
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 65-72.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190073
Special Issue: MAX相和MXene材料; 优秀作者论文集锦; 2019~2020年度优秀作者作品欣赏:环境材料; MXene材料专辑(2020~2021)
Previous Articles Next Articles
SONG Huan1,WANG Lin2,WANG Hong-Qing1( ),SHI Wei-Qun2(
),SHI Wei-Qun2( )
)
Received:2019-02-15
Revised:2019-03-20
Published:2020-01-20
Online:2019-05-29
About author:SONG Huan(1994-), male, Master candidate. E-mail:songhuan@ihep.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
SONG Huan, WANG Lin, WANG Hong-Qing, SHI Wei-Qun. Adsorption of Eu(III) on Alkalized Ti3C2Tx MXene Studied by Batch Experiment and Its Mechanism Investigation[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 65-72.
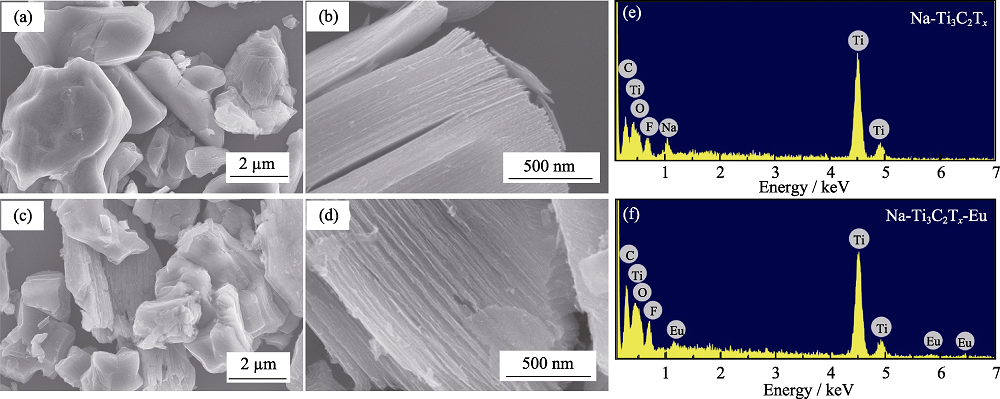
Fig. 2 SEM images of Na-Ti3C2Tx before (a-b), and after (c-d) adsorption of Eu(III), with EDS analysis resulted of Na-Ti3C2Tx before (e) and after (f) adsorption of Eu(III)
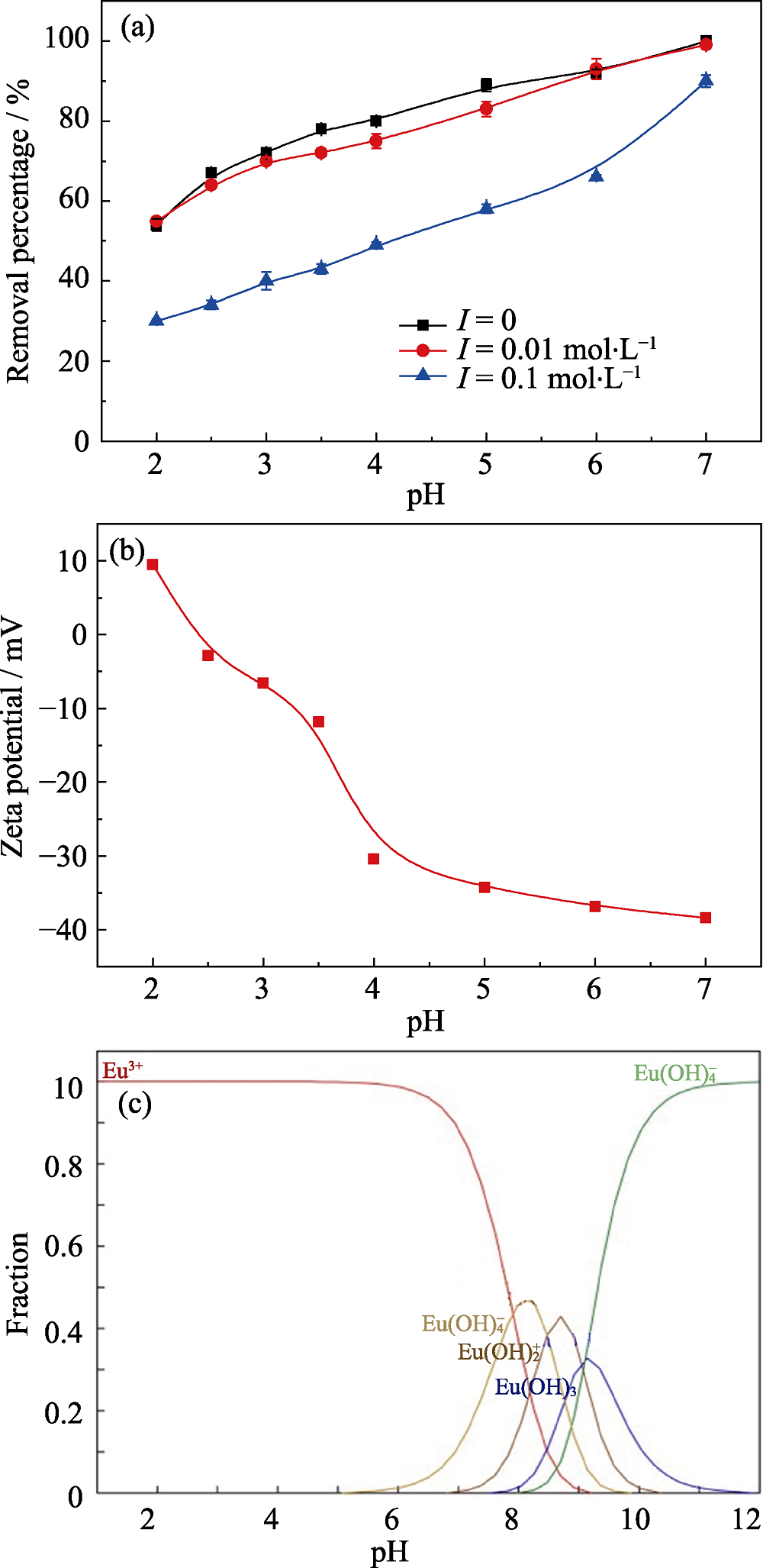
Fig. 4 Effect of solution pH and ionic strength on removal of Eu(III) by Na-Ti3C2Tx (a), Zeta potential of Na-Ti3C2Tx (b), and distribution of Eu(III) species in aqueous solution as a function of pH calculated using the MEDUSA program (c)
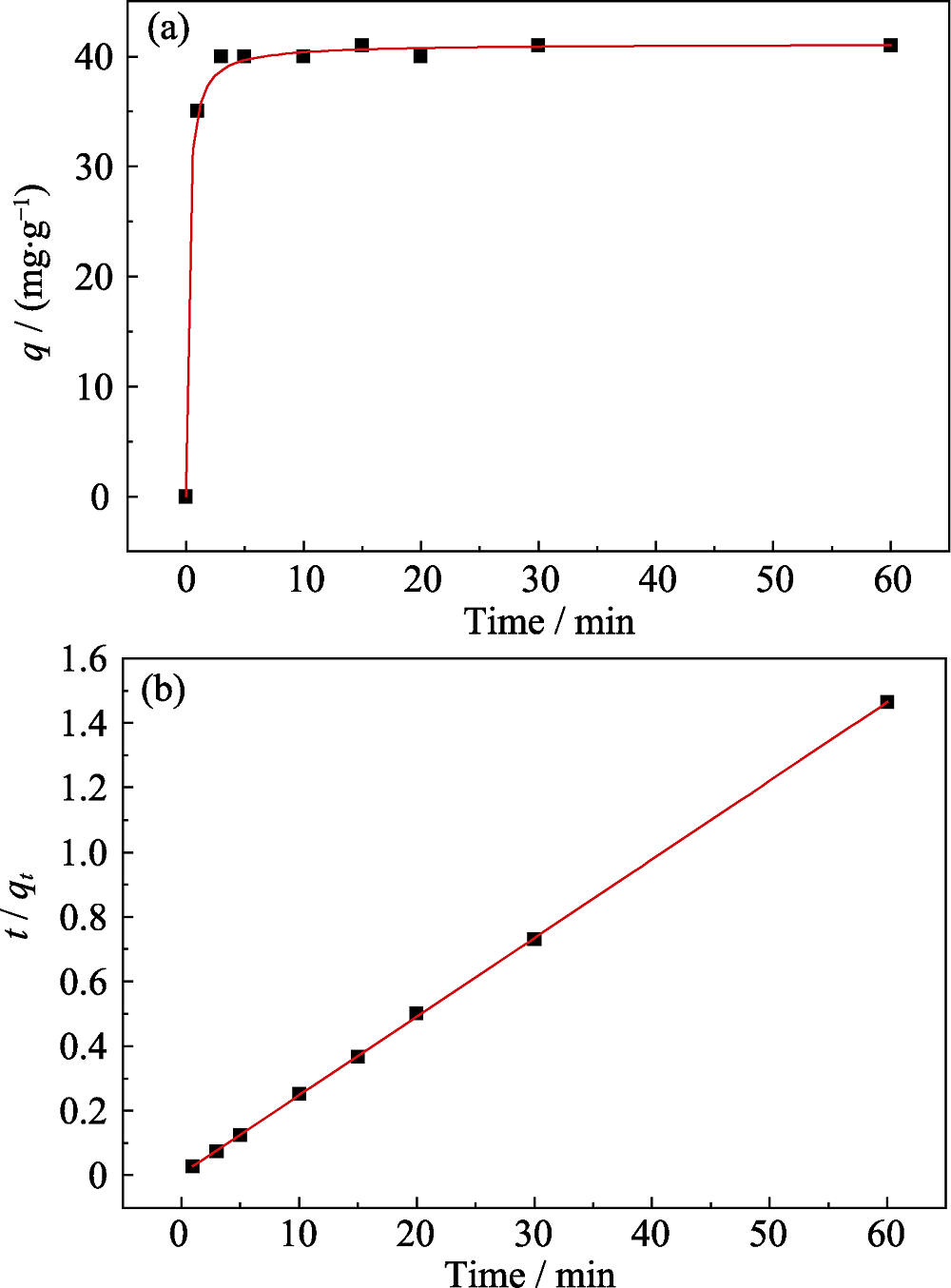
Fig. 5 Time-dependent adsorption of Eu(III) on Na-Ti3C2Tx (pH= (4.0±0.1), T = 293 K, m/V = 0.4 g/L) (a), and pseudo-second- order kinetic plots of Eu(III) on Na-Ti3C2Tx (b)
| Sample | Pseudo-first-order model | Pseudo-second-order model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na-Ti3C2Tx | k1/min-1 | R2 | k2/(g·mg-1·min-1) | R2 |
| 0.0212 | 0.4111 | 0.1312 | 0.9999 | |
Table 1 Optimized parameters of pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models
| Sample | Pseudo-first-order model | Pseudo-second-order model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na-Ti3C2Tx | k1/min-1 | R2 | k2/(g·mg-1·min-1) | R2 |
| 0.0212 | 0.4111 | 0.1312 | 0.9999 | |
| Models | Parameters | Temperature/K | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 306 | 314 | 322 | ||
| Langmuir | qm/(mg·g-1) | 54.05 | 57.14 | 66.67 | 88.50 |
| KL/(L·mg-1) | 0.49 | 5.00 | 3.49 | 1.04 | |
| R2 | 0.9931 | 0.9999 | 0.9981 | 0.9973 | |
| Freundlich | KF/(mg1-n·Ln·g-1) | 33.52 | 40.87 | 50.37 | 60.87 |
| 1/n | 9.78 | 10.50 | 10.88 | 10.92 | |
| R2 | 0.9436 | 0.9487 | 0.9212 | 0.9645 | |
Table 2 Fitting parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich models
| Models | Parameters | Temperature/K | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 306 | 314 | 322 | ||
| Langmuir | qm/(mg·g-1) | 54.05 | 57.14 | 66.67 | 88.50 |
| KL/(L·mg-1) | 0.49 | 5.00 | 3.49 | 1.04 | |
| R2 | 0.9931 | 0.9999 | 0.9981 | 0.9973 | |
| Freundlich | KF/(mg1-n·Ln·g-1) | 33.52 | 40.87 | 50.37 | 60.87 |
| 1/n | 9.78 | 10.50 | 10.88 | 10.92 | |
| R2 | 0.9436 | 0.9487 | 0.9212 | 0.9645 | |
| Temperature/K | ΔH/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔS/(J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔG/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 24.539 | 134.81 | -15.57 |
| 306 | -16.65 | ||
| 314 | -17.73 | ||
| 322 | -18.80 |
Table 3 Thermodynamic parameters for removal of Eu(III) by Na-Ti3C2Tx
| Temperature/K | ΔH/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔS/(J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔG/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 24.539 | 134.81 | -15.57 |
| 306 | -16.65 | ||
| 314 | -17.73 | ||
| 322 | -18.80 |
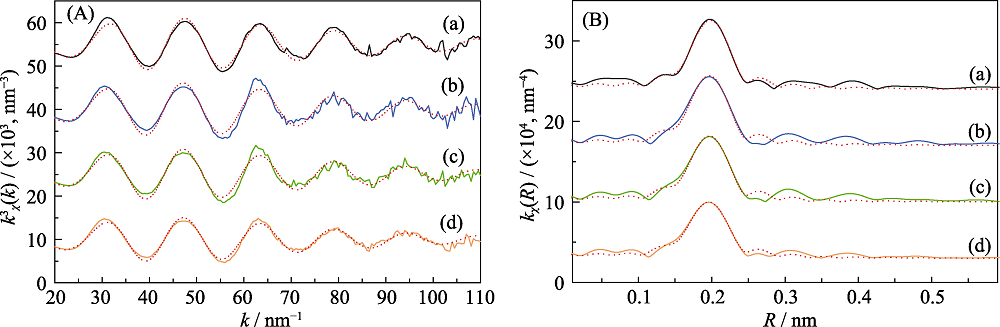
Fig. 7 (A) Eu L 3 edge k3-weighted EXAFS spectra (solid lines) and the best theoretical fits (dots lines) of Eu-loaded Na-Ti3C2Tx samples under different solution pH, and (B) corresponding non-phase shift corrected Fourier transforms
| Sample | Path | CNa | Rb/nm | σ2c/(×10-4, nm2) | ΔEd/eV | R-factore |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eu3+(aq) | Eu-O | (9.0±0.6) | (0.243±0.001) | 0.8 | (3.9±0.6) | 0.006 |
| pH=4.0 | Eu-O | (9.1±1.6) | (0.243±0.002) | 0.9 | (2.4±1.6) | 0.019 |
| pH=5.0 | Eu-O | (8.7±1.4) | (0.243±0.001) | 0.9 | (2.6±1.5) | 0.016 |
| pH=6.0 | Eu-O | (7.8±0.9) | (0.242±0.001) | 1.0 | (2.2±1.1) | 0.008 |
Table 4 Fitting parameters extracted from least-squares fitting analysis of EXAFS spectra
| Sample | Path | CNa | Rb/nm | σ2c/(×10-4, nm2) | ΔEd/eV | R-factore |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eu3+(aq) | Eu-O | (9.0±0.6) | (0.243±0.001) | 0.8 | (3.9±0.6) | 0.006 |
| pH=4.0 | Eu-O | (9.1±1.6) | (0.243±0.002) | 0.9 | (2.4±1.6) | 0.019 |
| pH=5.0 | Eu-O | (8.7±1.4) | (0.243±0.001) | 0.9 | (2.6±1.5) | 0.016 |
| pH=6.0 | Eu-O | (7.8±0.9) | (0.242±0.001) | 1.0 | (2.2±1.1) | 0.008 |
| [1] |
JOHNSTONE E V, HOFMSNN S, CHERKOUK A , et al. Study of the interaction of Eu3+ with microbiologically induced calcium carbonate precipitates using TRLFS. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016,50(22):12411-12420.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
ZHANG W, HE X, YE G , et al. Americium(III) capture using phosphonic acid-functionalized silicas with different mesoporous morphologies: adsorption behavior study and mechanism investigation by EXAFS/XPS. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014,48(12):6874-6881.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] |
XU L, ZHENG T, YANG S , et al. Uptake mechanisms of Eu(III) on hydroxyapatite: a potential permeable reactive barrier backfill material for trapping trivalent minor actinides. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016,50(7):3852-3859.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] |
WANG X, YU S, WANG X K . Removal of radionuclides by metal-organic framework-based materials. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019,34(1):17-26.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
WANG X, PANG H, WU Y , et al. >Removal of radionuclides by layered double hydroxides materials. Sci. Sin. Chim., 2019,49(1):2-11.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] | WANG S, YU S, WU Y ,et al. Highly efficient removal of radioactive uranium on polyaniline modified carbon nanofiber composites. Sci. Sin. Chim., 2019,49(1):71-79. |
| [7] | YAO W, WU Y, PANG H , et al. In-situ reduction synthesis of manganese dioxide@polypyrrole core/shell nanomaterial for highly efficient enrichment of U(VI) and Eu(III). Sci. China Chem., 2018,61(7):812-823. |
| [8] |
KUMAR S, GODBOLE S V, TOMAR B S . Speciation of Am(III)/Eu (III) sorbed on gammaalumina: effect of metal ion concentration. Radiochimica Acta, 2013,101(2):73-80.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
TAN X L, WANG X K, GECKEIS H , et al. Sorption of Eu(III) on humic acid or fulvic acid bound to hydrous alumina studied by SEM-E DS, XPS, TRLFS, and batch techniques. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008,42(17):6532-6537.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] |
NOEMIE J, BENEDETTI M F, REILLER P E . Colloidal α-Al2O3 europium (III) and humic substances interactions: a macroscopic and spectroscopic study. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011,45(8):3224-3230.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
TAN X, FAN Q, WANG X , et al. Eu(III) sorption to TiO2(anatase and rutile): batch, XPS, and EXAFS studies. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009,43(9):3115-3121.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
BOUBY M, LUTZENKIRCHEN J, DARDENNE K , et al. Sorption of Eu(III) onto titanium dioxide: measurements and modeling. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2010,350(2):551-561.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
RABUNG T, PIERRET MC, BAUER A , et al. Sorption of Eu(III)/Cm(III) on Ca-montmorillonite and Na-illite. Part 1: batch sorption and time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy experiments. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005,69(23):5393-5402.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
FAN Q H, TAN X L, LI J X , et al. Sorption of Eu(III) on attapulgite studied by batch, XPS, and EXAFS techniques. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009,43(15):5776-5782.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] |
GALUNIN E, ALBA M D, SANTOS M J , et al. Lanthanide sorption on smectitic clays in presence of cement leachates. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010,74(3):862-875.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
GAD H M H, AWWAD N S . Factors affecting on the sorption/ desorption of Eu (III) using activated carbon. Separation Science & Technology, 2007,42(16):3657-3680.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
ACCORSI G, ARMAROLI N, PARISINI A , et al. Wet adsorption of a luminescent Eu(III) complex on carbon nanotubes sidewalls. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010,17(15):2975-2982.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CHEN C L, WANG X K, NAGATSU M . Europium adsorption on multiwall carbon nanotube/iron oxide magnetic composite in the presence of polyacrylicacid. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009,43(7):2362-2367.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
SUN Y, WANG Q, CHEN C , et al. Interaction between Eu(III) and graphene oxide nanosheets investigated by batch and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy and by modeling techniques. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012,46(11):6020-6027.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] |
XIE Y, NAGUIB M, MOCHALIN V N , et al. Role of surface structure on Li-ion energy storage capacity of two-dimensional transition-metal carbides. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014,136(17):6385-6394.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHAO S, WEI K, XUE J . Role of strain and concentration on the Li adsorption and diffusion properties on Ti2C layer. Journal of Physical Chemistry Cv, 2014,118(27):14983-14990.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
EAMES C, ISLAM M S . Ion intercalation into two-dimensional transition-metal carbides: global screening for new high-capacity battery materials. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015,46(14):16270-16276.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] |
HU M, LI Z, ZHANG H , et al. Self-assembled Ti3C2Tx MXene film with high gravimetric capacitance. Chem. Commun., 2015,51(70):13531-13533.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] |
ZHU M, HUANG Y, DENG Q , et al. Highly flexible, freestanding supercapacitor electrode with enhanced performance obtained by hybridizing polypyrrole chains with MXene. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016,6(21):1600969.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHI W S, FREDRICKSON K D, ANASORI B , et al. Two- dimensional molybdenum carbide (MXene) as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. ACS Energy Letters, 2016,1(3):589-594.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LING C, SHI L, OUYANG Y , et al. Transition metal-promoted V2CO2(MXenes): a new and highly active catalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Advanced Science, 2016,3(11):1600180.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] |
MA T Y, CAO J L, JARONIEC M , et al. Interacting carbon nitride and titanium carbide nanosheets for high-performance oxygen evolution. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016,128(3):1150-1154.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] |
SHAHZAD F, ALHABEB M, HATTER C B , et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science, 2016,353(6304):1137-1140.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
HAN M, YIN X, WU H , et al. Ti3C2 MXenes with modified surface for high-performance electromagnetic absorption and shielding in the X-band. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016,8(32):21011-21019.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] |
QING Y, ZHOU W, LUO F , et al. Titanium carbide (MXene) nanosheets as promising microwave absorbers. Ceramics International, 2016,42(14):16412-16416.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
YU X F, LI Y, CHENG J B , et al. Monolayer Ti2CO2: a promising candidate for NH3 sensor or capturer with high sensitivity and selectivity. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015,7(24):13707-13713.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] |
LIU H, DUAN C, YANG C , et al. A novel nitrite biosensor based on the direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin immobilized on MXene- Ti3C2. Sensors & Actuators B Chemical, 2015,218:60-66.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] |
FAN M, WANG L, PEI C , et al. Alkalization intercalation of MXene for electrochemical detection of uranyl ion. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019,34(1):85-90.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
MICHAEL N, MURAT K, VOLKER P , et al. Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Advanced Materials, 2011,23(37):4248-4253.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] |
MINOLI G . Cation intercalation and high volumetric capacitance of two-dimensional titanium carbide. Science, 2013,341(6153):1502-1505.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
MASHTALIR O, NAGUIB M, MOCHALIN V N , et al. Intercalation and delamination of layered carbides and carbonitrides. Nature Communications, 2013,4(2):1716.
DOI URL PMID |
| [37] |
PENG Q, GUO J, ZHANG Q , et al. Unique lead adsorption behavior of activated hydroxyl group in two-dimensional titanium carbide. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014,136(11):4113-4116.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
SHAHZAD A, RASOOL K, MIRAN W , et al. Mercuric ion capturing by recoverable titanium carbide magnetic nanocomposite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017,344:811-818.
DOI URL PMID |
| [39] |
WANG L, SONG H, YUAN L , et al. Efficient U(VI) reduction and sequestration by Ti2CTx MXene. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018,52(18):10748-10756.
DOI URL PMID |
| [40] |
WANG L, TAO W, YUAN L , et al. Rational control of the interlayer space inside two-dimensional titanium carbides for highly efficient uranium removal and imprisonment. Chem. Commun., 2017,53(89):12084-12087.
DOI URL PMID |
| [41] |
MU W, DU S, YU Q , et al. Improving barium ions adsorption on two-dimensional titanium carbide by surface modification. Dalton Transactions, 2018,47(25):8375-8381.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] |
WANG L, YUAN L, CHEN K , et al. Loading actinides in multiayered structures for nuclear waste treatment: the first case study of uranium capture with vanadium carbide MXene. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2016,8(25):16396-16403.
DOI URL PMID |
| [43] | FAN M, WANG L, ZHANG Y , et al. Research progress of MXene materials in radioactive element and heavy metal ion sequestration. Sci. Sin. Chim., 2019,49(1):27-38. |
| [44] |
SCHLEGEL M L, INGMAR P, NATHALIE C , et al. Mechanism of europium retention by calcium silicate hydrates: an EXAFS study. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004,38(16):4423-4431.
DOI URL PMID |
| [45] |
MONTAVON G, MARKAI S, ANDRES Y , et al. Complexation studies of Eu(III) with alumina-bound polymaleic acid: effect of organic polymer loading and metal ion concentration. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002,36(15):3303-3309.
DOI URL PMID |
| [46] |
SHENG G D, YANG S T, ZHAO D L , et al. Adsorption of Eu (III) on titanate nanotubes studied by a combination of batch and EXAFS techique. Science China Chemistry, 2012,55(1):182-194.
DOI URL |
| [1] | MA Lei, HUANG Yi, DENG Hao, YIN Hang, TIAN Qiang, YAN Minghao. Removal of Uranium (VI) from Acidic Aqueous Solution by Fluorapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 395-403. |
| [2] | WANG Tingting, SHI Shumei, LIU Chenyuan, ZHU Wancheng, ZHANG Heng. Synthesis of Hierarchical Porous Nickel Phyllosilicate Microspheres as Efficient Adsorbents for Removal of Basic Fuchsin [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1330-1336. |
| [3] | HUANG Xiubing, WANG Peng, TAO Jinzhang, XI Zuoshuai. CeO2 Modified Mn-Fe-O Composites and their Catalytic Performance for NH3-SCR of NO [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 573-580. |
| [4] | HUANG Xieyi,WANG Peng,YIN Guoheng,ZHANG Shaoning,ZHAO Wei,WANG Dong,BI Qingyuan,HUANG Fuqiang. Removal of Volatile Organic Compounds Driven by Platinum Supported on Amorphous Phosphated Titanium Oxide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 482-490. |
| [5] | DONG Lijia, WU Siying, LI Shengbo, WEI Zuofu, YANG Guo, HU Baowei. Sorption Behaviors and Mechanisms of Eu(III) on Rice Straw-derived Biochar [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 390-398. |
| [6] | ZHANG Wei, LIU Chen, CHEN Yuantao, WU Wangsuo. Removal of Boron from Water by Mg-Al-Ce Hydrotalcite Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 337-344. |
| [7] | WANG Xiangxue, LI Xing, WANG Jiaqi, ZHU Hongtao. Recent Advances in Carbon Nitride-based Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 260-270. |
| [8] | GENG Rui-Wen, YANG Xiao-Jing, XIE Qi-Ming, LI Rui, LUO Liang. Material Removal Mechanism of Monocrystalline Germanium Based on Nano-scratch Experiment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(8): 867-872. |
| [9] | WANG Xiang-Xue, YU Shu-Jun, WANG Xiang-Ke. Removal of Radionuclides by Metal-organic Framework-based Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(1): 17-26. |
| [10] | XU Cong-Bin, YANG Wen-Jie, SUN Hong-Liang, LIU Wei-Jiang, YANG Yuan-Yu, LIN Ai-Jun. Performance and Mechanism of Pb(II) Removal by Expanded Graphite Loaded with Zero-Valent Iron [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(1): 41-47. |
| [11] | WANG Yan-Li, WANG Xu-Jian, ZHAN Liang, QIAO Wen-Ming, LIANG Xiao-Yi, LING Li-Cheng. Structure Control of V2O5/CNFs/Cordierite Monolith Catalyst and Its Catalytic Performance on NO Removal from Flue Gas [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(8): 800-806. |
| [12] |
LIU Shou-Xin,LIU Zheng-Feng.
Heterogeneous Photocatalytic Oxidation Removal of Gaseous Benzene over TiO2/ACF Composite Prepared by Improved Sol-Gel Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(2): 209-214. |
| [13] | MA Xin-Pei,LI Guang-Xin,SHEN Lian,JIN Zhi-Hao. Cut Behavior and Microstructure of a Novel Mica Glass-ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2004, 19(1): 48-52. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||