
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (4): 436-444.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210158
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
TANG Jieyin1,2( ), WANG Gang3,4, LIU Cong1,2, ZOU Xuenong3,4, CHEN Xiaofeng1,2(
), WANG Gang3,4, LIU Cong1,2, ZOU Xuenong3,4, CHEN Xiaofeng1,2( )
)
Received:2021-03-12
Revised:2021-04-08
Published:2022-04-20
Online:2021-04-30
Contact:
CHEN Xiaofeng, professor. E-mail: chenxf@scut.edu.cnAbout author:TANG Jieyin (1989-), female, Master. E-mail: 1720175343@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TANG Jieyin, WANG Gang, LIU Cong, ZOU Xuenong, CHEN Xiaofeng. Dentin Remineralization Induced by Micro-nano Bioactive Glass Spheres[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 436-444.
| Sample | SiO2 : CaO : P2O5 (molar ratio) | DDA/g | TEOS/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical | Measured | |||
| MNBGs-1 | 80 : 16 : 4 | 87.637 : 12.363 : 0 | 3 | 8 |
| MNBGs-2 | 86.289 : 13.696 : 0.015 | 6 | 16 | |
| MNBGs-3 | 89.071 : 10.875 : 0.054 | 6 | 24 | |
Table 1 Theoretical and measured chemical composition, reagent dosage of MNBGs with different particle sizes
| Sample | SiO2 : CaO : P2O5 (molar ratio) | DDA/g | TEOS/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical | Measured | |||
| MNBGs-1 | 80 : 16 : 4 | 87.637 : 12.363 : 0 | 3 | 8 |
| MNBGs-2 | 86.289 : 13.696 : 0.015 | 6 | 16 | |
| MNBGs-3 | 89.071 : 10.875 : 0.054 | 6 | 24 | |
| Samples | C/% | O/% | Ca/% | P/% | Ca/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without etching | 0 | 65.77 | 20.26 | 13.97 | 1.45 |
| With etching | 66.82 | 32.99 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.35 |
Table 2 Chemical components (molar percent) and Ca/P ratio on the surface of dentin before and after EDTA etching
| Samples | C/% | O/% | Ca/% | P/% | Ca/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without etching | 0 | 65.77 | 20.26 | 13.97 | 1.45 |
| With etching | 66.82 | 32.99 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.35 |
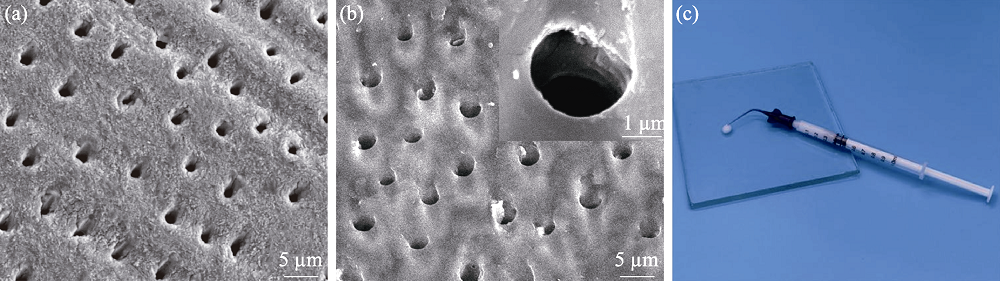
Fig. 3 SEM images of the dentin surface without (a) and with (b) EDTA-etching, magnified photo of dentin tubules (insert in (b)), and photo of bioactive glass paste (c)
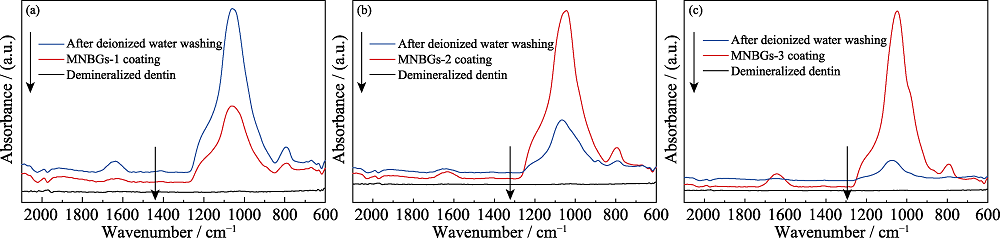
Fig. 5 ATR-FTIR spectra of demineralized dentin surface before and after coating with MNBGP, and after rinsing with water (a) MNBGP-1; (b) MNBGP-2; (c) MNBGP-3
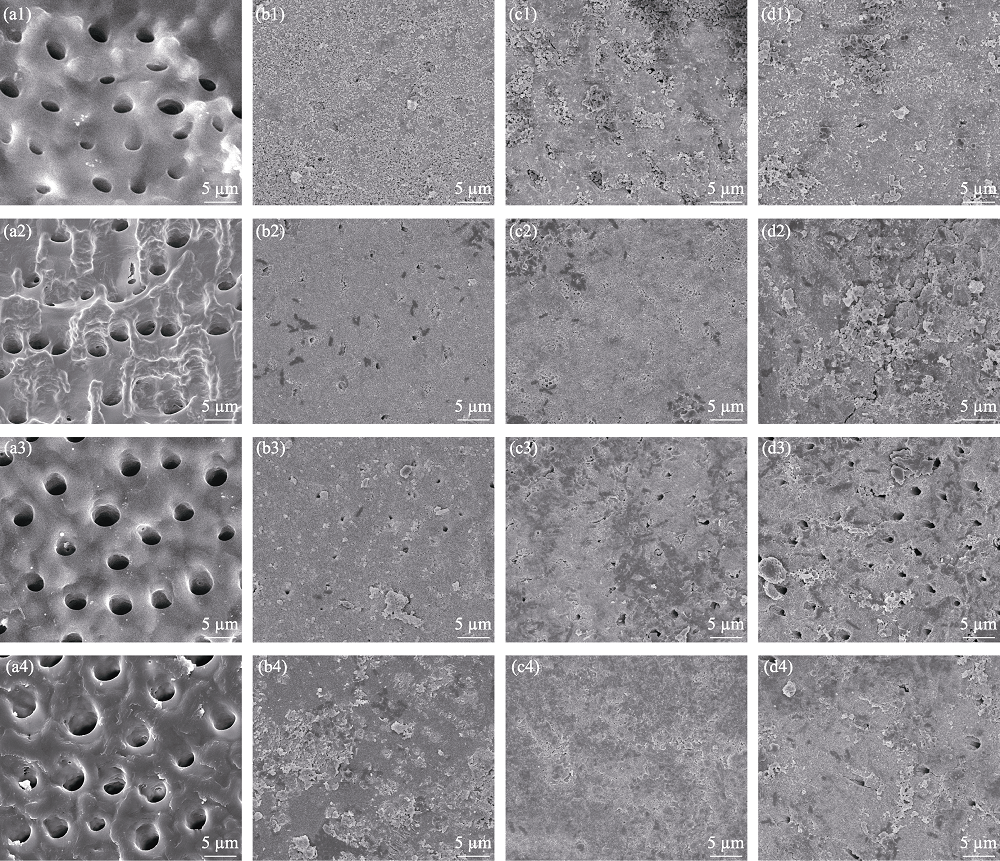
Fig. 6 SEM images of the surfaces of demineralized dentin slices without (a) (control) and with treatment by MNBGP-1 (b), MNBGP-2 (c), and MNBGP-3 (d) after soaking in AS for 1 d (a1-d1), 7 d (a2-d2), 14 d (a3-d3) and 28 d (a4-d4)

Fig. 7 SEM images of the longitudinal section of demineralized dentin samples without (a) (control) and with treatment by MNBGP-1 (b), MNBGP-2 (c), and MNBGP-3 (d) after soaking in AS for 1 d (a1-d1), 7 d (a2-d2), 14 d (a3-d3) and 28 d (a4-d4)
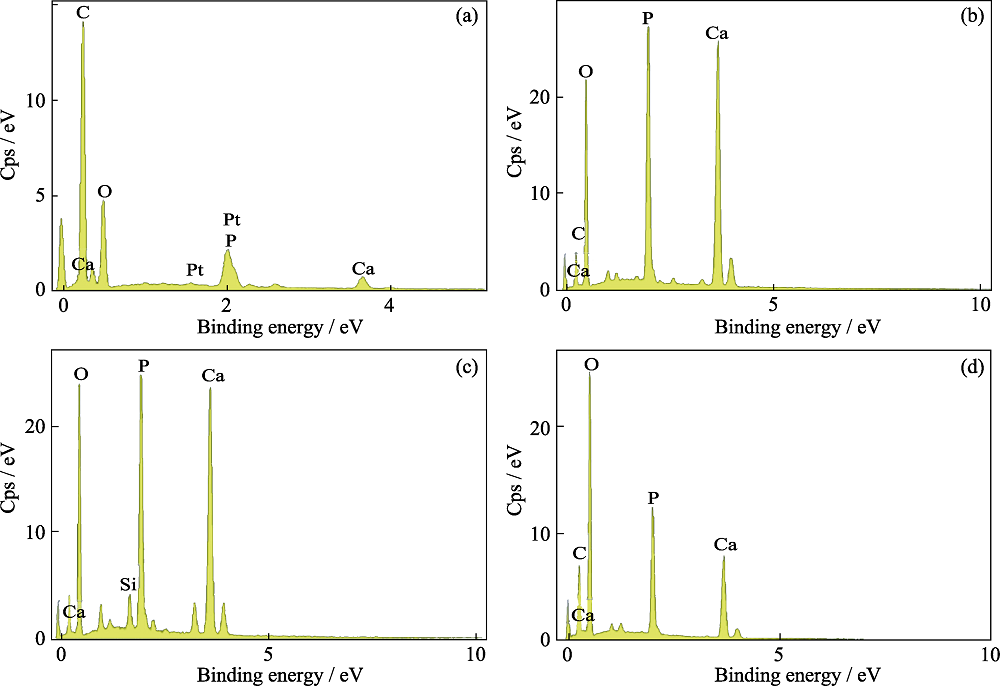
Fig. 8 EDS analyses of the surface of demineralized dentin slices without (a) (control) and with treatment by MNBGP-1 (b), MNBGP-2 (c), and MNBGP-3 (d) after soaking in AS for 28 d
| Sample | Ca/% | P/% | Ca/P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 2.49 | 1.82 | 1.37 |
| MNBGP-1 | 16.64 | 11.69 | 1.42 |
| MNBGP-2 | 18.37 | 12.97 | 1.42 |
| MNBGP-3 | 6.16 | 6.12 | 1.01 |
Table 3 Chemical components ( molar percent) and Ca/P ratio in molar on the surface of remineralized dentin
| Sample | Ca/% | P/% | Ca/P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 2.49 | 1.82 | 1.37 |
| MNBGP-1 | 16.64 | 11.69 | 1.42 |
| MNBGP-2 | 18.37 | 12.97 | 1.42 |
| MNBGP-3 | 6.16 | 6.12 | 1.01 |
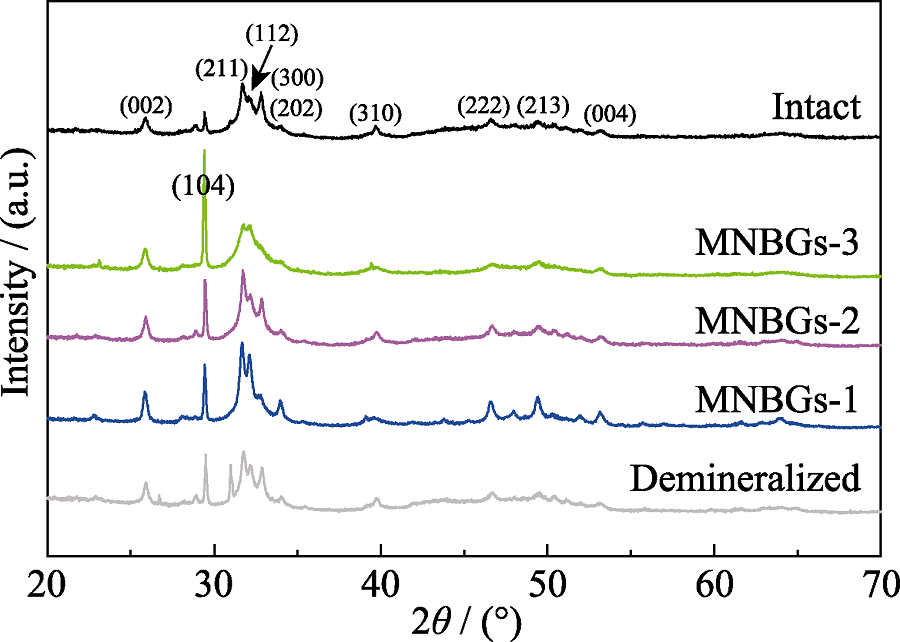
Fig. 9 XRD patterns of the surface of intact dentin, demineralized dentin and slices without treatment (control) and being treated with MNBGP after being soaked in AS for 28 d
| [1] |
HOLLAND G R, NARHI M N, ADDY M, et al. Guidelines for the design and conduct of clinical trials on dentine hypersensitivity. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 1997, 24(11): 808-813.
DOI URL |
| [2] | ADDY M, WEST N X. The role of toothpaste in the aetiology and treatment of dentine hypersensitivity. Monogr. Oral. Sci., 2013, 23: 75-87. |
| [3] |
ARNOLD W H, PRANGE M, NAUMOVA E A. Effectiveness of various toothpastes on dentine tubule occlusion. Journal of Dentistry, 2015, 43(4): 440-449.
DOI URL |
| [4] | BERKATHULLAH M, FAROOK M S, MAHMOUD O. The effectiveness of remineralizing agents on dentinal permeability. BioMed Research International, 2018, 2018: 4072815. |
| [5] |
BAINO F, HAMZEHLOU S, KARGOZAR S. Bioactive glasses: where are we and where are we going? Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 2018, 9(1):25.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
JONES J R. Review of bioactive glass: from Hench to hybrids. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(1): 4457-4486.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
SKALLEVOLD H E, ROKAYA D, KHURSHID Z, et al. Bioactive glass applications in dentistry. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(23):5960.
DOI URL |
| [8] | LITKOWSKI L, GREENSPAN D C. A clinical study of the effect of calcium sodium phosphosilicate on dentin hypersensitivity-proof of principle. J. Clin. Dent., 2010, 21(3): 77-81. |
| [9] | GENDREAU L, BARLOW A P, MASON S C. Overview of the clinical evidence for the use of NovaMin in providing relief from the pain of dentin hypersensitivity. J. Clin. Dent., 2011, 22(3): 90-95. |
| [10] |
HOFFMAN D A, CLARK A E, RODY W J, et al. A prospective randomized clinical trial into the capacity of a toothpaste containing NovaMin to prevent white spot lesions and gingivitis during orthodontic treatment. Progress in Orthodontics, 2015, 16(1):25.
DOI URL |
| [11] | FAROOQ I, MAJEED A, ALSHWAIMI E, et al. Efficacy of a novel fluoride containing bioactive glass based dentifrice in remineralizing artificially induced demineralization in human enamel. Fluoride, 2019, 52(3): 447-455. |
| [12] |
WANG Z, SA Y, SAURO S, et al. Effect of desensitising toothpastes on dentinal tubule occlusion: a dentine permeability measurement and SEM in vitro study. Journal of Dentistry, 2010, 38(5): 400-410.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
VOLLENWEIDER M, BRUNNER T J, KNECHT S, et al. Remineralization of human dentin using ultrafine bioactive glass particles. Acta Biomater., 2007, 3(6): 936-943.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
CURTIS A R, WEST N X, SU B. Synthesis of nanobioglass and formation of apatite rods to occlude exposed dentine tubules and eliminate hypersensitivity. Acta Biomater., 2010, 6(9): 3740-3746.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
SHENG X Y, GONG W Y, HU Q, et al. Mineral formation on dentin induced by nano-bioactive glass. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2016, 27(9): 1509-1514.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
FERNANDES H R, GADDAM A, REBELO A, et al. Bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics for healthcare applications in bone regeneration and tissue engineering. Materials, 2018, 11(12):2530.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHENG K, BOCCACCINI A R. Sol-Gel processing of bioactive glass nanoparticles: a review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 249: 363-373.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
HU Q, CHEN X, ZHAO N, et al. Fabrication and characterization of dodecylamine derived monodispersed mesoporous bioactive glass sub-micron spheres. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2014, 69(1): 9-16.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LIANG K, GAO Y, LI J, et al. Effective dentinal tubule occlusion induced by polyhydroxy-terminated PAMAM dendrimer in vitro. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(82): 43496-43503.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
GAL J Y, FOVET Y, ADIB-YADZI M. About a synthetic saliva for in vitro studies. Talanta, 2001, 53(6): 1103-1115.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SCHUMACHER M, HABIBOVIC P, van RIJT S. Mesoporous bioactive glass composition effects on degradation and bioactivity. Bioactive Materials, 2021, 6(7): 1921-1931.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHANG X, ZENG D, LI N, et al. Large-pore mesoporous Ca-Si-based bioceramics with high in vitro bioactivity and protein adsorption capability for bone tissue regeneration. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2016, 4(22): 3916-3924.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
XU Z, NEOH K G, KISHEN A. A biomimetic strategy to form calcium phosphate crystals on type I collagen substrate. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2010, 30(6): 822-826.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHAO F, ZHANG W, FU X, et al. Fabrication and characterization of bioactive glass/alginate composite scaffolds by a self-crosslinking processing for bone regeneration. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(94): 91201-91208.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
XU C, WANG X, ZHOU J, et al. Bioactive tricalcium silicate/alginate composite bone cements with enhanced physicochemical properties. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 2018, 106(1): 237-244.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
MARELLI B, GHEZZI C E, BARRALET J E, et al. Three-dimensional mineralization of dense nanofibrillar collagen- bioglass hybrid scaffolds. Biomacromolecules, 2010, 11(6): 1470-1479.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
FAN Y, SUN Z, MORADIAN-OLDAK J. Controlled remineralization of enamel in the presence of amelogenin and fluoride. Biomaterials, 2009, 30(4): 478-483.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
DAI L L, MEI M L, CHU C H, et al. Remineralizing effect of a new strontium-doped bioactive glass and fluoride on demineralized enamel and dentine. Journal of Dentistry, 2021, 108: 103633.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WU Y, TANG L, ZHANG Q, et al. A novel synthesis of monodispersed bioactive glass nanoparticles via ultrasonic-assisted surfactant-free microemulsion approach. Materials Letters, 2021, 285: 129053.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
NIRMALA DEVI M, SANJIV RAJ K, SUBRAMANIAN V K. Synergistic effects of magnesium and EDTA on polymorphism and morphology of CaCO3 and its influence on scale. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2021, 564: 126108.
DOI URL |
| [1] | MA Lei, HUANG Yi, DENG Hao, YIN Hang, TIAN Qiang, YAN Minghao. Removal of Uranium (VI) from Acidic Aqueous Solution by Fluorapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 395-403. |
| [2] | CHEN Yaling, SHU Song, WANG Shaoxin, LI Jianjun. Mn-HAP SCR Catalyst: Preparation and Sulfur Resistance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1065-1072. |
| [3] | ZHU Yutong, TAN Peijie, LIN Hai, ZHU Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingdong. Injectable Hyaluronan/Hydroxyapatite Composite: Preparation, Physicochemical Property and Biocompatibility [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 981-990. |
| [4] | LIN Ziyang, CHANG Yuchen, WU Zhangfan, BAO Rong, LIN Wenqing, WANG Deping. Different Simulated Body Fluid on Mineralization of Borosilicate Bioactive Glass-based Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 745-752. |
| [5] | WU Zhongcao, HUAN Zhiguang, ZHU Yufang, WU Chengtie. 3D Printing and Characterization of Microsphere Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 601-607. |
| [6] | WU Yonghao, LI Xiangfeng, ZHU Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingdong. Construction of Hydroxyapatite Nanoceramics with High Mechanical Strength and Efficiency in Promoting the Spreading and Viability of Osteoblasts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 552-560. |
| [7] | SONG Keke, HUANG Hao, LU Mengjie, YANG Anchun, WENG Jie, DUAN Ke. Hydrothermal Preparation and Characterization of Zn, Si, Mg, Fe Doped Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1091-1096. |
| [8] | SHAO Yueting, ZHU Yingjie, DONG Liying, CAI Anyong. Nanocomposite “Xuan Paper” Made from Ultralong Hydroxyapatite Nanowires and Cellulose Fibers and Its Anti-mildew Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 107-112. |
| [9] | SUN Tuanwei,ZHU Yingjie. One-step Solvothermal Synthesis of Strontium-doped Ultralong Hydroxyapatite Nanowires [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(6): 724-728. |
| [10] | LIU Ziyang, GENG Zhen, LI Zhaoyang. Preparing Biomedical CaCO3/HA Composite with Oyster Shell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 601-607. |
| [11] | DAI Zhao,WANG Ming,WANG Shuang,LI Jing,CHEN Xiang,WANG Da-Lin,ZHU Ying-Chun. Zirconia Reinforced Trace Element Co-doped Hydroxyapatite Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 179-186. |
| [12] | FU Ya-Kang,WENG Jie,LIU Yao-Wen,ZHANG Ke-Hong. hBMP-2 Contained Composite Coatings on Titanium Mesh Surface: Preparation and hBMP-2 Release [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 173-178. |
| [13] | HU Yaping, TIAN Zhengfang, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Controllable Preparation and in Vitro Bioactivity of Bioglass Microspheres via Spray Drying Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1268-1276. |
| [14] | ZHOU Zihang, WANG Qun, GE Xiang, LI Zhaoyang. Strontium Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Simulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1283-1289. |
| [15] | XIAO Wen-Qian,ZHANG Jing,LI Ke-Jiang,ZOU Xin-Yu,CAI Yu-Dong,LI Bo,LIU Xue,LIAO Xiao-Ling. Litchi-like Superparamagnetic Hydroxyapatite Microspheres with Hierarchically Mesoporous Microspheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 925-932. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||