
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (4): 452-458.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210381
Special Issue: 【结构材料】陶瓷基复合材料
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Hongda1,2( ), FENG Qian3, YOU Xiao1,2,4, ZHOU Haijun1,2(
), FENG Qian3, YOU Xiao1,2,4, ZHOU Haijun1,2( ), HU Jianbao1,2, KAN Yanmei1,2, CHEN Xiaowu1,2, DONG Shaoming1,2
), HU Jianbao1,2, KAN Yanmei1,2, CHEN Xiaowu1,2, DONG Shaoming1,2
Received:2021-06-18
Revised:2021-07-14
Published:2022-04-20
Online:2021-08-20
Contact:
ZHOU Haijun, associate professor. E-mail: zhouhj00000@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:WANG Hongda (1989–), male, associate professor. E-mail: wanghd@mail.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Hongda, FENG Qian, YOU Xiao, ZHOU Haijun, HU Jianbao, KAN Yanmei, CHEN Xiaowu, DONG Shaoming. Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of Brazed Joints of SiC/SiC Composites and Hastelloy N Alloy Using Cu-Ni Alloy[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 452-458.
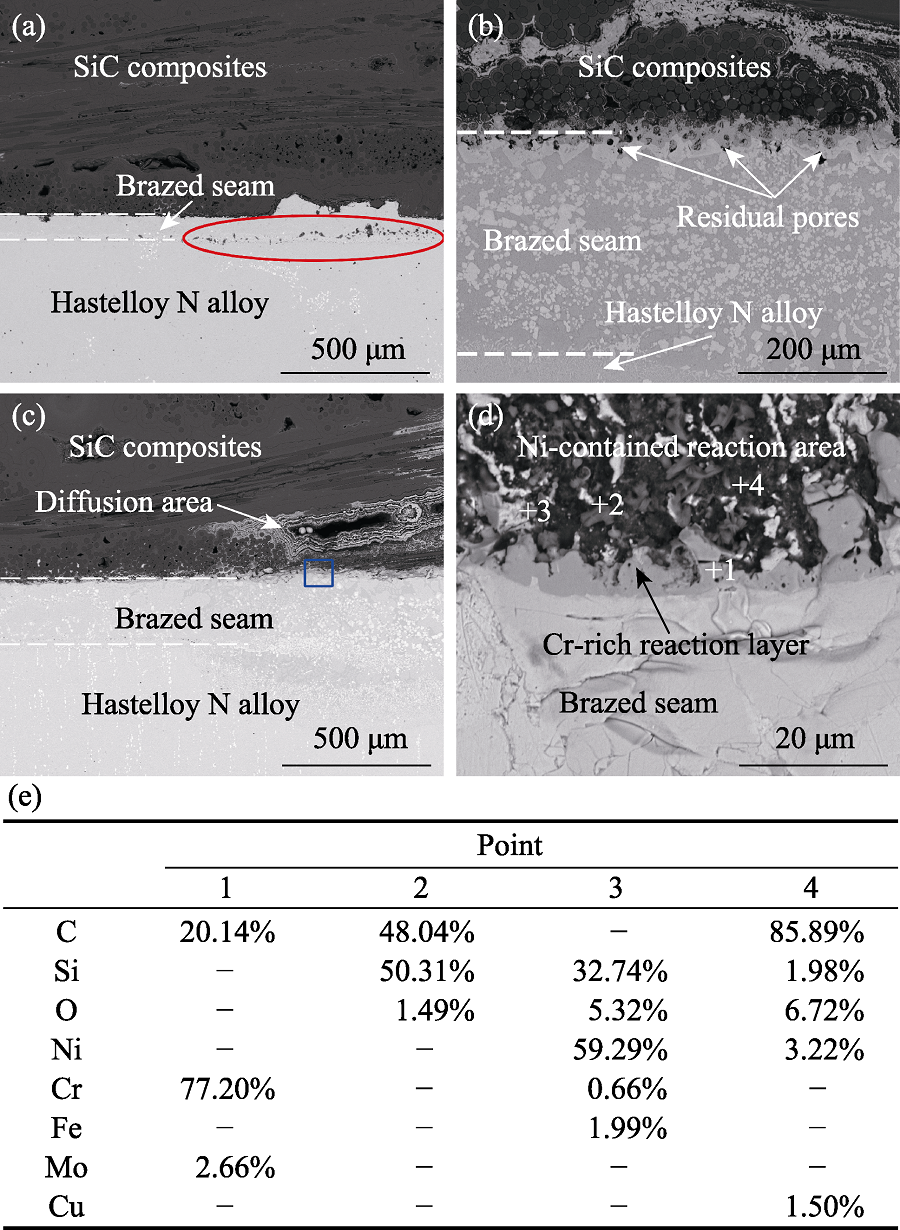
Fig. 2 SEM images of brazing joints obtained at (a) 1090, (b) 1110 ℃, (c) and (d) 1130 ℃, correspoding EDS analyses (atom fraction) (e) of the point in image (d)
| Element | Before corrosion | After corrosion |
|---|---|---|
| Ni | 10 | 20 |
| Cr | 20 | 210 |
| Fe | 30 | 40 |
| Mo | <10 | <10 |
Table 1 Content of main metal impurities in fluoride salts before and after corrosion (10-4% in mass)
| Element | Before corrosion | After corrosion |
|---|---|---|
| Ni | 10 | 20 |
| Cr | 20 | 210 |
| Fe | 30 | 40 |
| Mo | <10 | <10 |
| [1] | KRENKEL W. Ceramic Matrix Composites: Fiber Reinforced Ceramics and their Applications. Weinheim: John Wiley & Sons, 2008. |
| [2] |
PI H, SONG F, WANG H, et al. Influence of copper contamination on ablation damage of C/SiC composites under simulated thermal environment of arc heater. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(15): 22016-22024.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LEE K N, MILLER R A. Oxidation behavior of muilite-coated SiC and SiC/SiC composites under thermal cycling between room temperature and 1200 ℃-1400 ℃. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1996, 79(3): 620-626.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GOMINA M, FOURVEL P, ROUILLON M H. High temperature mechanical behaviour of an uncoated SiC-SiC composite material. Journal of Materials Science, 1991, 26(7): 1891-1898.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
JACOBSEN T K, BR NDSTED P. Mechanical properties of two plain-woven chemical vapor infiltrated silicon carbide-matrix composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001, 84(5): 1043-1051.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KATOH Y, OZAWA K, HINOKI T, et al. Mechanical properties of advanced SiC fiber composites irradiated at very high temperatures. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2011, 417(1): 416-420.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
JONES R H, HENAGER C H. Fusion reactor application issues for low activation SiC/SiC composites. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1995, 219(2): 55-62.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HE X, SONG J, TAN J, et al. SiC coating: an alternative for the protection of nuclear graphite from liquid fluoride salt. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 448(1): 1-3.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
NISHIMURA H, TERAI T, YONEOKA T, et al. Compatibility of structural candidate materials with LiF-BeF2 molten salt mixture. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2000, 283-287(Part 2): 1326-1331.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
YANG X, LIU M, GAO Y, et al. Effect of oxygen on the corrosion of SiC in LiF-NaF-KF molten salt. Corrosion Science, 2016, 103: 165-172.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WANG H, ZHOU H, DONG S, et al. Corrosion behavior of SiCf/SiC composites in high temperature fluoride salt environment. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(11): 1133-1140.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
RICCARDI B, GIANCARLI L, HASEGAWA A, et al. Issues and advances in SiCf/SiC composites development for fusion reactors. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2004, 329-333(Part A): 56-65.
DOI URL |
| [13] | WILLIAMS D F, TOTH L M, CLARNO K T. ORNL/TM-2006/12. Oak Ridge: Oak Ridge National Lab., 2006. |
| [14] |
HENAGER C H, SHIN Y, BLUM Y, et al. Coatings and joining for SiC and SiC-composites for nuclear energy systems. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2007, 367-370: 1139-1143.
DOI URL |
| [15] | ZHANG Y, FENG D, HE Z Y, et al. Progress in joining ceramics to metals. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2006, 13(2): 1-5. |
| [16] |
SINGH M, ASTHANA R, SHPARGEL T P. Brazing of ceramic- matrix composites to Ti and Hastealloy using Ni-base metallic glass interlayers. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 498(1): 19-30.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
HATTALI M L, VALETTE S, ROPITAL F, et al. Study of SiC- nickel alloy bonding for high temperature applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2009, 29(4): 813-819.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIN G, HUANG J, ZHANG H. Joints of carbon fiber-reinforced SiC composites to Ti-alloy brazed by Ag-Cu-Ti short carbon fibers. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 189(1): 256-261.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
XIONG H, LI X, MAO W, et al. Wetting behavior of Co based active brazing alloys on SiC and the interfacial reactions. Materials Letters, 2003, 57(22): 3417-3421.
DOI URL |
| [20] | LU J, XIA Z. The corrosion performance of a binary Cu-Ni Alloy used as an anode for aluminum electrolysis. Applied Mechanics & Materials, 2011, 55: 7-10. |
| [21] |
PARK J S, LANDRY K, PEREPEZKO J H. Kinetic control of silicon carbide/metal reactions. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1999, 259(2): 279-286.
DOI URL |
| [22] | FRANKE P, NEUSCH TZ D. Cu-NiCopper- Nickel//FRANKE P, NEUSCH TZ D. Cu-Ni(Copper- Nickel)//FRANKE P, NEUSCH TZ D. Binary systems Part 3: Binary Systems from Cs- K to Mg-Zr Heidelberg; Springer. 2005. |
| [23] |
ARAKI H, SUZUKI H, YANG W, et al. Effect of high temperature heat treatment in vacuum on microstructure and bending properties of SiCf/SiC composites prepared by CVI. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1998, 258-263(Part 2): 1540-1545.
DOI URL |
| [24] | OLSON L C, AMBROSEK J W, SRIDHARAN K, et al. Evaluation of Material Corrosion in Molten Fluoride Salt. Proceedings of the Presentation on AIChE Conference, San-Francisco, F, 2006. |
| [25] |
XIONG H P, CHEN B, KANG YS, et al. Wettability of Co-V, and PdNi-Cr-V system alloys on SiC ceramic and interfacial reactions. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 56(2): 173-176.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
OLSON L C, AMBROSEK J W, SRIDHARAN K, et al. Materials corrosion in molten LiF-NaF-KF salt. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 2009, 130(1): 67-73.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
SCHMIDT J, SCHEIFFELE M, CRIPPA M, et al. Design, fabrication, and testing of ceramic plat-type heat exchangers with integrated flow channel design. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2011, 8(5): 1073-1086.
DOI URL |
| [28] | SELLERS R S, CHENG W J, ANDERSON M H, et al. Materials Corrosion in Molten LiF-NaF-KF Eutectic Salt under Different Reduction-oxidation Conditions. Proceedings of the International Conference Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP’12), F, 2012. |
| [29] |
OZERYANAYA I N. Corrosion of metals by molten salts in heat- treatment processes. Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 1985, 27(3): 184-188.
DOI URL |
| [1] | TANG Shuai,ZHANG Wentai,QIAN Junyu,XIAN Peng,MO Xiaoshan,HUANG Nan,WAN Guojiang. Long-term in Vitro Corrosion Behavior of Zinc in Ringer’s Solution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 461-468. |
| [2] | SHI Wei, TAN Yi, HAO Jian-Jie, LI Jia-Yan. Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Materials Used in Crystalline Silicon Furnace in Silicon Vapor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 744-750. |
| [3] | WANG Hong-Da, ZHOU Hai-Jun, DONG Shao-Ming, WANG Zhen, HU Jian-Bao, FENG Qian. Corrosion Behavior of SiCf/SiC Composites in High Temperature Fluoride Salt Environment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(11): 1133-1140. |
| [4] | YU Jie, WEI Dong-Bo, WANG Yan, Lü Peng-Xiang, DI Shi-Chun. Structure and Property of Micro-arc Oxidation Coating Modified by Laser Melting and Solidifying on Aluminum Alloy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(8): 859-863. |
| [5] | XU Yong-Dong,CHENG Lai-Fei,ZHANG Li-Tong. Three Dimensional Textile SiC/SiC Composites by Chemical Vapor Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2001, 16(2): 344-348. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||