
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 337-344.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190383
Special Issue: 环境与催化材料论文精选; 【虚拟专辑】污染物吸附水处理(2020~2021)
Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Wei1,2,LIU Chen2,CHEN Yuantao2,WU Wangsuo1( )
)
Received:2019-07-24
Revised:2020-01-07
Published:2020-03-20
Online:2019-10-23
About author:ZHANG Wei(1972-), female, PhD candidate. E-mail: zhangwei@qhnu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
ZHANG Wei, LIU Chen, CHEN Yuantao, WU Wangsuo. Removal of Boron from Water by Mg-Al-Ce Hydrotalcite Adsorption[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 337-344.
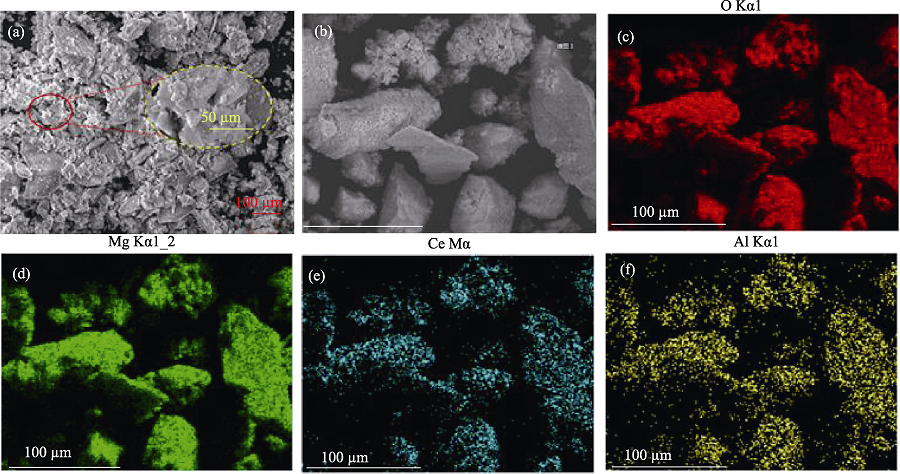
Fig. 4 SEM images of Mg-Al-Ce-HT (a) and EDS analysis of Mg-Al-Ce-HT (b) and the corresponding EDS mappings of O (c), Mg (d), Ce (e), and Al (f) elements
| T/K | ΔGθ/ (kJ· mol-1) | ΔHθ/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔSθ/ (kJ· mol-1·K-1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 308 | 12.16 | 89.90 | 0.25 | 0.99 |
| 313 | 10.90 | |||
| 323 | 8.37 |
| T/K | ΔGθ/ (kJ· mol-1) | ΔHθ/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔSθ/ (kJ· mol-1·K-1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 308 | 12.16 | 89.90 | 0.25 | 0.99 |
| 313 | 10.90 | |||
| 323 | 8.37 |
| [1] | TANAKA M, FUJIWARA T . Physiological roles and transport mechanisms of boron: perspectives from plants. Pflügers Archiv- European Journal of Physiology, 2008,456(4):671-677. |
| [2] | BLEVINS D G, LUKASZEWSKI K M . Proposed physiologic functions of boron in plants pertinent to animal and human metabolism. Environmental Health Perspectives, 1994,102(suppl 7):31-33. |
| [3] | DUYDU Y, AYDIN S, UNDEGER U , et al. Is boric acid toxic to reproduction in humans?assessment of the animal reproductive toxicity data and epidemiological study results. Current Drug Delivery, 2016, 13(3):324-329. |
| [4] | GEFFEN N, SEMIAT R, EISEN M S , et al. Boron removal from water by complexation to polyol compounds. Journal of Membrane Science, 2006,286(1):45-51. |
| [5] | TÜRKER O C, BARAN T . Evaluation and application of an innovative method based on various chitosan composites and Lemna gibba for boron removal from drinking water. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017 , 166:209-218. |
| [6] | HARADA A, TAKAGI T, KATAOKA S , et al. Boron adsorption mechanism on polyvinyl alcohol. Adsorption-journal of the International Adsorption Society, 2011,17(1):171-178. |
| [7] | KIR E, GURLER B, GULEC A . Boron removal from aqueous solution by using plasma-modified and unmodified anion-exchange membranes. Desalination, 2011,267(1):114-117. |
| [8] | SARI M A, CHELLAM S . Mechanisms of boron removal from hydraulic fracturing wastewater by aluminum electrocoagulation. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2015,458:103-111. |
| [9] | ARIFFIN M, HASSAN A, HUI L S , et al. Removal of boron from industrial wastewater by chitosan via chemical precipitation. Tree Physiology, 2009,17(8/9):521-535. |
| [10] | HUERTAS E, HERZBERG M, ORON G , et al. Influence of biofouling on boron removal by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2008,318(1):264-270. |
| [11] | PING Q, ABU-REESH I M, HE Z . Boron removal from saline water by a microbial desalination cell integrated with donnan dialysis. Desalination,, 2015,376:55-61. |
| [12] | WAITE T D, DAVIS J A, PAYNE T E , et al. Uranium(VI) adsorption to ferrihydrite: application of a surface complexation model. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994,58(24):5465-5478. |
| [13] | DARWISH N B, KOCHKODAN V, HILAL N . Boron removal from water with fractionized Amberlite IRA743 resin. Desalination, 2015,370:1-6. |
| [14] | POLOWCZYK I, ULATOWSKA J, KOŹLECKI T , et al. Studies on removal of boron from aqueous solution by fly ash agglomerates. Desalination, 2013,310(3):93-101. |
| [15] | LI J, CAO P, NI P , et al. Enhanced boron removal from metallurgical grade silicon by the slag refining method with the addition of tin. Separation Science & Technology, 2016,51(9):1598-1603. |
| [16] | WANI M A . Adsorption and desorption of boron as influenced by soil properties in temperate soils of lesser himalayas. Communications in Soil Science & Plant Analysis, 2015,46(6):683-698. |
| [17] | KAMEDA T, OBA J, YOSHIOKA T . New treatment method for boron in aqueous solutions using Mg-Al layered double hydroxide: kinetics and equilibrium studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015,293:54-63. |
| [18] | AY A N, ZÜMREOGLU-KARAN B, TEMEL A . Boron removal by hydrotalcite-like, carbonate-free Mg-Al-NO3-LDH and a rationale on the mechanism. Microporous & Mesoporous Materials, 2007,98(1):1-5. |
| [19] | LYU J, ZENG Z, ZHANG N , et al. Pyrocatechol-modified resins for boron recovery from water: synthesis, adsorption and isotopic separation studies. Reactive & Functional Polymers,2017, 112:1-8. |
| [20] | RODRIGUES E, PEREIRA P, MARTINS T , et al. Novel rare earth (Ce and La) hydrotalcite like material: synthesis and characterization. Materials Letters, 2012,78(7):195-198. |
| [21] | THEISS F L, AYOKO G A, FROST R L . Removal of boron species by layered double hydroxides: a review. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2013,402(14):B114-121. |
| [22] | WANG B, GUO X, BAI P . Removal technology of boron dissolved in aqueous solutions - a review. Colloids & Surfaces A Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects, 2014,444(4):338-344. |
| [1] | MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [2] | GUO Chunxia, CHEN Weidong, YAN Shufang, ZHAO Xueping, YANG Ao, MA Wen. Adsorption of Arsenate in Water by Zirconia-halloysite Nanotube Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 529-536. |
| [3] | WANG Shiyi, FENG Aihu, LI Xiaoyan, YU Yun. Pb (II) Adsorption Process of Fe3O4 Supported Ti3C2Tx [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [4] | YU Yefan, XU Ling, NI Zhongbing, SHI Dongjian, CHEN Mingqing. Prussian Blue Modified Biochar: Preparation and Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen from Sewage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 205-212. |
| [5] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Mesoporous Organic-inorganic Hybrid Siliceous Hollow Spheres: Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [6] | LIU Cheng, ZHAO Qian, MOU Zhiwei, LEI Jiehong, DUAN Tao. Adsorption Properties of Novel Bismuth-based SiOCNF Composite Membrane for Radioactive Gaseous Iodine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1043-1050. |
| [7] | ZHOU Fan, BI Hui, HUANG Fuqiang. Ultra-large Specific Surface Area Activated Carbon Synthesized from Rice Husk with High Adsorption Capacity for Methylene Blue [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 893-903. |
| [8] | YU Xiangkun, LIU Kun, LI Zhipeng, ZHAO Yulu, SHEN Jinyou, MAO Ping, SUN Aiwu, JIANG Jinlong. Efficient Adsorption of Radioactive Iodide by Copper/Palygorskite Composite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 856-864. |
| [9] | SU Li, YANG Jianping, LAN Yue, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Interface Design of Iron Nanoparticles for Environmental Remediation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 561-569. |
| [10] | XI Wen, LI Haibo. Preparation of TiO2/Ti3C2Tx Composite for Hybrid Capacitive Deionization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 283-291. |
| [11] | WANG Tingting, SHI Shumei, LIU Chenyuan, ZHU Wancheng, ZHANG Heng. Synthesis of Hierarchical Porous Nickel Phyllosilicate Microspheres as Efficient Adsorbents for Removal of Basic Fuchsin [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1330-1336. |
| [12] | LIU Wenwen, MIAO Yuxin, ZHANG Yifei, WANG Xinyu, LAN Yuting, ZHAO Zhen. Preparation of MgAl LDH with Various Morphologies and Catalytic Hydrogenation Performance of Pt/LDH Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1283-1289. |
| [13] | ZHANG Ruihong, WEI Xin, LU Zhanhui, AI Yuejie. Training Model for Predicting Adsorption Energy of Metal Ions Based on Machine Learning [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1178-1184. |
| [14] | GUO Yu, JIANG Xiaoqing, WU Hongmei, XIAO Yu, WU Dafu, LIU Xin. Preparation of 2-hydroxy-1-naphthalene Functionalized SBA-15 Adsorbent for the Adsorption of Chromium(III) Ions from Aqueous Solution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1163-1170. |
| [15] | HE Junlong, SONG Erhong, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. DFT Calculation of NO Adsorption on Cr Doped Graphene [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1047-1052. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||