
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (11): 1208-1216.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210124
Special Issue: 【生物材料】肿瘤治疗
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
WEI Chengxiong( ), JIN Xin, YIN Peinan, WU Chengwei, ZHANG Wei(
), JIN Xin, YIN Peinan, WU Chengwei, ZHANG Wei( )
)
Received:2021-03-01
Revised:2021-03-29
Published:2021-11-20
Online:2021-05-10
Contact:
ZHANG Wei, professor. E-mail: wei.zhang@dlut.edu.cn
About author:WEI Chengxiong(1992-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: weicx@mail.dlut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WEI Chengxiong, JIN Xin, YIN Peinan, WU Chengwei, ZHANG Wei. Carbon Spheres for Photothermal Therapy of Tumor Cells: Rapid Preparation and High Photothermal Effect[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1208-1216.
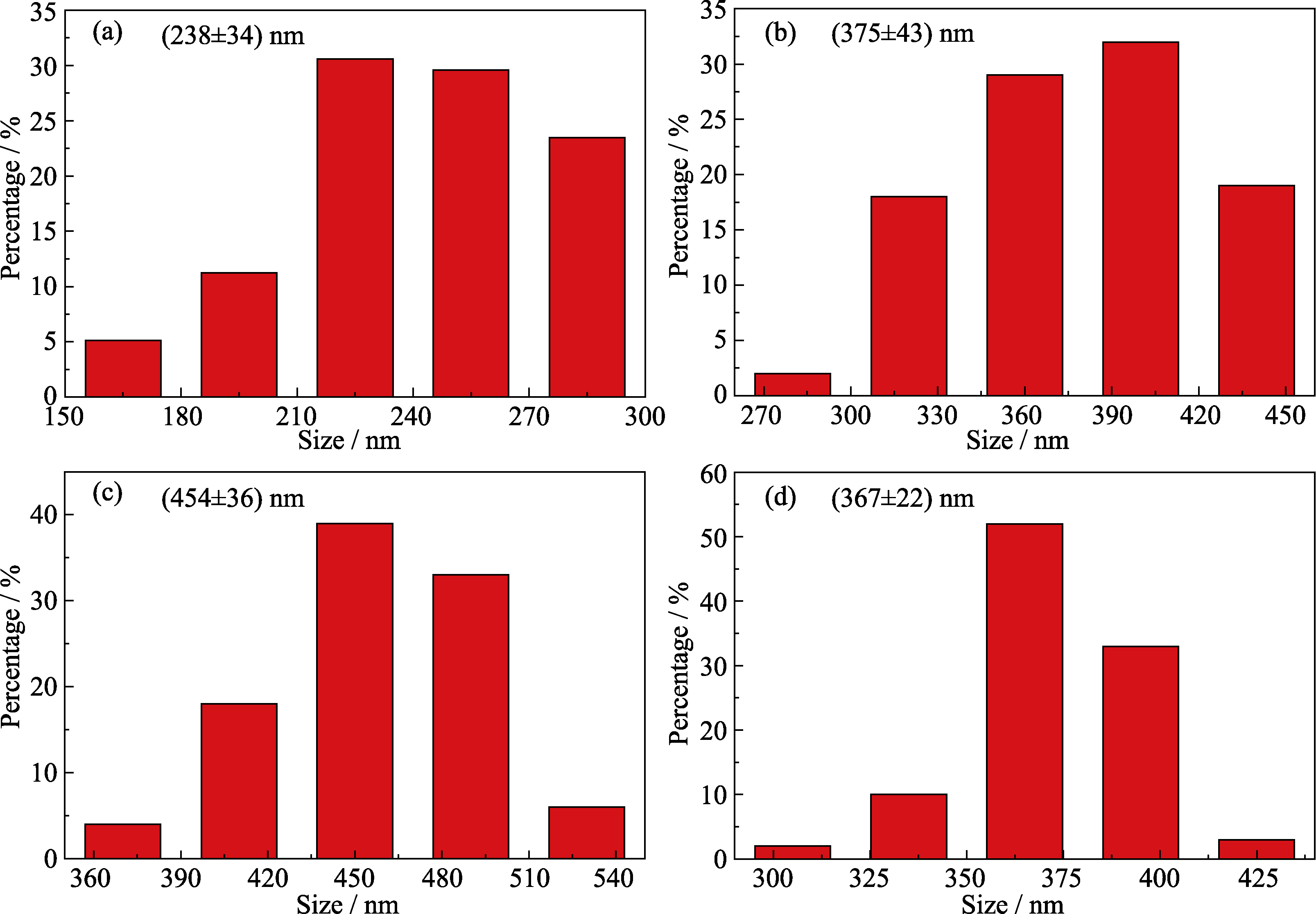
Fig. 3 Effects of molar ratios of pyrogallol to formaldehyde at (a) 2 : 1, (b) 1 : 1, (c) 1 : 2, and (d) 1 : 4 on particle sizes of phenolic resin spheres
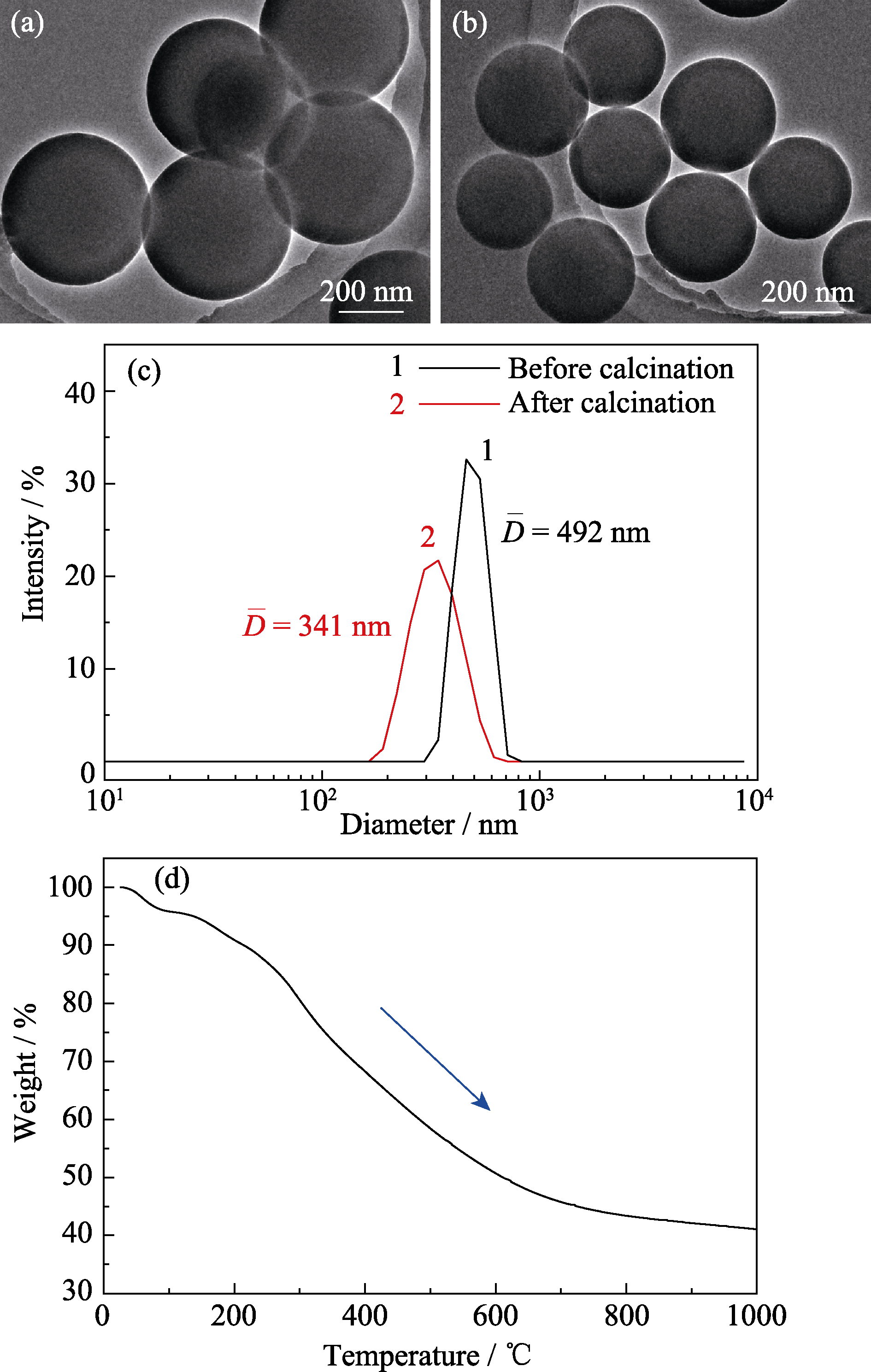
Fig. 4 TEM morphologies of phenolic resin spheres (a) before and (b) after calcination, their (c) particle size analysis curves of dynamic light scattering and (d) thermogravimetric analysis curve of carbon spheres after calcination in N2 atmosphere
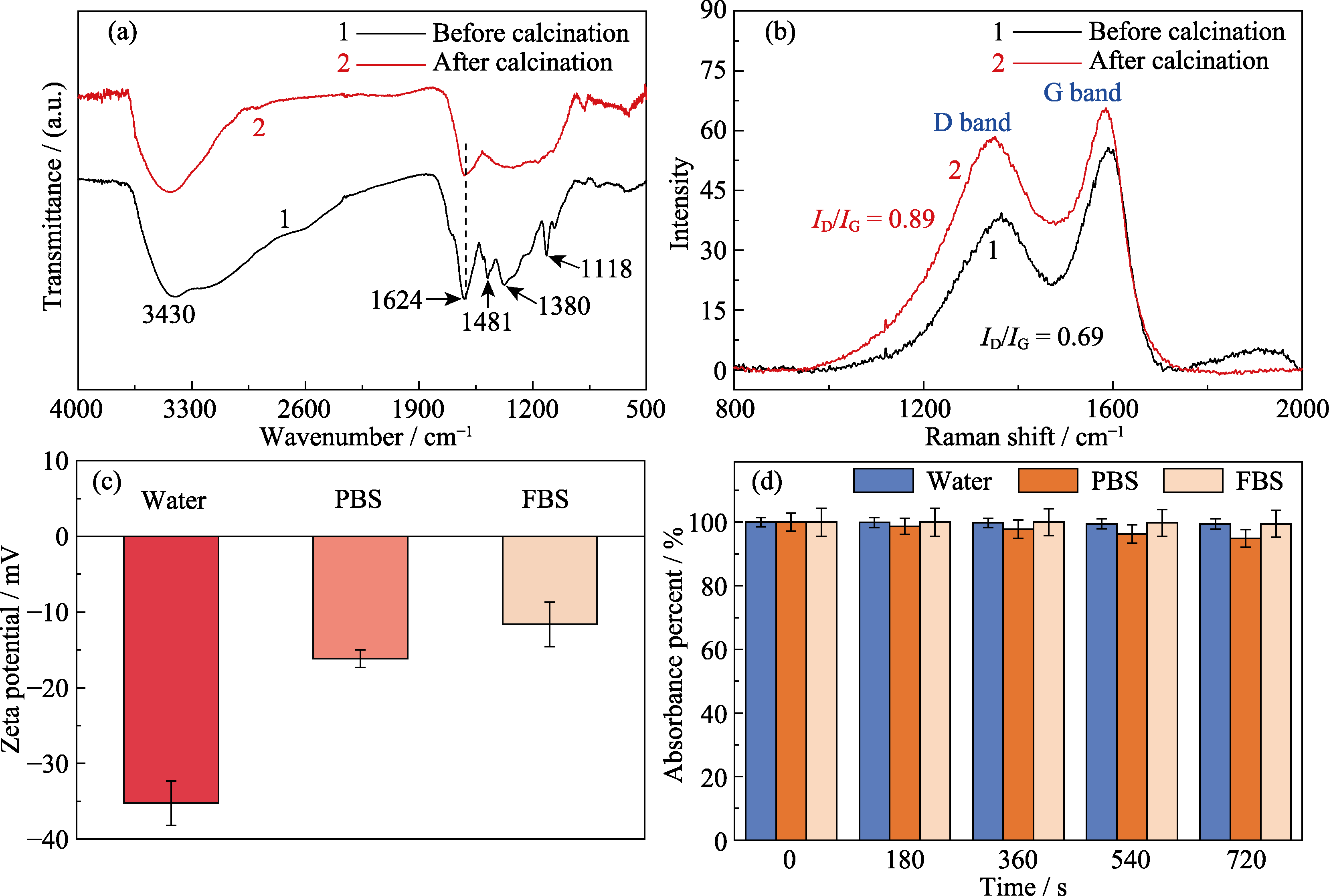
Fig. 5 (a) FT-IR and (b) Raman spectra of phenolic resin spheres before and after calcination, (c) Zeta potential of carbon spheres in different dispersion medium and (d) absorbance percent of carbon spheres in different dispersion medium at 808 nm
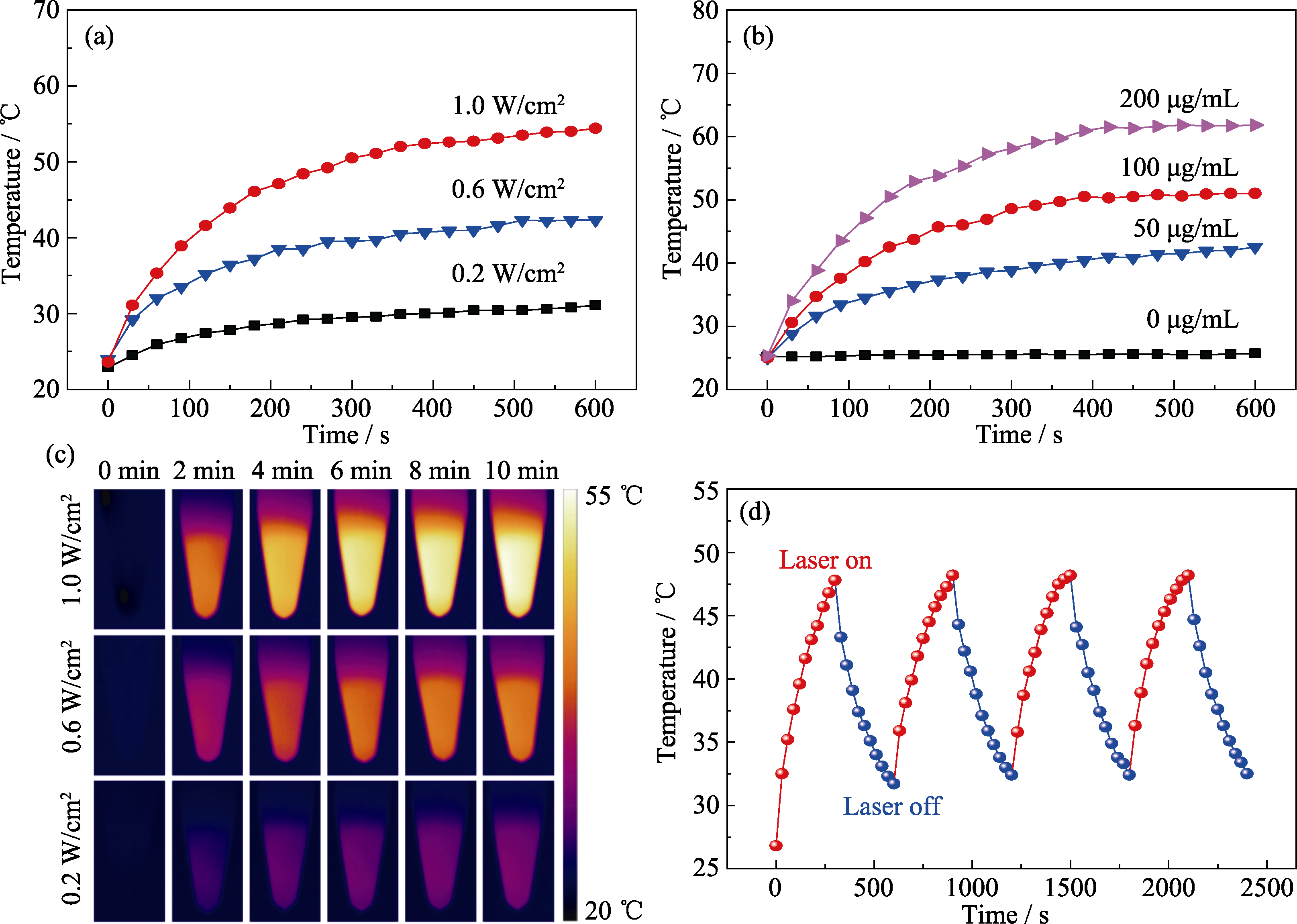
Fig. 6 Evaluation of photothermal effect of carbon spheres Influence of (a) laser power density (concentration: 100 μg/mL) and (b) concentration of carbon spheres (laser power density: 0.8 W/cm2) on photothermal effect; (c) Cloud images of temperature changes; (d) Measurement of the photothermal stability (concentration: 100 μg/mL, laser power density: 0.8 W/cm2)
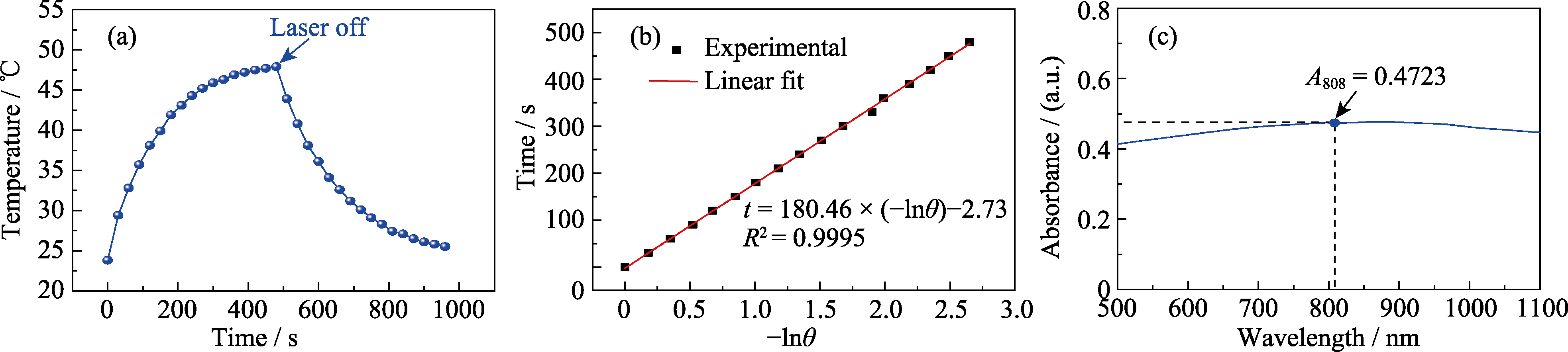
Fig. 7 Measurement of the photothermal conversion efficiency of carbon spheres (a) Heating and cooling curves of carbon sphere suspension (concentration: 100 μg/mL, laser power density: 0.8 W/cm2); (b) Linear fitting curve of t and -lnθ at cooling phase; (c) UV-visible absorption curve of carbon sphere suspension
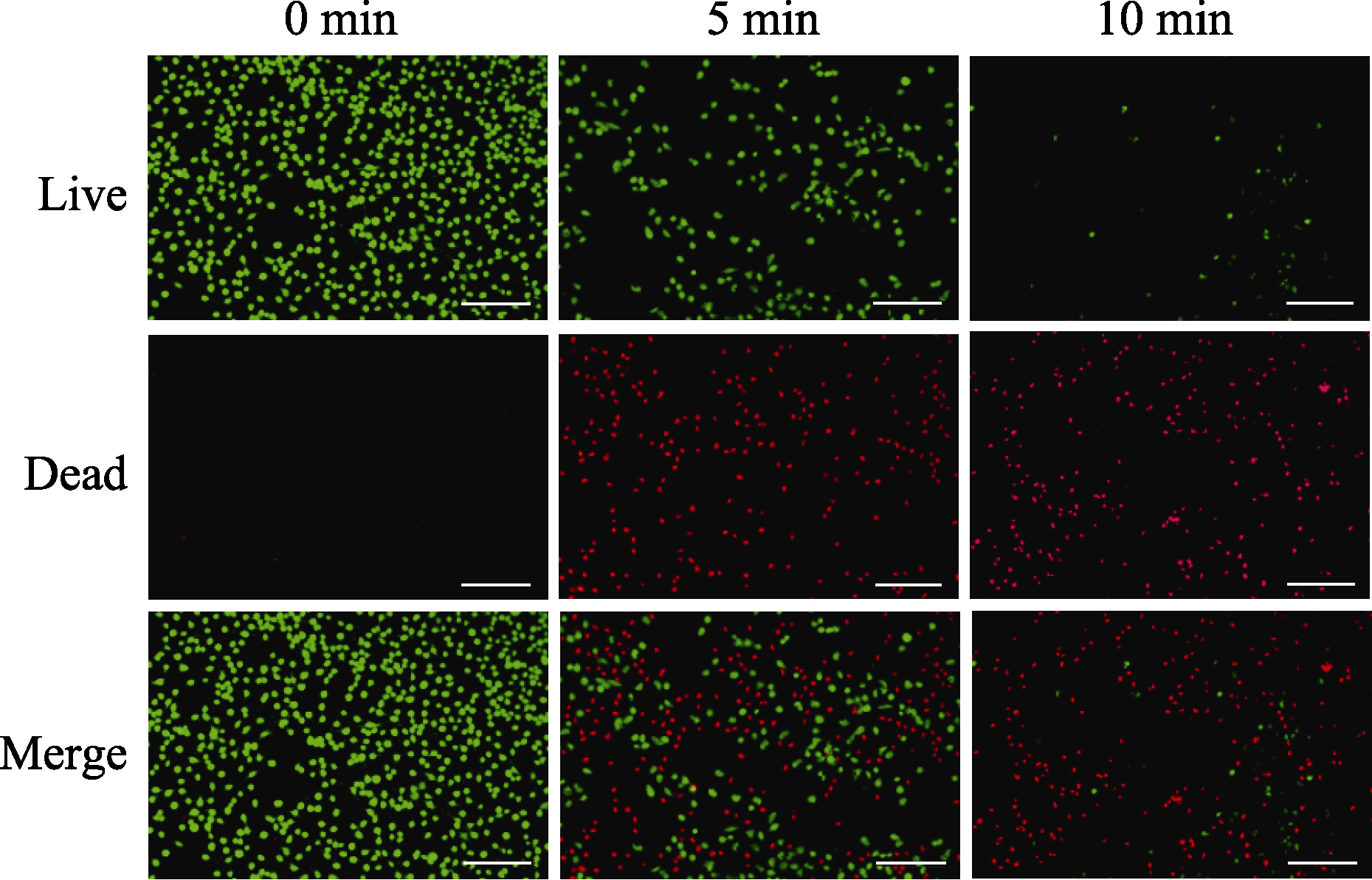
Fig. 10 Live/dead fluorescence images of tumor cells co-culcured with carbon spheres by different laser irradiation time (Green: live cells; Red: dead cells; Scale bar=200 μm)
| [1] |
SCHROEDER A, HELLER D A, WINSLOW M M, et al. Treating metastatic cancer with nanotechnology. Nature Reviews: Cancer, 2012, 12(1):39-50.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LUETKE A, MEYERS P A, LEWIS I, et al. Osteosarcoma treatment-where do we stand? A state of the art review. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 2014, 40(4):523-532.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ZOU L L, WANG H, HE B, et al. Current approaches of photothermal therapy in treating cancer metastasis with nanotherapeutics. Theranostics, 2016, 6(6):762-772.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHI D F, YANG T, O'HAGAN J, et al. Photothermal therapy. Journal of Controlled Release, 2020, 325:52-71.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LIU S, PAN X T, LIU H Y. Two-dimensional nanomaterials for photothermal therapy. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(15):5890-5900.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KIM H, CHUNG K, LEE S, et al. Near-infrared light-responsive nanomaterials for cancer theranostics. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology, 2016, 8(1):23-45.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
JAQUE D, MARTINEZ MAESTRO L, DEL ROSAL B, et al. Nanoparticles for photothermal therapies. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(16):9494-9530.
DOI URL |
| [8] | PAN H Y, ZHANG C, WANG T T, et al. In situ fabrication of intelligent photothermal indocyanine green-alginate hydrogel for localized tumor ablation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(3):2782-2789. |
| [9] |
LIU B, SUN J, ZHU J J, et al. Injectable and NIR-responsive DNA-inorganic hybrid hydrogels with outstanding photothermal therapy. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(39):2004460.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
FERNANDES N, RODRIGUES C F, MOREIRA A F, et al. Overview of the application of inorganic nanomaterials in cancer photothermal therapy. Biomaterials Science, 2020, 8(11):2990-3020.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
SONG X J, CHEN Q, LIU Z. Recent advances in the development of organic photothermal nano-agents. Nano Research, 2014, 8(2):340-354.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
JIN R M, YANG J, ZHAO D H, et al. Hollow gold nanoshells- incorporated injectable genetically engineered hydrogel for sustained chemo-photothermal therapy of tumor. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2019, 17(1):99.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHU X M, WAN H Y, JIA H L, et al. Porous Pt nanoparticles with high near-infrared photothermal conversion efficiencies for photothermal therapy. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2016, 5(24):3165-3172.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WENG Y Z W, GUAN S Y, WANG L, et al. Hollow carbon nanospheres derived from biomass by-product okara for imaging-guided photothermal therapy of cancers. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2019, 7(11):1920-1925.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LIU W, ZHANG X Y, ZHOU L, et al. Reduced graphene oxide (rGO) hybridized hydrogel as a near-infrared (NIR)/pH dual- responsive platform for combined chemo-photothermal therapy. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 536:160-170.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
WANG J X, YAO C J, SHEN B, et al. Upconversion-magnetic carbon sphere for near infrared light-triggered bioimaging and photothermal therapy. Theranostics, 2019, 9(2):608-619.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
XIE H H, LI Z B, SUN Z B, et al. Metabolizable ultrathin Bi2Se3 nanosheets in imaging-guided photothermal therapy. Small, 2016, 12(30):4136-4145.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
JIANG G B, HUA Q, WEN S W, et al. Carbon dot/WS2 heterojunctions for NIR-II enhanced photothermal therapy of osteosarcoma and bone regeneration. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 383:123102.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
DONG L L, JI G M, LIU Y, et al. Multifunctional Cu-Ag2S nanoparticles with high photothermal conversion efficiency for photoacoustic imaging-guided photothermal therapy in vivo. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(2):825-831.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
NEELGUND G M, OKI A R. Influence of carbon nanotubes and graphene nanosheets on photothermal effect of hydroxyapatite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 484:135-145.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG M, WANG W T, WU F, et al. Magnetic and fluorescent carbon nanotubes for dual modal imaging and photothermal and chemo-therapy of cancer cells in living mice. Carbon, 2017, 123:70-83.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LI P, YAN Y, CHEN B L, et al. Lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles complexed with nano-oxide graphene used for upconversion fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy. Biomaterials Science, 2018, 6(4):877-884.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LIU H J, LI C W, QIAN Y, et al. Magnetic-induced graphene quantum dots for imaging-guided photothermal therapy in the second near-infrared window. Biomaterials, 2020, 232:119700.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHOU L, DONG K, CHEN Z W, et al. Near-infrared absorbing mesoporous carbon nanoparticle as an intelligent drug carrier for dual-triggered synergistic cancer therapy. Carbon, 2015, 82:479-488.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
GE J C, JIA Q Y, LIU W M, et al. Red-emissive carbon dots for fluorescent, photoacoustic, and thermal theranostics in living mice. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(28):4169-4177.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LIU Y L, AI K L, LIU J H, et al. Dopamine-melanin colloidal nanospheres: an efficient near-infrared photothermal therapeutic agent for in vivo cancer therapy. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(9):1353-1359.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
WANG S J, WANG Y, BIAN C, et al. The thermal stability and pyrolysis mechanism of boron-containing phenolic resins: the effect of phenyl borates on the char formation. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 331:519-529.
DOI URL |
| [28] | POL V G, SHRESTHA L K, ARIGA K. Tunable, functional carbon spheres derived from rapid synthesis of resorcinol-formaldehyde resins. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(13):10649-10655. |
| [29] |
ZHAO X, ZHANG M, SUN X D, et al. Comprehensive understanding of the formation process on monodisperse resorcinol-formaldehyde polymer and carbon spheres and their use as substrates for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 506:144591.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
CAN M, BULUT E, ÖZACAR M. Synthesis and characterization of pyrogallol-formaldehyde nano resin and its usage as an adsorbent. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2012, 57(10):2710-2717.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
LIU M M, CAI C, LI J, et al. Stober synthesis of tannic acid-formaldehyde resin polymer spheres and their derived carbon nanospheres and nanocomposites for oxygen reduction reaction. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 528:1-9.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
GUAN Q, ZHOU L L, ZHOU L N, et al. A carbon nanomaterial derived from a nanoscale covalent organic framework for photothermal therapy in the NIR-II biowindow. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56:7793-7796.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LIANG Z G, XIA H, ZHANG L M, et al. One-pot synthesis of monodisperse phenolic resin spheres with high thermal stability and its derived carbon spheres as supercapacitor electrodes. Results in Physics, 2020, 16:102912.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
NEELGUND G M, OKI A. Advancement in photothermal effect of carbon nanotubes by grafting of poly(amidoamine) and deposition of CdS nanocrystallites. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(23):7826-7833.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
ZHOU L B, JING Y, LIU Y B, et al. Mesoporous carbon nanospheres as a multifunctional carrier for cancer theranostics. Theranostics, 2018, 8(3):663-675.
DOI URL |
| [36] | WENG Y Z W, GUAN S Y, WANG L, et al. Defective porous carbon polyhedra decorated with copper nanoparticles for enhanced NIR-driven photothermal cancer therapy. Small, 2020, 16(1):e1905184. |
| [37] |
ZHU J, MU S. Defect engineering in carbon-based electrocatalysts: insight into intrinsic carbon defects. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30:2001097.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
WANG W, SHANG L, CHANG G J, et al. Intrinsic carbon- defect-driven electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31:1808276.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ZHAO P, ZHU L L. Dispersibility of carbon dots in aqueous and/or organic solvents. Chemical Communications, 2018, 54:5401-5406.
DOI URL |
| [1] | BAI Zhiqiang, ZHAO Lu, BAI Yunfeng, FENG Feng. Research Progress on MXenes: Preparation, Property and Application in Tumor Theranostics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 361-375. |
| [2] | ZHANG Wenjun, ZHAO Xueying, LÜ Jiangwei, QU Youpeng. Progresses on Hollow Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas: Preparation and Application in Tumor Therapy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1192-1202. |
| [3] | WANG Yuwei, CHEN Jiajie, TIAN Zhengfang, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Potassium Ferrate-loaded Porphyrin-based (VI) Metal-organic Frameworks for Combined Photodymanic and Chemodynamic Tumor Therapy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1305-1315. |
| [4] | CHENG Xiaokun, ZHANG Yue, Lü Haijun, LIU Xinying, HOU Senlin, CHEN Aibing. Porous Carbon Nanomaterials Based Tumor Targeting Drug Delivery System: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 9-24. |
| [5] | XIE Xue, WU Jianrong, CAI Xiaojun, HAO Junnian, ZHENG Yuanyi. Photothermal/pH Responsive B-CuS-DOX Nanodrug for Chemo-photothermal Synergistic Therapy of Tumor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 81-87. |
| [6] | DU Juan, LIU Lei, YU Yifeng, ZHANG Yue, LÜ Haijun, CHEN Aibing. Hollow Carbon Sphere with Tunable Structure by Encapsulation Pyrolysis Synchronous Deposition for Cefalexin Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 608-616. |
| [7] | PAN Shan, LI Yong-Sheng, SHI Jian-Lin. Facile Synthesis of Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Co-loading of Doxorubicin and Hemoglobin [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1097-1102. |
| [8] | HU Feng-Xiang, LI Ling, LIN Kui, CUI Lan, SHI Cai-Jing, SAYYAR Ali Shah, CUI Shen. Preparation of N-doped Hollow Carbon Spheres and Investigation of Their Optical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(8): 827-833. |
| [9] | ZHAI Yun-Gang, DONG Wen-Jie, GAO Yong-Ping, NIU De-Chao, CHEN Jian-Zhuang, GU Jin-Lou, LI Yong-Sheng, SHI Jian-Lin. Preparation of Superparamagnetic Gold Nanocomposites with Different Diameters and Their Imaging and Therapy Applications [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(9): 950-956. |
| [10] | LIU Shou-Xin,SUN Jian. Carbon Sphere/Activated Carbon Composite Materials Prepared by Solvothermal Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(6): 1132-1136. |
| [11] | LU Feng,LONG Dong-Hui,QIAO Wen-Ming,ZHAN Liang,LING Li-Cheng. Structure Control of Ordered Mesoporous Carbon Spheres Prepared from Suspension-assist Evaporationinduced Selfassembly [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(3): 571-576. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||