
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (7): 768-774.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180450
Previous Articles Next Articles
XIE Ling-Ling1,2,3,NIU Ya-Ran2( ),WANG Liang2,CHEN Wen-Liang1,ZHENG Xue-Bin2(
),WANG Liang2,CHEN Wen-Liang1,ZHENG Xue-Bin2( ),HUANG Zhen-Yi3
),HUANG Zhen-Yi3
Received:2018-09-21
Revised:2018-11-28
Published:2019-07-20
Online:2019-06-26
Supported by:CLC Number:
XIE Ling-Ling, NIU Ya-Ran, WANG Liang, CHEN Wen-Liang, ZHENG Xue-Bin, HUANG Zhen-Yi. Residual Stresses of Plasma Sprayed ZrC-Based Coatings during Path-by-path and Layer-by-layer Deposition: Simulation and Experimental Verification[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(7): 768-774.
| Material | T/ ℃ | Ε/GPa | ρ/(kg·m-3) | α/(×10-6, K-1) | ν | k/(W·m-1·K-1) | C/(J·kg-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/C | 25 | 70 | 1800 | 1.00 | 0.340 | 8.00 | 800 |
| 200 | - | - | 3.58 | - | 8.13 | 934 | |
| 400 | - | - | 3.70 | - | 7.95 | 1115 | |
| 600 | - | - | 3.94 | - | 7.77 | 1239 | |
| 800 | - | - | 4.08 | - | 7.76 | 1344 | |
| 1000 | - | - | 4.20 | - | 8.21 | 1522 | |
| SiC | 2300 | 448 | 3050 | 4.50 | 0.142 | 16.70 | 670 |
| ZrC | 20 | 348 | 6730 | 6.70 | 0.180 | 20.50 | 366 |
| 3540 | 355 | 6730 | 6.70 | 0.191 | 20.50 | 366 | |
| MoSi2 | 2030 | 440 | 6240 | 8.10 | 0.115 | 45.00 | 540 |
Table 1 Thermo-physical performance parameters of the substrate and coating[16,17]
| Material | T/ ℃ | Ε/GPa | ρ/(kg·m-3) | α/(×10-6, K-1) | ν | k/(W·m-1·K-1) | C/(J·kg-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/C | 25 | 70 | 1800 | 1.00 | 0.340 | 8.00 | 800 |
| 200 | - | - | 3.58 | - | 8.13 | 934 | |
| 400 | - | - | 3.70 | - | 7.95 | 1115 | |
| 600 | - | - | 3.94 | - | 7.77 | 1239 | |
| 800 | - | - | 4.08 | - | 7.76 | 1344 | |
| 1000 | - | - | 4.20 | - | 8.21 | 1522 | |
| SiC | 2300 | 448 | 3050 | 4.50 | 0.142 | 16.70 | 670 |
| ZrC | 20 | 348 | 6730 | 6.70 | 0.180 | 20.50 | 366 |
| 3540 | 355 | 6730 | 6.70 | 0.191 | 20.50 | 366 | |
| MoSi2 | 2030 | 440 | 6240 | 8.10 | 0.115 | 45.00 | 540 |
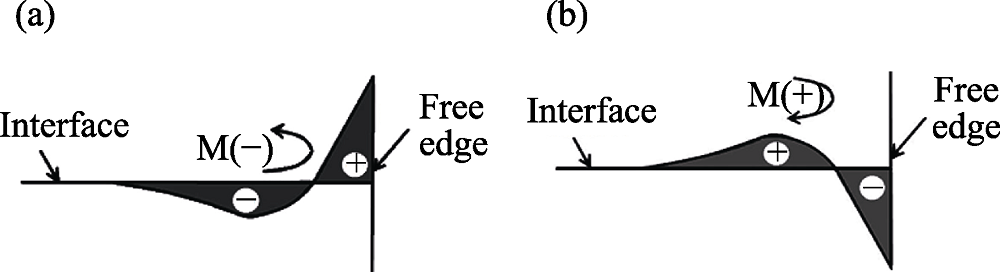
Fig. 15 Schematic of interfacial peeling stress distributions of the coating (a) The maximum tensile stress at the edge; (b) The maximum compressive stress at the edge
| [1] | LI HE-JUN, XUE HUI, FU QIAN-GANG , et al. Research status and prospect of anti-oxidation coatings for carbon/carbon composites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010,25(4):338-343. |
| [2] |
WANG YA-LEI, XIONG XIANG, LI GUO-DONG , et al. Preparation and ablation properties of Hf(Ta)C co-deposition coating for carbon/carbon composites. Corrosion Science, 2013,66:177-182.
DOI URL |
| [3] | FU QIAN-GANG, LI HE-JUN, WANG YONG-JIE , et al. Multilayer oxidation protective coating for C/C composites from room temperature 1500 ℃. Surface & Coating Technology, 2010,204:1831-1835. |
| [4] |
ZENG YI, XIONG XIANG, GUO SHUN , et al. SiC/SiC- YAG-YSZ oxidation protective coatings for carbon/carbon composites. Corrosion Science, 2013,70:68-73.
DOI URL |
| [5] | WANG SHAO-LEI, LI HONG, REN MU-SU , et al. Fabrication and ablation performances of ZrC-SiC-C/C composites. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2017,34(5):1040-1047. |
| [6] | NIU YA-RAN, ZHENG XU-EBIN, DING CHUAN-XIAN . Fabrication and characterization of plasma-sprayed oxidation-resistant coatings. Thermal Spray Technology, 2011,3(3):1-9. |
| [7] |
NIU YA-RAN, WANG HONG-YAN, LI HONG , et al. Dense ZrB2-MoSi2 composite coating fabricated by low pressure plasma spray (LPPS). Ceramics International, 2013,39(8):9773-9777.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
YAO DONG-JIA, LI HE-JUN, WU HENG , et al. Ablation resistance of ZrC/SiC gradient coating for SiC-coated carbon/carbon composites prepared by supersonic plasma spraying. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016,36(15):3739-3746.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
JIA YU-JUN, LI HE-JUN, FU QIAN-GANG , et al. Ablation resistance of supersonic atmosphere plasma spraying ZrC coating doped with ZrO2 for SiC-coated carbon/carbon composites. Corrosion Science, 2017,123:40-54.
DOI URL |
| [10] | ARAUJO P, CHICOT D, STAIA M , et al. Residual stresses and adhesion of thermal spray coatings. Surface Engineering, 2013,21(1):35-40. |
| [11] |
KURODA S, DENDO T, KITAHARA S . Quenching stress in plasma sprayed coatings and its correlation with the deposit microstructure. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 1995,4(1):75-84.
DOI URL |
| [12] | WANG L, ZHONG X H, ZHAO Y X , et al. Design and optimization of coating structure for the thermal barrier coatings fabricated by atmospheric plasma spraying via finite element method. Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies, 2014(2):102-116. |
| [13] | LI YAN-PING, ZHAO WAN-HUA, LU BING-HENG . Prediction and control of residual stresses in thermal sprayed coatings. Engineering Mechanics, 2005,22(5):236-240. |
| [14] |
GHAFOURHI-AZAR R, MOSTAGHIMIJ, CHANDRA S . Modeling development of residual stresses in thermal spray coatings. Computational Materials Science, 2006,35(1):13-26.
DOI URL |
| [15] | YANG JIA-SHENG, YU JIAN-HUA, ZHONG XING-HUA , et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of residual stresses in plasma-sprayed thermal barrier coatings. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013,28(12):1381-1386. |
| [16] | BANSAL N P . Handbook of ceramic composites. Springer, 2006: 207. |
| [17] | YI FA-JUN, ZHANG WEI, MENG SONG-HE , et al. An experimental study on thermophysical properties of C/C composites at elevated temperature. Journal of Astronautics, 2002,23(5):85-88. |
| [18] | LI ZHAN-CHANG, JIA HONG-SHENG, MA HONG-AN , et al. FEM analysis on the effect of cobalt content on thermal residual stress in polycrystalline diamond compact (PDC). Science China: Physics, Mechanics&Astronomy, 2012(55):639-643. |
| [19] | LU PING, LIU ZUOMING . Mixed-mode of elastic modulus composites based on the α factor. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2008,9(30):19-22. |
| [20] | ZHANG XIAN-CHENG, GONG JIAN-MING, TU SHAN-DONG , et al. The effect of coating size and material property on the residual stress in plasma spraying. Journal of Nanjing University of Technology, 2003,25(1):63-68. |
| [21] | 徐少辉 . 等离子喷涂工艺参数对ZrB2-SiC-ZrC涂层组织及结合强度的影响. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学硕士学位论文, 2017,3:33. |
| [22] | NIU LI-PING, ZHANG TING-AN, SHI GUAN-YONG , et al. Residual stresses of plasma-spraying coating of thin-walled part. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2011,32(10):1448-1451. |
| [23] | SINGH H, SIDHU B S, PURI D , et al. Use of plasma spray technology for deposition of high temperature oxidation/corrosion resistant coatings-a review. Mater. Corros., 2015,58(2):92-102. |
| [24] | SCHNEIBEL J H, RAWN C J, PAYZANT E A , et al. Controlling the thermal expansion anisotropy of Mo5Si3 and Ti5Si3 silicides. Intermetallics, 2014,12(7/8/9):845-850. |
| [25] | FEI XIAO-AI, NIU YA-RAN, JI HENG , et al. A comparative study of MoSi2 coatings manufactured by atmospheric and vacuum plasma spray processes. Ceramics International, 2011(37):813-817. |
| [26] | 张显程 . 面向再制造的等离子喷涂结构完整性及寿命预测基础研究. 上海: 上海交通大学博士学位论文, 2007,6:89-90. |
| [1] | PAN Yangyang, LIANG Bo, HONG Du, QI Zhixiang, NIU Yaran, ZHENG Xuebin. High Temperature Long-term Service Performance of TiAlCrY/YSZ Coating on TiAl Alloy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 105-112. |
| [2] | HONG Du, NIU Yaran, LI Hong, ZHONG Xin, ZHENG Xuebin. Tribological Properties of Plasma Sprayed TiC-Graphite Composite Coatings [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 643-650. |
| [3] | DAI Zhao,WANG Ming,WANG Shuang,LI Jing,CHEN Xiang,WANG Da-Lin,ZHU Ying-Chun. Zirconia Reinforced Trace Element Co-doped Hydroxyapatite Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 179-186. |
| [4] | FAN Jia-Feng,ZHANG Xiao-Feng,ZHOU Ke-Song,LIU Min,DENG Chang-Guang,DENG Chun-Ming,NIU Shao-Peng,DENG Zi-Qian. Influence of Al-modification on CMAS Corrosion Resistance of PS-PVD 7YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 938-946. |
| [5] | Yan-Zhe ZHOU, Min LIU, Kun YANG, Wei ZENG, Jin-Bing SONG, Chun-Ming DENG, Chang-Guang DENG. Microstructure and Property of MoSi2-30Al2O3 Electrothermal Coating Prepared by Atmospheric Plasma Spraying [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 646-652. |
| [6] | CHEN Shu-Ying, MA Guo-Zheng, HE Peng-Fei, LIU Zhe, LIU Ming, XING Zhi-Guo, WANG Hai-Dou, WANG Hai-Jun. Pore Formation Mechanism of WC-10Co4Cr Coatings Based on Collected In-flight Particles and Individual Splat [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(8): 895-902. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xiao-Feng, ZHOU Ke-Song, LIU Min, DENG Chun-Ming, NIU Shao-Peng, XU Shi-Ming. Preparation of Si/Mullite/Yb2SiO5 Environment Barrier Coating (EBC) by Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition (PS-PVD) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(3): 325-330. |
| [8] | LI Da-Chuan, ZHAO Hua-Yu, ZHONG Xing-Hua, TAO Shun-Yan. Research Progresses of Atmospheric Plasma Sprayed Splat [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(6): 571-580. |
| [9] | SUN Xu-Xuan, CHEN Hong-Fei, YANG Guang, LIU Bin, GAO Yan-Feng. YSZ- Ti3AlC2 Thermal Barrier Coating and Its Self-healing Behavior under High Temperatures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(12): 1269-1274. |
| [10] | ZHU Ming-Kang, DONG Xian-Lin, CHEN Yin, DING Guo-Ji, WANG Gen-Shui. Effect of Residual Stress on Magnetic and Electrical Transport Properties in SrRuO3 Thin Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 75-80. |
| [11] | YU Fang-Li, BAI Yu, WU Xiu-Ying, Wang Hai-Jun, WU Jiu-Hui. Corrosion Resistance and Anti-wear Property of Nickel Based Abradable Sealing Coating Deposited by Plasma Spraying [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(7): 687-693. |
| [12] | BAO Yi-Wang, LIU Zheng-Quan. Mechanism and Criterion of Spontaneous Breakage of Tempered Glass [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(4): 401-406. |
| [13] | LIN Chu-Cheng, KONG Ming-Guang, ZHU Hui-Ying, HUANG Li-Ping, ZHENG Xue-Bin, ZENG Yi. Tribological Behavior of Vacuum Plasma Sprayed B4C-Mo Composite Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(1): 100-106. |
| [14] | MAO Jin-Yuan, LIU Min, MAO Jie, DENG Chun-Min, ZENG De-Chang, XU Lin. Oxidation-resistance of ZrB2-MoSi2 Composite Coatings Prepared by Atmospheric Plasma Spraying [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 282-286. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xiao-Feng, ZHOU Ke-Song, SONG Jin-Bing, DENG Chun-Ming, NIU Shao-Peng, DENG Zi-Qian. Deposition and CMAS Corrosion Mechanism of 7YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings Prepared by Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 287-293. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||