
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 373-380.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190378
Special Issue: 2020年环境材料论文精选(一)放射性元素去除; 优秀作者论文集锦; 2019~2020年度优秀作者作品欣赏:环境材料; 【虚拟专辑】放射性污染物去除(2020~2021)
Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Jiaqi1,PANG Hongwei2,TANG Hao2,YU Shujun2,ZHU Hongtao1,WANG Xiangxue1,2,3( )
)
Received:2019-07-23
Revised:2019-09-05
Published:2020-03-20
Online:2019-10-23
About author:WANG Jiaqi(1996-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: wjqcepu@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Jiaqi, PANG Hongwei, TANG Hao, YU Shujun, ZHU Hongtao, WANG Xiangxue. Carbothermic Synthesis of Carbon-supported Zero-valent Iron Material for Removal of U(Ⅵ) from Aqueous Solution[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 373-380.

Fig. 2 XRD patterns (a) and N2 adsorption-desorption isotherm (b) of SA, nZVI and Fe-CB; FT-IR spectra (c) of SA and Fe-CB; magnetization curve (d) of Fe-CB
| Material | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|
| nZVI | 4.1 | 1.03 |
| SA | 0.2 | 2.12 |
| Fe-CB | 346.6 | 20.12 |
Table 1 BET results of nZVI, SA and Fe-CB
| Material | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|
| nZVI | 4.1 | 1.03 |
| SA | 0.2 | 2.12 |
| Fe-CB | 346.6 | 20.12 |
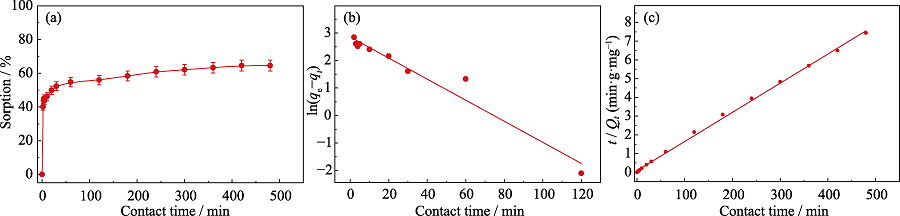
Fig. 3 Effect of contact time on the sorption of U(VI) by Fe-CB (a), and corresponding simulation of kinetics data by pseudo-first-order model (b) and pseudo-second-order model (c)
| Pseudo-first-order model | Pseudo-second-order model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min-1 | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R12 | k2/(g·mg-1·min-1) | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R22 |
| 0.4388 | 57.3 | 0.489 | 0.0026 | 64.3 | 0.998 |
Table 2 Kinetic model parameters for remove of U(Ⅵ) by Fe-CB
| Pseudo-first-order model | Pseudo-second-order model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min-1 | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R12 | k2/(g·mg-1·min-1) | Qe/(mg·g-1) | R22 |
| 0.4388 | 57.3 | 0.489 | 0.0026 | 64.3 | 0.998 |
| T/K | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm/(mg·g-1) | kL/(L·mg-1) | R12 | kF/(mg1-n·Ln·g-1) | n | R22 | |
| 298 | 77.3 | 1.40 | 0.971 | 62.6 | 18.62 | 0.788 |
| 313 | 89.7 | 1.54 | 0.970 | 71.1 | 16.29 | 0.884 |
| 328 | 103.7 | 1.25 | 0.959 | 76.4 | 12.15 | 0.901 |
Table 3 Fitting parameters of adsorption isotherms for U(Ⅵ) on Fe-CB
| T/K | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm/(mg·g-1) | kL/(L·mg-1) | R12 | kF/(mg1-n·Ln·g-1) | n | R22 | |
| 298 | 77.3 | 1.40 | 0.971 | 62.6 | 18.62 | 0.788 |
| 313 | 89.7 | 1.54 | 0.970 | 71.1 | 16.29 | 0.884 |
| 328 | 103.7 | 1.25 | 0.959 | 76.4 | 12.15 | 0.901 |
| T/K | ΔGθ/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔSθ/(J·K-1·mol-1) | ΔHθ/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | -5.74 | 34.84 | 4.64 |
| 313 | -6.61 | ||
| 328 | -7.72 |
Table 4 Thermodynamic parameters at different temperatures
| T/K | ΔGθ/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔSθ/(J·K-1·mol-1) | ΔHθ/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | -5.74 | 34.84 | 4.64 |
| 313 | -6.61 | ||
| 328 | -7.72 |
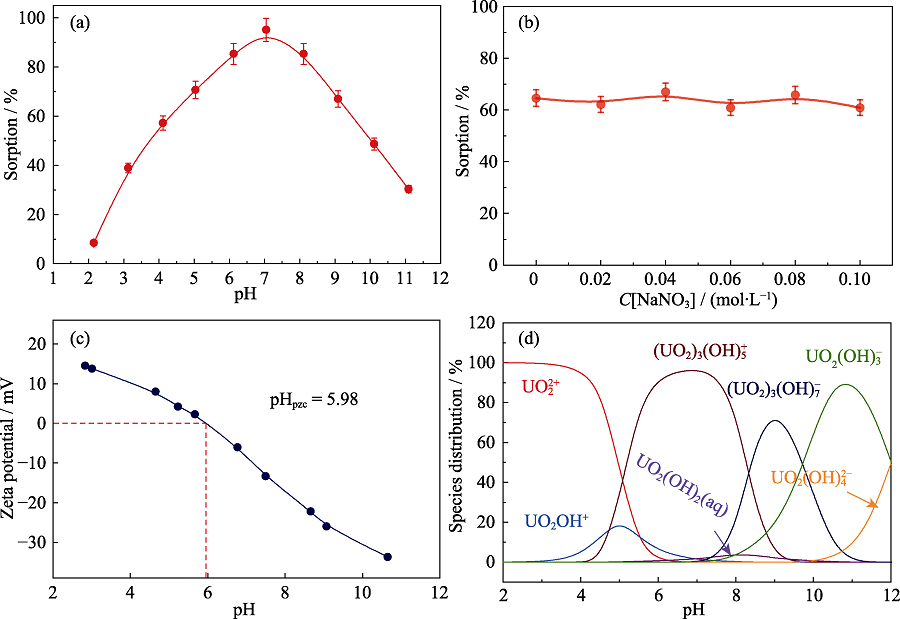
Fig. 5 Effect of pH (a) and ionic strength (b) on U(Ⅵ) sorption by Fe-CB, Zeta-potential of Fe-CB (c), and relative distribution of U(VI) species in different pH (d)
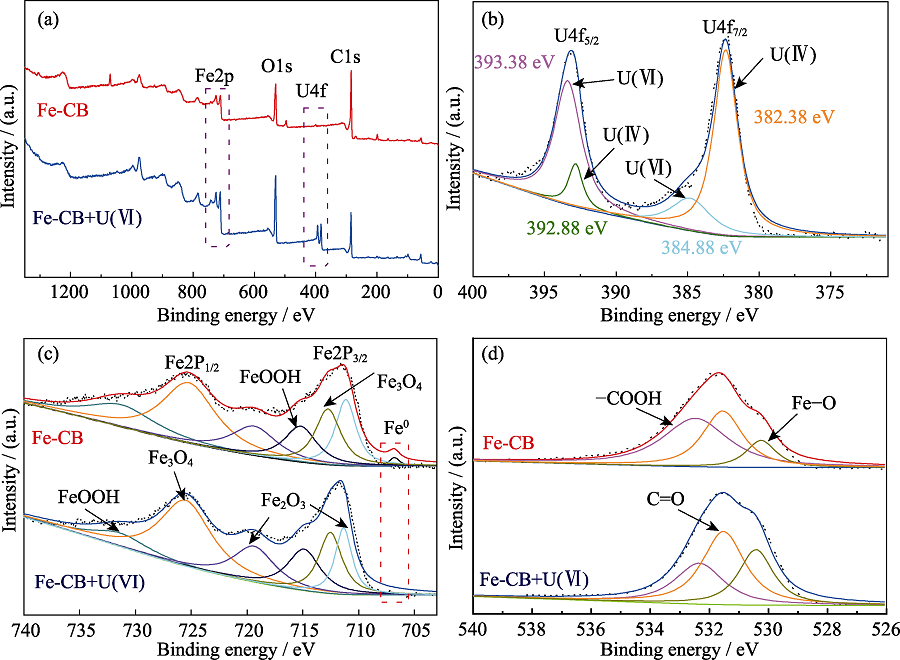
Fig. 6 XPS survey spectra of Fe-CB before and after reaction with U(Ⅵ) (a), high resolution XPS spectrum of U4f (b), and deconvolution analyses of Fe2p (c); O1s (d) for Fe-CB before and after U(Ⅵ) adsorption
| [1] | WU YI-HAN, PANG HONG-WEI, YAO WEN , et al. Synthesis of rod-like metal-organic framework (MOF-5) nanomaterial for efficient removal of U(VI): batch experiments and spectroscopy study. Sci. Bull., 2018,63(13):831-839. |
| [2] | WANG XIANG-XUE, YU SHU-JUN, WANG XIANG-KE . Removal of radionuclides by metal-organic framework-based materials. J. Inorg. Mater., 2019,34(1):17-26. |
| [3] | PANG HONG-WEI, DIAO ZHUO-FAN, WANG XIANG-XUE , et al. Adsorptive and reductive removal of U(VI) by dictyophora indusiate-derived biochar supported sulfide NZVI from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J., 2019,366:368-377. |
| [4] | WANG XIANG-XUE, CHEN LONG, WANG LIN , et al. Synthesis of novel nanomaterials and their application in efficient removal of radionuclides. Sci. China Chem., 2019,62(8):933-967. |
| [5] | CHEN ZHONG-SHAN, WANG JIAN, PU ZENG-XIN , et al. Synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4/CFA composites for the efficient removal of U(VI) from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J., 2017,320:448-457. |
| [6] | YU SHU-JUN, WANG XIANG-XUE, YANG SHI-TONG , et al. Interaction of radionuclides with natural and manmade materials using XAFS technique. Sci. China Chem., 2016,60(2):170-187. |
| [7] | LI XIAO-YAN, LIU YI-BAO, HUA MING , et al. Removal of U(VI) from aqueous solution by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Nucl. Power Eng., 2013,34(2):160-163. |
| [8] | PANG HONG-WEI, WU YI-HAN, HUANG SHU-YI , et al. Macroscopic and microscopic investigation of uranium elimination by Ca-Mg-Al-layered double hydroxide supported nanoscale zero valent iron. Inorg. Chem. Front., 2018,5(10):2657-2665. |
| [9] | LIU DA-QIAN, LIU ZHI-RONG, WANG CHANG-FU , et al. Removal of uranium(VI) from aqueous solution using nanoscale zero- valent iron supported on activated charcoal. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 2016,310(3):1131-1137. |
| [10] | ZHANG SI-HAI, WU MEI-FENG, TANG TING-TING , et al. Mechanism investigation of anoxic Cr(VI) removal by nano zero- valent iron based on XPS analysis in time scale. Chem. Eng. J.,, 2018,335:945-953. |
| [11] | TANG LIN, FENG HAO-PENG, TANG JING , et al. Treatment of arsenic in acid wastewater and river sediment by Fe@Fe2O3 nanobunches: the effect of environmental conditions and reaction mechanism. Water. Res., 2017,117:175-186. |
| [12] | CAO ZHEN, LIU XUE, XU JIANG , et al. Removal of antibiotic florfenicol by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2017,51(19):11269-11277. |
| [13] | XU CONG-BIN, YANG WEN-JIE, SUN HONG-LIANG , et al. Performance and mechanism of Pb(II) removal by expanded graphite loaded with zero-valent iron. J. Inorg. Mater., 2018,33(1):41-47. |
| [14] | YANG XIAO-DAN, WANG YU-RU, LI MIN-RUI . Preparation, modification of nanoscale zero valent iron and its application for the removal of heavy metals and organic pollutants from wastewater. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog., 2019,38(7):3412-3424. |
| [15] | MAHDAVINA GHOLAM-REZA, RAHMANI ZEINAB, KARAMIN SHIVA , et al. Magnetic/pH-sensitive kappa-carrageenan/sodium alginate hydrogel nanocomposite beads: preparation, swelling behavior, and drug delivery. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym Ed., 2014,25(17):1891-1906. |
| [16] | LI DA-HAO, LÜ CHUN-XIAO, LIU LONG , et al. Egg-box structure in cobalt alginate: a new approach to multifunctional hierarchical mesoporous N-doped carbon nanofibers for efficient catalysis and energy storage. ACS Central Sci., 2015,1(5):261-269. |
| [17] | BERTAGNOLLI CAROLINE, CARLOS DA-SILVA, GUIBAL ERIC . Chromium biosorption using the residue of alginate extraction from sargassum filipendula. Chem. Eng. J., 2014,237:362-371. |
| [18] | PAPAGEORGIOU S K, KOUVELOS E P, KATSAROS F K . Calcium alginate beads from Laminaria digitata for the removal of Cu 2+ and Cd 2+ from dilute aqueous metal solutions . Desalination, 2008,224(1/2/3):293-306. |
| [19] | YI XIAO-FENG, SUN FU-LIANG, HAN FU-HAO , et al. Graphene oxide encapsulated polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate hydrogel microspheres for Cu(II) and U(VI) removal. Ecotox. Environ. Safe, 2018,158:309-318. |
| [20] | HU SHU-HONG, LIN XIAO-YAN, ZHAO WEN-HUI , et al. Efficient simultaneous removal of U(VI) and Cu(II) from aqueous solution using core-shell nZVI@SA/CMC-Ca beads. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 2018,315(2):223-235. |
| [21] | CHOE SANG-RAK, HALDORAI YUVARAJ, JANG SUNG- CHAN , et al. Fabrication of alginate/humic acid/Fe-aminoclay hydrogel composed of a grafted-network for the efficient removal of strontium ions from aqueous solution. Environ. Technol. Inno., 2018,9:285-293. |
| [22] | CHO EUNBEE, KIM JONGHO, PARK CHAN-WOO , et al. Chemically bound Prussian blue in sodium alginate hydrogel for enhanced removal of Cs ions. J. Hazard. Mater., 2018,360:243-249. |
| [23] | AGBOVI HENRY-K, WILSON LEE-D . Flocculation optimization of orthophosphate with FeCl3 and alginate using the Box-behnken response surface methodology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2017,56(12):3145-3155. |
| [24] | LIU XIN, CHEN CHANG-FENG, YE HONG-WU , et al. One-step hydrothermal growth of carbon nanofibers and insitu assembly of Ag nanowire@carbon nanofiber@Ag nanoparticles ternary composites for efficient photocatalytic removal of organic pollutants. Carbon, 2018,131:213-222. |
| [25] | PANG HONG-WEI, HUANG SHU-YI, WU YI-HAN , et al. Efficient elimination of U(VI) by polyethyleneimine-decorated fly ash. Inorg. Chem. Front., 2018,5(10):2399-2407. |
| [26] | HU TAO, LIU QIN-ZE, GAO TING-TING , et al. Facile preparation of tannic acid-poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate hydrogel beads for methylene blue removal from simulated solution. ACS Omega, 2018,3(7):7523-7531. |
| [27] | MAHDAVINA GHOLAM-REZA, MOUSANEZHAD SEDIGHEH, HOSSEINZADEH HAMED , et al. Magnetic hydrogel beads based on PVA/sodium alginate/laponite RD and studying their BSA adsorption. Carbohydr. Polym., 2016,147:379-391. |
| [28] | WU YI-HAN, LI BI-YUN, WANG XIANG-XUE , et al. Magnetic metal-organic frameworks (Fe3O4@ZIF-8) composites for U(VI) and Eu(III) elimination: simultaneously achieve favorable stability and functionality. Chem. Eng. J., 2019,378:122105-122117. |
| [29] | LIU XIA, WANG XIANG-XUE, LI JIA-XING , et al. Ozonated graphene oxides as high efficient sorbents for Sr(II) and U(VI) removal from aqueous solutions. Sci. China Chem., 2016,59(7):869-877. |
| [30] | ZHU HONG-SHAN, YUAN JIN-YUN, TAN XIAO-LI , et al. Efficient removal of Pb 2+ by Tb-MOFs: identifying the adsorption mechanism through experimental and theoretical investigations. Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2019,6(1):261-272. |
| [31] | WU YI-HAN, LI BI-YUN, WANG XIANG-XUE , et al. Determination of practical application potential of highly stable UiO-66- AO in Eu(III) elimination investigated by macroscopic and spectroscopic techniques. Chem. Eng. J., 2019,365:249-258. |
| [32] | YU SHU-JUN, YIN LING, PANG HONG-WEI , et al. Constructing sphere-like cobalt-molybdenum-nickel ternary hydroxide and calcined ternary oxide nanocomposites for efficient removal of U(VI) from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,352:360-370. |
| [33] | XIA WEI, CHEN XING-XING, KUNDU SHANKHAMALA , et al. Chemical vapor synthesis of secondary carbon nanotubes catalyzed by iron nanoparticles electrodeposited on primary carbon nanotubes. Surf. Coat Tech., 2007,201(22/23):9232-9237. |
| [34] | SHENG GUO-DONG, YANG PENG-JIE, TANG YAN-NA , et al. New insights into the primary roles of diatomite in the enhanced sequestration of UO2 2+ by zerovalent iron nanoparticles: an advanced approach utilizing XPS and EXAFS. Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 2016,193:189-197. |
| [1] | MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [2] | GUO Chunxia, CHEN Weidong, YAN Shufang, ZHAO Xueping, YANG Ao, MA Wen. Adsorption of Arsenate in Water by Zirconia-halloysite Nanotube Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 529-536. |
| [3] | WANG Shiyi, FENG Aihu, LI Xiaoyan, YU Yun. Pb (II) Adsorption Process of Fe3O4 Supported Ti3C2Tx [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [4] | YU Yefan, XU Ling, NI Zhongbing, SHI Dongjian, CHEN Mingqing. Prussian Blue Modified Biochar: Preparation and Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen from Sewage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 205-212. |
| [5] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Mesoporous Organic-inorganic Hybrid Siliceous Hollow Spheres: Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [6] | HONG Jiahui, MA Ran, WU Yunchao, WEN Tao, AI Yuejie. CoNx/g-C3N4 Nanomaterials Preparation by MOFs Self-sacrificing Template Method for Efficient Photocatalytic Reduction of U(VI) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 741-749. |
| [7] | SUN Lian, GU Quanchao, YANG Yaping, WANG Honglei, YU Jinshan, ZHOU Xingui. Two-dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides for Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 697-709. |
| [8] | MA Lei, HUANG Yi, DENG Hao, YIN Hang, TIAN Qiang, YAN Minghao. Removal of Uranium (VI) from Acidic Aqueous Solution by Fluorapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 395-403. |
| [9] | MA Hui, TAO Jianghui, WANG Yanni, HAN Yu, WANG Yabin, DING Xiuping. Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Silica & Titania Hybrid Mesoporous Spheres and Their Catalytic Performance Regulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 404-412. |
| [10] | JIANG Lili, XU Shuaishuai, XIA Baokai, CHEN Sheng, ZHU Junwu. Defect Engineering of Graphene Hybrid Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 215-222. |
| [11] | LI Chengjin, XUE Yi, ZHOU Xiaoxia, CHEN Hangrong. BiZnx/Si Photocathode: Preparation and CO2 Reduction Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1093-1101. |
| [12] | WU Jing, YU Libing, LIU Shuaishuai, HUANG Qiuyan, JIANG Shanshan, ANTON Matveev, WANG Lianli, SONG Erhong, XIAO Beibei. NiN4/Cr Embedded Graphene for Electrochemical Nitrogen Fixation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1141-1148. |
| [13] | LIU Cheng, ZHAO Qian, MOU Zhiwei, LEI Jiehong, DUAN Tao. Adsorption Properties of Novel Bismuth-based SiOCNF Composite Membrane for Radioactive Gaseous Iodine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1043-1050. |
| [14] | LIU Peng, WU Shimiao, WU Yunfeng, ZHANG Ning. Synthesis of Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS Photocatalyst for CO2 Reduction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 15-21. |
| [15] | GUO Lina, HE Xuebing, LYU Lin, WU Dan, YUAN Hong. Modulation of CuO Surface Properties for Selective Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to HCOOH [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 29-37. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||