
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 283-291.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200243
Special Issue: 【虚拟专辑】层状MAX,MXene及其他二维材料; 【信息功能】Max层状材料、MXene及其他二维材料
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2020-05-08
Revised:2020-08-25
Published:2021-03-20
Online:2020-09-09
Contact:
LI Haibo, associate professor. E-mail: lihaibo@nxu.edu.cn
About author:XI Wen(1994-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: xiwen_1994@yeah.net
Supported by:CLC Number:
XI Wen, LI Haibo. Preparation of TiO2/Ti3C2Tx Composite for Hybrid Capacitive Deionization[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 283-291.
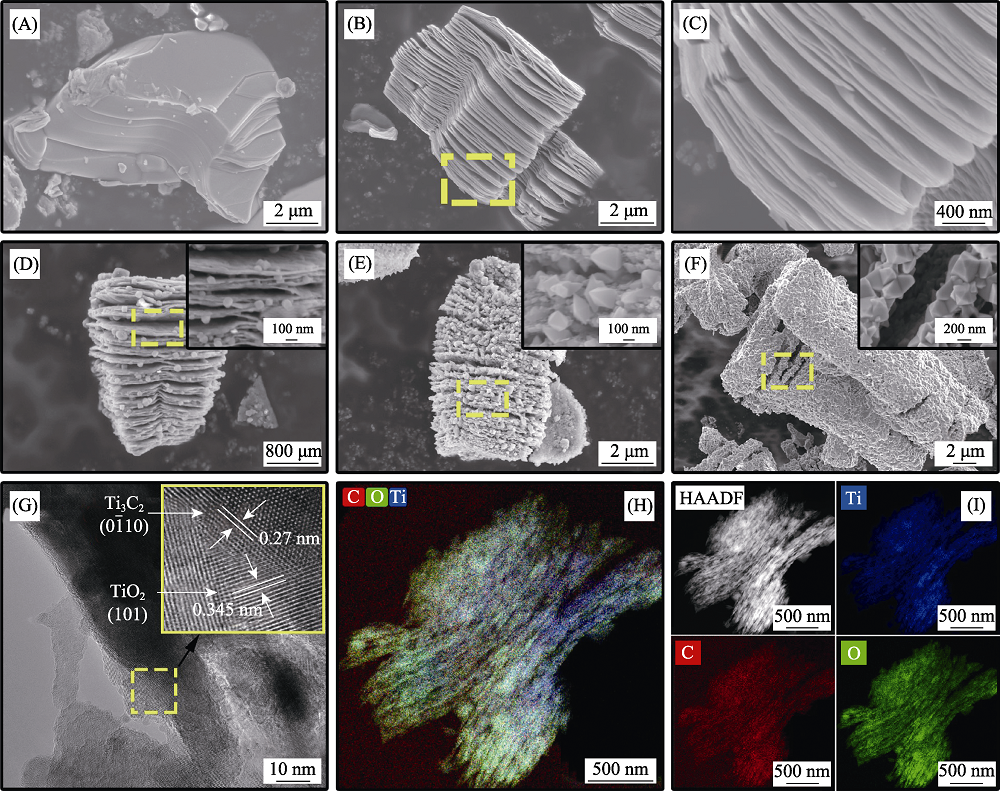
Fig. 3 SEM images of Ti3AlC2(A), Ti3C2Tx(B, C), TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-350(D), TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450(E) and TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-550(F), HRTEM (G) and elemental mapping(H, I) of TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450
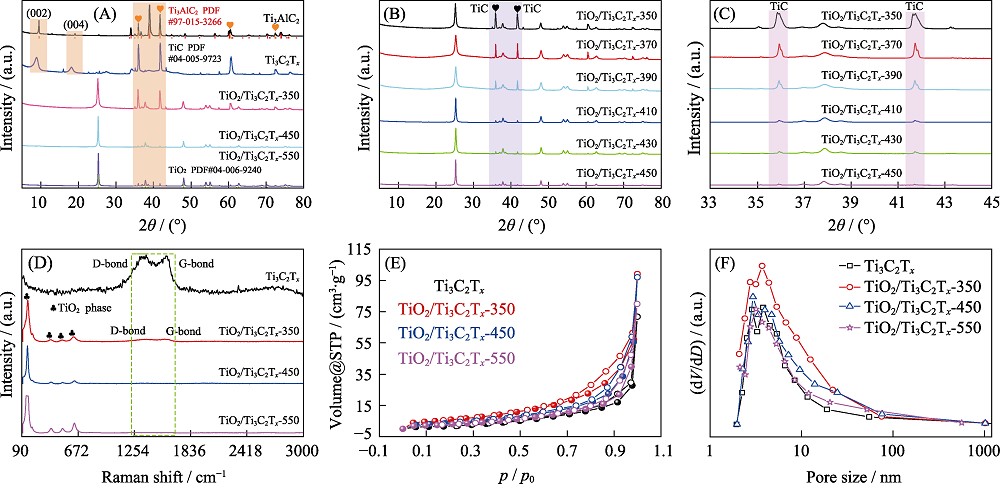
Fig. 4 XRD patterns (A) of various samples, XRD patterns (B, C) of TiO2/Ti3C2Tx calcined at different temperatures, Raman spectra (D), N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms (E) and pore size distributions (F) of various samples (A)Ti3AlC2, Ti3C2Tx, TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-350, TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450 and TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-550; (B-D) Ti3C2Tx and TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-350, TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450 and TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-550
| Sample | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore size /nm | Pore volume /(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti3C2Tx | 8.542 | 51.979 | 0.111 |
| TiO2-Ti3C2Tx-350 | 23.227 | 26.394 | 0.153 |
| TiO2-Ti3C2Tx-450 | 14.630 | 41.005 | 0.150 |
| TiO2-Ti3C2Tx-550 | 12.324 | 40.134 | 0.124 |
Table 1 Comparison of specific surface areas, pore sizes and pore volumes of Ti3C2Tx, TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-350, TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450 and TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-550
| Sample | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore size /nm | Pore volume /(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti3C2Tx | 8.542 | 51.979 | 0.111 |
| TiO2-Ti3C2Tx-350 | 23.227 | 26.394 | 0.153 |
| TiO2-Ti3C2Tx-450 | 14.630 | 41.005 | 0.150 |
| TiO2-Ti3C2Tx-550 | 12.324 | 40.134 | 0.124 |
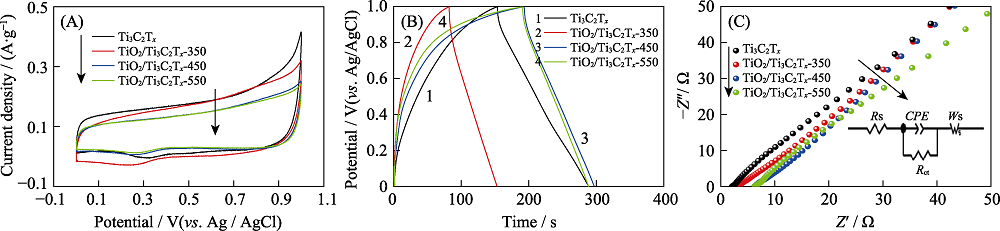
Fig. 6 CV curves(A), GCD(B) and EIS(C) of Ti3C2Tx, TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-350, TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450 and TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-550 with inset in (C) representing the equivalent circuit
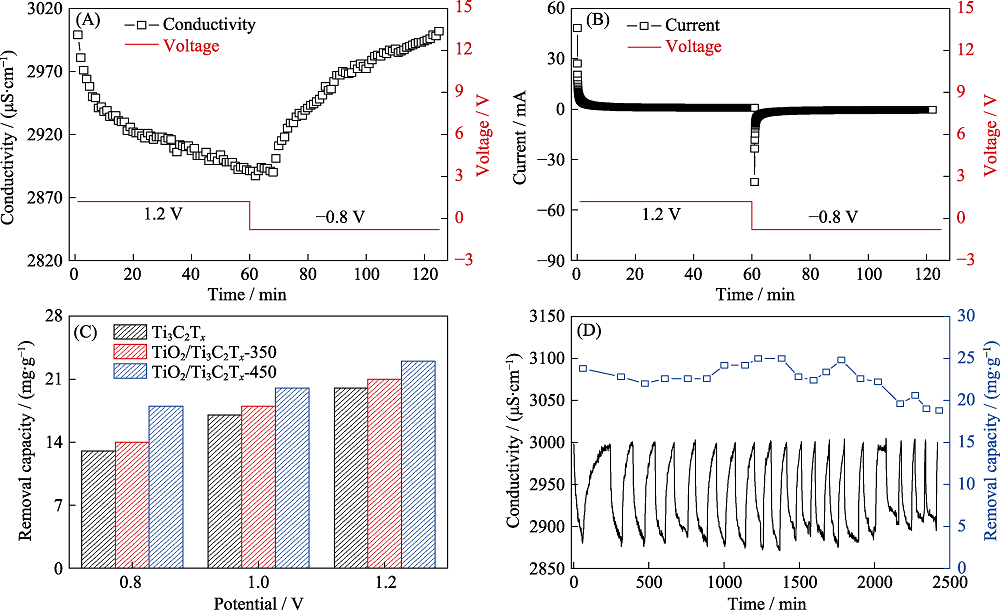
Fig. 7 Desalination performance of TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450‖AC device (A, B) Conductivity and current transient of TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450‖AC device in NaCl solution with an initial conductivity of 3000 μS·cm-1 at 1.2 V; (C) Salt removal capacity of Ti3C2Tx, TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-350 and TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450 at various voltages; (D) Regeneration curves of TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450‖AC device
| Sample | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Initial conductivity /(mg·L-1) | Voltage/V | Desalination capacity/(mg·g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-conditioned Ti3C2Tx MXene | - | 585.0 | -1.2 (discharge potential) | 9.19 | [42] |
| Ti3C2 MXene | 6.0 | 292.5 | 1.2 | 13.00 | [39] |
| Ar plasma modified Ti3C2Tx | - | 500.0 | 1.4 | 26.80 | [43] |
| LiH/HCl-etched Ti3C2Tx MXene | 2.1 | 585.0 | 1.2 | 67.70 | [44] |
| Porous Ti3C2Tx MXene | 293.0 | 10000.0 | 1.2 | 45.00 | [40] |
| Porous nitrogen-doped MXene sheets (N-Ti3C2Tx) | 368.8 | 5000.0 | 1.2 | 43.50±1.70 | [45] |
| TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450 | 14.6 | 1500.0 | 1.2 | 22.00 | This work |
Table 2 Comparison of salt removal capacity among various CDI electrodes
| Sample | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Initial conductivity /(mg·L-1) | Voltage/V | Desalination capacity/(mg·g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-conditioned Ti3C2Tx MXene | - | 585.0 | -1.2 (discharge potential) | 9.19 | [42] |
| Ti3C2 MXene | 6.0 | 292.5 | 1.2 | 13.00 | [39] |
| Ar plasma modified Ti3C2Tx | - | 500.0 | 1.4 | 26.80 | [43] |
| LiH/HCl-etched Ti3C2Tx MXene | 2.1 | 585.0 | 1.2 | 67.70 | [44] |
| Porous Ti3C2Tx MXene | 293.0 | 10000.0 | 1.2 | 45.00 | [40] |
| Porous nitrogen-doped MXene sheets (N-Ti3C2Tx) | 368.8 | 5000.0 | 1.2 | 43.50±1.70 | [45] |
| TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450 | 14.6 | 1500.0 | 1.2 | 22.00 | This work |
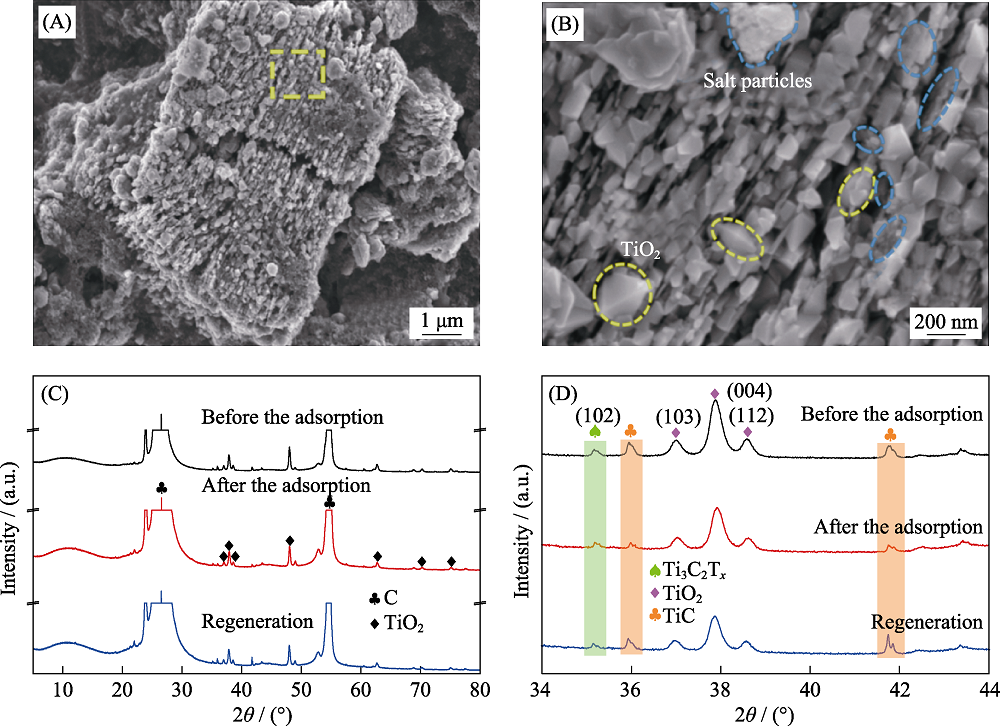
Fig. 8 SEM (A) and the enlarged (B) images of TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450 after 20 cycling, XRD patterns(C, D) of TiO2/Ti3C2Tx-450 before and after desalting and regeneration (B) Enlarged image of (A); (D) Enlarged image of (C) within 2θ = 34°-44°
| [1] |
XU X, TAN H, WANG Z, et al. Extraordinary capacitive deionization performance of highly-ordered mesoporous carbon nano- polyhedra for brackish water desalination. Environmental Science: Nano, 2019,6(3):981-989.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
SHANNON M A, BOHN P W, ELIMELECH M, et al. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature, 2008,452(7185):301-310.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] | LI L, ZHAO J, SUN Y, et al. Ionically cross-linked sodium alginate/ ĸ-carrageenan double-network gel beads with low-swelling, enhanced mechanical properties, and excellent adsorption performance. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019,372:1091-1103. |
| [4] | XU X, ALLAH A E, WANG C, et al. Capacitive deionization using nitrogen-doped mesostructured carbons for highly efficient brackish water desalination. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019,362:887-896. |
| [5] | CUI T, YANG T, XU C Y, et al. Assessment of the impact of climate change on flow regime at multiple temporal scales and potential ecological implications in an alpine river. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 2018,32(6):1849-1866. |
| [6] | ZHAO F, YUAN Z. H, ZHONG L B, et al. Review on electrode materials and Capacitive Deionization (CDI) technology for desalination. Technology of Water Treatment, 2016,42(5):38-44. |
| [7] | PEÑATE B, GARCÍA-RODRÍGUEZ L. Current trends and future prospects in the design of seawater reverse osmosis desalination technology. Desalination, 2012,284:1-8. |
| [8] | ZHAO D, LEE L Y, ONG S L, et al. Electrodialysis reversal for industrial reverse osmosis brine treatment. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019,213:339-347. |
| [9] | LEE K P, ARNOT T C, MATTIA D. A review of reverse osmosis membrane materials for desalination-development to date and future potential. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011,370(1/2):1-22. |
| [10] | GAO C J, ZHOU Y, LIU L F. Recent development and prospect of seawater reverse osmosis desalination technology. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2016,35(1):1-12. |
| [11] | ZHOU Y, YU S C, GAO C J. Reverse osmosis composite membrane (Ⅰ) chemical structure and performance. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2006,57(6):1370-1373. |
| [12] | CHEN Y, YUE M, HUANG Z H, et al. Electrospun carbon nanofiber networks from phenolic resin for capacitive deionization. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014,252:30-37. |
| [13] | TIAN X L, WANG L, CHI B, et al. Formation of a tubular assembly by ultrathin Ti0.8Co0.2N nanosheets as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts for hydrogen-/metal-air fuel cells. ACS Catalysis, 2018,8(10):8970-8975. |
| [14] |
GALAMA A H, SAAKES M, BRUNING H, et al. Seawater predesalination with electrodialysis. Desalination, 2014,342:61-69.
DOI URL |
| [15] | DENG D, AOUAD W, BRAFF W A, et al. Water purification by shock electrodialysis: deionization, filtration, separation, and disinfection. Desalination, 2015,357:77-83. |
| [16] | YAN H Y, WANG Y M, JIANG C X, et al. Ion exchange membrane electrodialysis for high salinity wastewater “zero liquid discharge”: applications, opportunities and challenges. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019,38(328):672-681. |
| [17] | AN X, LIU Z, HU Y. Amphiphobic surface modification of electrospun nanofibrous membranes for anti-wetting performance in membrane distillation. Desalination, 2018,432:23-31. |
| [18] | LIU L F, ZHOU Y S, XUE J, et al. Enhanced antipressure ability through graphene oxide membrane by intercalating g-C3N4 nanosheets for water purification. AICHE Journal, 2019, 65(10): e16699- 1-13. |
| [19] |
HOU Q Q, WU Y, ZHOU SH, et al. Ultra-tuning of the aperture size in stiffened ZIF-8_Cm frameworks with mixd-linker strategy for enhanced CO2/CH4 separation. Angewandte Chemie- International Edition, 2019,58(1):327-331.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] | AL-MUTAZ I S, WAZEER I. Comparative performance evaluation of conventional multi-effect evaporation desalination processes. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2014,73(1):1194-1203. |
| [21] | PORADA S, ZHAO R, VAN DER WAL A, et al. Review on the science and technology of water desalination by capacitive deionization. Progress in Materials Science, 2013,58(8):1388-1442. |
| [22] | YAN J J, SHAO S F, WANG J H, et al. Improvement of a multi- stage flash seawater desalination system for cogeneration power plants. Desalination, 2007,217(1/2/3):191-202. |
| [23] | AVLONITIS S A, KOUROUMBAS K, VLACHAKIS N. Energy consumption and membrane replacement cost for seawater RO desalination plants. Desalination, 2003,157(1):151-158. |
| [24] | WU Y C, YING D W, WANG Y L, et al. Capacitive desalination technology and its application in wastewater treatment. Technology of Water Treatment, 2019,45(8):1-15. |
| [25] | LEE J, KIM S, KIM C, et al. Hybrid capacitive deionization to enhance the desalination performance of capacitive techniques. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014,7:3683-3689. |
| [26] | WANG S Y, WANG G, CHE X P, et al. Enhancing the capacitive deionization performance of NaMnO2 by interface engineering and redox-reaction. Environmental Science: Nano, 2019,6:2379-2388. |
| [27] |
NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V, et al. Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Advanced Materials, 2011,23(37):4248-4253.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] | ANASORI B, LUKATSKAYA M R, GOGOTSI Y. 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017,2:16098. |
| [29] | NAGUIB M, MOCHALIN V N, BARSOUM M W, et al. Two- dimensional materials: 25th anniversary article: MXenes: a new family of two-dimensional materials. Advanced Materials, 2014,26(7):982-982. |
| [30] | ALHABEB M, MALESKI K, ANASORI B, et al. Guidelines for synthesis and processing of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene). Chemistry of Materials, 2017,29(18):7633-7644. |
| [31] | DING L, LI L B, LIU Y C, et al. Effective ion sieving with Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes for production of drinking water from seawater. Nature Sustainability, 2020,3(4):296. |
| [32] |
DING L, XIAO D, LU Z, et al. Oppositely charged Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes with 2D nanofluidic channels for osmotic energy harvesting. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2020,59(22):8720-8726.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] | GUO J, PENG Q, FU H, et al. Heavy-metal adsorption behavior of two-dimensional alkalization-intercalated MXene by first-principles calculations. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015,119(36):20923-20930. |
| [34] |
REN C E, HATZELL K B, ALHABEB M, et al. Charge-and size- selective ion sieving through Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2015,6(20):4026-4031.
URL PMID |
| [35] |
TANG Q, ZHOU Z, SHEN P. Are MXenes promising anode materials for Li ion batteries? computational studies on electronic properties and Li storage capability of Ti3C2 and Ti3C2X2 (X=F, OH) monolayer. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012,134(40):16909-16916.
DOI URL PMID |
| [36] |
GUO X, ZHANG X, ZHAO S, et al. High adsorption capacity of heavy metals on two-dimensional MXenes: an ab initio study with molecular dynamics simulation. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016,18(1):228-233.
URL PMID |
| [37] |
ANASORI B, XIE Y, BEIDAGHI M, et al. Two-dimensional, ordered, double transition metals carbides (MXenes). ACS Nano, 2015,9(10):9507-9516.
DOI URL PMID |
| [38] | LU ZONG, WEI Y Y, DENG J J, et al. Self-crosslinked MXene (Ti3C2Tx) membranes with good antiswelling property for monovalent metal ion exclusion. ACS Nano, 2019,3:10535-10544. |
| [39] | SRIMUK P, KAASIK F, KRÜNER B, et al. MXene as a novel intercalation-type pseudocapacitive cathode and anode for capacitive deionization. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2016,4(47):18265-18271. |
| [40] | BAO W, TANG X, GUO X, et al. Porous cryo-dried MXene for efficient capacitive deionization. Joule, 2018,2(4):778-787. |
| [41] | LOW J X, ZHANG L Y, TONG T, et al. TiO2/MXene Ti3C2 composite with excellent photocatalytic CO2 reduction activity. Journal of Catalysis, 2018,361:255-266. |
| [42] | AGARTAN L, HANTANASIRISAKUL K, BUCZEK S, et al. Influence of operating conditions on the desalination performance of a symmetric pre-conditioned Ti3C2Tx-MXene membrane capacitive deionization system. Desalination, 2020,477:114267. |
| [43] | GUO L, WANG X, LEONG Z Y, et al. Ar plasma modification of 2D MXene Ti3C2Tx nanosheets for efficient capacitive desalination. Flat. Chem., 2018,8:17-24. |
| [44] | MA J, CHENG Y, WANG L, et al. Free-standing Ti3C2Tx MXene film as binder-free electrode in capacitive deionization with an ultrahigh desalination capacity. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020,384:123329. |
| [45] | AMIRI A, CHEN Y, TENG C B, et al. Porous nitrogen-doped MXene-based electrodes for capacitive deionization. Energy Storage Mater., 2020,25:731-739. |
| [46] | XI W, LI H B. Pseudo-capacitive deionization behavior of CuAl- mixed metal. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, 2020,6(2):296-302. |
| [1] | MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [2] | GUO Chunxia, CHEN Weidong, YAN Shufang, ZHAO Xueping, YANG Ao, MA Wen. Adsorption of Arsenate in Water by Zirconia-halloysite Nanotube Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 529-536. |
| [3] | WANG Shiyi, FENG Aihu, LI Xiaoyan, YU Yun. Pb (II) Adsorption Process of Fe3O4 Supported Ti3C2Tx [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [4] | YU Yefan, XU Ling, NI Zhongbing, SHI Dongjian, CHEN Mingqing. Prussian Blue Modified Biochar: Preparation and Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen from Sewage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 205-212. |
| [5] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Mesoporous Organic-inorganic Hybrid Siliceous Hollow Spheres: Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [6] | LIU Cheng, ZHAO Qian, MOU Zhiwei, LEI Jiehong, DUAN Tao. Adsorption Properties of Novel Bismuth-based SiOCNF Composite Membrane for Radioactive Gaseous Iodine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1043-1050. |
| [7] | ZHOU Fan, BI Hui, HUANG Fuqiang. Ultra-large Specific Surface Area Activated Carbon Synthesized from Rice Husk with High Adsorption Capacity for Methylene Blue [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 893-903. |
| [8] | YU Xiangkun, LIU Kun, LI Zhipeng, ZHAO Yulu, SHEN Jinyou, MAO Ping, SUN Aiwu, JIANG Jinlong. Efficient Adsorption of Radioactive Iodide by Copper/Palygorskite Composite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 856-864. |
| [9] | SU Li, YANG Jianping, LAN Yue, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Interface Design of Iron Nanoparticles for Environmental Remediation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 561-569. |
| [10] | WANG Tingting, SHI Shumei, LIU Chenyuan, ZHU Wancheng, ZHANG Heng. Synthesis of Hierarchical Porous Nickel Phyllosilicate Microspheres as Efficient Adsorbents for Removal of Basic Fuchsin [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1330-1336. |
| [11] | GUO Yu, JIANG Xiaoqing, WU Hongmei, XIAO Yu, WU Dafu, LIU Xin. Preparation of 2-hydroxy-1-naphthalene Functionalized SBA-15 Adsorbent for the Adsorption of Chromium(III) Ions from Aqueous Solution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1163-1170. |
| [12] | ZHANG Ruihong, WEI Xin, LU Zhanhui, AI Yuejie. Training Model for Predicting Adsorption Energy of Metal Ions Based on Machine Learning [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1178-1184. |
| [13] | HE Junlong, SONG Erhong, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. DFT Calculation of NO Adsorption on Cr Doped Graphene [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1047-1052. |
| [14] | ZHU Enquan,MA Yuhua,AINIWA· Munire,SU Zhi. Adsorption-enrichment and Localized-photodegradation of Bentonite-supported Red Phosphorus Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 803-808. |
| [15] | ZHAI Wanru,WANG Jiahui,WANG Maohuai,DU Xuemei,WEI Shuxian. Adsorption and Separation of CO2/N2 in Metal Organic Frameworks: a Theoretical Investigation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(6): 697-702. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
