
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (8): 847-855.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200639
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Weiwei1( ), LU Chen1, YING Guobing1, ZHANG Jianfeng1(
), LU Chen1, YING Guobing1, ZHANG Jianfeng1( ), JIANG Wan2
), JIANG Wan2
Received:2020-11-09
Revised:2020-12-09
Published:2021-08-20
Online:2020-12-30
Contact:
ZHANG Jianfeng, professor. E-mail: jfzhang_sic@163.com
About author:ZHANG Weiwei(1996-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: zwwbob@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHANG Weiwei, LU Chen, YING Guobing, ZHANG Jianfeng, JIANG Wan. Effect and Mechanism of the Surface Treatment and Gradation Filling of AlN on the Performance of Insulation Layer of Copper Clad Laminate[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 847-855.
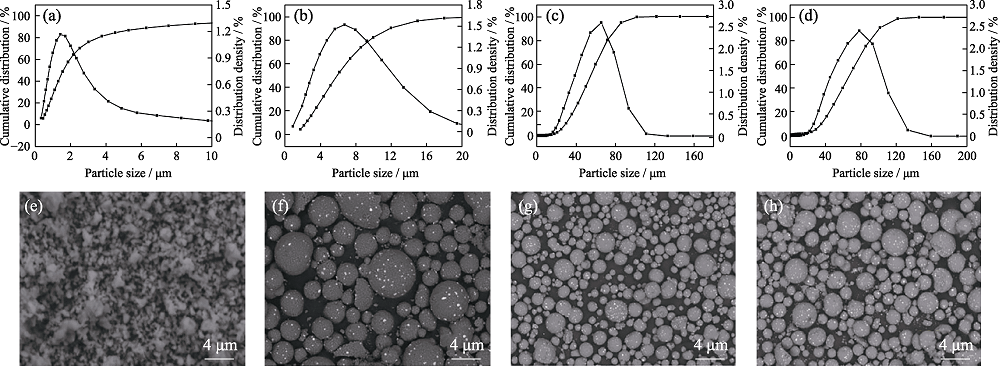
Fig. 2 (a-d) Particle size distribution curves and (e-h) SEM images of AlN with different particle sizes (a) 1 μm AlN; (b) 5 μm AlN; (c) 50 μm AlN; (d) 80 μm AlN; (e-h) SEM images of the AlN corresponding to (a-d)
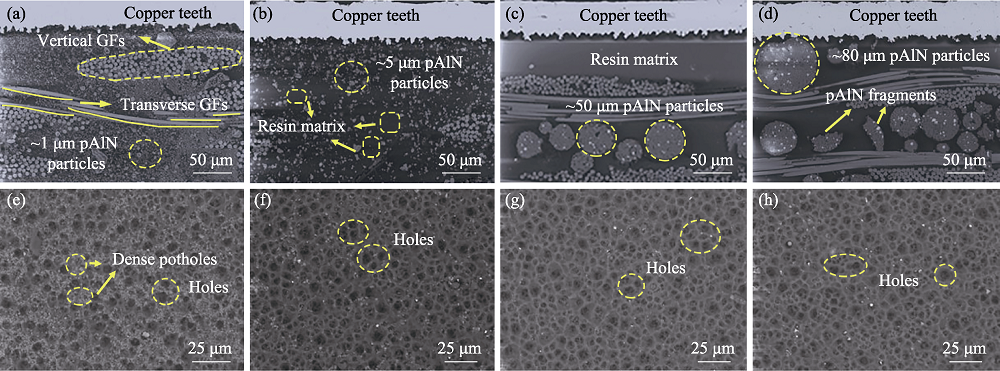
Fig. 4 SEM images of (a-d) cross-sections and (e-h) surfaces of CCLs filled with pAlN of same filling ratio but different sizes (a) pAlN-1 μm; (b) pAlN-5 μm; (c) pAlN-50 μm; (d) pAlN-80 μm; (e-h) SEM images corresponding to the surfaces of (a-d) CCLs
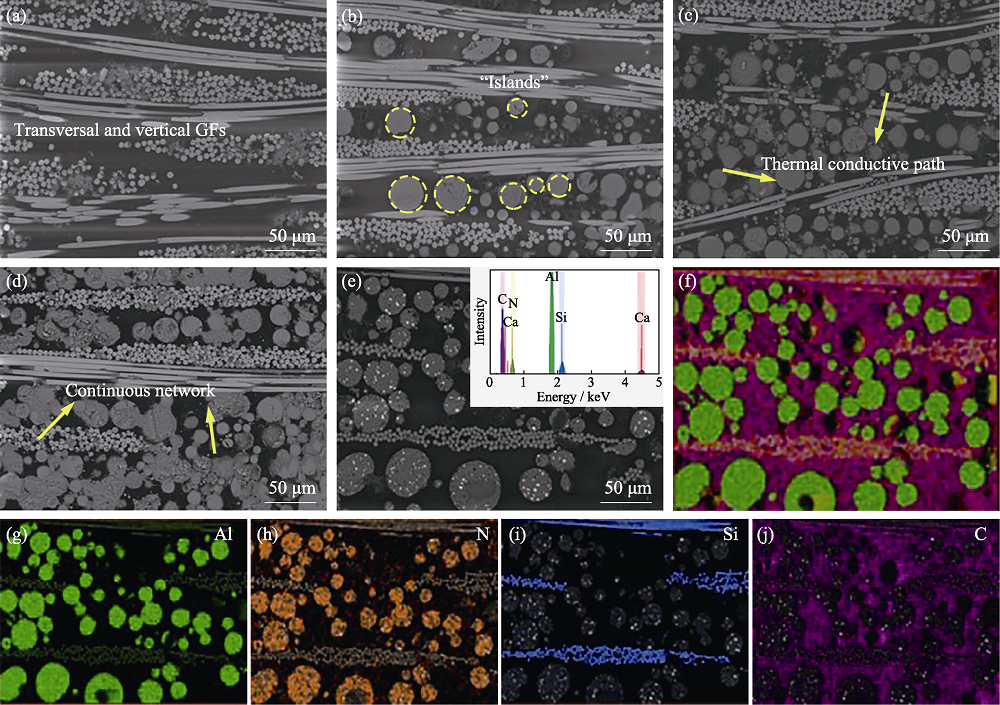
Fig. 5 SEM images of the cross-section of CCLs with different filling ratios of pAlN((a) no filler; (b) pAlN-50 μm-20%; (c) pAlN-50 μm-60%; (d) pAlN-50 μm60%-5 μm5%); (e) EDS scan selection area with the inset showing the element distribution; (f) the full element scan image; (g-j) corresponding element distributions of Al, N, Si, C

Fig. 6 Heat conduction mechanism diagram of CCLs under different filling schemes (a) Without filler; (b) With single-size filler; (c) With graded filler
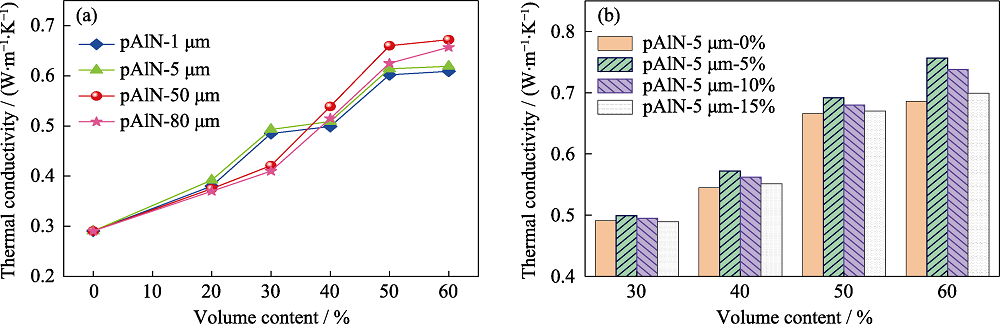
Fig. 7 (a) Effects of pAlN with different sizes, different filling amounts and (b) gradation filling (pAlN-50 μm x%-5 μm y%, x=0-60, y=0-15, same below) on the thermal conductivity of CCLs
| Treatment | Thermal conductivity/ (W·m-1·K-1) | Peel strength/ (N·mm-1) | Dielectric constant | Dielectric loss/×10-3 | Bending strength/MPa | Water absorption/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without fillers | 0.291 | 0.949 | 3.90 | 5.41 | 220 | 0.40 |
| AlN-1 μm60% | 0.390 | 0.380 | 5.10 | 9.10 | 208 | 0.76 |
| pAlN-1 μm60% | 0.610 | 0.980 | 4.55 | 9.04 | 282 | 0.47 |
Table 1 Effect of phosphoric acid treatment of AlN on the performance of CCLs
| Treatment | Thermal conductivity/ (W·m-1·K-1) | Peel strength/ (N·mm-1) | Dielectric constant | Dielectric loss/×10-3 | Bending strength/MPa | Water absorption/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without fillers | 0.291 | 0.949 | 3.90 | 5.41 | 220 | 0.40 |
| AlN-1 μm60% | 0.390 | 0.380 | 5.10 | 9.10 | 208 | 0.76 |
| pAlN-1 μm60% | 0.610 | 0.980 | 4.55 | 9.04 | 282 | 0.47 |
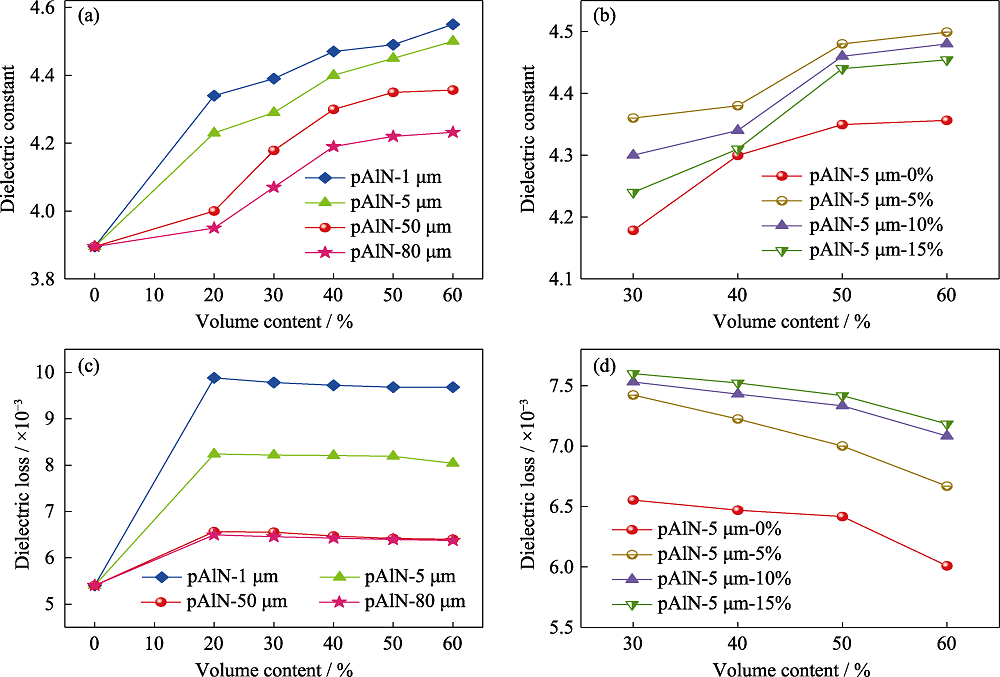
Fig. 10 Effect of pAlN with different size and filling amount on the dielectric constant (a) and dielectric loss (b) of the CCLs; Influence of gradation filling on the dielectric constant (c) and dielectric loss (d) of corresponding CCLs
| [1] |
WANG C, WEN N, ZHOU G Y, et al. Incorporation of Tin on copper clad laminate to increase the interface adhesion for signal loss reduction of high-frequency PCB lamination. Applied Surface Science , 2017, 422:738-744.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
GUO J M, WANG H, ZHANG C X, et al. MPPE/SEBS composites with low dielectric Loss for high-frequency copper clad laminates applications. Polymers , 2020, 12(9):1875.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
OUYANG Y, DING F, BAI L Y, et al. Design of network Al2O3 spheres for significantly enhanced thermal conductivity of polymer composites. Composites Part A , 2020, 128:105673.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GOLDIN N, DODIUK H, LEWITUS D. Enhanced thermal conductivity of photopolymerizable composites using surface modified hexagonal boron nitride fillers. Composites Science and Technology , 2017, 152(10):36-45.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
REN L L, ZENG X L, SUN R, et al. Spray-assisted assembled spherical boron nitride as fillers for polymers with enhanced thermally conductivity. Chemical Engineering Journal , 2019, 370:166-175.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZHANG L, ZHANG J, YUE Z X, et al. Thermally stable polymer-ceramic composites for microwave antenna applications. Journal of Advanced Ceramics , 2016, 5(4):269-276.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
PONRAJ B, BHIMIREDDI R, VARMA K B R. Effect of nano- and micron-sized K0.5Na0.5NbO3 fillers on the dielectric and piezoelectric properties of PVDF composites. Journal of Advanced Ceramics , 2016, 5(4):308-320.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
MENTLíK V, MICHAL O. Influence of SiO2 nanoparticles and nanofibrous filler on the dielectric properties of epoxy-based composites. Materials Letters , 2018, 223:41-44.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
OUYANG Y, LI X F, DING F, et al. Simultaneously enhance thermal conductive property and mechanical properties of silicon rubber composites by introducing ultrafine Al2O3 nanospheres prepared via thermal plasma. Composites Science and Technology , 2020, 190:108019.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GUERRA V, WAN C Y, MCNALLY T. Thermal conductivity of 2D nano-structured boron nitride (BN) and its composites with polymers. Progress in Materials Science , 2019, 100:170-186.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GUO Y Q, LYU Z Y, YANG X T, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivities and decreased thermal resistances of functionalized boron nitride/polyimide composites. Composites Part B , 2019, 164:732-739.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LULE Z, KIM J. Thermally conductive and highly rigid polylactic acid (PLA) hybrid composite filled with surface treated alumina/ nano-sized aluminum nitride. Composites Part A , 2019, 124:105506.
DOI URL |
| [13] | YANG Y, GAO J M, LEI T, et al. Thermal conductivity and mechanical properties of polyimide composites with mixed fillers of BN flakes and SiC@SiO2 whiskers. Polymer Engineering & Science , 2020, 60(5):1044-1053. |
| [14] |
KIM C Y, LINH DANG T M, ZHANG Y M, et al. The alignment of AlN platelets in polymer matrix and its anisotropic thermal properties. Journal of Materiomics , 2019, 5(4):679-687.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WU G L, WANG Y Q, WANG K K, et al. The effect of modified AlN on the thermal conductivity, mechanical and thermal properties of AlN/polystyrene composites. RSC Advances , 2016, 6(104):102542-102548.
DOI URL |
| [16] | HE D P, GAO H, ZHANG J J, et al. Simulation and experimental verification of thermal property for aluminum nitrides and copper clad laminates under space thermal environment. Journal of Inorganic Materials , 2019, 34(9):947-952. |
| [17] |
KOCJAN A. The hydrolysis of AlN powder - a powerful tool in advanced materials engineering. The Chemical Record , 2018, 18(7/8):1232-1246.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
TANG L, HE M K, NA X Y, et al. Functionalized glass fibers cloth/spherical BN fillers/epoxy laminated composites with excellent thermal conductivities and electrical insulation properties. Composites Communications , 2019, 16:5-10.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
GANESH I, OLHERO S M, FERREIRA J. Phosphoric acid treated AlN powder for aqueous processing of net-shape dense AlN and β-SiAlON parts. Advances in Applied Ceramics , 2009, 108(2):111-117.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
HU L H, WANG Y K, WANG S C. Aluminum nitride surface functionalized by polymer derived silicon oxycarbonitride ceramic for anti-hydrolysis. Journal of Alloys and Compounds , 2019, 772:828-833.
DOI URL |
| [21] | ZHANG W W, LU C, GE M N, et al. Surface modified and gradation-mixed Al2O3 as an effective filler for the polyphenylene oxide (PPO) insulative layer in copper clad laminates. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics , 2020 |
| [22] |
KUMAR R S, HAREESH U N, RAMAVATH P, et al. Hydrolysis control of alumina and AlN mixture for aqueous colloidal processing of aluminum oxynitride. Ceramics International , 2011, 37(7):2583-2590.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHANG J, QI S H. Mechanical, thermal and dielectric properties of aluminum nitride/epoxy resin composites. Journal of Elastomers and Plastics , 2015, 47(5):431-438.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
CHANG H C, LIN H T, LIN C H, et al. Facile preparation of a phosphinated bisphenol and its low water-absorption epoxy resins for halogen-free copper clad laminates. Polymer Degradation and Stability , 2013, 98(1):102-108.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LI A, ZHANG C, ZHANG Y F. Thermal conductivity of graphene-polymer composites: mechanisms, properties, and applications. Polymers , 2017, 9(437):1-17.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
GU J W, GUO Y Q, YANG X T, et al. Synergistic improvement of thermal conductivities of polyphenylene sulfide composites filled with boron nitride hybrid fillers. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing , 2017, 95:267-273.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
WANG W Q, MEYER J, ZENG Q X, et al. Adhesion characteristics of aromatic thermosetting copolyester and glass fiber laminates with copper foils for improved circuit boards. Polymers for Advanced Technologies , 2016, 27(12):1577-1585.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
JIN H Y, WANG W, GAO J Q, et al. Study of machinable AlN/BN ceramic composites. Materials Letters , 2006, 60(2):190-193.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
BIAN W C, YAO T, CHEN M, et al. The synergistic effects of the micro-BN and nano-Al2O3 in micro-nano composites on enhancing the thermal conductivity for insulating epoxy resin. Composites Science and Technology , 2018, 168:420-428.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
TANG D H, SU J Q, KONG M Q, et al. Preparation and properties of epoxy/BN highly thermal conductive composites reinforced with SiC whisker. Polymer Composites , 2015, 37(9):2611-2621.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
GAO R, GU A J, LIANG G Z, et al. Properties and origins of high-performance poly(phenylene oxide)/cyanate ester resins for high-frequency copper-clad laminates. Journal of Applied Polymer Science , 2011, 121(3):1675-1684.
DOI URL |
| [1] | YU Ruixian, WANG Guodong, WANG Shouzhi, HU Xiaobo, XU Xiangang, ZHANG Lei. Effect of High-temperature Annealing on AlN Crystal Grown by PVT Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 343-349. |
| [2] | CHENG Weijie, WANG Minglei, LIN Guoqiang. Composition, Structure and Properties of CrAlN-DLC Hard Composite Films Deposited by Arc Ion Plating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 764-772. |
| [3] | HE Duan-Peng,GAO Hong,ZHANG Jing-Jing,WU Jie,LIU Bo-Tian,WANG Xiang-Ke. Simulation and Experimental Verification of Thermal Property for Aluminum Nitrides and Copper Clad Laminates under Space Thermal Environment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 947-952. |
| [4] | Xiao XIE, Yin SUI, Xiao-Yu HUANG, Chen-Guang ZHU. Synthesis of AlN by Direct Combustion of Mg-Al Alloy Powder [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(4): 439-443. |
| [5] | HE Yong-Qin, LI Xiao-Yun, ZHANG Jing-Xian, LI Xiao-Guang. In situ Pyrolyzed Carbon on the Property of AlN-based Microwave Attenuation Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(4): 421-426. |
| [6] | LI Miao-Lei, WANG En-Qing, YUE Jian-Ling, HUANG Xiao-Zhong. Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Property of TiAlN/VN Nano-multilayer Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(12): 1280-1284. |
| [7] | PENG Xu, ZHU De-Gui, LI Yang-Xu, ZHOU Jia-Min, LV Zhen, GUO Peng-Chao. Fabrication and Property of AlN-BN Composites by Hot Isostatic Pressing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(5): 535-541. |
| [8] | YANG Ming-Ming, MO Ya-Juan, WANG Xiao-Dan, ZENG Xiong-Hui, LIU Xue-Hua, HUANG Jun, ZHANG Ji-Cai, WANG Jian-Feng, XU Ke. Stress Induced Microstructure Evolution of AlN: Er Film at Different Annealing Temperature [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(3): 285-290. |
| [9] |
HUANG Lin-Yun, LI Chen-Hui, KE Wen-Ming, SHI Yu-Sheng, HE Zhi-Yong, ZHANG Qi-Fu.
Effect of Rare Earth Oxides on Electrical Properties of Spark Plasma Sintered AlN Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 267-271. |
| [10] | SHU Xia, LI Jun, ZhANG Hai-Long, DONG Man-Jiang, SHUNZO Shi-Mai, WANG Shi-Wei. Gelcasting of Aluminum Nitride Using a Water-soluble Copolymer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(3): 327-330. |
| [11] | PENG Rong, ZHOU He-Ping, NING Xiao-Shan, XU Wei. Bonding Strength and Mechanism Between Aluminum and AlN [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(3): 249-253. |
| [12] | GAN Ping,, GU Min ,LIQiang , XIAN Xiao-Dong. Third-order Non-linearOptical Properties of Tellurium-based Composite Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(3): 295-299. |
| [13] | WU Jiang,LIN Hong,LI Jian-Bao,LI Jun-Feng. Corrosion Behavior of AlNbO4/Mullite Composite as Environmental Barrier Coating in Water Vapor Environment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(4): 445-448. |
| [14] | XIAO Jin,ZHOU Feng,CHEN Yan-Bin. Preparation of AlN Powder by Microwave Carbon Thermal Reduction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(4): 755-758. |
| [15] | ZHAO Hai-Yang,WANG Wei-Min,FU Zheng-Yi,WANG Hao. Effect of Combined Additives of CaF2-Y2O3 on Microstructrue and Thermal Conductivity of AlN-BN Composite Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(3): 496-500. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||