
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (12): 1349-1356.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200023
Special Issue: 能源材料论文精选(四):光催化与电催化(2020)
Previous Articles Next Articles
LIN hai1( ),SU Weitao1,ZHU Yu1,PENG Pai1,FENG Miao1,2(
),SU Weitao1,ZHU Yu1,PENG Pai1,FENG Miao1,2( ),YU Yan1,2(
),YU Yan1,2( )
)
Received:2020-01-13
Revised:2020-03-18
Published:2020-12-20
Online:2020-03-20
About author:LIN Hai(1994–), male, Master candidate. E-mail: linhaifj@outlook.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LIN hai, SU Weitao, ZHU Yu, PENG Pai, FENG Miao, YU Yan. Lattice Control of WO3 Nanoflowers by Heat Treatment and Construction of WO3/CdS/α-S Heterojuntion[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12): 1349-1356.
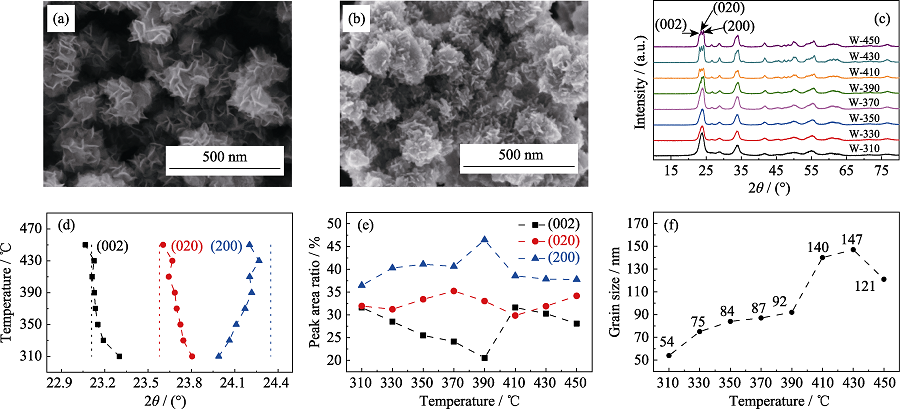
Fig. 1 SEM images of WO3 nanoflower precursor (a) and W-350 (b); XRD patterns of the samples heat-treated at different temperatures (c); (002), (020), and (200) crystal plane diffraction peak positions (d), diffraction peak integrated area ratios (e) and grain sizes (f) obtained by Rietveld refinement varied as functions of heat treatment temperature
| Sample | (002) 2θ/(°) | (020) 2θ/(°) | (200) 2θ/(°) | (002) Peak area ratio/% | (020) Peak area ratio/% | (200) Peak area ratio/% | R/%a | E/%b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W-310 | 23.302 | 23.805 | 23.989 | 31.60736 | 31.93592 | 36.45672 | 7.96 | 7.22 |
| W-330 | 23.191 | 23.744 | 24.063 | 28.51362 | 31.21225 | 40.27413 | 8.45 | 9.08 |
| W-350 | 23.152 | 23.724 | 24.110 | 25.48277 | 33.41551 | 41.10171 | 8.71 | 8.87 |
| W-370 | 23.136 | 23.698 | 24.171 | 24.13370 | 35.22923 | 40.63707 | 7.77 | 8.89 |
| W-390 | 23.128 | 23.685 | 24.217 | 20.52815 | 33.02325 | 46.4486 | 8.74 | 8.72 |
| W-410 | 23.113 | 23.643 | 24.203 | 31.60641 | 29.83773 | 38.55586 | 9.62 | 11.08 |
| W-430 | 23.126 | 23.668 | 24.268 | 30.26410 | 31.89507 | 37.84083 | 8.92 | 8.88 |
| W-450 | 23.066 | 23.604 | 24.202 | 28.08145 | 34.16319 | 37.75536 | 8.84 | 9.0 |
Table 1 Rietveld refinement results of XRD data of the samples heat-treated at different temperatures
| Sample | (002) 2θ/(°) | (020) 2θ/(°) | (200) 2θ/(°) | (002) Peak area ratio/% | (020) Peak area ratio/% | (200) Peak area ratio/% | R/%a | E/%b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W-310 | 23.302 | 23.805 | 23.989 | 31.60736 | 31.93592 | 36.45672 | 7.96 | 7.22 |
| W-330 | 23.191 | 23.744 | 24.063 | 28.51362 | 31.21225 | 40.27413 | 8.45 | 9.08 |
| W-350 | 23.152 | 23.724 | 24.110 | 25.48277 | 33.41551 | 41.10171 | 8.71 | 8.87 |
| W-370 | 23.136 | 23.698 | 24.171 | 24.13370 | 35.22923 | 40.63707 | 7.77 | 8.89 |
| W-390 | 23.128 | 23.685 | 24.217 | 20.52815 | 33.02325 | 46.4486 | 8.74 | 8.72 |
| W-410 | 23.113 | 23.643 | 24.203 | 31.60641 | 29.83773 | 38.55586 | 9.62 | 11.08 |
| W-430 | 23.126 | 23.668 | 24.268 | 30.26410 | 31.89507 | 37.84083 | 8.92 | 8.88 |
| W-450 | 23.066 | 23.604 | 24.202 | 28.08145 | 34.16319 | 37.75536 | 8.84 | 9.0 |
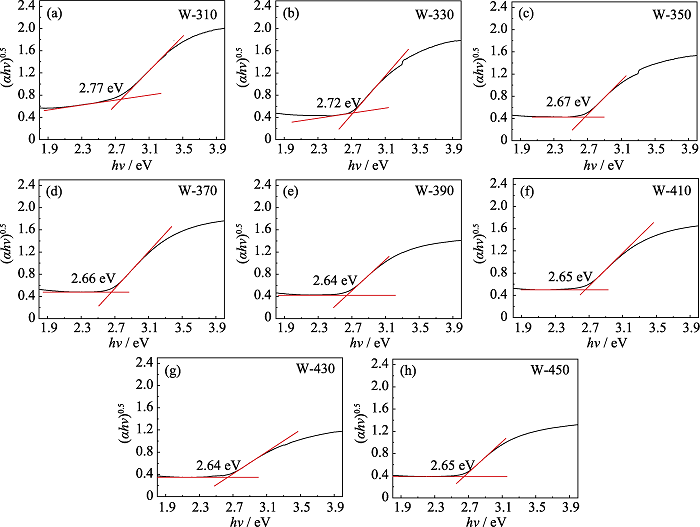
Fig. S3 Tauc plots of W-310 (a), W-330 (b), W-350 (c), W-370 (d), W-390 (e), W-410 (f), W-430 (g), W-450 (h) and the band gaps Eg obtained from the intersection of the absorption edge intercept line
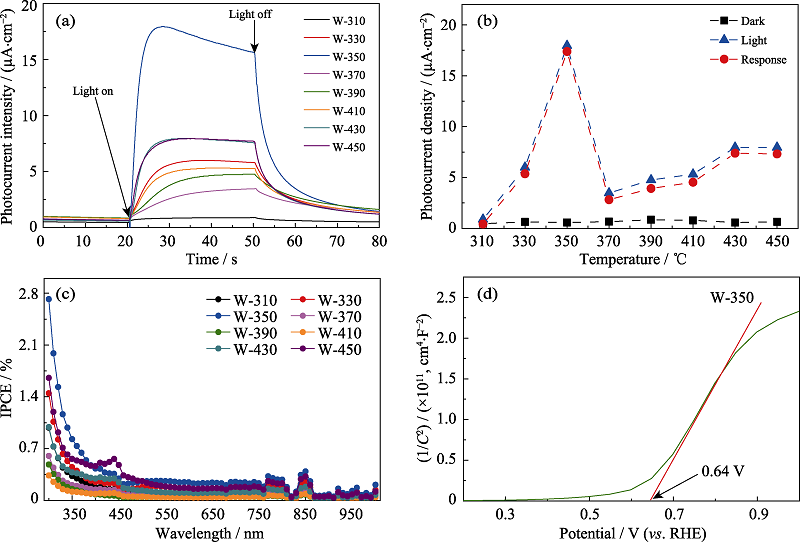
Fig. 3 Photocurrent response curves (a), photocurrent response peak values (b) and IPCE plots (c) of the samples heat-treated at different temperatures; Mott-Schottky curve of W-350 (d) Colourful version is available on offical website
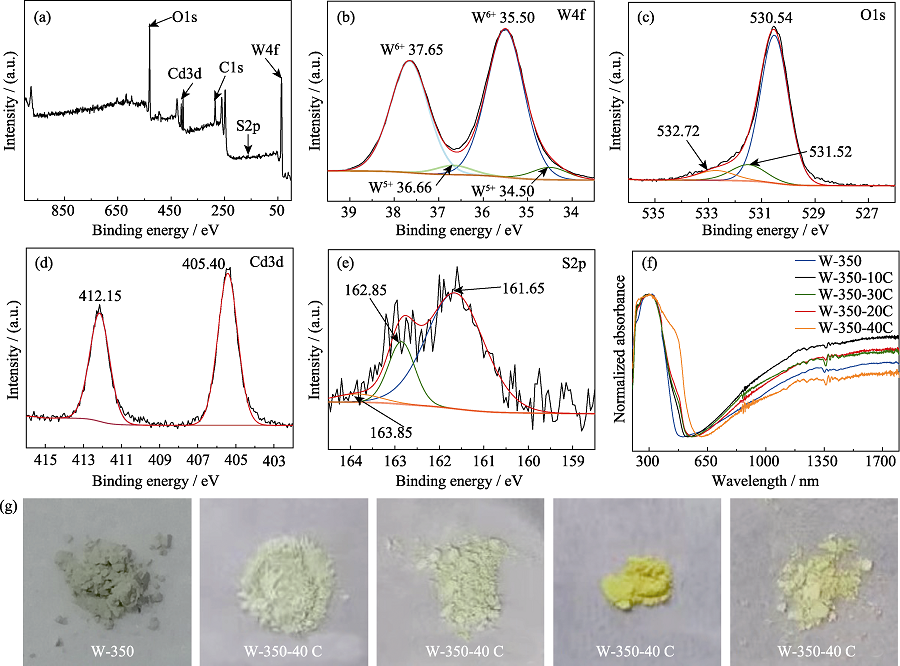
Fig. 5 XPS spectrum of sample W-350-30C (a); XPS high-resolution spectra of W4f (b), O1s (c), Cd3d (d) and S2p (e) for sample W- 350-30C; UV-Vis-IR absorption spectra (f) and photos (g) of γ-WO3 nanoflowers with different amounts of CdS/α-S modified on the surface Colourful version is available on offical website
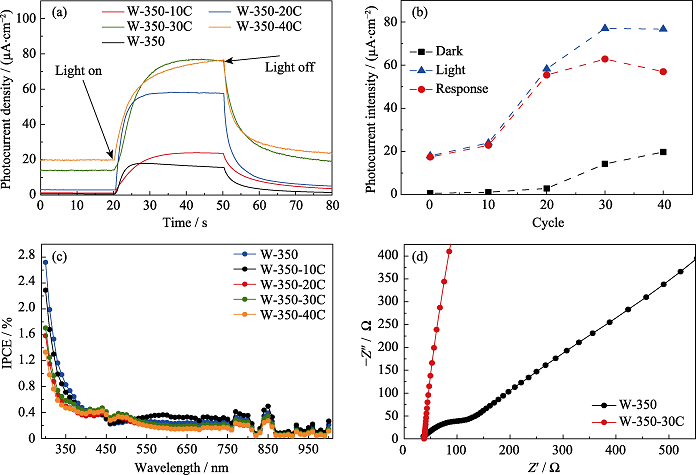
Fig. 6 Photocurrent response curves(a), photocurrent response peak values(b), and IPCE plots(c) of γ-WO3 nanoflowers modified with different amounts of CdS/α-S on the surface; EIS plots of W-350 and W-350-30C(d) Colourful version is available on offical website
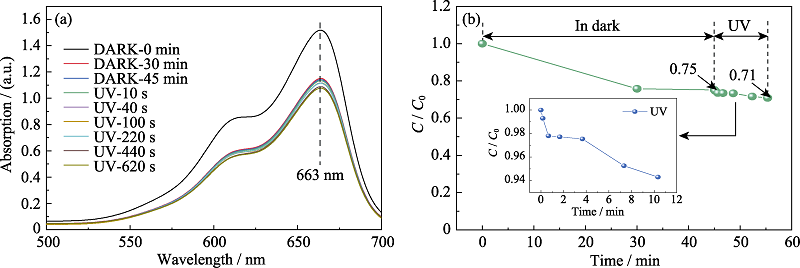
Fig. S7 UV-Vis spectra of methylene blue solution after absorbed by W-350 in the dark and UV irradiation for different time (a); Variation of methylene blue degradation rate with different time (b)
| [1] | YE S, DING C M, LIU M Y, et al. Water oxidation catalysts for artificial photosynthesis. Advanced Materials, 2019,31(50):1902069. |
| [2] |
LUO Z B, WANG T, GONG J L. Single-crystal silicon-based electrodes for unbiased solar water splitting: current status and prospects. Chemical Society Reviews, 2019,48:2158-2181.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] | WU Y S, LIU X J, HAN D D, et al. Electron density modulation of NiCo2S4 nanowires by nitrogen incorporation for highly efficient hydrogen evolution catalysis. Nature Communications, 2018,9(1425):1-9. |
| [4] | WEI J M, LÜ Q, WANG B C, et al. Synthesis of cubic-relievo Ag3PO4 with high visible-light photocatalytic activity. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019,34(7):786-790. |
| [5] | WANG Y D, TIAN W, CHEN C, et al. Tungsten trioxide nanostructures for photoelectrochemical water splitting: material engineering and charge carrier dynamic manipulation. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019,29(23):1809036. |
| [6] | ZHANG J J, CHANG X X, LI C C, et al. WO3 photoanodes with controllable bulk and surface oxygen vacancies for photoelectrochemical water oxidation. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018,6:3350-3354. |
| [7] | FU J W, XU Q L, LOW J X, et al. Ultrathin 2D/2D WO3/g-C3N4 step-scheme H2-production photocatalyst. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019,243:556-565. |
| [8] |
LI H J, GAO Y Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Construction and nanoscale detection of interfacial charge transfer of elegant Z-scheme WO3/Au/ In2S3 nanowire arrays. Nano Letters, 2016,16(9):5547-5552.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] | CAO F R, MENG L X, WANG M, et al. Gradient energy band driven high-performance self-powered perovskite/CdS photodetector. Advanced Materials, 2019,30(12):1806725-1-7. |
| [10] |
LIU G, NIU P, YIN L C, et al. α-Sulfur crystals as a visible-light- active photocatalyst. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012,134(22):9070-9073.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
HU W, LIN L, ZHANG R Q, et al. Highly efficient photocatalytic water splitting over edge-modified phosphorene nanoribbons. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017,139(43):15429-15436.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
ZHANG M Y, LIN H L, CAO J, et al. Construction of novel S/CdS type II heterojunction for photocatalytic H2 production under visible light: the intrinsic positive role of elementary α-S. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017,321:484-494.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SUN W T, YU Y, PAN H Y, et al. CdS quantum dots sensitized TiO2 nanotube-array photoelectrodes. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008,130(4):1124-1125.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] |
CHANDRASEKARAN S, ZHANG P X, PENG F, et al. Tailoring the geometric and electronic structure of tungsten oxide with manganese or vanadium doping toward highly efficient electrochemical and photoelectrochemical water splitting. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019,7:6161-6172.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHANG H F, ZHOU W W, YANG Y P, et al. 3D WO3/BiVO4/cobalt phosphate composites inverse opal photoanode for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting. Small, 2017,13(16):1603840-1-7.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LI W J, DA P M, ZHANG Y Y, et al. WO3 nanoflakes for enhanced photoelectrochemical conversion. ACS Nano, 2014,8(11):11770-11777.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
ZHENG T T, SANG W, HE Z H, et al. Conductive tungsten oxide nanosheets for highly efficient hydrogen evolution. Nano Letters, 2017,17(12):7968-7973.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] |
CONG S, GENG F X, ZHAO Z G. Tungsten oxide materials for optoelectronic applications. Advanced Materials, 2016,28(47):10518-10528.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] | CHEN S, ZENG L, TIAN H, et al. Enhanced lattice oxygen reactivity over Ni-modified WO3-based redox catalysts for chemical looping partial oxidation of methane. ACS Catalysis, 2017,7(5):3548-3559. |
| [20] | WANG F G, VALENTIN C D, PACCHIONI G. Semiconductor-to- metal transition in WO3-x: nature of the oxygen vacancy. Physical Review B, 2011,84(7):073103-1-5. |
| [21] | MA Y L, FENG B, LANG J Y, et al. Synthesis of semi-metallic tungsten trioxide for infrared light photoelectrocatalytic water splitting. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2019,123(42):25833-25843. |
| [22] |
YAN J Q, WANG T, WU G J, et al. Tungsten oxide single crystal nanosheets for enhanced multichannel solar light harvesting. Advanced Materials, 2019,27(9):1580-1586.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] | BAI S, ZHANG N, GAO C, et al. Defect engineering in photocatalytic materials. Nano Energy, 2018,53:296-336. |
| [24] |
HUANG Z F, SONG J J, PAN L, et al. Tungsten oxides for photocatalysis, electrochemistry, and phototherapy. Advanced Materials, 2015,27(36):5309-5327.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
FORMAL F L, PENDLEBURY S R, CORNUZ M, et al. Back electron-hole recombination in hematite photoanodes for water splitting. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014,136(6):2564-2574.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | FORMAL F L, SIVULA K, GRATZEL M. The transient photocurrent and photovoltage behavior of a hematite photoanode under working conditions and the influence of surface treatments. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012,116:26707-26720. |
| [27] |
ZHANG N, CHEN C, MEI Z W, et al. Monoclinic tungsten oxide with {100} facet orientation and tuned electronic band structure for enhanced photocatalytic oxidations. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016,8(16):10367-10374.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] | 张青莲, 姚凤仪, 郭德威, 桂明德. 无机化学丛书. 第五卷, 氧、硫、硒分族. 北京: 科学出版社, 1990: 173-237. |
| [29] | WANG G M, LING Y C, WANG H Y, et al. Hydrogen-treated WO3 nanoflakes show enhanced photostability. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012,5:6180-6187. |
| [30] | ZHANG J J, ZHANG P, WANG T, et al. Monoclinic WO3 nanomultilayers with preferentially exposed (002) facets for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Nano Energy, 2015,11:189-195. |
| [31] |
MENG J, LIN Q Y, CHEN T, et al. Oxygen vacancy regulation on tungsten oxides with specific exposed facets for enhanced visible- light-driven photocatalytic oxidation. Nanoscale, 2018,10:2908-2915.
URL PMID |
| [32] | LÜ Y, ZHU Y, ZHU Y. Enhanced photocatalytic performance for the BiPO4-x nanorod induced by surface oxygen vacancy. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013,117(36):18520-18528. |
| [33] | WANG J, JIANG W, LIU D et al. Photocatalytic performance enhanced via surface bismuth vacancy of Bi6S2O15 core/shell nanowires. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015,176-177:306-314. |
| [34] | LI Y S, TANG Z L, ZHANG J Y et al. Defect engineering of air- treated WO3 and its enhanced visible light-driven photocatalytic and electrochemical performance. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016,120:9750-9763. |
| [35] | ZHONG Y Y, ZHAO G, MA F K, et al. Utilizing photocorrosion- recrystallization to prepare a highly stable and efficient CdS/WS2 nanocomposite photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016,199:466-472. |
| [36] | JIN J, YU J G, GUO D P, et al. A hierarchical Z-scheme CdS-WO3 photocatalyst with enhanced CO2 reduction activity. Small, 2015,11(39):5262-5271. |
| [37] |
WANG M Y, CAI L J, WANG Y, et al. Graphene-draped semiconductors for enhanced photocorrosion resistance and photocatalytic properties. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017,139(11):4144-4151.
DOI URL PMID |
| [38] | ZONG X, HAN J F, MA G J, et al. Photocatalytic H2 evolution on CdS loaded with WS2 as cocatalyst under visible light irradiation. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011,115(24):12202-12208. |
| [39] |
LI J J, WANG Y A, GUO W Z, et al. Large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals using air-stable reagents via successive ion layer adsorption and reaction. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003,125(41):12567-12575.
DOI URL PMID |
| [40] | MENG S G, CAO Z S, FU X L, et al. Fabrication of hydrophilic S/In2O3 core-shell nanocomposite for enhancement of photocatalytic performance under visible light irradiation. Applied Surface Science, 2015,324:188-197. |
| [41] |
LIN R, WAN J W, XIONG Y, et al. Quantitative study of charge carrier dynamics in well-defined WO3 nanowires and nanosheets: insight into the crystal facet effect in photocatalysis. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018,140(29):9078-9082.
DOI URL |
| [1] | LI Wenbo, QIAN Rong, ZHUO Shangjun, JIANG Hong, SHENG Cheng, ZHU Yueqin. MoS2 with Different Morphologies: Preparation and Gas-sensing Property of NH3 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1135-1140. |
| [2] | WU Qi, CONG Shan, ZHAO Zhigang. Infrared Electrochromic Property of the Colorful Tungsten Oxide Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 485-491. |
| [3] | ZHONG Xiaolan, LIU Xueqing, DIAO Xungang. Electrochromic Devices Based on Tungsten Oxide and Nickel Oxide: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 128-139. |
| [4] | ZHAO Linyan, LIU Yangsi, XI Xiaoli, MA Liwen, NIE Zuoren. First-principles Study on Nanoscale Tungsten Oxide: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1125-1136. |
| [5] | QIAN Bai-Tai,SHEN Zi-Qiu. Super-hydrophobic CuO Nanoflowers by Controlled Surface Oxidation on Copper [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(3): 747-752. |
| [6] | CAO Guang-Sheng,YU Qing-Sen,DONG Xi-Gui,SONG Xu-Chun,TAN Fei. Synthesis of Tungsten Oxide Nanorods Doped with Transition Metal Molybdenum [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2005, 20(4): 815-820. |
| [7] | HUANG Yin-Song,ZHANG Yu-Zhi,SONG Li-Xin,HU Xing-Fang. Preparation and Infrared Reflectance Modulation Characteristics of Polycrystalline Tungsten Oxide Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2002, 17(6): 1263-1268. |
| [8] | CHEN Xiaofeng HU Xingfang LI Zhiyong TIAN Jingfen. The Laminated All-Solid-State Electrochromic Devices Using PEG-LiClO4 Gel Electrolyte [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1997, 12(4): 623-626. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||