
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (10): 1103-1110.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210091
Special Issue: 【结构材料】陶瓷基复合材料
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Junmin1,2,3( ), CHEN Xiaowu1,2(
), CHEN Xiaowu1,2( ), LIAO Chunjin1,2, GUO Feiyu1,2,3, YANG Jinshan1,2, ZHANG Xiangyu1,2, DONG Shaoming1,2(
), LIAO Chunjin1,2, GUO Feiyu1,2,3, YANG Jinshan1,2, ZHANG Xiangyu1,2, DONG Shaoming1,2( )
)
Received:2021-02-09
Revised:2021-03-24
Published:2021-10-20
Online:2021-04-05
Contact:
CHEN Xiaowu, lecturer. E-mail: xwchen@mail.sic.ac.cn; DONG Shaoming, professor. E-mail: smdong@mail.sic.ac.cn
About author:ZHANG Junmin(1996–), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: zhangjm2@shanghaitech.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHANG Junmin, CHEN Xiaowu, LIAO Chunjin, GUO Feiyu, YANG Jinshan, ZHANG Xiangyu, DONG Shaoming. Optimizing Microstructure and Properties of SiCf/SiC Composites Prepared by Reactive Melt Infiltration[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1103-1110.
| Preform | Preparing process | Further impregnation | Composites |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-1 | Slurry impregnation | None | Com-1 |
| Pre-2 | Slurry impregnation | Pure PF | Com-2 |
| Pre-3 | Slurry impregnation | Polymer blend | Com-3 |
| Preform | Preparing process | Further impregnation | Composites |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-1 | Slurry impregnation | None | Com-1 |
| Pre-2 | Slurry impregnation | Pure PF | Com-2 |
| Pre-3 | Slurry impregnation | Polymer blend | Com-3 |
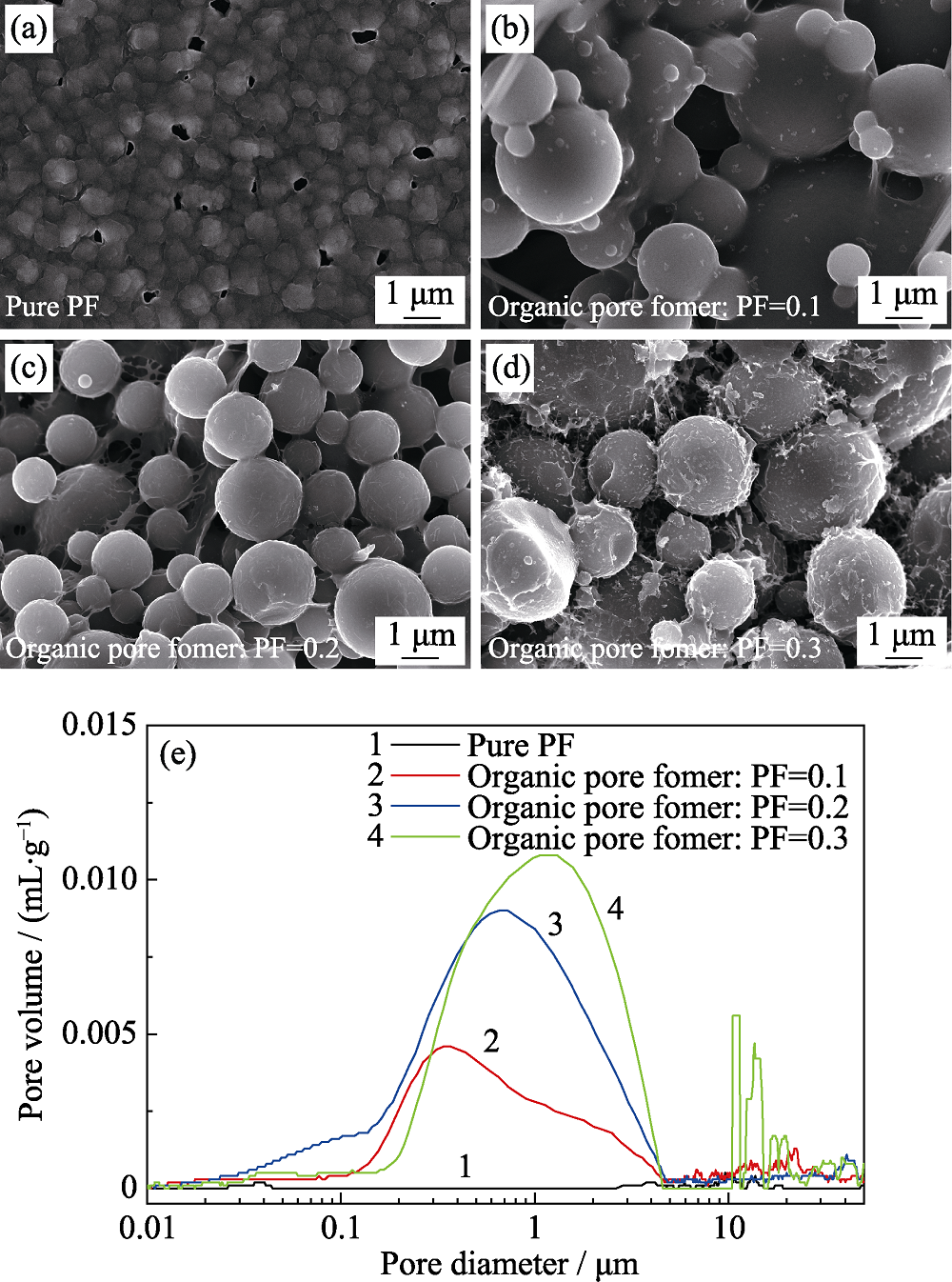
Fig. 2 SEM images of pyrolytic carbon prepared with different organic pore former contents ((a) Pure PF; (b) Organic pore former: PF=0.1; (c) Organic pore former: PF=0.2, (d) Organic pore former: PF=0.3); (e) Pore size distribution of pyrolytic carbon
| Composites | Density/(g·cm-3) | Open porosity/% | Flexural strength/MPa | Elastic modulus/GPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Com-1 | (2.41±0.08) | (10.08±0.50) | (96.04±9.50) | (42.53±0.73) |
| Com-2 | (2.57±0.08) | (8.39±0.58) | (176.76±3.78) | (67.55±0.46) |
| Com-3 | (2.61±0.05) | (7.92±0.61) | (200.50±7.33) | (79.19±0.65) |
| Composites | Density/(g·cm-3) | Open porosity/% | Flexural strength/MPa | Elastic modulus/GPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Com-1 | (2.41±0.08) | (10.08±0.50) | (96.04±9.50) | (42.53±0.73) |
| Com-2 | (2.57±0.08) | (8.39±0.58) | (176.76±3.78) | (67.55±0.46) |
| Com-3 | (2.61±0.05) | (7.92±0.61) | (200.50±7.33) | (79.19±0.65) |
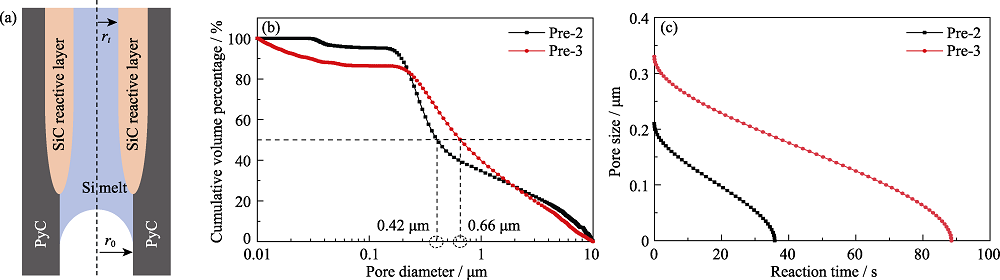
Fig. 8 (a) Schematic of reaction layer generated during the RMI, (b) curves of cumulative volume percentage vs pore diameter of preforms, and (c) variation of pore radius with infiltration time for preforms
| [1] |
ZHU Y, WANG S, LI W, et al. Preparation of carbon fiber-reinforced zirconium carbide matrix composites by reactive melt infiltration at relative low temperature. Scripta Materialia, 2012, 67(10):822-825.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
WANG J, LIN M, XU Z, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of C/C-SiC composites fabricated by a rapid processing method. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2009, 29(14):3091-3097.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
TIAN J T, SHOBU K. Fabrication of silicon carbide-mullite composite by melt infiltration. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2003, 86(1):39-42.
DOI URL |
| [4] | SINGH M, ALMAN D E, HAWK J A. Microstructure and Wear Behavior of SiC-based Composites Fabricated by Melt Infiltration, in: Alman D E, HAWK J A., SIMMONS J W (Eds.). Roll of Characterization in Understanding Environmental Degradation of Materials, ASM International, 1998: 169-175. |
| [5] |
WANG Y X, TAN S H, JIANG D L. The effect of porous carbon preform and the infiltration process on the properties of reaction- formed SiC. Carbon, 2004, 42(8/9):1833-1839.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
JIANG S Z, XIONG X, CHEN Z K, et al. Influence factors of C/C-SiC dual matrix composites prepared by reactive melt infiltration. Materials & Design, 2009, 30(9):3738-3742.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WANG D, DONG S M, ZHOU H J, et al. Fabrication and microstructure of 3D Cf/ZrC-SiC composites: through RMI method with ZrO2 powders as pore-making agent. Ceram. Int., 2016, 42(6):6720-6727.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ROGER J, CHOLLON G. Mechanisms and kinetics during reactive infiltration of molten silicon in porous graphite. Ceram. Int., 2019, 45(7):8690-8699.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
PILLLEE S, KIYOON H, SOOPARK J, et al. Processing and properties of SiC and SiC/SiC composite materials by melt infiltration process. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 2003, 17(8):1833-1838.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WASHBURN E W. The dynamics of capillary flow. Physical Review, 1921, 17(3):273-283.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
BOUGIOURI V, VOYTOVYCH R, ROJO-CALDERON N, et al. The role of the chemical reaction in the infiltration of porous carbon by NiSi alloys. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 54(11):1875-1878.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KUMAR S, KUMAR A, SHUKLA A, et al. Capillary infiltration studies of liquids into 3D-stitched C-C preforms Part A: Internal pore characterization by solvent infiltration, mercury porosimetry, and permeability studies. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2009, 29(12):2643-2650.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
KUMAR S, KUMAR A, DEVI R, et al. Capillary infiltration studies of liquids into 3D-stitched C-C preforms Part B: Kinetics of silicon infiltration. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2009, 29(12):2651-2657.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG Y, ZHU X, ZHANG L, et al. C/C-SiC-ZrC composites fabricated by reactive melt infiltration with Si0.87Zr0.13 alloy. Ceram. Int., 2012, 38(5):4337-4343.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
CHEN X W, NI D W, KAN Y M, et al. Reaction mechanism and microstructure development of ZrSi2 melt-infiltrated Cf/SiC-ZrC- ZrB2 composites: the influence of preform pore structures. Journal of Materiomics, 2018, 4(3):266-275.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
CHEN X W, FENG Q, KAN Y M, et al. Effects of preform pore structure on infiltration kinetics and microstructure evolution of RMI-derived Cf/SiC-ZrC-ZrB2 composite. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 40(7):2683-2690.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHONG Q, ZHANG X Y, DONG S M, et al. Reactive melt infiltrated Cf/SiC composites with robust matrix derived from novel engineered pyrolytic carbon structure. Ceram. Int., 2017, 43(7):5832-5836.
DOI URL |
| [18] | LEE S P, PARK J S, KATOH Y, et al. Process, microstructure and flexural properties of reaction sintered Tyranno SA/SiC composites. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2002, 307:1191-1195. |
| [19] |
ZHAO Y Y, XIA H Y, TANG R, et al. A low cost preparation of C/SiC composites by infiltrating molten Si into gelcasted pure porous carbon preform. Ceram. Int., 2015, 41(5):6478-6487.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SINGH M, FARMER S C. Morphological characterization of microporous carbon materials. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1997, 16(11):946-949.
DOI URL |
| [21] | LEVENSPIEL O. Ingenieria de las Reacciones. 2nd ed. Wiley (ed.). Barcelona: Revertre, 1978. |
| [22] |
HON M H, DAVIS R F. Self-diffusion of C-14 in polycrystalline beta-sic. J. Mater. Sci., 1979, 14(10):2411-2421.
DOI URL |
| [1] | HE Danqi, WEI Mingxu, LIU Ruizhi, TANG Zhixin, ZHAI Pengcheng, ZHAO Wenyu. Heavy-Fermion YbAl3 Materials: One-step Synthesis and Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [2] | WU Shuang, GOU Yanzi, WANG Yongshou, SONG Quzhi, ZHANG Qingyu, WANG Yingde. Effect of Heat Treatment on Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Domestic KD-SA SiC Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 569-576. |
| [3] | ZHANG Ye, ZENG Yuping. Progress of Porous Silicon Nitride Ceramics Prepared via Self-propagating High Temperature Synthesis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 853-864. |
| [4] | XIA Qian, SUN Shihao, ZHAO Yiliang, ZHANG Cuiping, RU Hongqiang, WANG Wei, YUE Xinyan. Effect of Boron Carbide Particle Size Distribution on the Microstructure and Properties of Reaction Bonded Boron Carbide Ceramic Composites by Silicon Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 636-642. |
| [5] | HONG Du, NIU Yaran, LI Hong, ZHONG Xin, ZHENG Xuebin. Tribological Properties of Plasma Sprayed TiC-Graphite Composite Coatings [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 643-650. |
| [6] | XU Puhao, ZHANG Xiangzhao, LIU Guiwu, ZHANG Mingfen, GUI Xinyi, QIAO Guanjun. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SiC Joint Brazed by Al-Ti Alloys as Filler Metal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 683-690. |
| [7] | HUANG Longzhi, YIN Jie, CHEN Xiao, WANG Xinguang, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Selective Laser Sintering of SiC Green Body with Low Binder Content [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(3): 347-352. |
| [8] | WU Xishi, ZHU Yunzhou, HUANG Qing, HUANG Zhengren. Effect of Pore Structure of Organic Resin-based Porous Carbon on Joining Properties of Cf/SiC Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1275-1280. |
| [9] | SUN Luchao, ZHOU Cui, DU Tiefeng, WU Zhen, LEI Yiming, LI Jialin, SU Haijun, WANG Jingyang. Directionally Solidified Al2O3/Er3Al5O12 and Al2O3/Yb3Al5O12 Eutectic Ceramics Prepared by Optical Floating Zone Melting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 652-658. |
| [10] | HUANG Xinyou, LIU Yumin, LIU Yang, LI Xiaoying, FENG Yagang, CHEN Xiaopu, CHEN Penghui, LIU Xin, XIE Tengfei, LI Jiang. Fabrication and Characterizations of Yb:YAG Transparent Ceramics Using Alcohol-water Co-precipitation Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 217-224. |
| [11] | ZHU Danyang, QIAN Kang, CHEN Xiaopu, HU Zewang, LIU Xin, LI Xiaoying, PAN Yubai, MIHÓKOVÁ Eva, NIKL Martin, LI Jiang. Fine-grained Ce,Y:SrHfO3 Scintillation Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Isostatic Pressing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1118-1124. |
| [12] | CHEN Lei,WANG Kai,SU Wentao,ZHANG Wen,XU Chenguang,WANG Yujin,ZHOU Yu. Research Progress of Transition Metal Non-oxide High-entropy Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 748-758. |
| [13] | WU Xiaojun,YANG Jie,ZHENG Rui,ZHANG Zhaofu,YANG Yi. Effect of Ablation Surface Microstructure on Plasma Arc Ablation Properties of C/C Throat Insert Fabricated via CVI+HPIC Methods [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(6): 654-660. |
| [14] | DONG Lijia, GUO Xiaojie, LI Xue, CHEN Chaogui, JIN Yang, AHMED Alsaedi, TASAWAR Hayat, ZHAO Qingzhou, SHENG Guodong. Microscopic Insights into pH-dependent Adsorption of Cd(II) on Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheets [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 293-300. |
| [15] | LÜ Xiaoxu, JIANG Zhuyu, ZHOU Yiran, QI Zhe, ZHAO Wenqing, JIAO Jian. Effect of BN/SiC Multilayered Interphases on Mechanical Properties of SiC Fibers and Minicomposites by PIP [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1099-1104. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||