
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (7): 761-767.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180493
Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Chong1,GENG Xiao-Wei1,GAO Xiang-Di1,ZHANG Xin1,GUO Rao1,WANG Yu-Jing1,XU Jian-Zhong1,MA Hai-Yun1,2( )
)
Received:2018-10-17
Revised:2018-12-27
Published:2019-07-20
Online:2019-06-26
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHANG Chong, GENG Xiao-Wei, GAO Xiang-Di, ZHANG Xin, GUO Rao, WANG Yu-Jing, XU Jian-Zhong, MA Hai-Yun. Strontium Hydroxystannate Nanorods Encapsulated by Hybrid Polyphosphazene: Synthesis and Flame Retardancy on Epoxy Resin[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(7): 761-767.
| Sample | T5%/℃ | Tmax/℃ | Residue at 800 ℃/wt% | Theoretical residue at 800 ℃/wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PZS | 442.8 | 507.9 | 48.2 | — |
| SrSn(OH)6 | 217.3 | 237.7 | 80.4 | — |
| PZS@SrSn(OH)6 | 218.5 | 487.5 | 69.4 | — |
| Pure EP | 364.2 | 375.3 | 13.0 | — |
| 3% EP/SrSn(OH)6 | 354.0 | 367.3 | 16.2 | 15.0 |
| 3% EP/PZS@SrSn(OH)6 | 360.0 | 368.6 | 17.0 | 14.7 |
Table 1 Thermogravimetric properties of PZS, SrSn(OH)6, PZS@SrSn(OH)6 and EP nanocomposites
| Sample | T5%/℃ | Tmax/℃ | Residue at 800 ℃/wt% | Theoretical residue at 800 ℃/wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PZS | 442.8 | 507.9 | 48.2 | — |
| SrSn(OH)6 | 217.3 | 237.7 | 80.4 | — |
| PZS@SrSn(OH)6 | 218.5 | 487.5 | 69.4 | — |
| Pure EP | 364.2 | 375.3 | 13.0 | — |
| 3% EP/SrSn(OH)6 | 354.0 | 367.3 | 16.2 | 15.0 |
| 3% EP/PZS@SrSn(OH)6 | 360.0 | 368.6 | 17.0 | 14.7 |
| Sample | Pure EP | 1wt% EP/SrSn(OH)6 | 3wt% EP/SrSn(OH)6 | 1wt% EP/PZS@SrSn(OH)6 | 3wt% EP/PZS@SrSn(OH)6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Char residue/g | 5.6 | 13.2 | 12.4 | 13.8 | 19.2 |
| THR/(MJ·m-2) | 100.4 | 93.2 | 92.6 | 93.1 | 88.9 |
| PHRR/(kW·m-2) | 1141.1 | 971.7 | 888.9 | 777.3 | 809.7 |
| PSPR/(m2·s) | 0.33 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.21 |
| TSP/m2 | 27.6 | 23.7 | 23.9 | 25.1 | 21.2 |
Table 2 Cone calorimetry data for EP composites
| Sample | Pure EP | 1wt% EP/SrSn(OH)6 | 3wt% EP/SrSn(OH)6 | 1wt% EP/PZS@SrSn(OH)6 | 3wt% EP/PZS@SrSn(OH)6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Char residue/g | 5.6 | 13.2 | 12.4 | 13.8 | 19.2 |
| THR/(MJ·m-2) | 100.4 | 93.2 | 92.6 | 93.1 | 88.9 |
| PHRR/(kW·m-2) | 1141.1 | 971.7 | 888.9 | 777.3 | 809.7 |
| PSPR/(m2·s) | 0.33 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.21 |
| TSP/m2 | 27.6 | 23.7 | 23.9 | 25.1 | 21.2 |
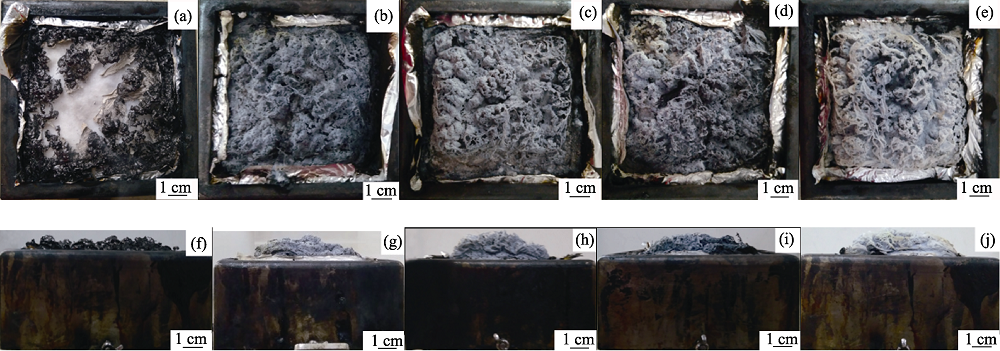
Fig. 7 Digital photos of the char residues for composites after cone calorimeter tests (a,f) EP; (b,g) 1wt% EP/SrSn(OH)6; (c,h)3wt% EP/SrSn(OH)6; (d,i) 1wt% EP/PZS@SrSn(OH)6; (e,j) 3wt% EP/PZS@SrSn(OH)6
| [1] |
SHAO Z B, ZHANG M X, LI Y , et al. A novel multi-functional polymeric curing agent: synthesis, characterization, and its epoxy resin with simultaneous excellent flame retardance and transparency. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,345:471-482.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
QIAN L J, QIU Y, WANG J Y , et al. High-performance flame retardancy by char-cage hindering and free radical quenching effects in epoxy thermosets. Polymer, 2015,68:262-269.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
JIAN X Y, HE Y, LI Y D , et al. Curing of epoxidized soybean oil with crystalline oligomeric poly(butylene succinate) towards high performance and sustainable epoxy resins. Chem. Eng. J., 2017,326:875-885.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
WANG P, XIA L, JIAN R K , et al. Flame-retarding epoxy resin with an efficient P/N/S-containing flame retardant: preparation, thermal stability, and flame retardance. Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 2018,149:69-77.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CHEN T, CHEN X M, WANG M J , et al. A novel halogen-free co-curing agent with linear multi-aromatic rigid structure as flame- retardant modifier in epoxy resin. Polym. Advan. Technol., 2018,29(1):603-611.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
XIE H L, LAI X J, LI H Q , et al. Fabrication of ZrP nanosheet decorated macromolecular charring agent and its efficient synergism with ammonium polyphosphate in flame-retarding polypro-pylene. Compos. Part A-Appl. S., 2018,105:223-234.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
YANG Y Y, LIU J, CAI X F . Antagonistic flame retardancy between hexakis(4-nitrophenoxy) cyclotriphosphazene and potassium diphenylsulfone sulfonate in the PC system. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim., 2016,126(2):571-583.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
SHI X X, PENG X F, ZHU J Y , et al. Synjournal of DOPO-HQ-functionalized graphene oxide as a novel and efficient flame retardant and its application on polylactic acid: thermal property, flame retardancy, and mechanical performance.[J]. Colloid. Interf. Sci., 2018,524:267-278.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
YANG W, TAWIAH B, YU C , et al. Manufacturing, mechanical and flame retardant properties of poly(lactic acid) biocomposites based on calcium magnesium phytate and carbon nanotubes. Compos. Part A-Appl. S., 2018,110:227-236.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
CHEN G G, HU Y J, PENG F , et al. Fabrication of strong nanocomposite films with renewable forestry waste/montmorillonite/ reduction of graphene oxide for fire retardant. Chem. Eng. J., 2018,337:436-445.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHANG B, LIU H, HAN J . Synthesis of zinc hydroxystannate microcapsule for improving flame retardancy and smoke suppression of poly(lactic acid). Mater.Lett., 2018,213:35-39.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
XU R, DENG B, MIN L , et al. CuSn(OH)6 submicrospheres: room-temperature synthesis and weak antiferromagnetic behavior. Mater. Lett., 2011,65(4):733-735.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
GAO T T, SANG B, SHAO B , et al. Flame retardancy and mechanical properties of a novel zinc hydroxystannate/epoxy resin nanocomposite. J. Nanosci.Nanotech no., 2017,17(12):8856-8863.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
QIU S L, MA C, WANG X , et al. Melamine-containing polyphosphazene wrapped ammonium polyphosphate: a novel multifunctional organic-inorganic hybrid flame retardant.[J]. Hazard. Mater., 2018,344:839-848.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
YANG R, WANG B, HAN X F , et al. Synthesis and characterization of flame retardant rigid polyurethane foam based on a reactive flame retardant containing phosphazene and cyclophosphonate. Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 2017,144:62-69.
DOI URL |
| [16] | ZHAO S S, HE M, SONG W Y , et al. Synthesis of a phosphorus/ nitrogen/sulphur containing phosphazene micro-nanotube and its flame retardancy on epoxy nanocomposite. Chem. J. Chinese U., 2017,38(12):2337-2343. |
| [17] | LI P, FU H, ZHAO O , et al. Influence of polyphosphate flame retardant couple with ammonium polyphosphate on epoxy resin. Chem. J. Chinese U., 2017,38(2):294-302. |
| [18] |
WEN P Y, WANG X F, XING W Y , et al. Synthesis of a novel triazine- based hyperbranched char foaming agent and the study of its enhancement on flame retardancy and thermal stability of polypropylene. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2013,52(48):17015-17022.
DOI URL |
| [1] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Mesoporous Organic-inorganic Hybrid Siliceous Hollow Spheres: Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [2] | MA Hui, TAO Jianghui, WANG Yanni, HAN Yu, WANG Yabin, DING Xiuping. Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Silica & Titania Hybrid Mesoporous Spheres and Their Catalytic Performance Regulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 404-412. |
| [3] | XIONG Jinyan, LUO Qiang, ZHAO Kai, ZHANG Mengmeng, HAN Chao, CHENG Gang. Facilely Anchoring Cu nanoparticles on WO3 Nanocubes for Enhanced Photocatalysis through Efficient Interface Charge Transfer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 325-331. |
| [4] | LU Xiaoqing,WANG Maohuai. Theoretical Investigation on Adsorption and Separation of CO2/N2 in Hybrid Ultramicroporous Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 469-474. |
| [5] | LI Zhao, SUN Qiangqiang, CHEN Suoqian, ZHOU Chunsheng, CAO Jing, WANG Yongfeng, WANG Yanan. Hydrothermal Synthesized Nickel Copper Composite Phosphides as Bifunctional Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution and Hydrazine Oxidation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1149-1156. |
| [6] | ZHANG Jiao-Xia, YI Jing, JIAO Yue-Ting, LI Shi-Yun, SHI Xin-Lan, SUN Kai. Preparation and Application of Water-soluble TiO2-ionic Liquids Hybrid Nanomaterials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(5): 577-581. |
| [7] | ZHANG Heng-Fei, LIU Wei, LEI Jiao-Jiao, SONG Hua-Ting, QI Hong. Pd Doping on H2/CO2 Separation Performance and Hydrothermal Stability of Organic-inorganic Hybrid SiO2 Membranes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(12): 1316-1322. |
| [8] | CHU Zeng-Yong, LI Gao-Lin, JIANG Zhen-Hua, WANG Chun-Hua. Recent Progress in High-quality Perovskite CH3NH3PbI3 Single Crystal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1035-1045. |
| [9] | MA Xi-Fei, LIN Gen-Lian, KANG Zhuang, HUANG Xiao. Crystallization Behavior of Hybrid Mullite Fiber Precursors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 739-743. |
| [10] | LIAO Fan, MA Jian-Qi, GE Hong-Guang. Preparation, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Core-satellite Ag/PDA@SiO2@CoFe2O4 Magnetic Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 523-528. |
| [11] | JIANG Li, LIU Jia-Nan, FAN Wen-Pei, LIU Yan-Yan, NI Da-Long, BU Wen-Bo. Performance Study of TiO2-Au Photoelectric Nanocomposites for Novel Neuromodulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 550-554. |
| [12] | ZHENG Xuan, GONG Chun-Li, LIU Hai, WANG Guang-Jin, CHENG Fan, ZHENG Gen-Wen, WEN Sheng, XIONG Chuan-Xi. Preparation of Phosphomolybdic Acid Coated Carbon Nanotubes and Its Supercapacitive Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(2): 127-134. |
| [13] | HUANG Wei, ZHU Jia-Yi, LI Hao, YANG Xi, WANG Chao-Yang, FU Zhi-Bing. Preparation and Characterization of Graphene/Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Thin Films by Drop-coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(2): 203-209. |
| [14] | YANG Zhi-Sheng, KE Wei-Fang, WANG Yan-Xiang, HUANG Li-Qun, GUO Ping-Chun, ZHU Hua. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Hybrid Perovskite (HOC2H4NH3)2CuCl4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(10): 1063-1067. |
| [15] | WANG Chao-Fei, LU Shuang, CHEN Hui-Long, GONG Fei-Long, GONG Yu-Yin, LI Feng. One-pot Synthesis and Application in Asymmetric Supercapacitors of Mn3O4@RGO Nanocomposites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(6): 581-587. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||