
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (8): 931-938.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190595
Special Issue: 结构陶瓷论文精选(2020); 【虚拟专辑】分离膜,复相陶瓷(2020~2021)
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
WEI Yuquan1,2,3( ),YANG Yong1,2(
),YANG Yong1,2( ),LIU Meng1,2,LI Qile1,2,HUANG Zhengren1,2(
),LIU Meng1,2,LI Qile1,2,HUANG Zhengren1,2( )
)
Received:2019-11-25
Revised:2019-12-10
Published:2020-08-20
Online:2020-01-15
Supported by:CLC Number:
WEI Yuquan,YANG Yong,LIU Meng,LI Qile,HUANG Zhengren. Effect of High Temperature Heat Treatment on Phase Composition and Microstructure of SiBCN/HfC Ceramic Composites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 931-938.
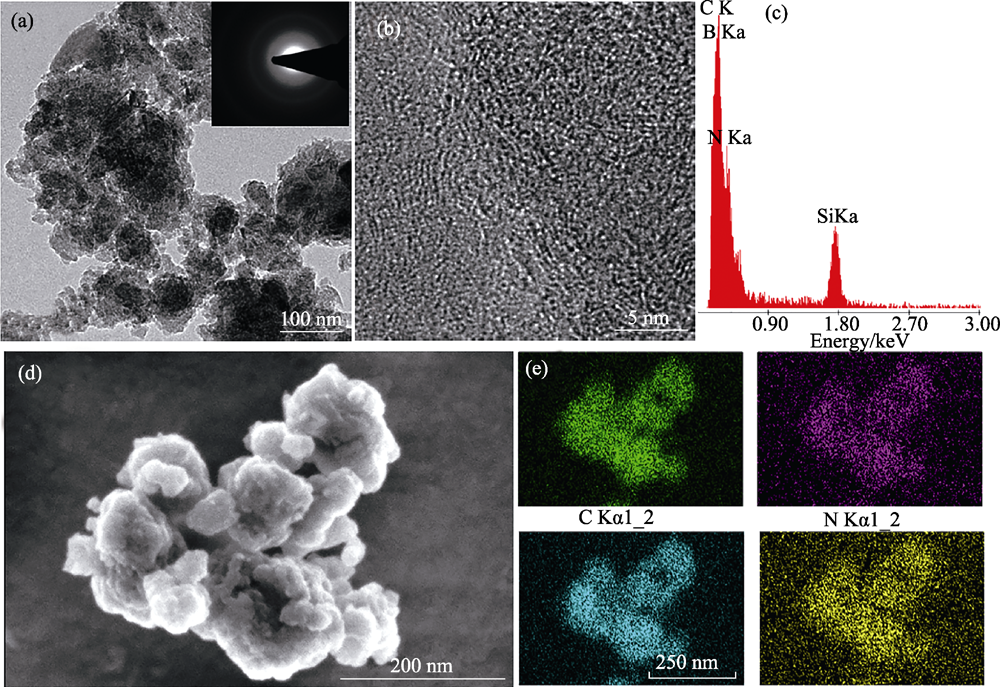
Fig. 2 Microstructure and EDS element mapping of the amorphous SiBCN powders (a) TEM image with inset showing selected area electron diffraction; (b) HRTEM image; (c) EDS spot analysis of (a); (d) SEM image and (e) EDS elemental maps of (d)

Fig. 6 Microstructure (a) and EDS element overlap mapping (b) of the as-sintered SiBCN/HfC ceramic composites, and its corresponding element distribution displayed in lower two rows
| Reaction | ΔG1300 ℃/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔG1400 ℃/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔG1500 ℃/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔG1600 ℃/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔG1650 ℃/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔG1800 ℃/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HfO2 + B2O3 + 5C = HfB2 + 5CO(g) | 169.8 | 91.0 | 12.6 | -65.3 | -104.1 | -210.0 |
| HfO2 + 2BN + 2C = HfB2 + 2CO(g) + N2(g) | 246.5 | 196.6 | 146.9 | 97.4 | 72.8 | -0.7 |
| HfO2 + 3C = HfC + 2CO(g) | 115.6 | 82.1 | 48.8 | 15.7 | -0.8 | -50.1 |
| HfC + 2C + B2O3 = HfB2 + 3CO(g) | 54.1 | 8.8 | -36.2 | -81.0 | -103.3 | -169.9 |
Table 1 Change of standard Gibbs free energies of reactions (6-9) at different heat treatment temperature
| Reaction | ΔG1300 ℃/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔG1400 ℃/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔG1500 ℃/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔG1600 ℃/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔG1650 ℃/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔG1800 ℃/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HfO2 + B2O3 + 5C = HfB2 + 5CO(g) | 169.8 | 91.0 | 12.6 | -65.3 | -104.1 | -210.0 |
| HfO2 + 2BN + 2C = HfB2 + 2CO(g) + N2(g) | 246.5 | 196.6 | 146.9 | 97.4 | 72.8 | -0.7 |
| HfO2 + 3C = HfC + 2CO(g) | 115.6 | 82.1 | 48.8 | 15.7 | -0.8 | -50.1 |
| HfC + 2C + B2O3 = HfB2 + 3CO(g) | 54.1 | 8.8 | -36.2 | -81.0 | -103.3 | -169.9 |

Fig. 9 Surface morphologies and corresponding EDS results of the SiBCN/HfC ceramic composites before and after heat treatment at different temperatures (a) As sintered; (b)1400 ℃; (c)1600 ℃; (d)1800 ℃
| [1] |
YANG ZHI-HUA, LIANG BIN, JIA DE-CHANG, et al. Amorphous silicoboron carbonitride monoliths resistant to flowing air up to 1800 ◦C . Corros. Sci., 2016,109:162-173.
DOI URL |
| [2] | YANG ZHI-HUA, MIAO YANG, LIANG BIN, et al. Oxidation behavior of SiBCN-Zr composites at 1500 ℃ prepared by reactive spark plasma sintering. Coros. Sci., 2018,132:293-299. |
| [3] |
LU BIAO, ZHANG YUE. Oxidation behavior of SiC-SiBCN ceramics. Ceram. Int., 2015,41:1023-1030.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LI DA-XIN, YANG ZHI-HUA, JIA DE-CHANG, et al. High- temperature oxidation behavior of dense SiBCN monoliths: carboncontent dependent oxidation structure, kinetics and mechanisms. Corros. Sci., 2017,124:103-120.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LIANG BIN, YANG ZHI-HUA, LI YUE-TONG, et al. Ablation behavior and mechanism of SiCf/Cf/SiBCN ceramic composites with improved thermal shock resistance under oxyacetylene combustion flow. Ceram. Int., 2015,41:8868-8877.
DOI URL |
| [6] | LI DAXIN, YANG ZHI-HUA, JIA DE-CHANG, et al. Ablation behavior of graphene reinforced SiBCN ceramics in an oxyacetylene combustion flame. Corros. Sci., 2015,100:85-100. |
| [7] |
WANG JIA-YING, DUAN XIAO-MING, YANG ZHI-HUA, et al. Ablation mechanism and properties of SiCf/SiBCN ceramic composites under an oxyacetylene torch environment. Corros. Sci., 2014,82:101-107.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
MIAO YANG, YANG ZHI-HUA, ZHU QI-SHUAI, et al. Thermal ablation behavior of SiBCN-Zr composites prepared by reactive spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int., 2017,43:7978-7983.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI DA-XIN, YANG ZHI-HUA, JIA DE-CHANG, et al. Carbon content-dependent microstructures, surface characteristics and thermal stability of mechanical alloying derived SiBCN powders. Ceram. Int., 2018,44:3614-3624.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
YANG ZHI-HUA, ZHOU YU, JIA DE-CAHNG, et al. Microstructures and properties of SiB0.5C1.5N0.5 ceramics consolidated by mechanical alloying and hot pressing. Mat. Sci. and Eng. A, 2008,489:187-192.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LI DA-XIN, YANG ZHI-HUA, MAO ZHU-BO, et al. Microstructures, mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of SiBCN ceramics with the addition of MgO, ZrO2 and SiO2(MZS) as sintering additives. RSC Adv., 2015,5:52194-52205.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LI DA-XIN, YANG ZHI-HUA, JIA DE-CHANG, et al. Preparation, microstructures, mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of SiBCN/ZrB2-ZrN ceramics by reactive hot pressing. J. Euro. Ceram. Soc., 2015,35:4399-4410.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LI DA-XIN, YANG ZHI-HUA, JIA DE-CHANG, et al. Effects of boron addition on the high temperature oxidation resistance of dense SiBCN monoliths at 1500 ℃. Corrs. Sci., 2017,126:10-25.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MIAO YANG, YANG ZHI-HUA, RAO JIAN-CUN, et al. Influence of Sol-Gel derived ZrB2 additions on microstructure and mechanical properties of SiBCN composites. Ceram. Int., 2017,43:4372-4378.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
TANG BAO-JUN, FENG ZE-LONG, HU SHU-JUAN, et al. Preparation and anti-oxidation characteristics of ZrSiO4-SiBCN(O) amorphous coating. Appl Surf Sci., 2015,331:490-496.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
YANG YANG, LI KE-ZHI, ZHANG ZI-GANG, et al. Ablation resistance of HfC-SiC coating prepared by supersonic atmospheric plasma spraying for SiC-coated C/C composites. Ceram. Int., 2016,42:4768-4774.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
YUAN JIA, LUAN XIN-GANG, RIEDEL RALF, et al. Preparation and hydrothermal corrosion behavior of Cf/SiCN and Cf/SiHfBCN ceramic matrix composites. J. Euro. Ceram. Soc., 2015,35:3329-3337.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WEI YU-QUAN, YANG YONG, LIU MENG, et al. Effect of HfC addition on ablation behavior of SiBCN ceramics. Ceram. Int., 2019. doi. org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.10.121.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
SUJITH R, KOUSAALYA A B, KUMAR R. Coarsening induced phase transformation of Hafnia in polymer-derived Si-Hf-C-N-O Ceramics. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2011,94:2788-2791.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
KLEEBE HANS-JOACHIM, NONNENMACHER KATHARINA, IONESCU EMANUEL. Decomposition-coarsening model of SiOC/HfO2 ceramic nanocomposites upon isothermal anneal at 1300 ℃. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2012,95:2290-2297.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG PENG-FEI, JIA DE-CHANG, YANG ZHI-HUA. Crystallization and microstructural evolution process from the mechanically alloyed amorphous SiBCN powder to the hot-pressed nano SiC/BN(C) ceramic. J. Mat. Sci., 2012,47:7291-7304.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
XIONG Y H, XIONG C S, WEI S Q, et al. Study on the bonding state for carbon-boron nitrogen with different ball milling time. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2006,253:2515-2521.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
YANG ZHI-HUA, JIA DE-CAHNG, ZHOU YU, et al. Fabrication and characterization of amorphous SiBCN powders. Ceram. Int., 2007,33:1573-1577.
DOI URL |
| [24] | BLUM Y, KLEEBE HANS-JOACHIM. Chemical reactivities of hafnium and its derived boride, carbide and nitride compounds at relatively mild temperature. J.Mat. Sci., 2004,39:6023-6042. |
| [1] | XIAO Peng, ZHU Yulin, WANG Song, YU Yiping, LI Hao. Research Progress on the Preparation and Characterization of Ultra Refractory TaxHf1-xC Solid Solution Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 685-694. |
| [2] | DING Shan-Shan, CHEN Xin-Xin, LI Yu-Zhen, HAN Wen-Feng, LV De-Yi, LI Ying, TANG Hao-Dong. High-surface-area Magnesium Fluoride: Preparation by Template Method and Catalytic Activity for the Dehydrofluorination of HFC-152a [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(11): 1186-1192. |
| [3] | LI Ya-Jing, ZHANG Yue. Pyrolysis Mechanism of SiBCN Polymer Precursor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(3): 321-326. |
| [4] | LI Shu-Ping,LI Ke-Zhi,GUO Ling-Jun,HE Yong-Gang. Ablation Performances of the HfC Modified Carbon/carbon Composite Integrated Throat [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(6): 1155-1158. |
| [5] | LIU Wei-Ping,YU Qing-Xuan,TIAN Yu-Quan,LIAO Yuan,WANG Guan-Zhong,FANG Rong-Chuan. Effects of Boron Doping on the Growth Characteristic of Diamond Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2005, 20(5): 1270-1274. |
| [6] | NIU Xiao-Bin,LIAO Yuan,CHANG Chao,YU Qing-Xuan,FANG Rong-Chuan. Silicon Carbon Nitride Films Grown by Hot-Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2004, 19(2): 397-403. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||