
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (12): 1305-1315.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210157
Special Issue: 【生物材料】肿瘤治疗; 【能源环境】金属有机框架材料
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Yuwei1,2( ), CHEN Jiajie2, TIAN Zhengfang3, ZHU Min1(
), CHEN Jiajie2, TIAN Zhengfang3, ZHU Min1( ), ZHU Yufang2(
), ZHU Yufang2( )
)
Received:2021-03-12
Revised:2021-04-15
Published:2021-12-20
Online:2021-06-01
Contact:
ZHU Min, associate professor. E-mail: mzhu@usst.edu.cn;ZHU Yufang, professor. E-mail:zjf2412@163.com
About author:WANG Yuwei (1993-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 676627664@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Yuwei, CHEN Jiajie, TIAN Zhengfang, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Potassium Ferrate-loaded Porphyrin-based (VI) Metal-organic Frameworks for Combined Photodymanic and Chemodynamic Tumor Therapy[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1305-1315.
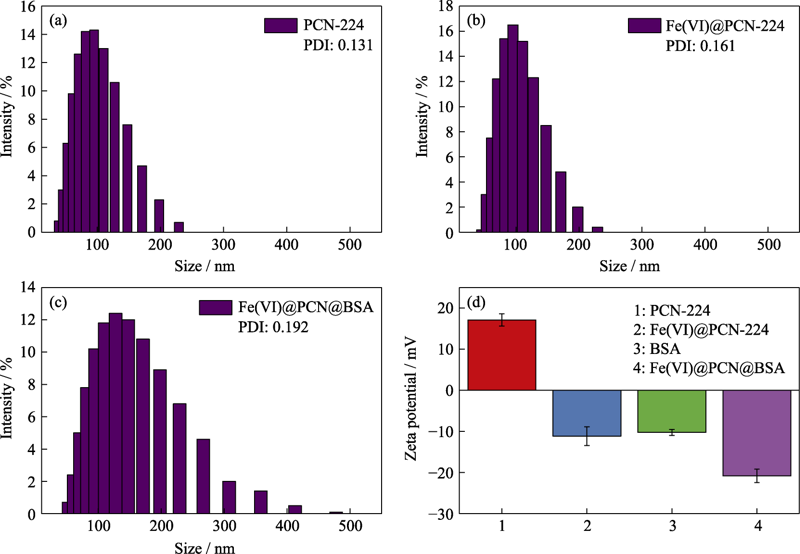
Fig. 3 DLS size distributions of (a) PCN-224, (b) Fe(VI)@PCN-224 and (c) Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles, and (d) Zeta potentials of BSA, PCN-224, Fe(VI)@PCN, and Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles
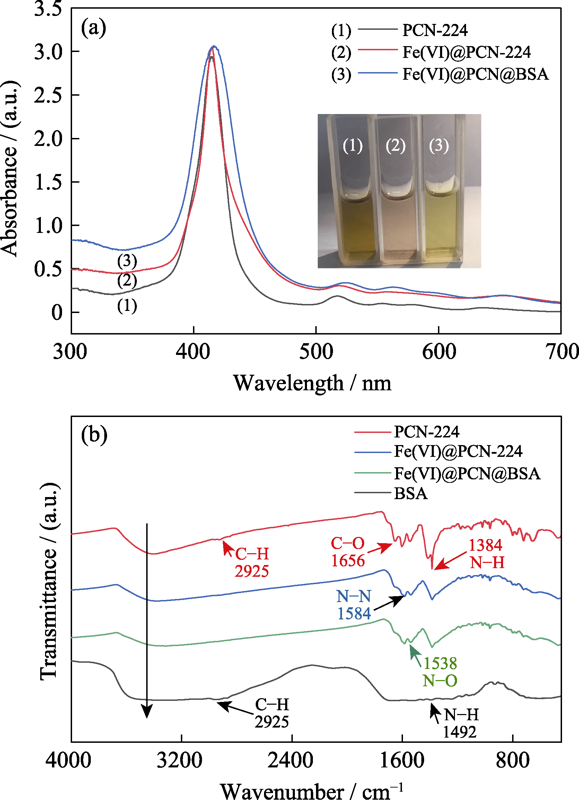
Fig. 5 (a) UV-Vis absorption spectra of PCN-224, Fe(VI)@PCN-224, and Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA suspensions (inset is pictures of the suspensions), and (b) Fourier transform infrared spectra of BSA, PCN-224, Fe(VI)@PCN-224, and Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles
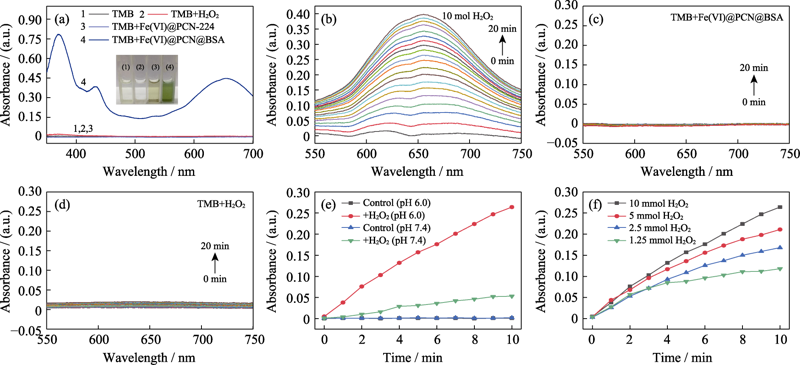
Fig. 6 Chemodynamic properties of Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles (a) UV-Vis absorption spectra of TMB solutions under different conditions with inset showing photographs of TMB solutions after reaction for 10 min under different conditions; (b) Absorbance changes of TMB solutions with time after adding Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles (50 µg/mL) into TMB solutions under pH 6.0 with H2O2 (10 mmol/L); (c) Absorbance changes of TMB solutions with time after adding Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles (50 µg/mL) into TMB solutions with pH 6.0; (d) Absorbance changes of TMB solutions with time under pH 6.0 with H2O2 (10 mmol/L); (e) Curves of absorbance at 652 nm versus time for TMB solutions with Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles under acidic (pH 6.0) or neutral (pH 7.4) conditions with or without H2O2; (f) Absorbance changes at 652 nm versus time for TMB solutions under pH 6.0 with different concentrations of H2O2 after adding the same amount of Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles
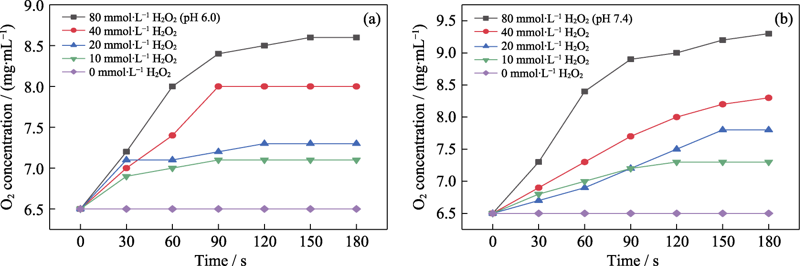
Fig. 7 Changes of dissolved O2 in NaAc solutions under (a) pH 6.0 and (b) pH 7.4 with different H2O2 concentrations after the addition of Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles (50 μg/mL)
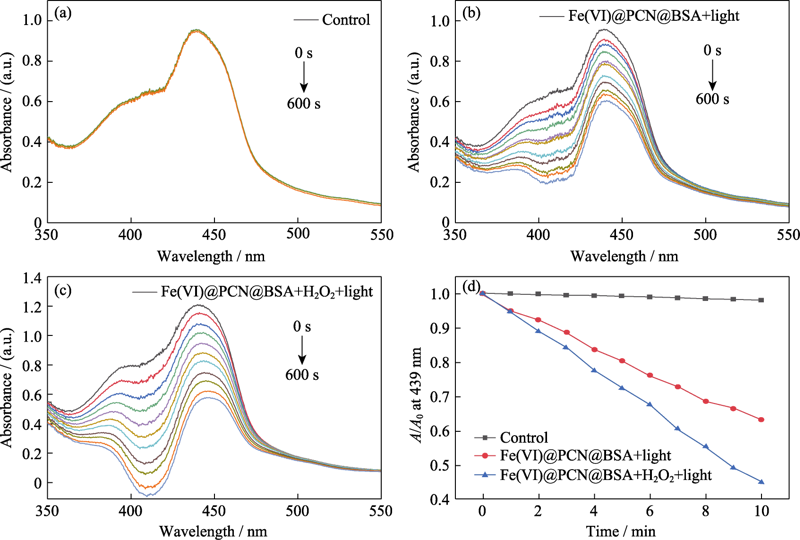
Fig. 8 (a-c) UV-Vis absorbance spectra of the DPBF solutions with Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles (50 μg/mL) and (d) absorbance changes of DPBF solutions at 439 nm for different groups (a) Without 660 nm laser irradiation; (b) With 660 nm laser irradiation; (c) With H2O2 (10 mmol/L) and 660 nm laser irradiation
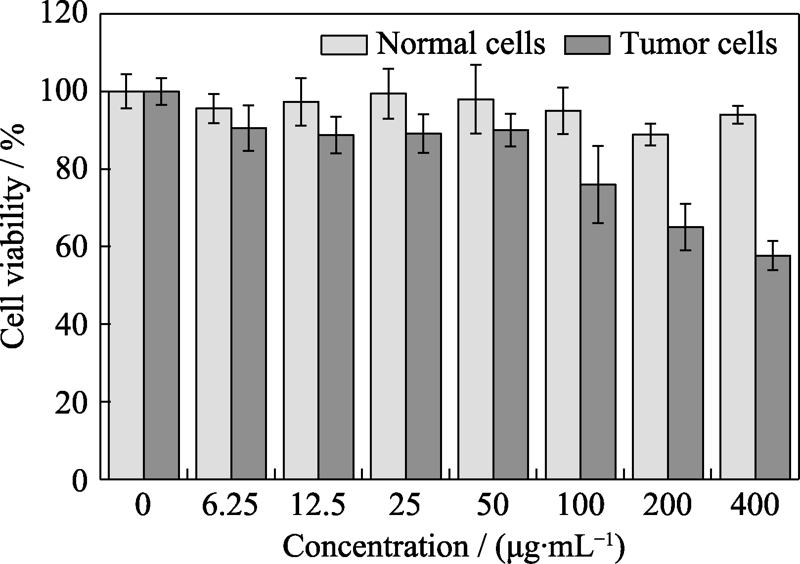
Fig. 9 Cell viabilities of MDA-MB-231 cells and human dermal fibroblasts after 24 h incubation with Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles at different concentrations
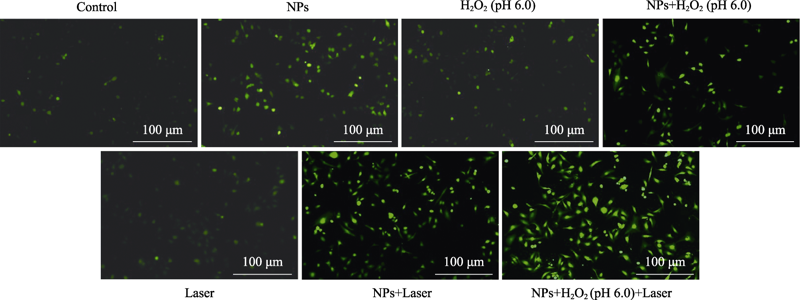
Fig. 10 Fluorescence images of MDA-MB-231 cells after different treatments for observing intracellular ROS Control: cells were cultured in normal medium; NPs: cells were cultured in normal medium with Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles; H2O2 (pH 6.0): cells were cultured in the medium at pH 6.0 with H2O2 (100 µmol/L); NPs+H2O2 (pH 6.0): cells were cultured in the medium at pH 6.0 with H2O2 (100 µmol/L) and Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles; Laser: 660 nm laser irradiation after cells culture in normal medium; NPs+Laser: 660 nm laser irradiation after cell culture in normal medium with Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles; NPs+H2O2 (pH 6.0)+Laser: 660 nm laser irradiation after cell culture in the medium at pH 6.0 with H2O2 (100 µmol/L) and Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles
| [1] |
LIU CHUANG, XING JIE, AKAKURU OZIOMA UDOCHUKWU, et al. Nanozymes-engineered metal-organic frameworks for catalytic cascades-enhanced synergistic cancer therapy. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(8): 5674-5682.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
TANG ZHONGMIN, LIU YTANTAN, HE MINGYUAN, et al. Chemodynamic therapy: tumor microenvironment-mediated fenton and fenton-like reaction. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(4): 946-956.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
MIN HUAN, WANG JING, QI YINGQIU, et al. Biomimetic metal-organic framework nanoparticles for cooperative combination of antiangiogenesis and photodynamic therapy for enhanced efficacy. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(15): 1808200.
DOI URL |
| [4] | DAI XINXIN, DU TING, HAN KAI. Engineering nanoparticles for optimized photodynamic therapy. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2019, 5(12): 6342-6354. |
| [5] |
CHANG MENGYU, WANG MAN, WANG MEIFANG, et al. A multifunctional cascade bioreactor based on hollow structured Cu2MoS4 for synergetic cancer chemo-dynamic therapy/starvation therapy/phototherapy/immunotherapy with remarkably enhanced efficacy. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(51): 1905271.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SCHUBERT JONAS, RADEKE CARMEN, FERY ANDREAS, et al. The role of pH, metal ions and their hydroxides in charge reversal of protein-coated nanoparticles. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2019, 21(21): 11011-11018.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZENG JINYUE, ZHANG MINGKANG, PENG MENGYUN, et al. Porphyrinic metal-organic frameworks coated gold nanorods as a versatile nanoplatform for combined photodynamic/photothermal/ chemotherapy of tumor. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(8): 1705451.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHEN JIAJIE, LIU JIAXING, HU YAPING, et al. Metal-organic framework-coated magnetite nanoparticles for synergistic magnetic hyperthermia and chemotherapy with pH-triggered drug release. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2019, 20(1): 1043-1054.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
CHEN JIAJIE, ZHU YUFANG, WU CHENGTIE, et al. Nanoplatform-based cascade engineering for cancer therapy. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(24): 9057-9094.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WANG ZHENG, ZHANG FAN, SHAO DAN, et al. Janus nanobullets combine photodynamic therapy and magnetic hyperthermia to potentiate synergetic anti-metastatic immunotherapy. Advanced Science, 2019, 6(22): 1901690.
DOI URL |
| [11] | ZHANG YA-RU, LIN RUN, LI HONG-JUN, et al. Strategies to improve tumor penetration of nano-medicines through nanoparticle design. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology, 2019, 11(1): e1519. |
| [12] |
PRASAD MINAKSHI, LAMBE UPENDRA P, BRAR BASANTI, et al. Nanotherapeutics: an insight into healthcare and multi- dimensional applications in medical sector of the modern world. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2018, 97: 1521-1537.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LU KUANGDA, AUNG THEIET, GUO NINING, et al. Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for therapeutic, imaging, and sensing applications. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(37): 1707634.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MAO FANGXIN, WEN LING, SUN CAIXIA, et al. Ultrasmall biocompatible Bi2Se3 nanodots for multimodal imaging-guided synergistic radiophotothermal therapy against cancer. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(12): 11145-11155.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WU CHUANDE, ZHAO MIN. Incorporation of molecular catalysts in metal-organic frameworks for highly efficient heterogeneous catalysis. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(14): 1605446.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
CHEN JIAJIE, LIN SHIYANG, ZHAO DOUDOU, et al. Palladium nanocrystals-engineered metalorganic frameworks for enhanced tumor inhibition by synergistic hydrogen/photodynamic therapy. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 31(4): 2006853.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG SHUNZHI, MCGUIRK C MICHAEL, D’AQUINO ANDREA, et al. Metal-organic framework nanoparticles. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(37): 1800202.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CHEN HUANG, ZHANG LINGYU, LIU SONG, et al. Double enhanced energy storage density via polarization gradient design in ferroelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based nanocomposites. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 411(18): 128585.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHANG YAN, WANG FAMING, LIU CHAOQUN, et al. Nanozymes decorated metal-organic frameworks for enhanced photodynamic therapy. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(1): 651-661.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
FU JINGKE, LI TAO, ZHU YINGCHUN, et al. Ultrasound- activated oxygen and ROS generation nanosystem systematically modulates tumor microenvironment and sensitizes sonodynamic therapy for hypoxic solid tumors. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(51): 1906195.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
NOVIKOV ALEXANDER S, KUZNETSOV MAXIM L, POMBEIRO ARMANDO J L, et al. Generation of HO• radical from hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by aqua complexes of the group III metals [M(H2O)n]3+ (M=Ga, In, Sc, Y, or La): a theoretical study. ACS Catalysis, 2013, 3(6): 1195-1208.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LIN WENXIN, GONG JIANQIU, FANG LIQUAN, et al. A photodynamic system based on endogenous bioluminescence for in vitro anticancer studies. Zeitschrift fur Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie, 2019, 645(18/19): 1161-1164.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
PARK JIHYE, JIANG QIN, FENG DAWEI, et al. Size-controlled synthesis of porphyrinic metal-organic framework and functionalization for targeted photodynamic therapy. Journal American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(10): 3518-3525.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHAO WEI, ZHAO YONGMEI, WANG QINGFU, et al. Remote light-responsive nanocarriers for controlled drug delivery: advances and perspectives. Small, 2019, 15(45): 1903060.
DOI URL |
| [25] | ElSHAMI FAWZYA I, RAMADAN ABD EL-MOTALEB M, IBRAHIM MOHAMED M, et al. Metformin containing nickel (II) complexes: synthesis, structural characterization, binding and kinetic interactions with BSA, antibacterial and in-vitro cytotoxicity studies. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2020, 34(3): e5437. |
| [26] |
NIU JIN, LIANG JINGJING, GAO ANG, et al. Micropore-confined amorphous SnO2 subnanoclusters as robust anode materials for Na-ion capacitors. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 7(38): 21711-21721.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZHOU BENQING, SONG JUN, WANG MENG, et al. BSA- bioinspired gold nanorods loaded with immunoadjuvant for the treatment of melanoma by combined photothermal therapy and immunotherapy. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(46): 21640-21647.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LIU WEI, WANG YONGMEI, LI YUHAO, et al. Fluorescent imaging-guided chemotherapy-and photodynamic dual therapy with nanoscale porphyrin metal-organic framework. Small, 2017, 13(17): 1603459.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SHOME ARPITA, RATHER ADIL MAJEED, MANNA UTTAM. Chemically reactive protein nanoparticles for synthesis of a durable and deformable superhydrophobic material. Nanoscale Advances, 2019, 1(5): 1746-1753.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZHANG YUAN, XING YANG, XIAN MING, et al. Folate- targeting and bovine serum albumin-gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a redox-responsive carrier for epirubicin release. New Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 43(6): 2694-2701.
DOI URL |
| [31] | GUO MINGZHEN, HE JIANAG, MA SHUANG, et al. Determination of Hg2+ based on the selective enhancement of peroxidase mimetic activity of hollow porous gold nanoparticles. Nano Brief Reports and Reviews, 2017, 12(4): 1750050. |
| [32] | FENG WEI, HAN XIUGUO, WANG RONGYAN, et al. Nanocatalysts-augmented and photothermal-enhanced tumor-specific sequential nanocatalytic therapy in both NIR-I and NIR-II biowindows. Advance Material, 2019, 31(5): 1805919. |
| [33] | ZHANG YONGHE, WANG BEILEI, ZHAO RUIBO, et al. Multifunctional nanoparticles as photosensitizer delivery carriers for enhanced photodynamic cancer therapy. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Application, 2020, 115: 111099. |
| [34] |
HANDE GUNDYZ, SAFACAN KONLEMEN, EENGIN U AKKAYA. Singlet oxygen probes: diversity in signal generation mechanisms yields a larger color palette. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2021, 429: 213641.
DOI URL |
| [35] | YIN SHENGYAN, SONG GUOSHENG, YANG YUE, et al. Persistent regulation of tumor microenvironment via circulating catalysis of MnFe2O4@metal-organic frameworks for enhanced photodynamic therapy. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(25): 2006853. |
| [36] | BAJAJ AVINASH, SAMANTA BAPPADITYA, YAN HAOHENG, et al. Stability, toxicity and differential cellular uptake of protein passivated-Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Chenistry, 2009, 19(35): 6328-6331. |
| [37] |
LIN LISEN, SONG JIBIN, SONG LIANG, et al. Simultaneous fenton-like ion delivery and glutathione depletion by MnO2-based nanoagent to enhance chemodynamic therapy. Angewandte Chemie- International Edition, 2018, 57(18): 4902-4906.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
TARPEY MARGARRT M, FRIDOVICH IRWIN. Methods of detection of vascular reactive species nitric oxide, superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and peroxynitrite. Circulation Research, 2001, 89(3): 224.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ETHIRAJAN MANIVANNAN, CHEN YIHUI, JOSHI PENNY, et al. The role of porphyrin chemistry in tumor imaging and photodynamic therapy. Chemical Society Reviews, 2011, 40(1): 340-362.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
CHEN JIAJIE, ZHU YUFANG, KASKEL STEFAN. Porphyrin- based metal-organic frameworks for biomedical applications. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2020, 60(10): 5010-5035.
DOI URL |
| [1] | CHEN Cheng, DING Jingxin, WANG Hui, WANG Deping. Nd-doped Mesoporous Borosilicate Bioactive Glass-ceramic Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1245-1258. |
| [2] | LIANG Fengqing, WEN Zhaoyin. MOF/Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Composite Polymer Electrolyte for Solid-state Lithium Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 332-336. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xincong,GUO Ke,PENG Lianlian,WU Jieyu,ZHANG Fumin,ZHU Weidong,FU Yanghe. Degradation of Dye Wastewater over NH2-UiO-66: Piezoelectrically Induced Mechano-Catalytic Effect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 1023-1028. |
| [4] | Shi-Qiang LUO, Chun-Man ZHENG, Wei-Wei SUN, Wei XIE, Jian-Huang KE, Shuang-Ke LIU, Xiao-Bin HONG, Yu-Jie LI, Jing XU. Controllable Preparation of Co-NC Nanoporous Carbon Derived from ZIF-67 for Advanced Lithium-sulfur Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(5): 502-508. |
| [5] | HAN Li, ZHANG Xiao-Min, WU De-Yong. MoS2 Quantum Dots Decorated NH2-MIL-125 Heterojunction: Preparation and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1205-1209. |
| [6] | WANG Xiang-Xue, YU Shu-Jun, WANG Xiang-Ke. Removal of Radionuclides by Metal-organic Framework-based Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(1): 17-26. |
| [7] | YUAN Bei-Bei, ZHOU Bei-Bei, ZHANG Yue-Biao, SHI Jian-Lin. Charge-switchable Metal-organic Framework for Size/Charge-selective Molecular Inclusions [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(3): 352-356. |
| [8] | HUA Cheng-Jiang, WANG Ming-Hui, LUAN Guo-You, LIU Yan, WU Hua. Rapid in situ Crystallization and Catalytic Performance of Cu3(BTC)2-based Film on Copper Mesh [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(5): 529-534. |
| [9] | GUO Yan-Rong, CHANG Wei, ZHANG Wen, WANG Hui. Photocatalytic Properties of MOF-derived ZnO/C, Ag/ZnO/C Porous Composite Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(12): 1321-1326. |
| [10] | DU Shu-Hui, LIU Ya-Guang, KONG Ling-Yin, ZHANG Jian, LIU Hai-Ou, ZHANG Xiong-Fu. Seeded Secondary Growth Synthesis of ZIF-8 Membranes Supported on α-Al2O3 Ceramic Tubes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(10): 1105-1111. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||