
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (8): 820-834.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200582
Special Issue: 【虚拟专辑】燃料电池(2020~2021)
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
HAO Ce( ), LIU Ziruo, LIU Wei, SHI Yantao(
), LIU Ziruo, LIU Wei, SHI Yantao( )
)
Received:2020-10-10
Revised:2020-12-07
Published:2021-08-20
Online:2021-01-07
Contact:
SHI Yantao, professor. E-mail: shiyantao@dlut.edu.cn
About author:HAO Ce(1974-), male, professor. E-mail: haoce@dlut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
HAO Ce, LIU Ziruo, LIU Wei, SHI Yantao. Research Progress of Carbon-supported Metal Single Atom Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 820-834.
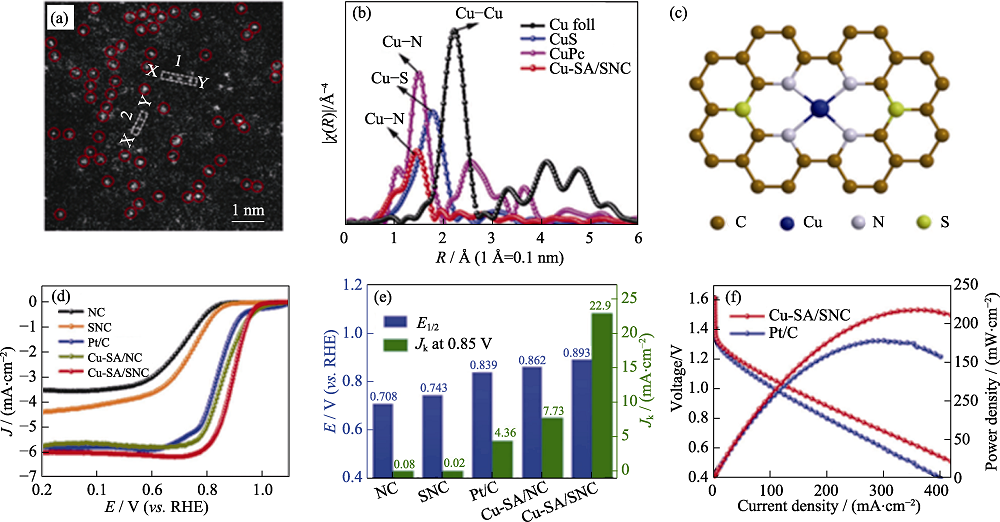
Fig. 1 (a) Magnified HAADF-STEM image of Cu-SA/SNC; (b) Ex situFT k3-weighted Cu K-edge EXAFS spectra of Cu-SA/SNC; (c) Schematic interfacial model of Cu-SA/SNC; (d) ORR polarization curves of different catalysts; (e) Kinetic currents at 0.85 V (vs. RHE) and half-wave potentials of Cu-SA/SNC and their references; (f) Performances of Cu-SA/SNC and Pt/C-based Zn-air batteries[31] Colorful figures are available on website
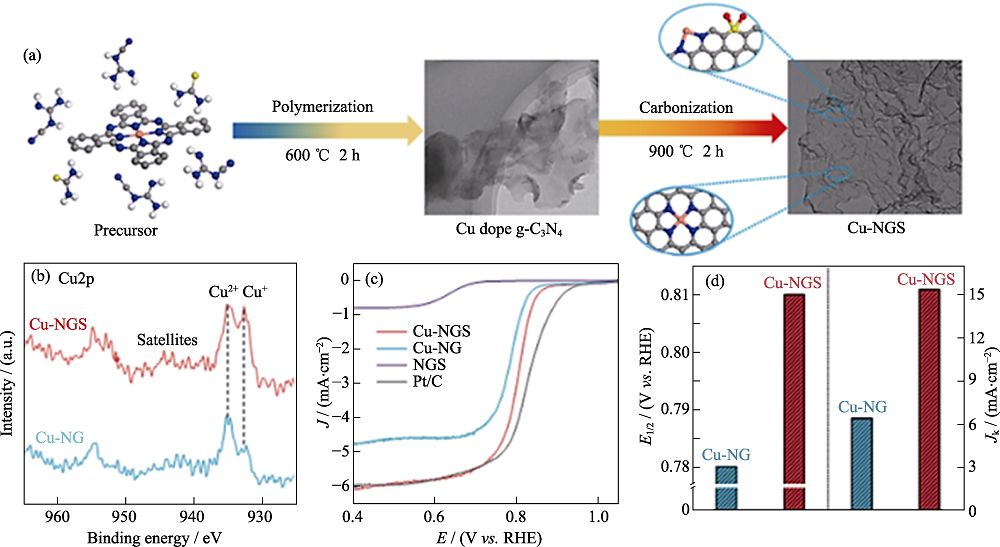
Fig. 2 Schematic, characterization and electrochemical test of atomically dispersed Cu-Nx site catalyst synthesis[34] (a) Schematic of atomically dispersed Cu-Nx site catalyst synthesis; (b) Cu2p XPS spectra; (c) Steady-state ORR polarization plots;(d) Kinetic currents at 0.78 V (vs. RHE) and half-wave potentials of Cu-NGS and Cu-NG Colorful figures are available on website
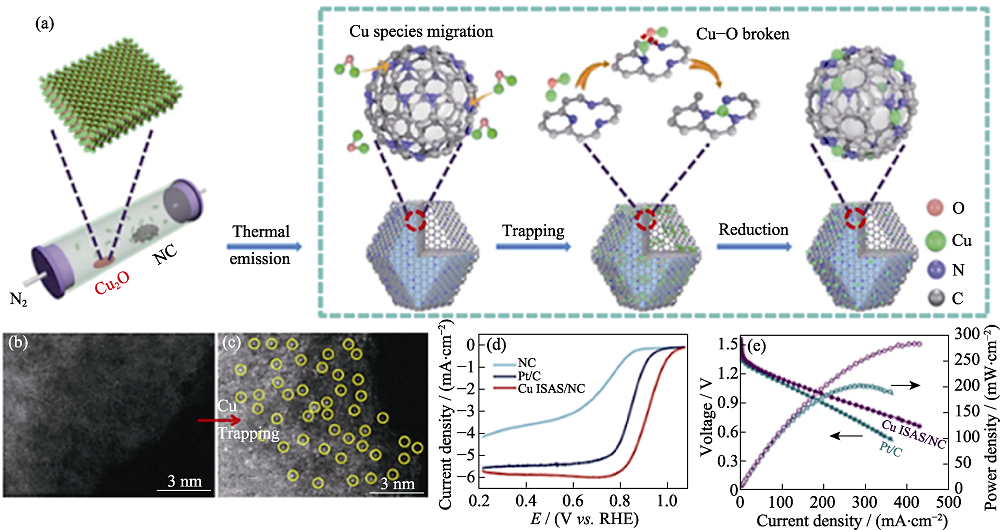
Fig. 3 (a) Scheme of the formation of Cu ISAS/N-C catalyst; Aberration-corrected high-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscope (AC HAADF-STEM) images of (b) NC and (c) Cu ISAS/NC; (d) ORR polarization curves and (e) performances of Cu ISAS/NC and Pt/C-based Zn-air batteries[37] Colorful figures are available on website
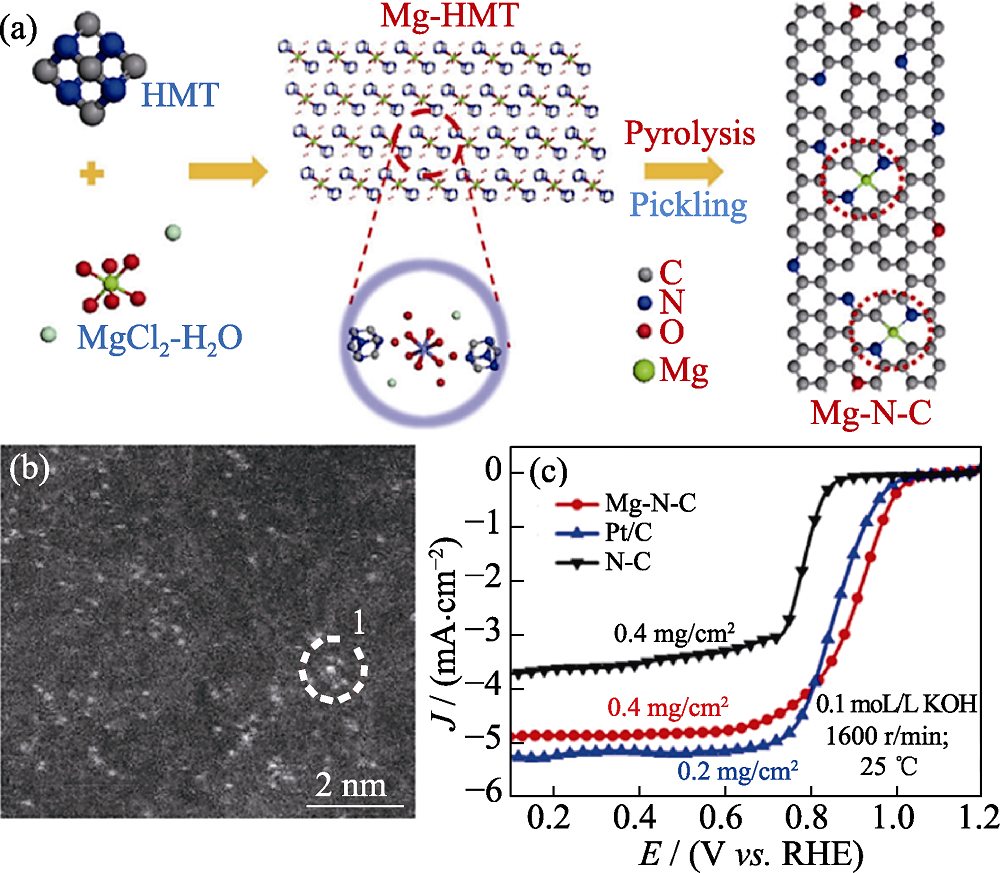
Fig. 4 (a) Schematic illustration of the synthesis procedure, (b) HAADF-STEM image and (c) ORR polarization curves of Mg-N-C[48] Colorful figures are available on website
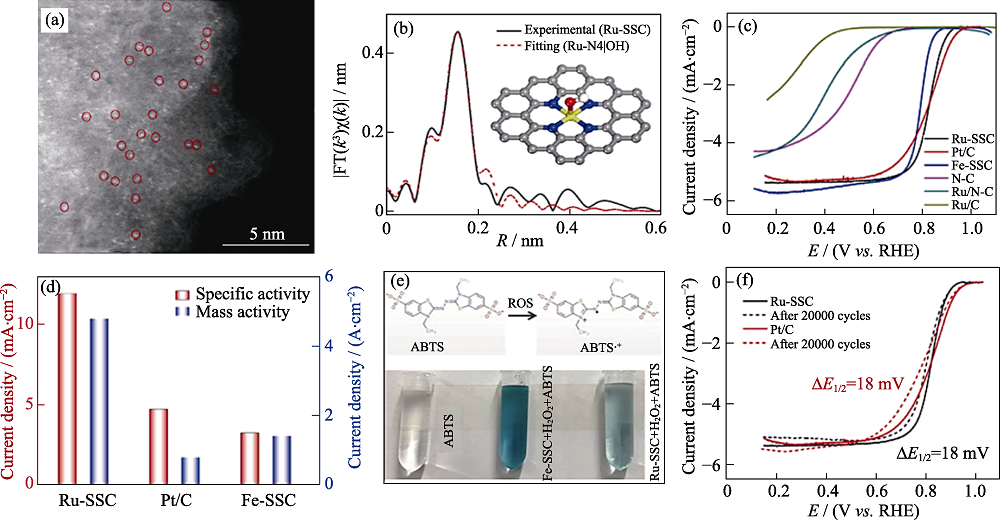
Fig. 5 Atomic dispersion of Ru-SSC, electrocatalytic tests towards ORR and probe experiment[52] (a) High-resolution HAADF-STEM image of Ru-SSC; (b) EXAFS fitting curve for Ru-SSC;(c) ORR polarization curves of the synthesized catalysts; (d) Specific activity and mass activity comparison among Ru-SSC, Pt/C, and Fe-SSC; (e) Reaction between ROS and ABTS (top) and photographs showing the color change of the solution after Fenton reaction (bottom); (f) ORR polarization plots before and after potential cycling stability tests Colorful figures are available on website
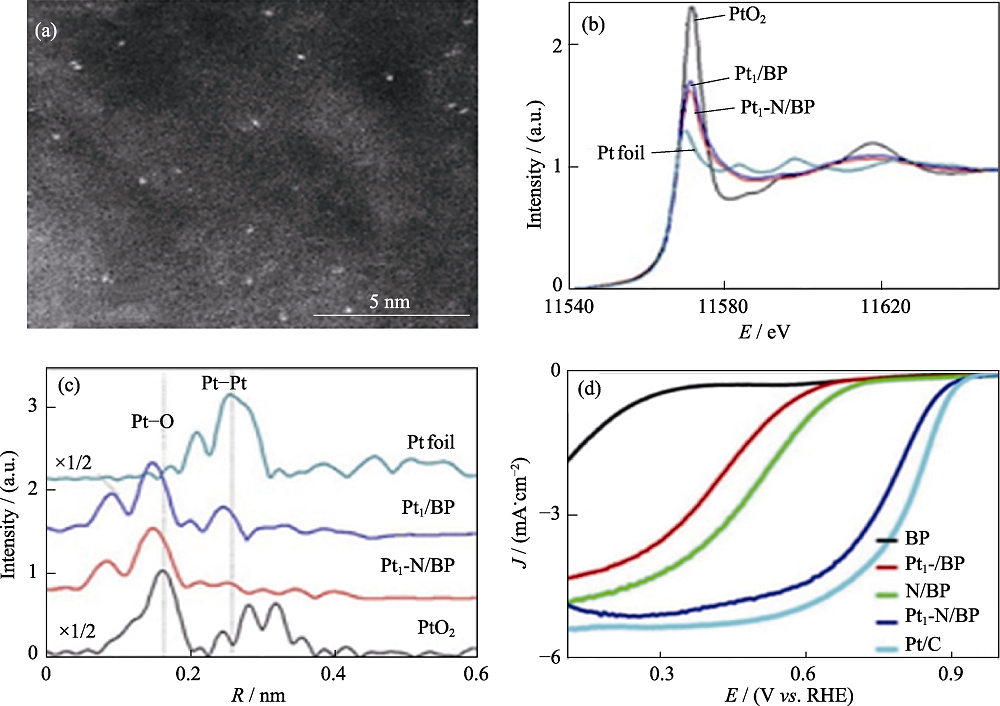
Fig. 6 (a) HAADF-STEM image of Pt1-N/BP, (b) Pt L3-edge XANES, k2-weighted R-space FT spectra from (c) EXAFS, (d) ORR polarization curves for all samples[60] Colorful figures are available on website
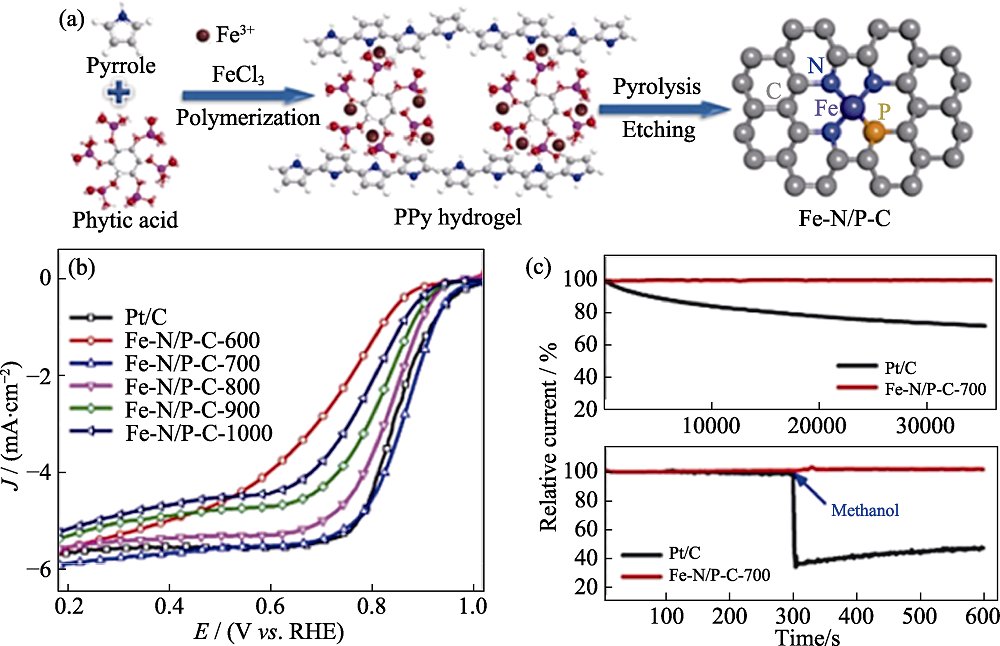
Fig. 7 (a) Schematic diagram of Fe-N/P-C preparation and (b, c) corresponding electrochemical performances[65] Colorful figures are available on website
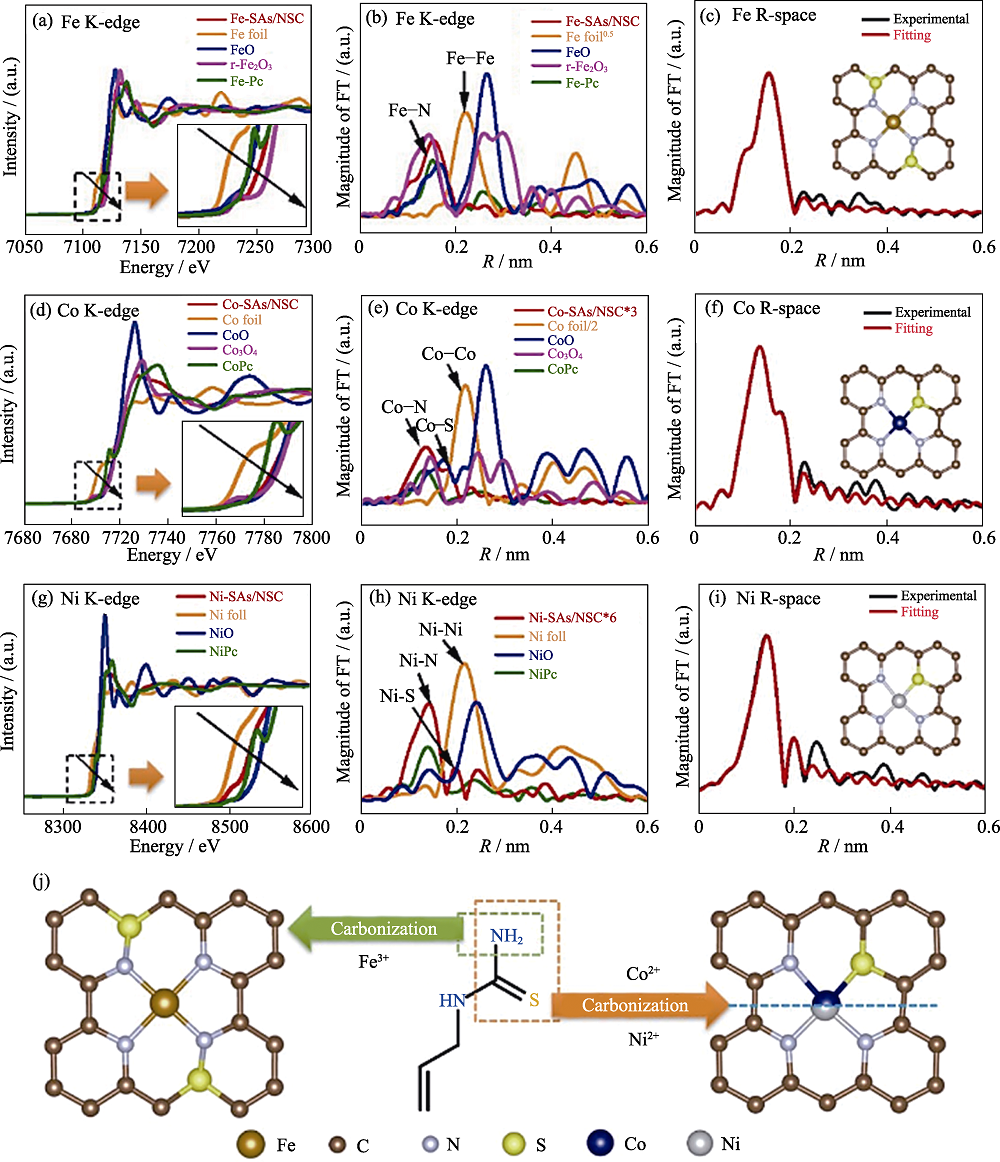
Fig. 8 Structural characterizations of Fe-SAs/NSC, Co-SAs/NSC and Ni-SAs/NSC[70] The normalized XANES spectra and the k3-weighted Fourier transform of EXAFS spectra at (a,b) Fe K-edge of Fe-SAs/NSC and the reference materials, (d,e) Co K-edge of Co-SAs/NSC and the reference materials, and (g,h) Ni K-edge of Ni-SAs/NSC and the reference materials with insets showing the enlarged boxed area in the same picture; EXAFS curves between the experimental data and the fit of (c) Fe-SAs/NSC, (f) Co-SAs/NSC, and (i) Ni-SAs/NSC with insets showing the fitted structures; (j) Schematic illustration of the formation of Fe-SAs/NSC, Co-SAs/NSC, and Ni-SAs/NSC with different coordination environments Colorful figures are available on website
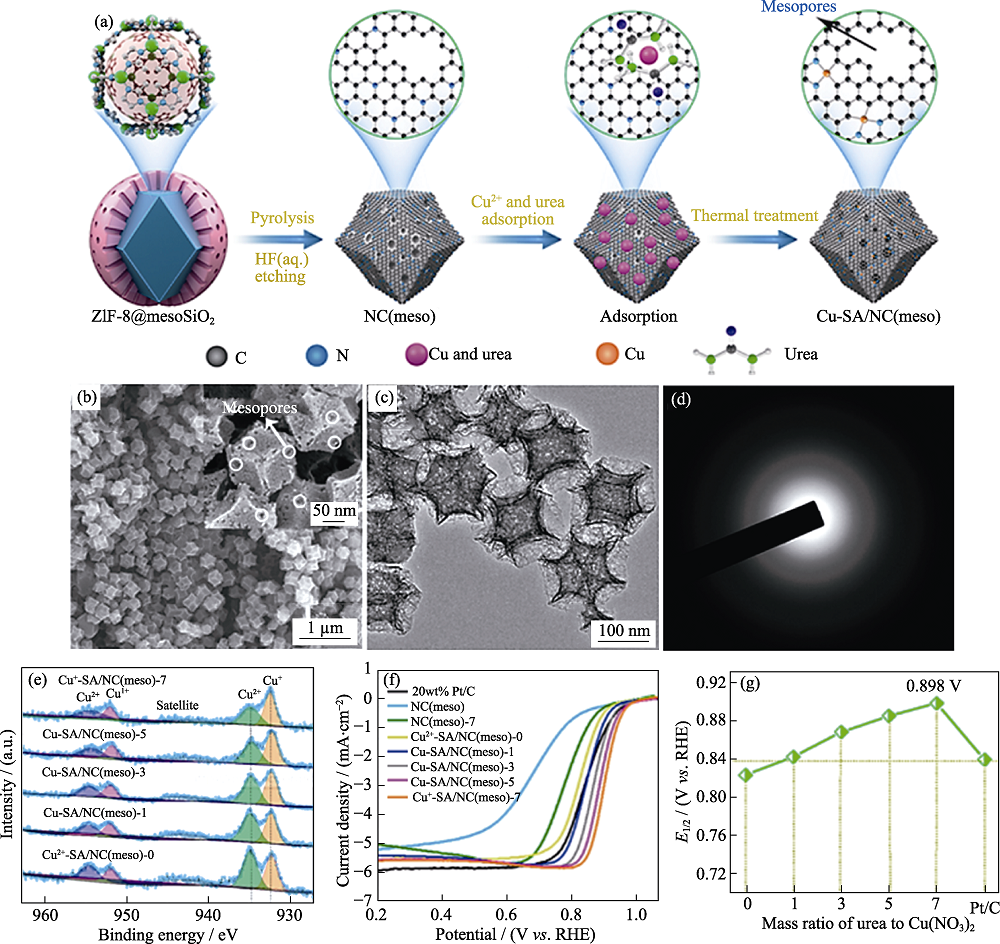
Fig. 9 (a) Formation process of Cu-SA/NC(meso) catalysts; (b) SEM image, (c) TEM image, and (d) corresponding SAED pattern of Cu +-SA/NC(meso)-7; (e) Cu2p high-resolution XPS surveys of Cu-SA/NC (meso) catalysts; (f) Linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) curves of Cu+-SA/NC (meso)-7 and comparison samples; (g) Comparison of ORR activities for Cu-SA/NC (meso) catalysts[74] Colorful figures are available on website
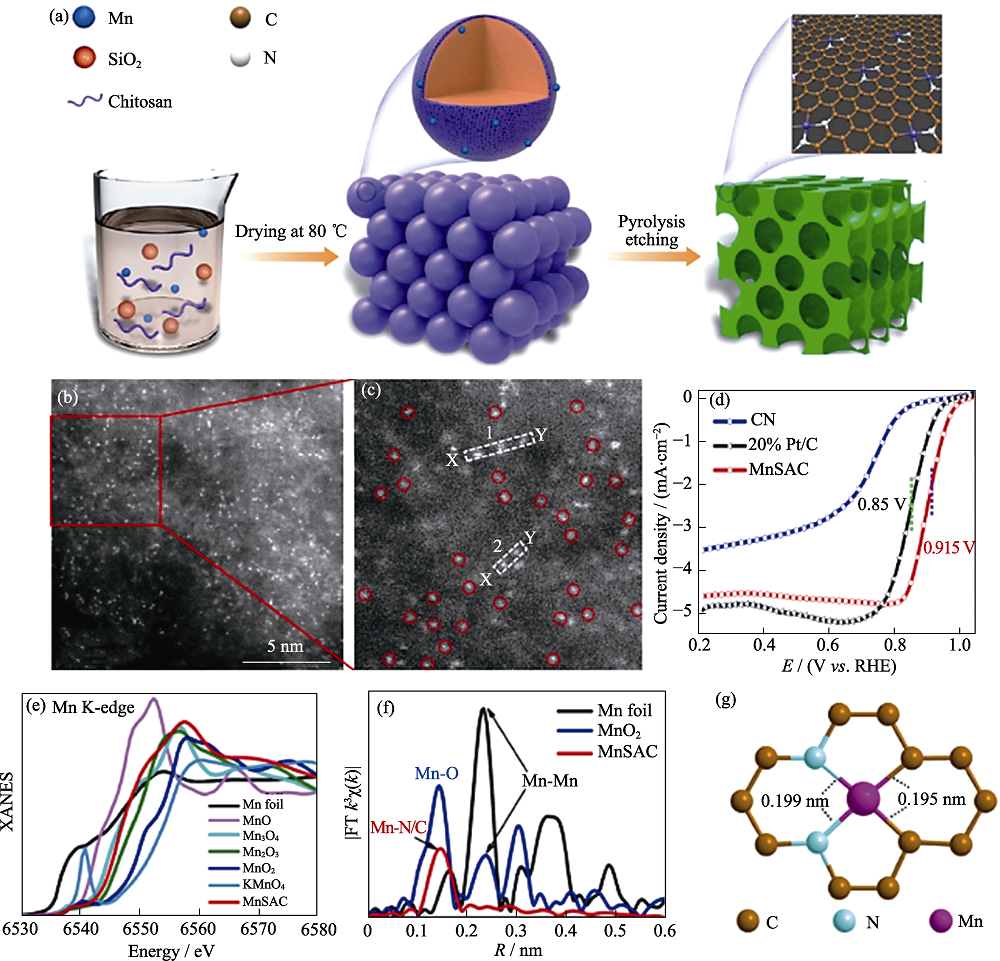
Fig. 10 Formation process and structural characterizations of Mn-N2C2[75] (a) Illustration of the formation of MnSAC; (b, c) HAADF-STEM images of MnSAC; (d) iR-corrected ORR polarization curves for MnSAC, CN, and 20% Pt/C; (e) Mn K-edge XANES and (f) FT EXAFS spectra of MnSAC and their references; (g) Atomic structure model for MnSAC Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] |
DEBE M K. Electrocatalyst approaches and challenges for automotive fuel cells. Nature , 2012, 486(7401):43-51.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BANHAM D, YE S. Current status and future development of catalyst materials and catalyst layers for proton exchange membrane fuel cells: an industrial perspective. ACS Energy Letters , 2017, 2(3):629-638.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LEE J S, TAI KIM S, CAO R, et al. Metal-air batteries with high energy density: Li-air versus Zn-air. Advanced Energy Materials , 2011, 1(1):34-50.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GUO S, ZHANG S, SUN S. Tuning nanoparticle catalysis for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2013, 52(33):8526-8544.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GONG M, LI Y, WANG H, et al. An advanced Ni-Fe layered double hydroxide electrocatalyst for water oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 2013, 135(23):8452-8455.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
QIAO J, LIU Y, HONG F, et al. A review of catalysts for the electroreduction of carbon dioxide to produce low-carbon fuels. Chem. Soc. Rev. , 2014, 43(2):631-675.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
SHAO M, CHANG Q, DODELET J P, et al. Recent advances in electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Rev. , 2016, 116(6):3594-3657.
DOI URL |
| [8] | HU B C, WU Z Y, CHU S Q, et al. SiO2-protected shell mediated templating synthesis of Fe-N-doped carbon nanofibers and their enhanced oxygen reduction reaction performance. Energy & Environmental Science , 2018, 11(8):2208-2215. |
| [9] |
SHARIFI T, GRACIA ESPINO E, CHEN A, et al. Oxygen reduction reactions on single- or few-atom discrete active sites for heterogeneous catalysis. Advanced Energy Materials , 2019, 10(11):1902084.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ZHU J, MU S. Defect engineering in carbon-based electrocatalysts: insight into intrinsic carbon defects. Advanced Functional Materials , 2020, 30(25):2001097.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
YAN X, JIA Y, YAO X. Defects on carbons for electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Chem. Soc. Rev. , 2018, 47(20):7628-7658.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHAO C X, LI B Q, LIU J N, et al. Intrinsic electrocatalytic activity regulation of M-N-C single-atom catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2021, 60(9):4448-4468.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
QIAO B, WANG A, YANG X, et al. Single-atom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt1/FeOx. Nat. Chem. , 2011, 3(8):634-641.
DOI URL |
| [14] | DENG J, LI H, XIAO J, et al. Triggering the electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution activity of the inert two-dimensional MoS2 surface via single-atom metal doping. Energy & Environmental Science , 2015, 8(5):1594-1601. |
| [15] |
LANG R, LI T, MATSUMURA D, et al. Hydroformylation of olefins by a rhodium single-atom catalyst with activity comparable to RhCl(PPh3)3. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2016, 55(52):16054-16058.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LIN J, WANG A, QIAO B, et al. Remarkable performance of Ir1/FeOx single-atom catalyst in water gas shift reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 2013, 135(41):15314-15317.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LIU P, ZHAO Y, QIN R, et al. Photochemical route for synthesizing atomically dispersed palladium catalysts. Science , 2016, 352(6287):797-801.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CHEN Y, JI S, WANG Y, et al. Isolated single iron atoms anchored on N-doped porous carbon as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2017, 56(24):6937-6941.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHANG C, SHA J, FEI H, et al. Single-atomic ruthenium catalytic sites on nitrogen-doped graphene for oxygen reduction reaction in acidic medium. ACS Nano , 2017, 11(7):6930-6941.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
CHEN K, LIU K, AN P, et al. Iron phthalocyanine with coordination induced electronic localization to boost oxygen reduction reaction. Nat. Commun. , 2020, 11(1):4173.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHU J, MU S. Defect engineering in the carbon-based electrocatalysts: insight into the intrinsic carbon defects. Advanced Functional Materials , 2020, 30(25):2001097.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
BAI X, SHI Y, GUO J, et al. Catalytic activities enhanced by abundant structural defects and balanced N distribution of N-doped graphene in oxygen reduction reaction. Journal of Power Sources , 2016, 306:85-91.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LI Y, WEN H, YANG J, et al. Boosting oxygen reduction catalysis with N, F, and S tri-doped porous graphene: tertiary N-precursors regulates the constitution of catalytic active sites. Carbon , 2019, 142:1-12.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
QIU X, YAN X, PANG H, et al. Isolated Fe single atomic sites anchored on highly steady hollow graphene nanospheres as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Sci. , 2019, 6(2):1801103.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WU Y, ZHOU H, YANG T, et al. Negative pressure pyrolysis induced highly accessible single sites dispersed on 3D graphene frameworks for enhanced oxygen reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2020, 59(46):20465-20469.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
DENG Y, CHI B, LI J, et al. Atomic Fe-doped MOF-derived carbon polyhedrons with high active-center density and ultra-high performance toward pem fuel cells. Advanced Energy Materials , 2019, 9(13):1802856.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
HUANG K, ZHANG L, XU T, et al. -60 ℃ solution synthesis of atomically dispersed cobalt electrocatalyst with superior performance. Nat. Commun. , 2019, 10(1):606.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WALLING C. Fentons reagent revisited. Accounts of Chemical Research , 1975, 8(4):125-131.
DOI URL |
| [29] | ZHONG Y, LIANG X, HE Z, et al. The constraints of transition metal substitutions (Ti, Cr, Mn, Co and Ni) in magnetite on its catalytic activity in heterogeneous Fenton and UV/Fenton reaction: from the perspective of hydroxyl radical generation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental , 2014, 150:612-618. |
| [30] |
QU Y, LI Z, CHEN W, et al. Direct transformation of bulk copper into copper single sites via emitting and trapping of atoms. Nature Catalysis , 2018, 1(10):781-786.
DOI URL |
| [31] | JIANG Z, SUN W, SHANG H, et al. Atomic interface effect of a single atom copper catalyst for enhanced oxygen reduction reactions. Energy & Environmental Science , 2019, 12(12):3508-3514. |
| [32] |
CUI L, CUI L, LI Z, et al. A copper single-atom catalyst towards efficient and durable oxygen reduction for fuel cells. Journal of Materials Chemistry A , 2019, 7(28):16690-16695.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
BAI L, HOU C, WEN X, et al. Catalysis of oxygen reduction reaction on atomically dispersed copper- and nitrogen-codoped graphene. ACS Applied Energy Materials , 2019, 2(7):4755-4762.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
WANG D, AO C, LIU X, et al. Coordination-engineered Cu-Nx single-site catalyst for enhancing oxygen reduction reaction. ACS Applied Energy Materials , 2019, 2(9):6497-6504.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
HAN G, ZHENG Y, ZHANG X, et al. High loading single-atom Cu dispersed on graphene for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Energy , 2019, 66:104088.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WAGH N K, SHINDE S S, LEE C H, et al. Densely colonized isolated Cu-N single sites for efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts and rechargeable advanced Zn-air batteries. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental , 2020, 268:118746.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
YANG Z, CHEN B, CHEN W, et al. Directly transforming copper (I) oxide bulk into isolated single-atom copper sites catalyst through gas-transport approach. Nat. Commun. , 2019, 10(1):3734.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
LI J, CHEN M, CULLEN D A, et al. Atomically dispersed manganese catalysts for oxygen reduction in proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Nature Catalysis , 2018, 1(12):935-945.
DOI URL |
| [39] | YANG Y, MAO K, GAO S, et al. O-, N-atoms-coordinated Mn cofactors within a graphene framework as bioinspired oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysts. Adv. Mater. , 2018, 30(28):e1801732. |
| [40] | ZHU X, AMAL R, LU X. N, P co-coordinated manganese atoms in mesoporous carbon for electrochemical oxygen reduction. Small , 2019, 15(29):e1804524. |
| [41] |
BAI L, DUAN Z, WEN X, et al. Atomically dispersed manganese- based catalysts for efficient catalysis of oxygen reduction reaction. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental , 2019, 257:117930.
DOI URL |
| [42] | LIN Z, HUANG H, CHENG L, et al. Atomically dispersed Mn within carbon frameworks as high-performance oxygen reduction electrocatalysts for zinc-air battery. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering , 2019, 8(1):427-434. |
| [43] |
CHEN Z, GONG W, LIU Z, et al. Coordination-controlled single-atom tungsten as a non-3d-metal oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalyst with ultrahigh mass activity. Nano Energy , 2019, 60:394-403.
DOI URL |
| [44] | SONG P, LUO M, LIU X, et al. Zn single atom catalyst for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Advanced Functional Materials , 2017, 27(28):1100802. |
| [45] |
LI J, CHEN S, YANG N, et al. Ultrahigh-loading zinc single-atom catalyst for highly efficient oxygen reduction in both acidic and alkaline media. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2019, 58(21):7035-7039.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
LUO E, ZHANG H, WANG X, et al. Single-atom Cr-N4 sites designed for durable oxygen reduction catalysis in acid media. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2019, 58(36):12469-12475.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
CALLE-VALLEJO F, IGNACIO MARTINEZ J, ROSSMEISL J. Density functional studies of functionalized graphitic materials with late transition metals for oxygen reduction reactions. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics , 2011, 13(34):15639-15643.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
LIU S, LI Z, WANG C, et al. Turning main-group element magnesium into a highly active electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Nat. Commun. , 2020, 11(1):938.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
CAO Y, GAO Y, ZHOU H, et al. Highly efficient ammonia synthesis electrocatalyst: single Ru atom on naturally nanoporous carbon materials. Advanced Theory and Simulations , 2018, 1(5):1800018.
DOI URL |
| [50] | YU B, LI H, WHITE J, et al. Tuning the catalytic preference of ruthenium catalysts for nitrogen reduction by atomic dispersion. Advanced Functional Materials , 2019, 30(6):1905665. |
| [51] |
JI S, CHEN Y, FU Q, et al. Confined pyrolysis within metal- organic frameworks to form uniform Ru3 clusters for efficient oxidation of alcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 2017, 139(29):9795-9798.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
XIAO M, GAO L, WANG Y, et al. Engineering energy level of metal center: Ru single-atom site for efficient and durable oxygen reduction catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 2019, 141(50):19800-19806.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
XIAO M, ZHU J, LI G, et al. A single-atom iridium heterogeneous catalyst in oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2019, 58(28):9640-9645.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
LIU Q, LI Y, ZHENG L, et al. Sequential synthesis and active-site coordination principle of precious metal single-atom catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction and PEM fuel cells. Advanced Energy Materials , 2020, 10(20):2000689.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
LIU W, JI J, YAN X, et al. A cascade surface immobilization strategy to access high-density and closely distanced atomic Pt sites for enhancing alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. Journal of Materials Chemistry A , 2020, 8(10):5255-5262.
DOI URL |
| [56] | ZHANG L, DOYLE-DAVIS K, SUN X. Pt-based electrocatalysts with high atom utilization efficiency: from nanostructures to single atoms. Energy & Environmental Science , 2019, 12(2):492-517. |
| [57] |
CHOI C H, KIM M, KWON H C, et al. Tuning selectivity of electrochemical reactions by atomically dispersed platinum catalyst. Nat. Commun. , 2016, 7:10922.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
SONG X, LI N, ZHANG H, et al. Promotion of hydrogen peroxide production on graphene-supported atomically dispersed platinum: effects of size on oxygen reduction reaction pathway. Journal of Power Sources , 2019, 435:226771.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
LIU J, JIAO M, MEI B, et al. Carbon-supported divacancy- anchored platinum single-atom electrocatalysts with superhigh Pt utilization for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2019, 58(4):1163-1167.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
LIU J, JIAO M, LU L, et al. High performance platinum single atom electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Nat. Commun. , 2017, 8:15938.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
ZHANG L, LIU H, LIU S, et al. Pt/Pd single-atom alloys as highly active electrochemical catalysts and the origin of enhanced activity. ACS Catalysis , 2019, 9(10):9350-9358.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
ZHANG Q, QIN X X, DUAN-MU F P, et al. Isolated platinum atoms stabilized by amorphous tungstenic acid: metal-support interaction for synergistic oxygen activation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2018, 57(30):9351-9356.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
ZHU Y, SOKOLOWSKI J, SONG X, et al. Engineering local coordination environments of atomically dispersed and heteroatom- coordinated single metal site electrocatalysts for clean energy- conversion. Advanced Energy Materials , 2020, 10(11):1902844.
DOI URL |
| [64] | HAN X, LING X, YU D, et al. Atomically dispersed binary Co-Ni sites in nitrogen-doped hollow carbon nanocubes for reversible oxygen reduction and evolution. Adv. Mater. , 2019, 31(49):e1905622. |
| [65] |
YUAN K, LUTZENKIRCHEN-HECHT D, LI L, et al. Boosting oxygen reduction of single iron active sitesviageometric and electronic engineering: nitrogen and phosphorus dual coordination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 2020, 142(5):2404-2412.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
ZHAO Y M, ZHANG P C, XU C, et al. Design and preparation of Fe-N5 catalytic sites in single-atom catalysts for enhancing the oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces , 2020, 12(15):17334-17342.
DOI URL |
| [67] | LIN Y, LIU P, VELASCO E, et al. Fabricating single-atom catalysts from chelating metal in open frameworks. Adv. Mater. , 2019, 31(18):e1808193. |
| [68] |
SUN T, ZHANG P, CHEN W, et al. Single iron atoms coordinated to g-C3N4 on hierarchical porous N-doped carbon polyhedra as a high-performance electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Commun. , 2020, 56(5):798-801.
DOI URL |
| [69] | ZHANG J, ZHANG M, ZENG Y, et al. Single Fe atom on hierarchically porous S, N-codoped nanocarbon derived from porphyra enable boosted oxygen catalysis for rechargeable Zn-air batteries. Small , 2019, 15(24):e1900307. |
| [70] |
ZHANG J, ZHAO Y, CHEN C, et al. Tuning the coordination environment in single-atom catalysts to achieve highly efficient oxygen reduction reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 2019, 141(51):20118-20126.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
WEI X, ZHENG D, ZHAO M, et al. Cross-linked polyphosphazene hollow nanosphere-derived N/P-doped porous carbon with single nonprecious metal atoms for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2020, 59(34):14639-14646.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
CHEN P, ZHANG N, ZHOU T, et al. Tailoring electronic structure of atomically dispersed metal-N3S1 active sites for highly efficient oxygen reduction catalysis. ACS Materials Letters , 2019, 1(1):139-146.
DOI URL |
| [73] | MA S, HAN Z, LENG K, et al. Ionic exchange of metal-organic frameworks for constructing unsaturated copper single-atom catalysts for boosting oxygen reduction reaction. Small , 2020, 16(23):e2001384. |
| [74] |
SUN T, LI Y, CUI T, et al. Engineering of coordination environment and multiscale structure in single-site copper catalyst for superior electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Nano Lett. , 2020, 20(8):6206-6214.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
SHANG H, SUN W, SUI R, et al. Engineering isolated Mn-N2C2 atomic interface sites for efficient bifunctional oxygen reduction and evolution reaction. Nano Lett. , 2020, 20(7):5443-5450.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
SUN H, WANG M, DU X, et al. Modulating the d-band center of boron doped single-atom sites to boost the oxygen reduction reaction. Journal of Materials Chemistry A , 2019, 7(36):20952-20957.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
SUN H, LIU S, WANG M, et al. Updating the intrinsic activity of a single-atom site with a P-O bond for a rechargeable Zn-air battery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces , 2019, 11(36):33054-33061.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
CHEN Y, JI S, ZHAO S, et al. Enhanced oxygen reduction with single-atomic-site iron catalysts for a zinc-air battery and hydrogen-air fuel cell. Nat. Commun. , 2018, 9(1):5422.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
NI W, GAO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. O-doping boosts the electrochemical oxygen reduction activity of a single Fe site in hydrophilic carbon with deep mesopores. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces , 2019, 11(49):45825-45831.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
CAO L, LUO Q, CHEN J, et al. Dynamic oxygen adsorption on single-atomic ruthenium catalyst with high performance for acidic oxygen evolution reaction. Nat. Commun. , 2019, 10(1):4849.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
XU Y, ZHANG W, LI Y, et al. A general bimetal-ion adsorption strategy to prepare nickel single atom catalysts anchored on graphene for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Journal of Energy Chemistry , 2020, 43:52-57.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
YAO Y, HU S, CHEN W, et al. Engineering the electronic structure of single atom Ru sites viacompressive strain boosts acidic water oxidation electrocatalysis. Nature Catalysis , 2019, 2(4):304-313.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
SHI Y, HUANG W M, LI J, et al. Site-specific electrodeposition enables self-terminating growth of atomically dispersed metal catalysts. Nat. Commun. , 2020, 11(1):4558.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
HOSSAIN M D, LIU Z, ZHUANG M, et al. Rational design of graphene-supported single atom catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Advanced Energy Materials , 2019, 9(10):1803689.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
YUAN S, PU Z, ZHOU H, et al. A universal synthesis strategy for single atom dispersed cobalt/metal clusters heterostructure boosting hydrogen evolution catalysis at all pH values. Nano Energy , 2019, 59:472-480.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
WANG G, HE C T, HUANG R, et al. Photoinduction of Cu single atoms decorated on UiO-66-NH 2 for enhanced photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to liquid fuels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 2020, 142(45):19339-19345.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
LI Y, WANG S, WANG X S, et al. Facile top-down strategy for direct metal atomization and coordination achieving a high turnover number in CO2 photoreduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 2020, 142(45):19259-19267.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
FAN Q, HOU P, CHOI C, et al. Activation of Ni particles into single Ni-N atoms for efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2. Advanced Energy Materials , 2019, 10(5):1903068.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
LI Y, HAO J, SONG H, et al. Selective light absorber-assisted single nickel atom catalysts for ambient sunlight-driven CO2 methanation. Nat. Commun. , 2019, 10(1):2359.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
ZHENG W, YANG J, CHEN H, et al. Atomically defined undercoordinated active sites for highly efficient CO2 electroreduction. Advanced Functional Materials , 2020, 30(4):1907658.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
TAO H, CHOI C, DING L X, et al. Nitrogen fixation by Ru single-atom electrocatalytic reduction. Chem. , 2019, 5(1):204-214.
DOI URL |
| [92] |
ZANG W, YANG T, ZOU H, et al. Copper single atoms anchored in porous nitrogen-doped carbon as efficient pH-universal catalysts for the nitrogen reduction reaction. ACS Catalysis , 2019, 9(11):10166-10173.
DOI URL |
| [93] |
HUANG Y, YANG T, YANG L, et al. Graphene-boron nitride hybrid-supported single Mo atom electrocatalysts for efficient nitrogen reduction reaction. Journal of Materials Chemistry A , 2019, 7(25):15173-15180.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
ZHU T, CHEN Q, LIAO P, et al. Single-atom Cu catalysts for enhanced electrocatalytic nitrate reduction with significant alleviation of nitrite production. Small , 2020, 16:2004526.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
GAN G, LI X, WANG L, et al. Active sites in single-atom Fe-Nx-C nanosheets for selective electrochemical dechlorination of 1,2-dichloroethane to ethylene. ACS Nano , 2020, 14(8):9929-9937.
DOI URL |
| [96] | XIONG Y, SUN W, XIN P, et al. Gram-scale synthesis of high-loading single-atomic-site Fe catalysts for effective epoxidation of styrene. Adv. Mater. , 2020, 32(34):e2000896. |
| [97] |
WAN X, LIU X, LI Y, et al. Fe-N-C electrocatalyst with dense active sites and efficient mass transport for high-performance proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Nature Catalysis , 2019, 2(3):259-268.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
CHENG Y, HE S, LU S, et al. Iron single atoms on graphene as nonprecious metal catalysts for high-temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Advanced Science , 2019, 6(10):1802066.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
LI B, ZHAO C, CHEN S, et al. Framework-porphyrin-derived single-atom bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts and their applications in Zn-air batteries. Adv. Mater. , 2019, 31(19):1900592.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
HAN J, MENG X, LU L, et al. Single-atom Fe-Nx-C as an efficient electrocatalyst for zinc-air batteries. Advanced Functional Materials , 2019, 29(41):1808872.
DOI URL |
| [101] |
CHEN L, ZHANG Y, DONG L, et al. Synergistic effect between atomically dispersed Fe and Co metal sites for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction. Journal of Materials Chemistry A , 2020, 8(8):4369-4375.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
XIAO M, XING Z, JIN Z, et al. Preferentially engineering FeN4 edge sites onto graphitic nanosheets for highly active and durable oxygen electrocatalysis in rechargeable Zn-air batteries. Adv. Mater. , 2020, 32(49):2004900.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
ZHANG Z, ZHAO X, XI S, et al. Atomically dispersed cobalt trifunctional electrocatalysts with tailored coordination environment for flexible rechargeable Zn-air battery and self-driven water splitting. Advanced Energy Materials , 2020, 10(48):2002896.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
ZHOU Y, TAO X, CHEN G, et al. Multilayer stabilization for fabricating high-loading single-atom catalysts. Nat. Commun. , 2020, 11(1):5892.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
NOH W Y, KIM E M, KIM K Y, et al. Immobilizing single atom catalytic sites onto highly reduced carbon hosts: Fe-N4/CNT as a durable oxygen reduction catalyst for Na-air batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A , 2020, 8(36):18891-18902.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
ZHANG L, LIU D, MUHAMMAD Z, et al. Single nickel atoms on nitrogen-doped graphene enabling enhanced kinetics of lithium-sulfur batteries. Adv. Mater. , 2019, 31(40):1903955.
DOI URL |
| [107] | LI B Q, KONG L, ZHAO C X, et al. Expediting redox kinetics of sulfur species by atomic-scale electrocatalysts in lithium-sulfur batteries. InforMat , 2019, 1(4):533-541. |
| [108] | YANG W, XU X, HOU L, et al. Nitrogen-enriched hollow carbon spheres coupled with efficient Co-Nx-C species as cathode catalysts for triiodide reduction in dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering , 2019, 7(2):2679-2685. |
| [109] |
YANG W, LI Z, XU X, et al. Atomic N-coordinated cobalt sites within nanomesh graphene as highly efficient electrocatalysts for triiodide reduction in dye-sensitized solar cells. Chemical Engineering Journal , 2018, 349:782-790.
DOI URL |
| [1] | DING Ling, JIANG Rui, TANG Zilong, YANG Yunqiong. MXene: Nanoengineering and Application as Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | YANG Zhuo, LU Yong, ZHAO Qing, CHEN Jun. X-ray Diffraction Rietveld Refinement and Its Application in Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | CHEN Qiang, BAI Shuxin, YE Yicong. Highly Thermal Conductive Silicon Carbide Ceramics Matrix Composites for Thermal Management: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | LIN Junliang, WANG Zhanjie. Research Progress on Ferroelectric Superlattices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [5] | NIU Jiaxue, SUN Si, LIU Pengfei, ZHANG Xiaodong, MU Xiaoyu. Copper-based Nanozymes: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [6] | YUAN Jingkun, XIONG Shufeng, CHEN Zhangwei. Research Trends and Challenges of Additive Manufacturing of Polymer-derived Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [7] | DU Jianyu, GE Chen. Recent Progress in Optoelectronic Artificial Synapse Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [8] | YANG Yang, CUI Hangyuan, ZHU Ying, WAN Changjin, WAN Qing. Research Progress of Flexible Neuromorphic Transistors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [9] | YOU Junqi, LI Ce, YANG Dongliang, SUN Linfeng. Double Dielectric Layer Metal-oxide Memristor: Design and Applications [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [10] | CHEN Kunfeng, HU Qianyu, LIU Feng, XUE Dongfeng. Multi-scale Crystallization Materials: Advances in in-situ Characterization Techniques and Computational Simulations [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [11] | ZHANG Chaoyi, TANG Huili, LI Xianke, WANG Qingguo, LUO Ping, WU Feng, ZHANG Chenbo, XUE Yanyan, XU Jun, HAN Jianfeng, LU Zhanwen. Research Progress of ScAlMgO4 Crystal: a Novel GaN and ZnO Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [12] | QI Zhanguo, LIU Lei, WANG Shouzhi, WANG Guogong, YU Jiaoxian, WANG Zhongxin, DUAN Xiulan, XU Xiangang, ZHANG Lei. Progress in GaN Single Crystals: HVPE Growth and Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [13] | LIN Siqi, LI Airan, FU Chenguang, LI Rongbing, JIN Min. Crystal Growth and Thermoelectric Properties of Zintl Phase Mg3X2 (X=Sb, Bi) Based Materials: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [14] | LIU Yan, ZHANG Keying, LI Tianyu, ZHOU Bo, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Electric-field Assisted Joining Technology for the Ceramics Materials: Current Status and Development Trend [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 113-124. |
| [15] | XIE Bing, CAI Jinxia, WANG Tongtong, LIU Zhiyong, JIANG Shenglin, ZHANG Haibo. Research Progress of Polymer-based Multilayer Composite Dielectrics with High Energy Storage Density [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||