
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (12): 1340-1348.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200133
Special Issue: 环境材料论文精选(2020); 【虚拟专辑】放射性污染物去除(2020~2021)
Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Xucong1,2,3( ),DENG Hao3,JIANG Zhongyi1,2(
),DENG Hao3,JIANG Zhongyi1,2( ),YUAN Liyong3(
),YUAN Liyong3( )
)
Received:2020-03-16
Revised:2020-04-20
Published:2020-12-20
Online:2020-06-09
About author:WANG Xucong(1994–), male, Master candidate. E-mail: wangxc@ihep.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Xucong, DENG Hao, JIANG Zhongyi, YUAN Liyong. Photocatalytic Reduction of Re (VII) on Amorphous TiO2/g-C3N4 Derived from Different N Sources[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12): 1340-1348.
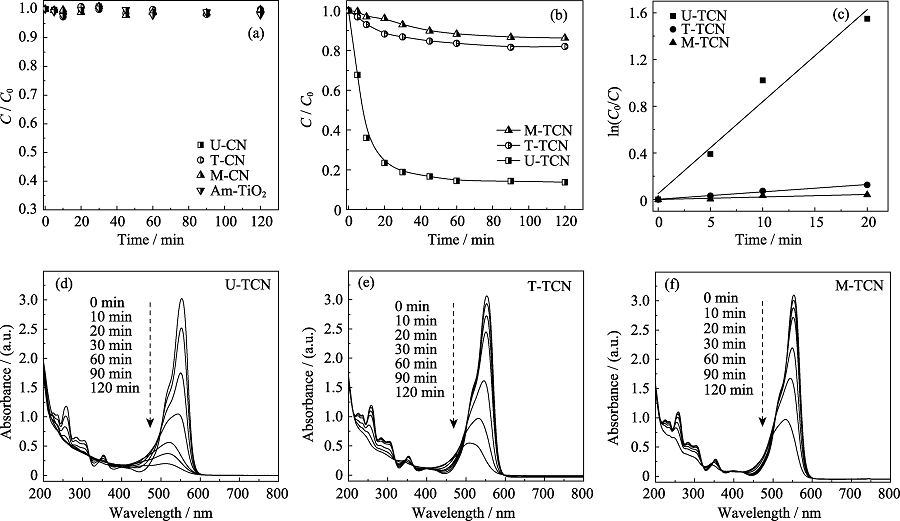
Fig. 7 Photocatalytic reduction and removal of Re(VII) using (a) U-CN, T-CN, M-CN, Am-TiO2 and (b) U-TCN, T-TCN and M-TCN composites under UV-Vis irradiation; (c) Linear fitting of Langmuir-Hinshelwood equation; The photodegradation of RhB using 0.4 g?L-1 (d) U-TCN, (e) T-TCN and (f) M-TCN under UV-Vis irradiation
| Sample | Re(VII) removed | k/min-1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-TCN | 90% | 0.0788 | 0.9524 |
| T-TCN | 20% | 0.0063 | 0.9861 |
| M-TCN | 15% | 0.0021 | 0.7954 |
Table 1 Kinetic parameters of photocatalytic reduction and removal of Re(VII) using TCN composites
| Sample | Re(VII) removed | k/min-1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-TCN | 90% | 0.0788 | 0.9524 |
| T-TCN | 20% | 0.0063 | 0.9861 |
| M-TCN | 15% | 0.0021 | 0.7954 |
| Sample | Bond | Na | R/nmb | σ2/nm2 c | R-factord |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Am-TiO2 | Ti-O | 1.2 | 0.198(3) | 3×10-6 | |
| Ti-O | 1.2 | 0.183(2) | 0 | 0.001 | |
| Ti-Ti | 1.0 | 0.306(2) | 6.5×10-5 | ||
| U-TCN | Ti-O | 1.5 | 0.192(2) | 2×10-5 | |
| Ti-O | 1.0 | 0.184(3) | 0 | 0.017 | |
| Ti-Ti | 1.7 | 0.312(2) | 8.9×10-5 | ||
| U-TCN/Re | Ti-O | 1.2 | 0.203(3) | 1.0×10-5 | |
| Ti-O | 1.2 | 0.188(2) | 3×10-6 | 0.017 | |
| Ti-Ti | 1.6 | 0.314(2) | 9.8×10-5 |
Table 2 Fitting parameters from the analysis of EXAFS data
| Sample | Bond | Na | R/nmb | σ2/nm2 c | R-factord |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Am-TiO2 | Ti-O | 1.2 | 0.198(3) | 3×10-6 | |
| Ti-O | 1.2 | 0.183(2) | 0 | 0.001 | |
| Ti-Ti | 1.0 | 0.306(2) | 6.5×10-5 | ||
| U-TCN | Ti-O | 1.5 | 0.192(2) | 2×10-5 | |
| Ti-O | 1.0 | 0.184(3) | 0 | 0.017 | |
| Ti-Ti | 1.7 | 0.312(2) | 8.9×10-5 | ||
| U-TCN/Re | Ti-O | 1.2 | 0.203(3) | 1.0×10-5 | |
| Ti-O | 1.2 | 0.188(2) | 3×10-6 | 0.017 | |
| Ti-Ti | 1.6 | 0.314(2) | 9.8×10-5 |
| [1] | SHEN D, FAN X, SU X, et al. Study of sorption of technetium on pyrrhotine. Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemistry, 2001,23(2):72-78. |
| [2] |
MEI L, LI F Z, LAN J H, et al. Anion-adaptive crystalline cationic material for 99TcO4- trapping. Nature Communications, 2019,10(1):1532.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] |
MEENA A H, ARAI Y. Environmental geochemistry of technetium. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2017,15(2):241-263.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZACHARA J M, HEALD S M, JEON B H, et al. Reduction of pertechnetate [Tc(VII)] by aqueous Fe(II) and the nature of solid phase redox products. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007,71(9):2137-2157.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
PEARCE C I, ICENHOWER J P, ASMUSSEN R M, et al. Technetium stabilization in low-solubility sulfide phases: a review. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2018,2(6):532-547.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SHANG Y, XIAO J, WENG H, et al. Efficient separation of Re(VII) by radiation-induced reduction from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018,341:317-326.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WANG L, SONG H, YUAN L, et al. Effective removal of anionic Re(VII) by surface-modified Ti2CTx MXene nanocomposites: implications for Tc(VII) sequestration. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019,53(7):3739-3747.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] |
DENG H, LI Z, WANG X, et al. Efficient photocatalytic reduction of aqueous perrhenate and pertechnetate. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019,53(18):10917-10925.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] |
BURTON-PYE B P, RADIVOJEVIC I, MCGREGOR D, et al. Photoreduction of 99Tc pertechnetate by nanometer-sized metal oxides: new strategies for formation and sequestration of low-valent technetium . Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011,133(46):18802-18815.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
RAZIQ F, SUN L Q, WANG Y Y, et al. Synthesis of large surface-area g-C3N4 comodified with MnOx and Au-TiO2 as efficient visible-light photocatalysts for fuel production. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018,8(3):1701580.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
PELAEZ M, NOLAN N T, PILLAI S C, et al. A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2012,125:331-349.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WEI K, LIE K X, YAN L S, et al. One-step fabrication of g-C3N4 nanosheets/TiO2 hollow microspheres heterojunctions with atomic level hybridization and their application in the multi-component synergistic photocatalytic systems. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2018,222:88-98.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LI Z J, HUANG Z W, GUO W L, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic removal of Uranium(VI) from aqueous solution by magnetic TiO2/Fe3O4 and its graphene composite. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017,51(10):5666-5674.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] |
TIAN C, ZHAO H, MEI J, et al. Cost-efficient graphitic carbon nitride as an effective photocatalyst for antibiotic degradation: an insight into the effects of different precursors and coexisting ions, and photocatalytic mechanism. Chemistry - An Asian Journal, 2019,14(1):162-169.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WANG X, MAEDA K, THOMAS A, et al. A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light. Nature Materials, 2009,8(1):76-80.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
ONG W, TAN L, NG Y H, et al. Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-based photocatalysts for artificial photosynthesis and environmental remediation: are we a step closer to achieving sustainability? Chemical Reviews, 2016,116(12):7159-7329.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
DONG H, GUO X, YANG C, et al. Synthesis of g-C3N4 by different precursors under burning explosion effect and its photocatalytic degradation for tylosin. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018,230:65-76.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
PHAM T T, SHIN E W. Influence of g-C3N4 precursors in g-C3N4/NiTiO3 composites on photocatalytic behavior and the interconnection between g-C3N4 and NiTiO3. Langmuir, 2018,34(44):13144-13154.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
HOLST J R, GILLAN E G. From triazines to heptazines: deciphering the local structure of amorphous nitrogen-rich carbon nitride materials. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008,130(23):7373-7379.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] |
DONG F, WANG Z, SUN Y, et al. Engineering the nanoarchitecture and texture of polymeric carbon nitride semiconductor for enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2013,401:70-79.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
YAN S C, LI Z S, ZOU Z G. Photodegradation performance of g-C3N4 fabricated by directly heating melamine. Langmuir, 2009,25(17):10397-10401.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] |
ZHANG G, ZHANG J, ZHANG M, et al. Polycondensation of thiourea into carbon nitride semiconductors as visible light photocatalysts. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012,22(16):8083-8091.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
TONG Z W, YANG D, XIAO T X, et al. Biomimetic fabrication of g-C3N4/TiO2 nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic activity toward organic pollutant degradation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015,260:117-125.
DOI URL |
| [24] | LI J, ZHANG M, LI X, et al. Effect of the calcination temperature on the visible light photocatalytic activity of direct contact Z-scheme g-C3N4-TiO2 heterojunction. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2017,212:106-114. |
| [25] |
LIU J, ZHANG T, WANG Z, et al. Simple pyrolysis of urea into graphitic carbon nitride with recyclable adsorption and photocatalytic activity. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011,21(38):14398-14401.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
YANG W, LI B. A novel liquid template corrosion approach for layered silica with various morphologies and different nanolayer thicknesses. Nanoscale, 2014,6(4):2292-2298.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
XIA P, ZHU B, YU J, et al. Ultra-thin nanosheet assemblies of graphitic carbon nitride for enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017,5(7):3230-3238.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LI Y, SASAKI T, SHIMIZU Y, et al. Hexagonal-close-packed, hierarchical amorphous TiO2 nanocolumn arrays: transferability, enhanced photocatalytic activity, and superamphiphilicity without UV irradiation. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008,130(44):14755-14762.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
KONSTANTINOU I K, ALBANIS T A. TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations: a review. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2004,49(1):1-14.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
HUO L, XIE W, QIAN T, et al. Reductive immobilization of pertechnetate in soil and groundwater using synthetic pyrite nanoparticles. Chemosphere, 2017,174:456-465.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] |
FU H, ZHANG S, XU T, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of RhB by fluorinated Bi2WO6 and distributions of the intermediate products. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008,42(6):2085-2091.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] |
LEI P, CHEN C, YANG J, et al. Degradation of dye pollutants by immobilized polyoxometalate with H2O2 under visible-light irradiation. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005,39(21):8466-8474.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] |
CHEN C, ZHAO W, LI J, et al. Formation and identification of intermediates in the visible-light-assisted photodegradation of Sulforhodamine-B dye in aqueous TiO2 dispersion. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002,36(16):3604-3611.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] |
JIANG Z, WAN W, LI H, et al. A hierarchical Z-Scheme α-Fe2O3/ g-C3N4 hybrid for enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Advanced Materials, 2018,30(10):1706108.
DOI URL |
| [35] | LIU H, CHEN D, WANG Z, et al. Microwave-assisted molten-salt rapid synthesis of isotype triazine-/heptazine based g-C3N4 heterojunctions with highly enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2017,203:300-313. |
| [36] |
ZHANG H, CHEN B, BANFIELD J F, et al. Atomic structure of nanometer-sized amorphous TiO2. Physical Review B, 2008,78(21):214106.
DOI URL |
| [1] | HONG Jiahui, MA Ran, WU Yunchao, WEN Tao, AI Yuejie. CoNx/g-C3N4 Nanomaterials Preparation by MOFs Self-sacrificing Template Method for Efficient Photocatalytic Reduction of U(VI) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 741-749. |
| [2] | CAI Miao, CHEN Zihang, ZENG Shi, DU Jianghui, XIONG Juan. CuS Nanosheet Decorated Bi5O7I Composite for the Enhanced Photocatalytic Reduction Activity of Aqueous Cr(VI) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 665-672. |
| [3] | JIANG Li, GAO Huihui, CAO Ruya, ZHANG Shouwei, LI Jiaxing. Construction of Novel Three Dimensionally Macroporous g-C3N4 for Efficient Adsorption/Photocatalytic Reduction of U(VI) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 359-366. |
| [4] | ZHANG Li, ZHANG Xiu-Xiu, DAI Chao-Hua, OUYANG Jie, YAN Jian-Hui. Photocatalytic Reduction of CO2 over Sulfied-Loaded ZnO/ZnAl2O4 Composite Hollow Sphere [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(7): 731-738. |
| [5] | ZHOU Min-Jie, ZHANG Na, HOU Zhao-Hui. Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity for Hydrogen Evolution of Graphene-ZnIn2S4 Nanocomposite Spheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(7): 713-718. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||