
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 3-14.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210368
Special Issue: 【能源环境】CO2绿色转换; 2022年度中国知网高下载论文
• TOPICAL SECTION: Green Conversion of CO2 (Contributing Editor: OUYANG Shuxin, WANG Wenzhong) • Previous Articles Next Articles
GAO Wa1( ), XIONG Yujie2, WU Congping1,3,4(
), XIONG Yujie2, WU Congping1,3,4( ), ZHOU Yong1,3(
), ZHOU Yong1,3( ), ZOU Zhigang1,3,4
), ZOU Zhigang1,3,4
Received:2021-06-10
Revised:2021-07-30
Published:2022-01-20
Online:2021-07-20
Contact:
ZHOU Yong, professor. E-mail: zhouyong1999@nju.edu.cn; WU Congping, senior engineer. E-mail: cpwu@nju.edu.cn
About author:GAO Wa (1994-), female, PhD candidate. E-mail: dz1622007@smail.nju.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
GAO Wa, XIONG Yujie, WU Congping, ZHOU Yong, ZOU Zhigang. Recent Progress on Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction with Ultrathin Nanostructures[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 3-14.
| Half electrochemical thermodynamic reactions | Standard potential /V (vs SHE) |
|---|---|
| CO2(g) + 2H+ + 2e- = HCOOH(1) | -0.250 |
| CO2(g) + 2H+ + 2e- = CO(g)+ H2O (1) | -0.106 |
| 2CO2(g) + 2H+ + 2e- = H2C2O4(aq) | -0.500 |
| 2CO2(g) + 2e- = C2O42-(aq) | -0.590 |
| CO2(g) + 4H+ + 4e- = C(s) + 2H2O(1) | 0.210 |
| CO2(g) + 4H+ + 4e- = CH2O(1) + H2O(1) | -0.070 |
| CO2(g) + 6H+ + 6e- = CH3OH(1) + H2O(1) | 0.016 |
| CO2(g) + 8H+ + 8e- = CH4(g) + 2H2O(1) | 0.169 |
| 2CO2(g) + 12H+ + 12e- = CH2CH2(g) + 4H2O(1) | 0.064 |
| 2CO2(g) + 12H+ + 12e- = CH3CH2OH(1) + 3H2O(1) | 0.084 |
Table 1 Standard potentials of convert CO2 to various C1 and C2 products in aqueous solutions at standard conditions (1.01×105 Pa and 25 ℃) [34]
| Half electrochemical thermodynamic reactions | Standard potential /V (vs SHE) |
|---|---|
| CO2(g) + 2H+ + 2e- = HCOOH(1) | -0.250 |
| CO2(g) + 2H+ + 2e- = CO(g)+ H2O (1) | -0.106 |
| 2CO2(g) + 2H+ + 2e- = H2C2O4(aq) | -0.500 |
| 2CO2(g) + 2e- = C2O42-(aq) | -0.590 |
| CO2(g) + 4H+ + 4e- = C(s) + 2H2O(1) | 0.210 |
| CO2(g) + 4H+ + 4e- = CH2O(1) + H2O(1) | -0.070 |
| CO2(g) + 6H+ + 6e- = CH3OH(1) + H2O(1) | 0.016 |
| CO2(g) + 8H+ + 8e- = CH4(g) + 2H2O(1) | 0.169 |
| 2CO2(g) + 12H+ + 12e- = CH2CH2(g) + 4H2O(1) | 0.064 |
| 2CO2(g) + 12H+ + 12e- = CH3CH2OH(1) + 3H2O(1) | 0.084 |
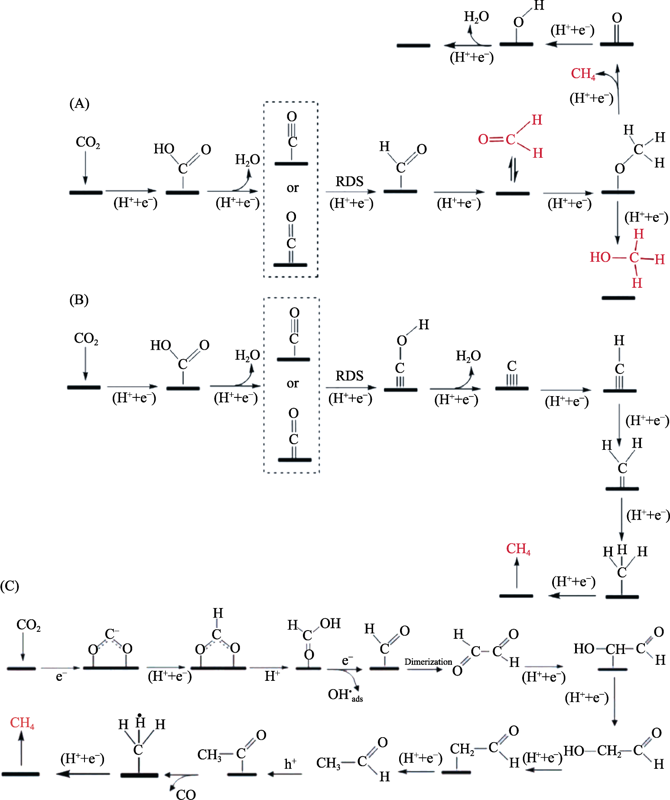
Fig. 2 Possible reaction paths for CO2 reduction to produce HCHO, CH3OH, and CH4[35,36] (A) A thermodynamic analysis; (B) A combined thermodynamic and kinetic analysis; (C) Glyoxal route
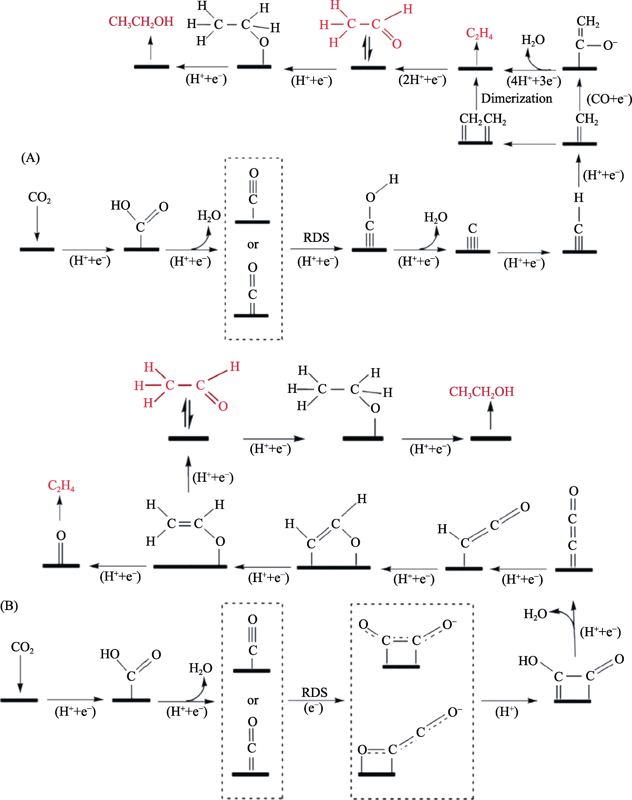
Fig. 3 Possible reaction paths for CO2 reduction to produce C2H4, CH3CHO, and C2H5OH[35] (A) Coupling of two *CH2 species or CO insertion in a Fischer-Tropsch-like step; (B) *CO dimerization
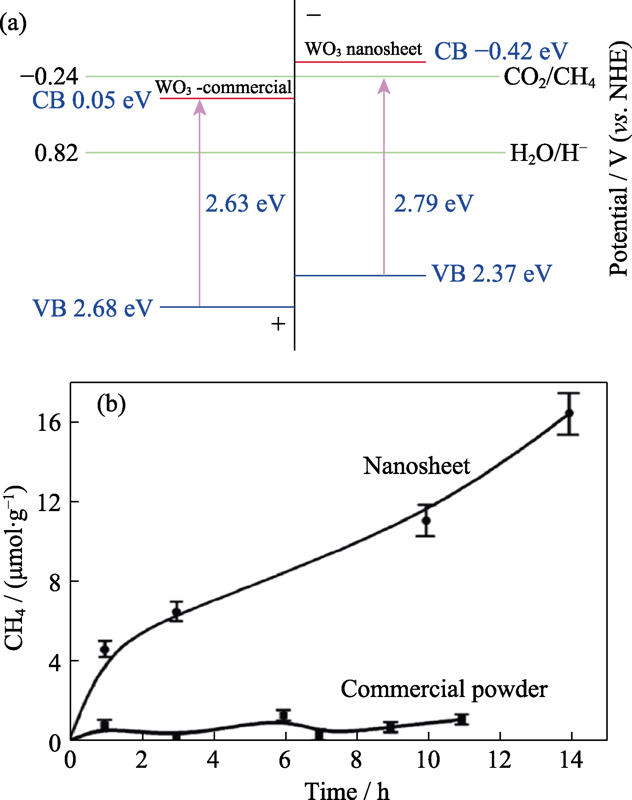
Fig. 4 (a) Calculated band positions of the WO3 nanosheet and commercial WO3, relative to the redox potential of CO2/CH4 in the presence of water, and (b) CH4 generation over the nanosheet and commercial powder as a function of visible light irradiation time (λ≥420 nm)[38]
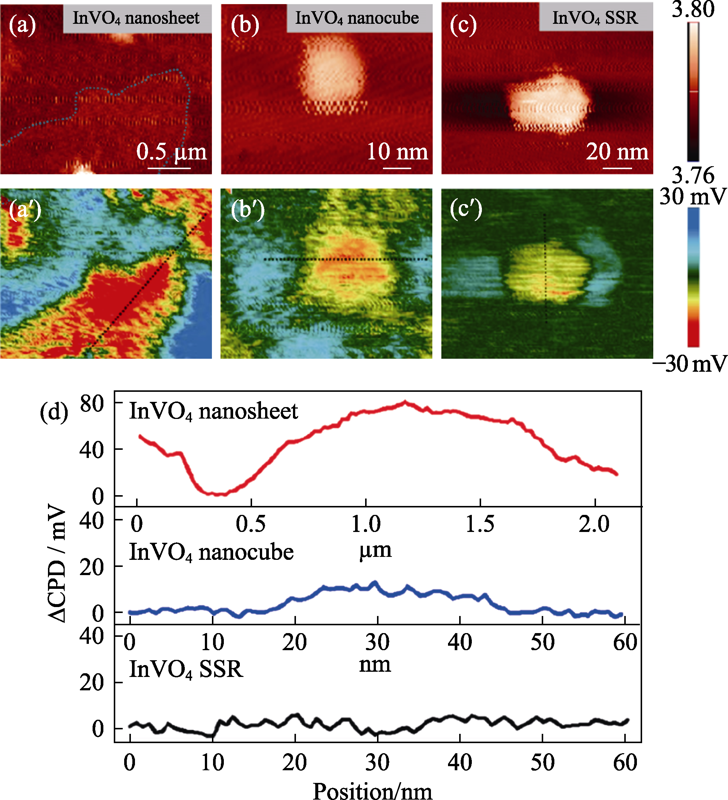
Fig. 5 Height images of (a) atomically thin InVO4 nanosheet, (b) nanocube, and (c) bulk materials obtained by conventional solid-state reaction, surface photovoltage spectroscopy (SPV) images in (a′), (b′), and (c′) displaying differential images between potential images under light and in the dark, and (d) surface photovoltage change by subtracting the potential under dark conditions from that under illumination (SPV, ΔCPD = CPDdark - CPDlight)[13]
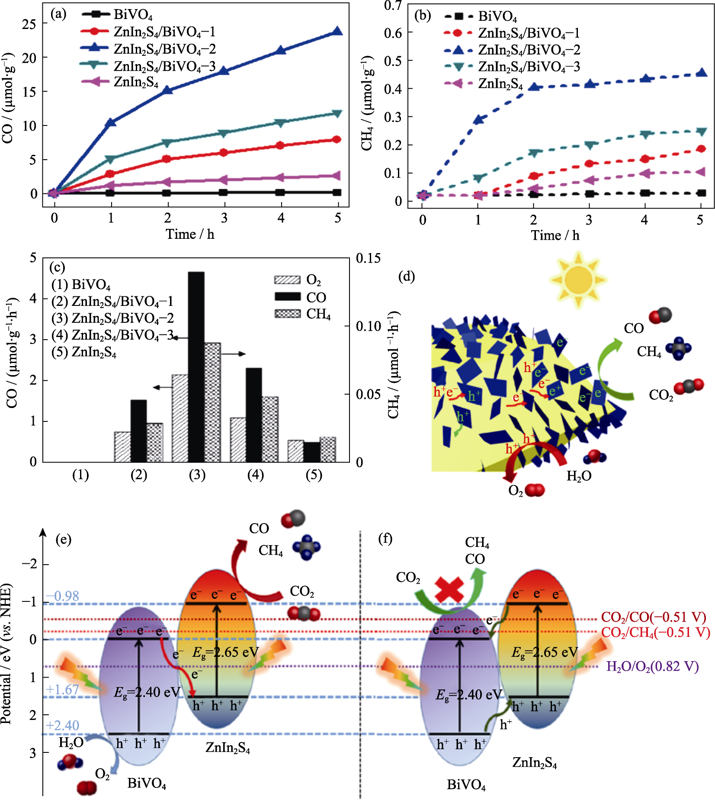
Fig. 7 Photocatalytic (a) CO and (b) CH4 output changing with light irradiation time, (c) comparison of photocatalytic activity over different samples, (d)schematic illustration of the photocatalytic CO2 reduction for ZnIn2S4/BiVO4 nanocomposite, schematic representation of (e) Z-scheme electron-hole transfer mechanisms, and (f) heterojunction-type electron-hole transfer mechanisms under light irradiation[50]
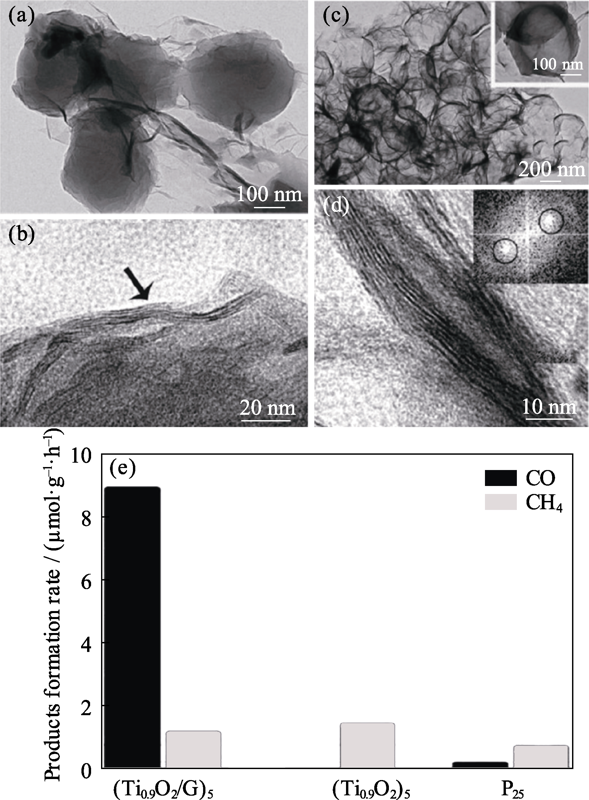
Fig. 8 TEM images of (a, b) poly(methylmethacrylate) spheres coated with (protonic polyethylenimine (PEI)/Ti0.91O2/ PEI/GO)5, (c, d) (G-Ti0.91O2)5 hollow spheres, and (e)comparation of the average product formation rates[53]
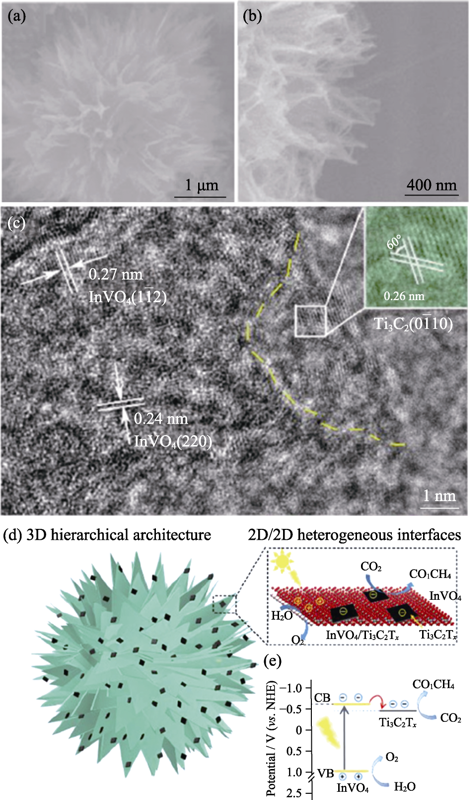
Fig. 9 (a, b) SEM images of InVO4/Ti3C2Tx at higher magnification, (c) HRTEM images of InVO4/Ti3C2Tx, (d)scheme for spatial charge separation and transport during the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 over hierarchical InVO4/Ti3C2Tx heterosystem, and (e)energy level alignment of InVO4/Ti3C2Tx hybrid[56]
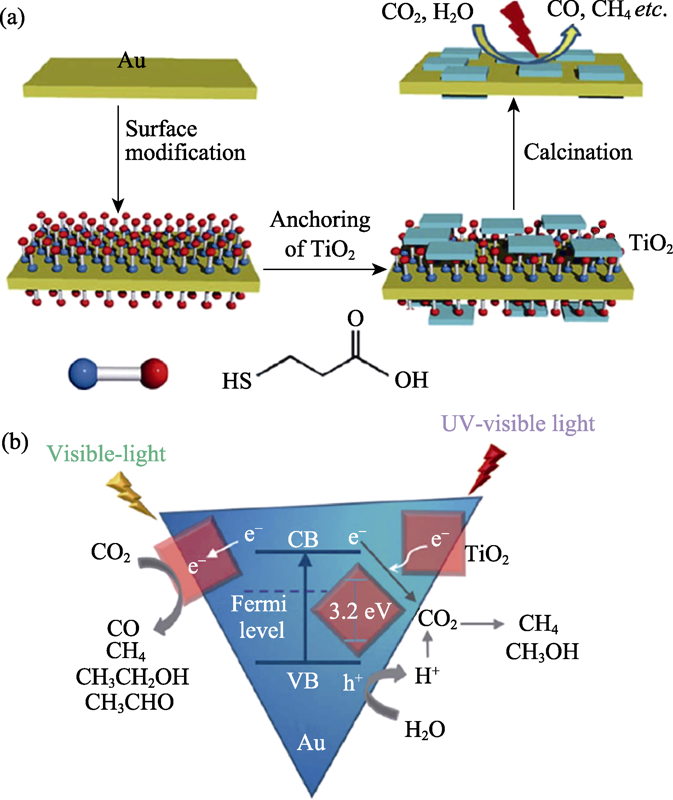
Fig. 10 Schematic illustration of the preparation procedure of the Au-TiO2 composites (b), schematic illustration of charge separation and transfer in the Au-TiO2 system and photoreduction of CO2 into different products[57]
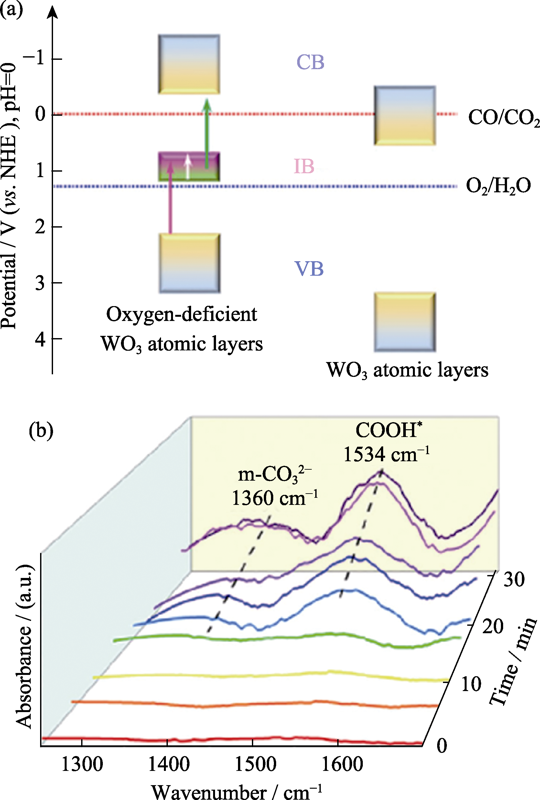
Fig. 11 (a) Scheme of the electronic band structures of Vo-rich WO3 atomic layers and WO3 atomic layers, and (b) in situ FT-IR spectra for the IR light-driven CO2 reduction process on the Vo-rich WO3 atomic layers[60]
| [1] |
ZHOU YAN-SONG, WANG ZHI-TONG, HUANG LEI, et al. Engineering 2D photocatalysts toward carbon dioxide reduction. Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11(8):2003159.
DOI URL |
| [2] | VU NHU-NANG, SERGE KALIAGUINE, DO TRONG-ON. Critical aspects and recent advances in structural engineering of photocatalysts for sunlight-driven photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into fuels. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29(31): 1901825. |
| [3] |
JIAO XING-CHEN, ZHENG KAI, LIANG LIANG, et al. Fundamentals and challenges of ultrathin 2D photocatalysts in boosting CO2 photoreduction. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49(18):6592-6604.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
FU JUN-WEI, JIANG KE-XIN, QIU XIAO-QING, et al. Product selectivity of photocatalytic CO2 reduction reactions. Mater. Today, 2020, 32:222-243.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
TU WEN-GUANG, ZHOU YONG, ZOU ZHI-GANG. Versatile graphene-promoting photocatalytic performance of semiconductors: basic principles, synthesis, solar energy conversion, and environmental applications. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23(40):4996-5008.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
TU WEN-GUANG, ZHOU YONG, ZOU ZHI-GANG. Photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into renewable hydrocarbon fuels: state-of-the-art accomplishment, challenges, and prospects. Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(27):4607-4626.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHAO YU-FEI, GEOFFREY I N WATERHOUSE, CHEN GUAN-BO, et al. Two-dimensional-related catalytic materials for solar-driven conversion of CO:X into valuable chemical feedstocks. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48(7):1972-2010.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
XIONG JUN, SONG PIN, DI JUN, et al. Ultrathin structured photocatalysts: a versatile platform for CO2 reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ., 2019, 256:117788.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
CHEN SHAN-SHAN, QI YU, LI CAN, et al. Surface strategies for particulate photocatalysts toward artificial photosynthesis. Joule, 2018, 2(11):2260-2288.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 涂文广, 周勇, 邹志刚. 半导体纳米催化剂的结构调控及其光还原CO2的研究进展. 影像科学与光化学, 2015, 33:347-357. |
| [11] | 王冰, 赵美明, 周勇, 等. 光催化还原二氧化碳制备太阳燃料研究进展及挑战. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2017, 44:286-296. |
| [12] | 崔新江, 石峰. 基于单原子催化剂的二氧化碳选择性转化. 物理化学学报, 2021, 37(5): 2006080. |
| [13] |
HAN QIU-TONG, BAI XIAO-WAN, MAN ZAI-QIN, et al. Convincing synthesis of atomically thin, single-crystalline InVO4 sheets toward promoting highly selective and efficient solar conversion of CO2 into CO. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(10):4209-4213.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WU XIAO-YONG, LI YUAN, ZHANG GAO-KE, et al. Photocatalytic CO2 conversion of M0.33WO3 directly from the air with high selectivity: insight into full spectrum-induced reaction mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(13):5267-5274.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LIU QI, WU DI, ZHOU YONG, et al. Single-crystalline, ultrathin ZnGa2O4 nanosheet scaffolds to promote photocatalytic activity in CO2 reduction into methane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6(4):2356-2361.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
GAO WA, BAI XIAO-WAN, GAO YU-YING, et al. Anchoring of black phosphorus quantum dots onto WO3 nanowires to boost photocatalytic CO2 conversion into solar fuels. Chem. Commun., 2020, 56(56):7777-7780.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
TU WEN-GUANG, ZHOU YONG, LIU QI, et al. An in situ simultaneous reduction-hydrolysis technique for fabrication of TiO2-graphene 2D sandwich-like hybrid nanosheets: graphene- promoted selectivity of photocatalytic-driven hydrogenation and coupling of CO2 into methane and ethane. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23(14):1743-1749.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CAO SHAO-WEN, SHEN BAO-JIA, TONG TONG, et al. 2D/2D heterojunction of ultrathin MXene/Bi2WO6 nanosheets for improved photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28(21):1800136.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
YANG SI-ZHOU, HU WEN-HUI, ZHANG XIN, et al. 2D covalent organic frameworks as intrinsic photocatalysts for visible light-driven CO2 reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140(44):14614-14618.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LIU WEN-BO, LI XIAO-KANG, WANG CHI-MING, et al. A scalable general synthetic approach toward ultrathin imine-linked two-dimensional covalent organic framework nanosheets for photocatalytic CO2 reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(43):17431-17440.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LI XIAO-DONG, SUN YONG-FU, XU JIA-QI, et al. Selective visible-light-driven photocatalytic CO2 reduction to CH4 mediated by atomically thin CuIn5S8 layers. Nat. Energy, 2019, 4(8):690-699.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
JIAO XING-CHEN, CHEN ZONG-WEI, LI XIAO-DONG, et al. Defect-mediated electron-hole separation in one-unit-cell ZnIn2S4 layers for boosted solar-driven CO2 reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(22):7586-7594.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LIANG LIANG, LI XIAO-DONG, ZHANG JIA-CHEN, et al. Efficient infrared light induced CO2 reduction with nearly 100% CO selectivity enabled by metallic CoN porous atomic layers. Nano Energy, 2020, 69:104421.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WU JU, LI XIAO-DONG, SHI WEN, et al. Efficient visible- light-driven CO2 reduction mediated by defect-engineered BiOBr atomic layers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(28):8719-8723.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LIANG LIANG, LI XIAO-DONG, SUN YONG-FU, et al. Infrared light-driven CO2 overall splitting at room temperature. Joule, 2018, 2(5):1004-1016.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
JIAO XING-CHEN, LI XIAO-DONG, JIN XIU-YU, et al. Partially oxidized SnS2 atomic layers achieving efficient visible- light-driven CO2 reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(49):18044-18051.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZHENG HUI-LI, HUANG SHAN-LIN, LUO MING-BU, et al. Photochemical in situ exfoliation of metal-organic frameworks for enhanced visible-light-driven CO2 reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(52):23588-23592.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LI XIAO-DONG, LIANG LIANG, SUN YONG-FU, et al. Ultrathin conductor enabling efficient IR light CO2 reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(1):423-430.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
HAN BIN, OU XIN-WEN, DENG ZI-QI, et al. Nickel metal- organic framework monolayers for photoreduction of diluted CO2: metal-node-dependent activity and selectivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(51):16811-16815.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZHAO YU-FEI, CHEN GUAN-GBO, BIAN TONG, et al. Defect-rich ultrathin ZnAl-layered double hydroxide nanosheets for efficient photoreduction of CO2 to CO with water. Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(47):7824-7831.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
DI JUN, ZHAO XIAO-XU, LIAN CHENG, et al. Atomically-thin Bi2MoO6 nanosheets with vacancy pairs for improved photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Nano Energy, 2019, 61:54-59.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
GAO SHAN, GU BING-CHUAN, JIAO XING-CHEN, et al. Highly efficient and exceptionally durable CO2 photoreduction to methanol over freestanding defective single-unit-cell bismuth vanadate layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(9):3438-3445.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ZHU XING-WANG, HUANG SHU-QUAN, YU QING, et al. In-situ hydroxyl modification of monolayer black phosphorus for stable photocatalytic carbon dioxide conversion. Appl. Catal. B Environ., 2020, 269:118760.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
LI XIAO-DONG, WANG SHU-MIN, LI LI, et al. Opportunity of atomically thin two-dimensional catalysts for promoting CO2 electroreduction. Acc. Chem. Res., 2020, 53(12):2964-2974.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
SUN ZHEN-YU, MA TAO, TAO HENG-CONG, et al. Fundamentals and challenges of electrochemical CO2 reduction using two-dimensional materials. Chem, 2017, 3(4):560-587.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WANG LI-MING, CHEN WEN-LONG, ZHANG DOU-DOU, et al. Surface strategies for catalytic CO2 reduction: from two-dimensional materials to nanoclusters to single atoms. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48(21):5310-5349.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZHUA XING-WANG, HUANG SHU-QUAN, YU QING, et al. In-situ hydroxyl modification of monolayer black phosphorus for stable photocatalytic carbon dioxide conversion. Appl. Catal. B Environ., 2020, 269:118760.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
CHEN XIAO-YU, ZHOU YONG, LIU QI, et al. Ultrathin, single-crystal WO3 nanosheets by two-dimensional oriented attachment toward enhanced photocatalystic reduction of CO2 into hydrocarbon fuels under visible light. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2012, 4(7):3372-3377.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
JIAO XING-CHEN, LI XIAO-DONG, JIN XIU-YU, et al. Partially oxidized SnS2 atomic layers achieving efficient visible- light-driven CO2 reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(49):18044-18051.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
LIU QI, ZHOU YONG, KOU JIAHUI, et al. High-yield synthesis of ultralong and ultrathin Zn2GeO4 nanoribbons toward improved photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into renewable hydrocarbon fuel. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(41):14385-14387.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
LI PING, ZHOU YONG, TU WEN-GUANG, et al. Direct growth of Fe2V4O13 nanoribbons on a stainless-steel mesh for visible-light photoreduction of CO2 into renewable hydrocarbon fuel and degradation of gaseous isopropyl alcohol. ChemPlusChem, 2013, 78(3):274-278.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
ZHOU YONG, TIAN ZHONG-PING, ZHAO ZONG-YAN, et al. High-yield synthesis of ultrathin and uniform Bi2WO6 square nanoplates benefitting from photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into renewable hydrocarbon fuel under visible light. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2011, 3(9):3594-3601.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
SU JUAN, LI GUO-DONG, LI XIN-HAO, et al. 2D/2D heterojunctions for catalysis. Adv. Sci., 2019, 6(7):1801702.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
WANG SI-BO, GUAN BU YUAN, WEN XIONG, et al. Construction of ZnIn2S4-In2O3 hierarchical tubular heterostructures for efficient CO2 photoreduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140:5037-5040.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
ZHOU YANG-EN, ZHANG YONG-FAN, LIN MOU-SHENG, et al. Monolayered Bi2WO6 nanosheets mimicking heterojunction interface with open surfaces for photocatalysis. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6:8340.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
TU WEN-GUANG, ZHOU YONG, FENG SHI-CHAO, et al. Hollow spheres consisting of Ti0.91O2/CdS nanohybrids for CO2 photofixation. Chem. Commun., 2015, 51(69):13354-13357.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
GAO WA, WANG LU, GAO CHAO, et al. Exquisite design of porous carbon microtubule-scaffolding hierarchical In2O3-ZnIn2S4 heterostructures toward efficient photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into CO. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(27):14676-14681.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
SURENDAR TONDA, SANTOSH KUMAR, MONIKA BHARDWAJ, et al. g-C3N4/NiAl-LDH 2D/2D hybrid heterojunction for high-performance photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into renewable fuels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10:2667-2678.
DOI URL |
| [49] | 韩布兴. 直接和间接Z-型异质结耦合的高效CO2光催化还原系统. 物理化学学报, 2021, 37(5):2011071. |
| [50] |
HAN QIU-TONG, LI LIANG, GAO WA, et al. Elegant construction of ZnIn2S4/BiVO4 hierarchical heterostructures as direct Z-scheme photocatalysts for efficient CO2 photoreduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(13):15092-15100.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
YANG YONG, WU JIA-JIA, XIAO TING-TING, et al. Urchin-like hierarchical CoZnAl-LDH/RGO/g-C3N4 hybrid as a Z-Scheme photocatalyst for efficient and selective CO2 reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ., 2019, 255:117771.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
JO WAN-KUEN, KUMAR SANTOSH, ESLAVA SALVADOR, et al. Construction of Bi2WO6/RGO/g-C3N4 2D/2D/2D hybrid Z-scheme heterojunctions with large interfacial contact area for efficient charge separation and high-performance photoreduction of CO2 and H2O into solar fuels. Appl. Catal. B Environ., 2018, 239:586-598.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
TU WEN-GUAG, ZHOU YONG, LIU QI, et al. Robust hollow spheres consisting of alternating titania nanosheets and graphene nanosheets with high photocatalytic activity for CO2 conversion into renewable fuels. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2012, 22(6):1215-1221.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
FENG SHI-CHAO, CHEN XIAO-YU, ZHOU YONG, et al. Na2V6O16·xH2O nanoribbons: large-scale synthesis and visible- light photocatalytic activity of CO2 into solar fuels. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(3):1896-1900.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
CAO SHAO-WEN, SHEN BAO-JIA, TONG TONG, et al. 2D/2D heterojunction of ultrathin MXene / Bi2WO6 nanosheets for improved photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28:1800136.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
LI LIANG, YANG YONG, YANG LIU-QING, et al. 3D hydrangea-like InVO4/Ti3C2Tx hierarchical heterosystem collaborating with 2D/2D interface interaction for enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction. ChemNanoMat, 2021, 7(7):815-823.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
WANG MENG, HAN QIU-TONG, ZHOU YONG, et al. TiO2 nanosheet-anchoring Au nanoplates: high-energy facet and wide spectra surface plasmon-promoting photocatalytic efficiency and selectivity for CO2 reduction. RSC Adv., 2016, 6(85):81510-81516
DOI URL |
| [58] |
XIONG JUN, DI JUN, XIA JIE-XIANG, et al. Surface defect engineering in 2D nanomaterials for photocatalysis. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28:1801983.
DOI URL |
| [59] | 李景虹. 类水滑石材料的缺陷调控对光催化CO2 还原产物的选择性. 科学通报, 2019, 64(31):3151-3152. |
| [60] |
LIANG LIANG, LI XIAO-DONG, SUN YONG-FU, et al. Infrared light-driven CO2 overall splitting at room temperature. Joule, 2018, 2:1004-1016.
DOI URL |
| [1] | DING Ling, JIANG Rui, TANG Zilong, YANG Yunqiong. MXene: Nanoengineering and Application as Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | YANG Zhuo, LU Yong, ZHAO Qing, CHEN Jun. X-ray Diffraction Rietveld Refinement and Its Application in Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | CHEN Qiang, BAI Shuxin, YE Yicong. Highly Thermal Conductive Silicon Carbide Ceramics Matrix Composites for Thermal Management: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | LIN Junliang, WANG Zhanjie. Research Progress on Ferroelectric Superlattices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [5] | NIU Jiaxue, SUN Si, LIU Pengfei, ZHANG Xiaodong, MU Xiaoyu. Copper-based Nanozymes: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [6] | YUAN Jingkun, XIONG Shufeng, CHEN Zhangwei. Research Trends and Challenges of Additive Manufacturing of Polymer-derived Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [7] | DU Jianyu, GE Chen. Recent Progress in Optoelectronic Artificial Synapse Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [8] | YANG Yang, CUI Hangyuan, ZHU Ying, WAN Changjin, WAN Qing. Research Progress of Flexible Neuromorphic Transistors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [9] | YOU Junqi, LI Ce, YANG Dongliang, SUN Linfeng. Double Dielectric Layer Metal-oxide Memristor: Design and Applications [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [10] | CHEN Kunfeng, HU Qianyu, LIU Feng, XUE Dongfeng. Multi-scale Crystallization Materials: Advances in in-situ Characterization Techniques and Computational Simulations [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [11] | ZHANG Chaoyi, TANG Huili, LI Xianke, WANG Qingguo, LUO Ping, WU Feng, ZHANG Chenbo, XUE Yanyan, XU Jun, HAN Jianfeng, LU Zhanwen. Research Progress of ScAlMgO4 Crystal: a Novel GaN and ZnO Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [12] | QI Zhanguo, LIU Lei, WANG Shouzhi, WANG Guogong, YU Jiaoxian, WANG Zhongxin, DUAN Xiulan, XU Xiangang, ZHANG Lei. Progress in GaN Single Crystals: HVPE Growth and Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [13] | LIN Siqi, LI Airan, FU Chenguang, LI Rongbing, JIN Min. Crystal Growth and Thermoelectric Properties of Zintl Phase Mg3X2 (X=Sb, Bi) Based Materials: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [14] | LIU Yan, ZHANG Keying, LI Tianyu, ZHOU Bo, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Electric-field Assisted Joining Technology for the Ceramics Materials: Current Status and Development Trend [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 113-124. |
| [15] | XIE Bing, CAI Jinxia, WANG Tongtong, LIU Zhiyong, JIANG Shenglin, ZHANG Haibo. Research Progress of Polymer-based Multilayer Composite Dielectrics with High Energy Storage Density [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||