
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (8): 841-846.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200512
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Chuang1,2( ), YANG Qingfeng1(
), YANG Qingfeng1( ), LU Shengsen1, LIU Yangqiao3(
), LU Shengsen1, LIU Yangqiao3( )
)
Received:2020-09-02
Revised:2020-11-23
Published:2021-08-20
Online:2021-01-25
Contact:
YANG Qingfeng, professor. E-mail: yangqf@sari.ac.cn; LIU Yangqiao, professor. E-mail: yqliu@mail.sic.ac.cn
About author:LI Chuang(1991-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: lichuang740@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LI Chuang, YANG Qingfeng, LU Shengsen, LIU Yangqiao. Adsorption of Phosphonate Antiscalant HEDP from Reverse Osmosis Concentrates by La/FeOOH@PAC[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 841-846.
| Concentration/(mg·L-1) | T/K | Initial pH | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEDP | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | Cl- | SO42- | HCO- | ||
| 18.00 | 298 | 8.00 | 204.54 | 397.86 | 407.62 | 542.46 | 298 | 8.00 |
Table 1 Simulation solution of RO concentrates
| Concentration/(mg·L-1) | T/K | Initial pH | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEDP | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | Cl- | SO42- | HCO- | ||
| 18.00 | 298 | 8.00 | 204.54 | 397.86 | 407.62 | 542.46 | 298 | 8.00 |
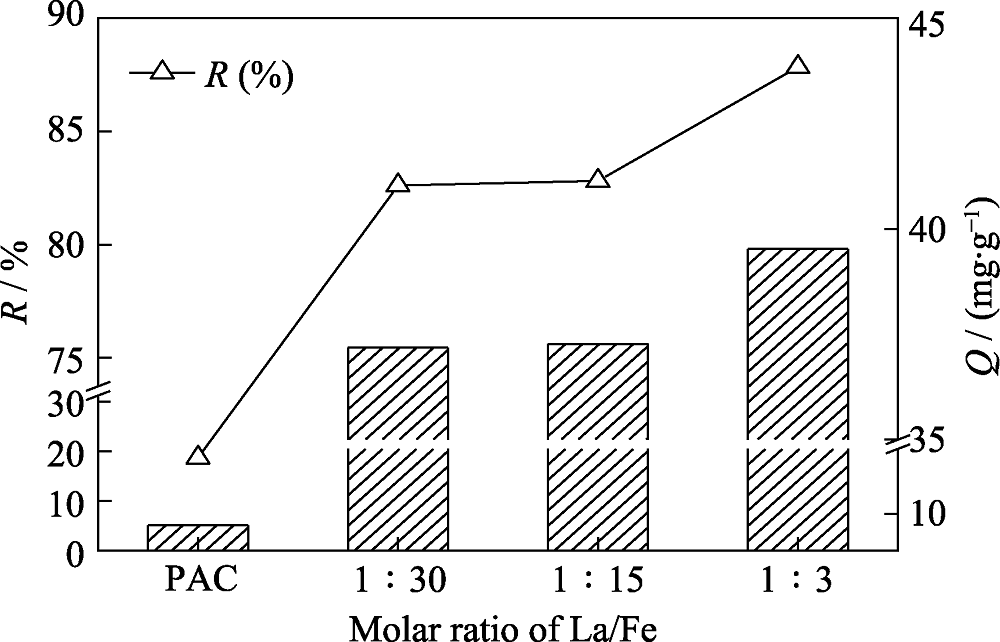
Fig. 1 Variation of HEDP adsorption capacity on La/FeOOH@PAC with different molar ratios of the La/Fe Absorbent dosage: 0.4 g/L, Absorption time: 12 h
| Element | C | O | Fe | La |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | 86.27 | 12.04 | 1.05 | 0.64 |
Table 2 Elemental composition of the adsorbent
| Element | C | O | Fe | La |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | 86.27 | 12.04 | 1.05 | 0.64 |
| T/K | Qe,exp/(mg·g-1) | Pseudo-first-order equation | Pseudo-second-order equation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/h-1 | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | k2/(g·mg-1·h-1) | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | ||
| 298 | 41.600 | 0.476 | 24.143 | 0.983 | 0.0659 | 42.553 | 0.999 |
Table 3 Parameters of kinetic models for HEDP adsorption onto the La/FeOOH@PAC composite
| T/K | Qe,exp/(mg·g-1) | Pseudo-first-order equation | Pseudo-second-order equation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/h-1 | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | k2/(g·mg-1·h-1) | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R2 | ||
| 298 | 41.600 | 0.476 | 24.143 | 0.983 | 0.0659 | 42.553 | 0.999 |
| T/K | Langmuir model parameters | Freundlich model parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm/ (mg·g-1) | KL/ (L·mg-1) | R2 | n | KF | R2 | |
| 298 | 65.359 | 0.455 | 0.974 | 1.880 | 19.249 | 0.864 |
| 308 | 56.818 | 0.674 | 0.992 | 2.446 | 21.509 | 0.949 |
| 318 | 56.689 | 0.512 | 0.993 | 2.211 | 18.571 | 0.940 |
Table 4 Parameters of isotherm models for HEDP adsorption onto the adsorbent
| T/K | Langmuir model parameters | Freundlich model parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm/ (mg·g-1) | KL/ (L·mg-1) | R2 | n | KF | R2 | |
| 298 | 65.359 | 0.455 | 0.974 | 1.880 | 19.249 | 0.864 |
| 308 | 56.818 | 0.674 | 0.992 | 2.446 | 21.509 | 0.949 |
| 318 | 56.689 | 0.512 | 0.993 | 2.211 | 18.571 | 0.940 |
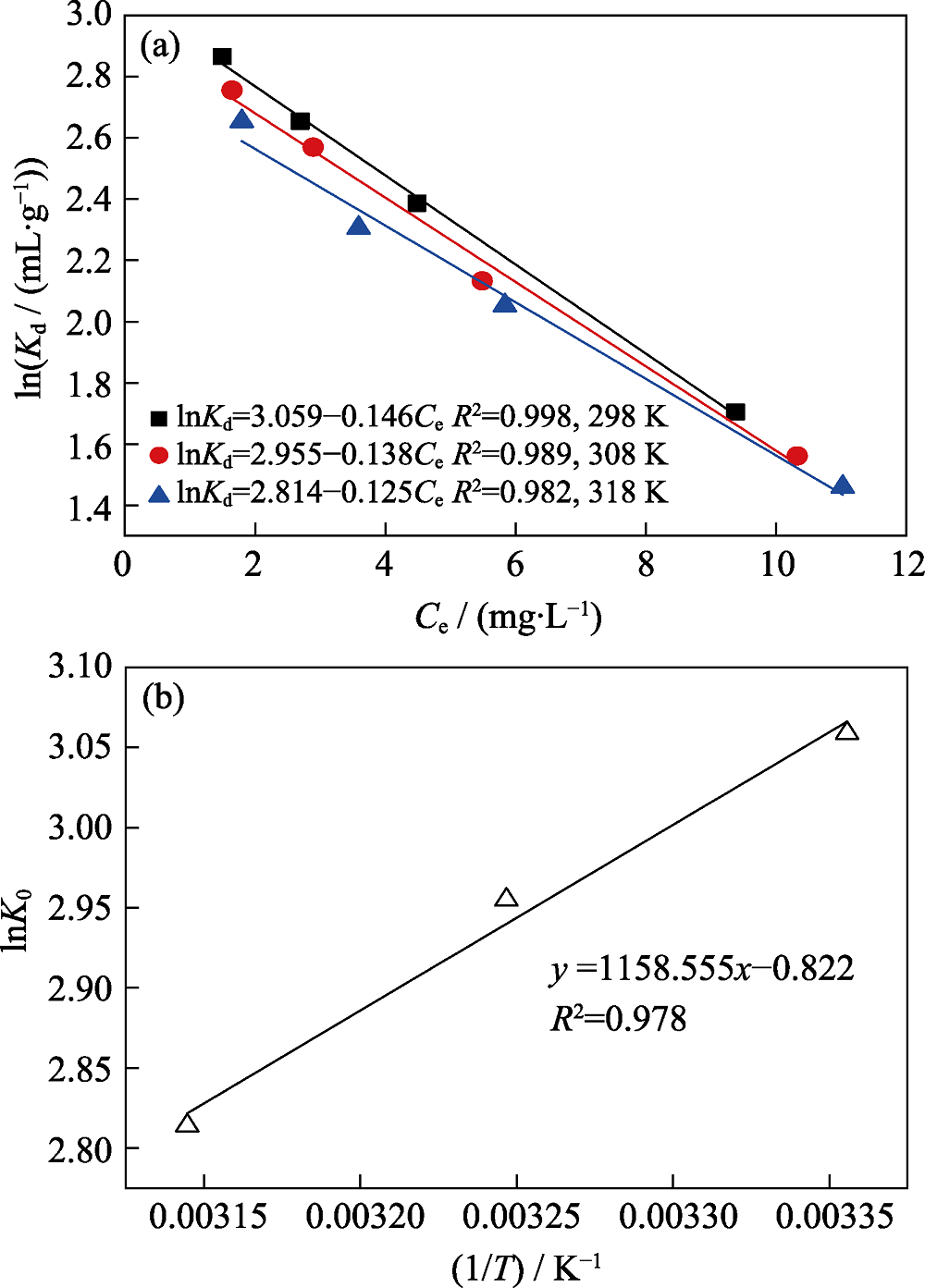
Fig. 6 Linear plots fit of lnKd versus Cefor the adsorption HEDP onto the adsorbent at different temperatures (a); linear plots of lnK0 versus 1/T for the adsorption of HEDP onto the adsorbent (b)
| T/K | ΔGo/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔHo/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔSo/(J·mol-1 K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | -7.579 | -9.632 | -6.834 |
| 308 | -7.567 | ||
| 318 | -7.440 |
Table 5 Thermodynamic parameters for HEDP adsorption onto the adsorbent
| T/K | ΔGo/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔHo/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔSo/(J·mol-1 K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | -7.579 | -9.632 | -6.834 |
| 308 | -7.567 | ||
| 318 | -7.440 |
| [1] |
HUANG N, WANG W L, XU Z B, et al. UV/chlorine oxidation of the phosphonate antiscalant 1-hydroxyethane-1,1-diphosphonic acid (HEDP) used for reverse osmosis processes: organic phosphorus removal and scale inhibition properties changes. Journal of Environmental Management , 2019, 237:180-186.
DOI URL |
| [2] | BENAMMARA L, MENASRIAB T, AYACHIC A, et al. Phosphate removal using aerobic bacterial consortium and pure cultures isolated from activated sludge. Process Safety & Environmental Protection , 2015, 95:237-246. |
| [3] |
SHEN C, ZHAO Y Q, LIU R B, et al. Adsorption of phosphorus with calcium alginate beads containing drinking water treatment residual. Water Science and Technology , 2018, 78(9):1980-1989.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ROTT E, MINKE R STEINMETZ H. Removal of phosphorus from phosphonate-loaded industrial wastewaters via precipitation/ flocculation. Journal of Water Process Engineering , 2017, 17:188-196.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
ISTIROKHATUN T, DEWI M N, ILMA H I, et al. Separation of antiscalants from reverse osmosis concentrates using nanofiltration. Desalination , 2018, 429:105-110.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
XU Z B, WANG W L, HUANG N, et al. 2-Phosphonobutane- 1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid (PBTCA) degradation by ozonation: kinetics, phosphorus transformation, anti-precipitation property changes and phosphorus removal. Water Research , 2019, 148:334-343.
DOI URL |
| [7] | CHEN D, JIA J, LIAO X, et al. Phosphate removal by polystyrene anion exchanger (PsAX)-supporting Fe-loaded nanocomposites: effects of PsAX functional groups and ferric (hydr)oxide crystallinity. Chemical Engineering Journal , 2020, 387:124193-1-9. |
| [8] |
LI JING, LIU XIAOYUE, QIU QIANFENG, et al. Phosphorus sorption characteristics on aluminum oxides with different structures. Journal of Inorganic Materials , 2020, 35(9):1005-1010.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
REINHARDT T, ELORDI M. G, MINKE R, et al. Batch studies of phosphonate adsorption on granular ferric hydroxides. Water Science and Technology , 2020, 81:10-20.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
CHEN Y, BAYGENTS J C, FARRELL J. Removing phosphonate antiscalants from membrane concentrate solutions using granular ferric hydroxide. Journal of Water Process Engineering , 2017, 19:18-25.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
NOWACK B, STONE A T. Adsorption of phosphonates onto the goethite-water interface. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science , 1999, 214(1):20-30.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZENOBI M C, HEIN L, RUEDA E. The effects of 1-hydroxyethane-(1,1-diphosphonic acid) on the adsorptive partitioning of metal ions onto gamma-AlOOH. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science , 2005, 284(2):447-454.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
WANG Z H, SHEN D K, SHEN F, et al. Phosphate adsorption on lanthanum loaded biochar. Chemosphere , 2016, 150:1-7.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 李茂东, 曾彬, 杨麟, 等. 工业锅炉炉水中HEDP的测定. 工业水处理, 2013, 33(1):75-77. |
| [15] |
NUR A, CHAE A, JO S, et al. Synthesis of β-FeOOH/Fe3O4 hybrid photocatalyst using catechol-quaternized poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone) as a double-sided molecular tape. Journal of Materials Science , 2017, 52(14):8493-8501.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MI X, WANG M J, ZHOU F Y, et al. Preparation of La-modified magnetic composite for enhanced adsorptive removal of tetracycline. Environmental Science and Pollution Research , 2017, 24(20):17127-17135.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHANG T, XU H Y, LI H H, et al. Microwave digestion-assisted HFO/biochar adsorption to recover phosphorus from swine manure. Science of the Total Environment , 2018, 621:1512-1526.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
FAN Q H, SHAO D D, HU J, et al. Comparison of Ni2+ sorption to bare and ACT-graft attapulgites: effect of pH, temperature and foreign ions. Surface Science , 2008, 602(3):778-785.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
YU J, XIANG C, ZHANG G, et al. Activation of lattice oxygen in lafe (oxy)hydroxides for efficient phosphorus removal. Environmental Science & Technology , 2019, 53:9073-9080.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
FANG L P, HUANG L Z, HOLM P E, et al. Facile upscaled synthesis of layered iron oxide nanosheets and their application in phosphate removal. Journal of Materials Chemistry A , 2015, 3:7505-7512.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
FANG L P, LIU R, LI J, et al. Magnetite/lanthanum hydroxide for phosphate sequestration and recovery from lake and the attenuation effects of sediment particles. Water Research , 2018, 130:243-254.
DOI URL |
| [1] | LIU Yang, LU Youjun, LI Yanrui, LIN Liqun, YUAN Zhenxia, HUANG Zhenkun. HfN Formation and Phase Relationships in the Hf-Si-La-O-N System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 443-448. |
| [2] | YANG Jin-Ping, JI Wen-Ling, ZHANG Hao, LIU Pan, CUI Yi, WEI Heng-Yong. Preparation and Luminescence Property of Eu 3+ Doped Porous Lanthanum Zirconate Powder [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(7): 727-733. |
| [3] | LU Dong-Liang, DAI Guang-Zhou, YAO Ying-Bang, TAO Tao, LIANG Bo, LU Sheng-Guo. Influence of Calcining Temperature on the Property of Li0.33La0.56TiO3 Solid-state Ionic Capacitor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1077-1082. |
| [4] | WANG Feng, BU Cong-Hao, YE Jian-Ke, LI Jiang-Tao, HE Zhi-Yong, ZHANG Qi-Fu. Preparation and Infrared Radiation Property of Lanthanum-cerium Oxide Ceramics by (Ca,Fe) Co-doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(2): 185-189. |
| [5] | XIE Hui-Dong, LI Fei, CHEN Chao, XI Hai-Hong, SHI Ling. Microwave Dielectric Properties of LaPO4 Ceramics Synthesized by a Hydrothermal Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(8): 882-886. |
| [6] | LONG Lian-Jun, XU Jian-Mei, GONG Yan-Sheng, WU Ming-Yang, CUI Xin-You. Effect of Microwave Sintering on Electrical Properties of PLZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(5): 500-504. |
| [7] | XIANG Li, DING Xiao-Fang. Influence of NH4HCO3 on Microstructure of Ni/La10Si5.8Mg0.2O26.8 Anode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(9): 924-930. |
| [8] | XIE Yi-Jun, GUO Yi-Ping, DONG Wen, GUO Bing, LI Hua, LIU He-Zhou. Preparation of La-doped BiFeO3 Thin Film and Its Photovoltaic Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(4): 436-440. |
| [9] | WANG Song-Lin, FENG Yi, WANG Dong-Sheng, MENG Guang-Yao. Fabrication of Dense La0.7Ca0.3Cr0.97O3−δ Interconnect Membrane on Novel SOFC Composite Support by Co-firing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(9): 911-916. |
| [10] | XU Xiu-Hua,XIAO Han-Ning,GUO Wen-Ming,GAO Peng-Zhao,PENG Su-Hua. Preparation and Reaction Mechanism of LaB6 Powder by Solid-state Reaction at Atmospheric Pressure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(4): 417-421. |
| [11] |
LI Ke-Feng,WANG Guo-Nian,HU Li-Li,ZHANG Jun-Jie,HU Jun-Jiang.
Effects of WO3 Contents on the Thermal and Spectroscopic Properties of Tm3+-doped TeO2-WO3-La2O3Glasses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(4): 429-434. |
| [12] | MA Wen,GUO Hong-Bo,GONG Sheng-Kai,DONG Hong-Ying. Lanthanum-cerium Oxide Thermal Barrier Coatings Prepared by Atmospheric Plasma Spraying [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(5): 983-988. |
| [13] | ZHOU Shen-Lin,LIU Dan-Min,ZHANG Jiu-Xing. Fabrication and Characterization of High-purity Nanostructured Bulk LaB6 Polycrystal Cathode Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(6): 1199-1204. |
| [14] | LIU Wei-Ming,LI Sheng-Li,LI Shi-Gang,WANG Xiao. Synthesis and Low-temperature Sintering Behavior of Sr-doped Lanthanum Chromite Powders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(6): 1061-1064. |
| [15] | PU Yong-Ping,CHEN Shou-Tian,LANGHAMMER H. T.,MAKOVEC D.. Mechanism Investigation of Grain Boundary Reoxidation of Barium-lanthanum Titanate Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(4): 919-926. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||