
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 615-622.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200437
Special Issue: 【能源环境】光催化降解有机分子
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
AN Weijia1( ), LI Jing1,2, WANG Shuyao1, HU Jinshan1, LIN Zaiyuan2, CUI Wenquan1(
), LI Jing1,2, WANG Shuyao1, HU Jinshan1, LIN Zaiyuan2, CUI Wenquan1( ), LIU Li1, XIE Jun3, LIANG Yinghua1(
), LIU Li1, XIE Jun3, LIANG Yinghua1( )
)
Received:2020-08-10
Revised:2020-11-12
Published:2021-06-20
Online:2020-12-10
Contact:
CUI Wenquan, professor. E-mail: wkcui@ncst.edu.cn; LIANG Yinghua, professor. E-mail: liangyh@ncst.edu.cn
About author:AN Weijia(1989-), male, senior laboratory technician. E-mail: anweijia@ncst.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
AN Weijia, LI Jing, WANG Shuyao, HU Jinshan, LIN Zaiyuan, CUI Wenquan, LIU Li, XIE Jun, LIANG Yinghua. Fe(III)/rGO/Bi2MoO6 Composite Photocatalyst Preparation and Phenol Degradation by Photocatalytic Fenton Synergy[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 615-622.
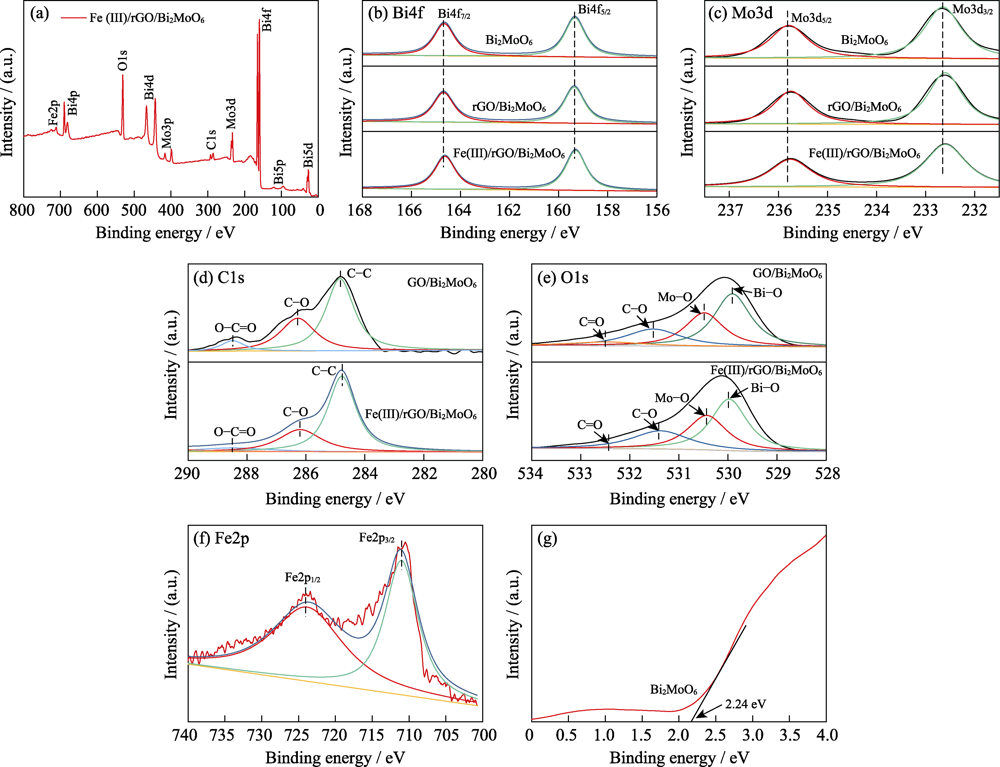
Fig. 3 XPS spectra of the compared composites (a) Full spectrum analysis; (b-f) XPS spectra of various element; (g) XPS spectra of valence band in Bi2MoO6
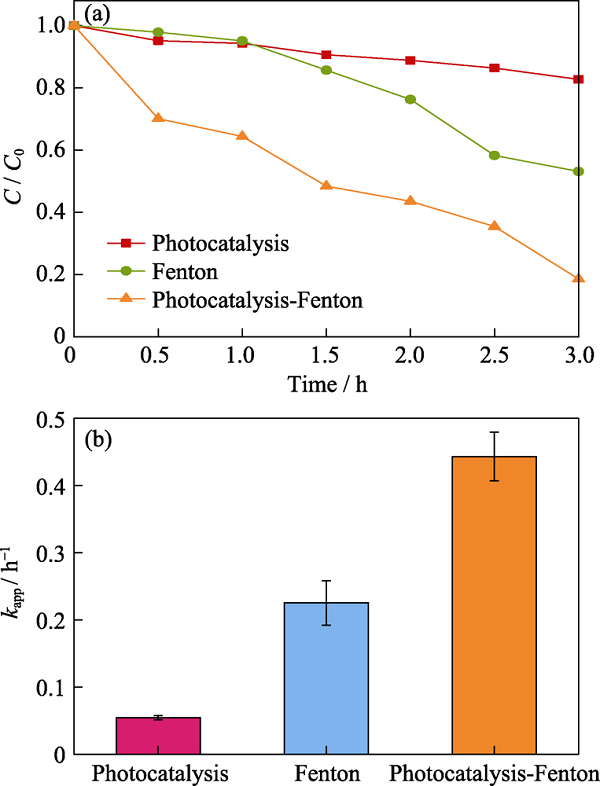
Fig. 4 (a) Phenol degradation activity by photocatalysis, Fenton, and photocatalysis-Fenton synergy, and (b) degradation rate constant over different conditions
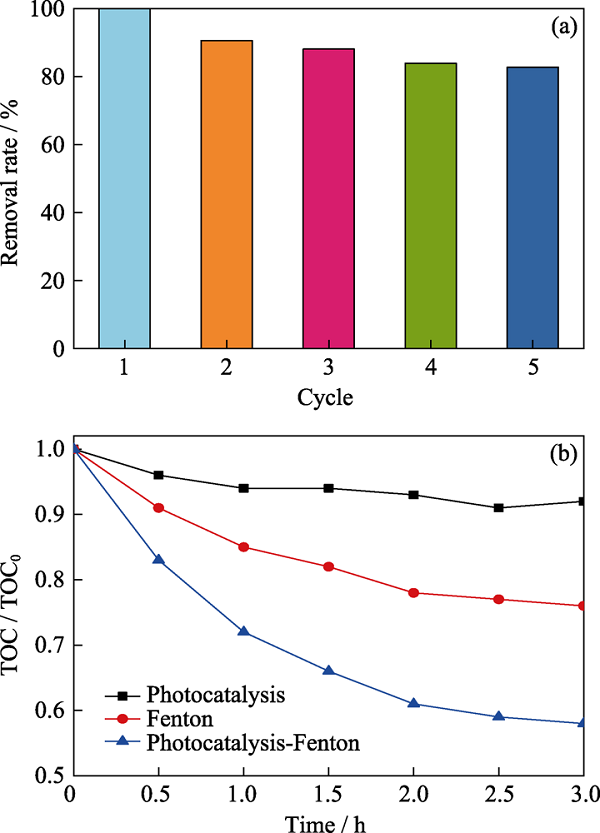
Fig. 5 (a) Photocatalysis-Fenton synergy degradation stability test, (b) TOC removal of phenol over photocatalysis, Fenton reaction, and photocatalysis-Fenton synergy
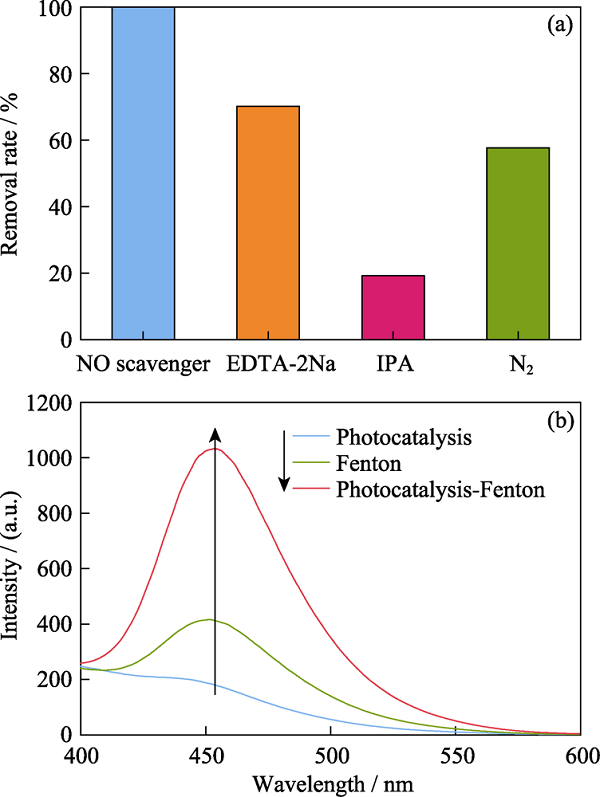
Fig. 7 (a) Influence of degradation activity with the addition of quenchers, and (b) concentration of ?OH generated at photocatalysis, Fenton and photocatalysis-Fenton synergy

Fig. S3 Comparison of the activity of different phenol removal efficiency (a) different proportions of Fe (III) (C0 = 5 ppm); (b) Different catalyst dosages (C0 = 5 ppm, 20% Fe (III)/rGO/Bi2MoO6); (c) different amounts of hydrogen peroxide (C0 = 5 ppm, 20% Fe (III)/rGO/Bi2MoO6, catalyst concentration: 1.0 g/L); (d) different pH (C0 = 5 ppm, 20 % Fe (III)/rGO/Bi2MoO6, catalyst concentration: 1.0 g/L, H2O2 = 19.5 mmol/L) *ppm=mg/L
| [1] |
ZHANG D S, CAI H, GAO K Y, et al. Preparation and visible-light photocatalytic degradation on metronidazole of Zn2SiO4-ZnO-biochar composites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020,35(8):923-930.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
AN W J, TIAN L Y, HU J S, et al. Efficient degradation of organic pollutants by catalytic ozonation and photocatalysis synergy system using double-functional MgO/g-C3N4 catalyst. Applied Surface Science, 2020,534:147518.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
AN W J, SUN K L, HU J S, et al. The Z-scheme Ag2CO3@g-C3N4 core-shell structure for increased photoinduced charge separation and stable photocatalytic degradation. Applied Surface Science, 2020,504:144345.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
HU J S, ZHANG P F, AN W J, et al. In-situ Fe-doped g-C3N4 heterogeneous catalyst via photocatalysis-Fenton reaction with enriched photocatalytic performance for removal of complex wastewater. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2019,245:130-142.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DU X, ZHAO T Y, XIU Z Y, et al. Nano-zero-valent iron and MnOx selective deposition on BiVO4 decahedron superstructures for promoted spatial charge separation and exceptional catalytic activity in visible-light-driven photocatalysis-Fenton coupling system. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019,377:330-340.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WU Q S, YANG H P, KANG L, et al. Fe-based metal-organic frameworks as Fenton-like catalysts for highly efficient degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride over a wide pH range: acceleration of Fe(II)/Fe(III) cycle under visible light irradiation. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2020,263:118282.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
XU P, XU H, ZHENG D Y, et al. The efficiency and mechanism in a novel electro-Fenton process assisted by anodic photocatalysis on advanced treatment of coal gasification wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019,361:968-974.
DOI URL |
| [8] | STEFFI T, ANOOP K V, VIKAS K S, et al. Once through continuous flow removal of metronidazole by dual effect of photo- Fenton and photocatalysis in a compound parabolic concentrator at pilot plant scale. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020,388:124184. |
| [9] | XU Z M, ZHENG R, CHEN Y, et al. Ordered mesoporous Fe/TiO2 with light enhanced photo-Fenton activity. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2019,40:631-637. |
| [10] |
HU J S, ZHANG P F, CUI J F, et al. High-efficiency removal of phenol and coking wastewater via photocatalysis-Fenton synergy over a Fe-g-C3N4 graphene hydrogel 3D structure. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2020,84:305-314.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GUO L, ZHANG K L, HAN X X, et al. 2D/2D type-II Cu2ZnSnS4/Bi2WO6 heterojunctions to promote visible-light-driven photo-Fenton catalytic activity. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2020,41:503-513.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
XING M Y, XU W J, DONG C C, et al. Metal sulfides as excellent co-catalysts for H2O2 decomposition in advanced oxidation processes. Chem, 2018,4:1359-1372.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHAO W H, WEI Z Q, ZHANG X D, et al. Magnetic recyclable MnFe2O4/CeO2/SnS2 ternary nano-photocatalyst for photo-Fenton degradation. Applied Catalysis A-General, 2020,593:117443.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MENG Q Q, LÜ C D, SUN J X, et al. High-efficiency Fe-Mediated Bi2MoO6 nitrogen-fixing photocatalyst: reduced surface work function and ameliorated surface reaction. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2019,256:117781.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
XIE Y Y, SHANG X T, LIU D, et al. Non-noble metal thickness- tunable Bi2MoO6 nanosheets for highly efficient visible-light-driven nitrobenzene reduction into aniline. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2019,259:118087.
DOI URL |
| [16] | WANG J L, DONG M R, ZHANG Q C, et al. Preparation of Bi2MoO6 microspheres with hollow structure and degradation performance of ofloxacin antibiotics. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2020,36:827-834. |
| [17] |
XIANG S W, ZHANG Z Y, WU ZHI, et al. 3D Heterostructured Ti-Based Bi2MoO6/Pd/TiO2 photocatalysts for high-efficiency solar light driven photo electrocatalytic hydrogen generation. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019,2:558-568.
DOI URL |
| [18] | LV J L, ZHANG J F, LIU J, et al. Bi SPR-promoted Z-scheme Bi2MoO6/CdS-diethylenetriamine composite with effectively enhanced visible light photocatalytic hydrogen evolution activity and stability. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018,6:696-706. |
| [19] |
XIU Z Y, CAO Y, XING Z P, et al. Wide spectral response photothermal catalysis-Fenton coupling systems with 3D hierarchical Fe3O4/Ag/Bi2MoO6 ternary hetero-superstructural magnetic microspheres for efficient high-toxic organic pollutants removal. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019,533:24-33.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
JING K Q, WEN M, REN Y H, et al. Hierarchical Bi2MoO6 spheres in situ assembled by monolayer nanosheets toward photocatalytic selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2019,243:10-18.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WANG S Y, DING X, YANG N, et al. Insight into the effect of bromine on facet-dependent surface oxygen vacancies construction and stabilization of Bi2MoO6 for efficient photocatalytic NO removal. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2020,265:118585.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
HU J S, LI J, CUI J F, et al. Surface oxygen vacancies enriched FeOOH/Bi2MoO6 photocatalysis-Fenton synergy degradation of organic pollutants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020,384:121399.
DOI URL |
| [23] | ZHU P F, CHEN Y J, DUAN M, et al. Construction and mechanism of a highly efficient and stable Z-scheme Ag3PO4/ reduced graphene oxide/Bi2MoO6 visible-light photocatalyst. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2018,8:3818-3832. |
| [24] |
XUE C, LI H, AN H, et al. Cross-linked bond accelerated interfacial charge transfer in monolayer zinc indium sulfide (ZnIn2S4)/reduced graphene oxide (RGO) heterostructure for photocatalytic hydrogen production with mechanistic insight. ACS Catalysis, 2018,8:1532-1545.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LIANG Y H, WANG X, AN W J, et al. A g-C3N4@ppy-rGO 3D structure hydrogel for efficient photocatalysis. Applied Surface Science, 2019,466:666-672.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZENG P, ZHANG Q G, PENG T Y, et al. One-pot synthesis of reduced graphene oxide-cadmium sulfide nanocomposite and its photocatalytic hydrogen production. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2011,13:21496-21502.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
XU Y S, ZHANG W D. Monodispersed Ag3PO4 nanocrystals loaded on the surface of spherical Bi2MoO6 with enhanced photocatalytic performance. Dalton Transactions, 2013,42:1094-1101.
DOI URL |
| [28] | YU H G, CAO G Q, CHEN FENG, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic performance of Ag3PO4 by simultaneous loading of Ag nanoparticles and Fe(III) cocatalyst. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2014,160:658-665. |
| [29] |
YANG L, DU C Y, TAN S Y, et al. Improved photocatalytic properties of Fe(III) ion doped Bi2MoO6 for the oxidation of organic pollutants. Ceramics International, 2021,47(4):5786-5794.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
MENG X C, ZHANG Z S. Bi2MoO6 co-modified by reduced graphene oxide and palladium (PdPd2+ and Pd0) with enhanced photocatalytic decomposition of phenol. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2017,209:383-393.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
WANG D J, SHEN H D, GUO L, et al. Design and construction of the sandwich-like Z-scheme multicomponent CdS/Ag/Bi2MoO6 heterostructure with enhanced photocatalytic performance in RhB photodegradation. New Journal of Chemistry, 2016,40(10):8614-8624.
DOI URL |
| [1] | WANG Lei, LI Jianjun, NING Jun, HU Tianyu, WANG Hongyang, ZHANG Zhanqun, WU Linxin. Enhanced Degradation of Methyl Orange with CoFe2O4@Zeolite Catalyst as Peroxymonosulfate Activator: Performance and Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 469-476. |
| [2] | CHEN Ying, LUAN Weiling, CHEN Haofeng, ZHU Xuanchen. Multi-scale Failure Behavior of Cathode in Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Stress Field [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 918-924. |
| [3] | CHEN Shikun, WANG Chuchu, CHEN Ye, LI Li, PAN Lu, WEN Guilin. Magnetic Ag2S/Ag/CoFe1.95Sm0.05O4 Z-scheme Heterojunction: Preparation and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1329-1336. |
| [4] | LI Tie, LI Yue, WANG Yingyi, ZHANG Ting. Preparation and Catalytic Properties of Graphene-Bismuth Ferrite Nanocrystal Nanocomposite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 725-732. |
| [5] | XIONG Jinyan, LUO Qiang, ZHAO Kai, ZHANG Mengmeng, HAN Chao, CHENG Gang. Facilely Anchoring Cu nanoparticles on WO3 Nanocubes for Enhanced Photocatalysis through Efficient Interface Charge Transfer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 325-331. |
| [6] | LAN Qing, SUN Shengrui, WU Ping, YANG Qingfeng, LIU Yangqiao. Co-doped CuO/Visible Light Synergistic Activation of PMS for Degradation of Rhodamine B and Its Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1171-1177. |
| [7] | LIU Cai, LIU Fang, HUANG Fang, WANG Xiaojuan. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Alga-based CDs-Cu-TiO2 Composite Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1154-1162. |
| [8] | BAO Feng, CHANG Jiang. Calcium Silicate Nanowires Based Composite Electrospun Scaffolds: Preparation, Ion Release and Cytocompatibility [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1199-1207. |
| [9] | ZHANG Xincong,GUO Ke,PENG Lianlian,WU Jieyu,ZHANG Fumin,ZHU Weidong,FU Yanghe. Degradation of Dye Wastewater over NH2-UiO-66: Piezoelectrically Induced Mechano-Catalytic Effect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 1023-1028. |
| [10] | ZHU Enquan,MA Yuhua,AINIWA· Munire,SU Zhi. Adsorption-enrichment and Localized-photodegradation of Bentonite-supported Red Phosphorus Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 803-808. |
| [11] | XU Jingwei,LI Zheng,WANG Zepu,YU Han,HE Qi,FU Nian,DING Bangfu,ZHENG Shukai,YAN Xiaobing. Morphology and Photocatalytic Performance Regulation of Nd3+-doped BiVO4 with Staggered Band Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 789-795. |
| [12] | ZHANG Xiaoxu,ZHU Dongbin,LIANG Jinsheng. Progress on Hydrothermal Stability of Dental Zirconia Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 759-768. |
| [13] | JI Bang, ZHAO Wenfeng, DUAN Jieli, MA Lizhe, FU Lanhui, YANG Zhou. Synthesis of TiO2/WO3 on Nickel Foam for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Ethylene [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 581-588. |
| [14] | LIU Ziyang, GENG Zhen, LI Zhaoyang. Preparing Biomedical CaCO3/HA Composite with Oyster Shell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 601-607. |
| [15] | QIANG Xiao-Hu, LI Bin-Bin, HUANG Da-Jian, ZHOU Song-Yi. Boron Oxide on Mechanical and Degradation Property of Calcium Polyphosphate Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 201-206. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||