, and conductive carbon. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2017, 8(19): 4820-4825.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
XIE K, ZHENG C, LI Y, et al. Storage aging mechanism of LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2/graphite Li-ion batteries at high state of charge. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 175-180.
DOI URL |
| [7] | JUNG R, METZGER M, MAGLIA F, et al. Oxygen release and its effect on the cycling stability of LiNixMnyCozO2(NMC) cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(7): A1361-A1377. |
| [8] |
FAN X, WANG C. High-voltage liquid electrolytes for Li batteries progress and perspectives. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(18): 10486-10566.
DOI URL |
| [9] | ZHAO D, WANG J, LU H, et al. Tailoring interfacial architecture of high-voltage cathode with lithium difluoro(bisoxalato) phosphate for high energy density battery. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 456: 228006. |
| [10] |
LEE W J, PRASANNA K, JO Y N, et al. Depth profile studies on nickel rich cathode material surfaces after cycling with an electrolyte containing vinylene carbonate at elevated temperature. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(32): 17062-17071.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
MICHAN A L, PARIMALAM B S, LESKES M, et al. Fluoroethylene carbonate and vinylene carbonate reduction: understanding lithium-ion battery electrolyte additives and solid electrolyte interphase formation. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28(22): 8149-8159.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MARKEVICH E, SALITRA G, FRIDMAN K, et al. Fluoroethylene carbonate as an important component in electrolyte solutions for high-voltage lithium batteries: role of surface chemistry on the cathode. Langmuir, 2014, 30(25): 7414-7424.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LI J, XING L, ZHANG R, et al. Tris(trimethylsilyl)borate as an electrolyte additive for improving interfacial stability of high voltage layered lithium-rich oxide cathode/carbonate-based electrolyte. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 285: 360-376.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG K, XING L, ZHU Y, et al. A comparative study of Si-containing electrolyte additives for lithium ion battery: which one is better and why is it better. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 342: 677-684.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
DENG B, SUN D, WAN Q, et al. Review of electrolyte additives for ternary cathode lithium-ion battery. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2018, 76(4): 259.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LIAO X, ZHENG X, CHEN J, et al. Tris(trimethylsilyl)-phosphate as electrolyte additive for self-discharge suppression of layered nickel cobalt manganese oxide. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 212: 352-359.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
KIM K, PARK I, HA S Y, et al. Understanding the thermal instability of fluoroethylene carbonate in LiPF6-based electrolytes for lithium ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 225: 358-368.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
QI X, TAO L, HAHN, H, et al. Lifetime limit of tris(trimethylsilyl) phosphite as electrolyte additive for high voltage lithium ion batteries. RSC Advance, 2016, 6(44): 38342-38349.
DOI URL |
| [19] | OH J, KIM J, LEE Y M, et al. Effects of vinylene carbonate and 1,3-propane sultone on high-rate cycle performance and surface properties of high-nickel layered oxide cathodes. Materials Research Bulletin, 2020, 132: 111008. |
| [20] |
XU M, LI W, LUCHT B L. Effect of propane sultone on elevated temperature performance of anode and cathode materials in lithium- ion batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 193(2): 804-809.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WANG Y, NAKAMURA S, UE M, et al. Theoretical studies to understand surface chemistry on carbon anodes for lithium-ion batteries: reduction mechanisms of ethylene carbonate. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 123: 11708-11718.
DOI URL |
| [22] | LI J, LIU H, XIA J, et al. The impact of electrolyte additives and upper cut-off voltage on the formation of a rocksalt surface layer in LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 electrodes. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(4): A655-A665. |
| [23] |
HONG P, XU M, ZHENG X, et al. Effect of ethylene glycol bis (propionitrile) ether (EGBE) on the performance and interfacial chemistry of lithium-rich layered oxide cathode. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 329: 216-224.
DOI URL |
| [24] | YAN X, CHEN C, ZHU X, et al. Aminoalkyldisiloxane as effective electrolyte additive for improving high temperature cycle life of nickel-rich LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2/graphite batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 461: 228099. |
| [25] | BUBERGER I, SEIDLMAYER S, GASTEIGER H A, et al. Aging analysis of graphite/LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2 cells using XRD, PGAA, and AC Impedance. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2015, 162(14): A2737-A2746. |
| [26] |
GILBERT J A, SHKROB I A, ABRAHAM D P. Transition metal dissolution, ion migration, electrocatalytic reduction and capacity loss in lithium-ion full cells. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(2): A389.
DOI URL |
| [27] | TENG X, BAI Y, MA L, et al. In-situ analysis of gas generation in lithium ion batteries with different carbonate-based electrolytes. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(41): 22751-22755. |
| [28] |
YAO W, ZHANG H, ZHONG S, et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis and Co, Al co-modification of Ni-rich LiNi0.8Mn0.2O2 materials for Li-ion battery electrode. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 718-732.
DOI URL |
| [29] | KEEFE A S, BUTEAU S, HILL I G, et al. Temperature dependent EIS studies separating charge transfer impedance from contact impedance in lithium-ion symmetric cells. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2019, 166(14): A3272-A3279. |
| [30] | LI Y K, CHENG B, JIAO F P, et al. The roles and working mechanism of salt-type additives on the performance of high-voltage lithium-ion batteries. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12: 16298-16307. |
| [1] | ZHANG Shuo, FU Qiangang, ZHANG Pei, FEI Jie, LI Wei. Influence of High Temperature Treatment of C/C Porous Preform on Friction and Wear Behavior of C/C-SiC Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 561-568. |
| [2] | YU Ruixian, WANG Guodong, WANG Shouzhi, HU Xiaobo, XU Xiangang, ZHANG Lei. Effect of High-temperature Annealing on AlN Crystal Grown by PVT Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 343-349. |
| [3] | PAN Yangyang, LIANG Bo, HONG Du, QI Zhixiang, NIU Yaran, ZHENG Xuebin. High Temperature Long-term Service Performance of TiAlCrY/YSZ Coating on TiAl Alloy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 105-112. |
| [4] | CHENG Cheng, LI Jianbo, TIAN Zhen, WANG Pengjiang, KANG Huijun, WANG Tongmin. Thermoelectric Property of In2O3/InNbO4 Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 724-730. |
| [5] | WANG Xingang, YANG Qingqing, LIN Genlian, GAO Wei, QIN Fulin, LI Rongzhen, KANG Zhuang, WANG Xiaofei, JIANG Danyu, YAN Jina. High Temperature Tensile Property of Domestic 550-grade Continuous Alumina Ceramic Fiber [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 629-635. |
| [6] | JU Yinchao, LIU Xiaoyong, WANG Qin, ZHANG Weigang, WEI Xi. Ablation Behavior of Ultra-high Temperature Composite Ceramic Matrix Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 86-92. |
| [7] | XIAO Peng, ZHU Yulin, WANG Song, YU Yiping, LI Hao. Research Progress on the Preparation and Characterization of Ultra Refractory TaxHf1-xC Solid Solution Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 685-694. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xiaoshan, WANG Bing, WU Nan, HAN Cheng, WU Chunzhi, WANG Yingde. Micro-nano Ceramic Fibers for High Temperature Thermal Insulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 245-256. |
| [9] | ZHANG Yachen, MENG Jia, CAI Kun, SHENG Xiaochen, LE Jun, SONG Lixin. Bending Failure Mechanism Study of Si-Cr-Ti High Temperature Oxidation Resistance Coating via Acoustic Emission Technique [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1185-1192. |
| [10] | ZENG Fanxin, LIU Chuang, CAO Yuliang. Sodium Storage Behavior of Nanoporous Sb/MCNT Anode Material with High Cycle Stability by Dealloying Route [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1137-1144. |
| [11] | WEI Yuquan,YANG Yong,LIU Meng,LI Qile,HUANG Zhengren. Effect of High Temperature Heat Treatment on Phase Composition and Microstructure of SiBCN/HfC Ceramic Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 931-938. |
| [12] | CHEN Bowen, WANG Jingxiao, JIANG Youlin, ZHOU Haijun, LIAO Chunjing, ZHANG Xiangyu, KAN Yanmei, NI Dewei, DONG Shaoming. Stable Zirconium Carbide Fibers Fabricated by Centrifugal Spinning Technique [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12): 1385-1390. |
| [13] | ZHANG Zhao-Fu,SHA Jian-Jun,ZU Yu-Fei,DAI Ji-Xiang. ZrB2-SiC Composites Toughened by Interlocking Microstructure and Chopped Carbon Fiber [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 918-924. |
| [14] | Xing-Peng LIU, Bin PENG, Wan-Li ZHANG, Jun ZHU. Al2O3 Coating Layer on the High Temperature Conductive Stability of Pt/ZnO/Al2O3 Film Electrode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 605-610. |
| [15] | Shi-Qiang LUO, Chun-Man ZHENG, Wei-Wei SUN, Wei XIE, Jian-Huang KE, Shuang-Ke LIU, Xiao-Bin HONG, Yu-Jie LI, Jing XU. Controllable Preparation of Co-NC Nanoporous Carbon Derived from ZIF-67 for Advanced Lithium-sulfur Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(5): 502-508. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||