
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (10): 1047-1054.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190003
Special Issue: MAX相和MXene材料; 副主编黄庆研究员专辑
Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Zhong1,2,ZHA Xian-Hu2,WU Ze1( ),HUANG Qing2,DU Shi-Yu2(
),HUANG Qing2,DU Shi-Yu2( )
)
Received:2018-12-29
Revised:2019-02-11
Published:2019-09-23
Online:2019-05-29
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Zhong, ZHA Xian-Hu, WU Ze, HUANG Qing, DU Shi-Yu. First-principles Study on Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Mn-doped Strontium Ferrite SrFe12O19[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(10): 1047-1054.
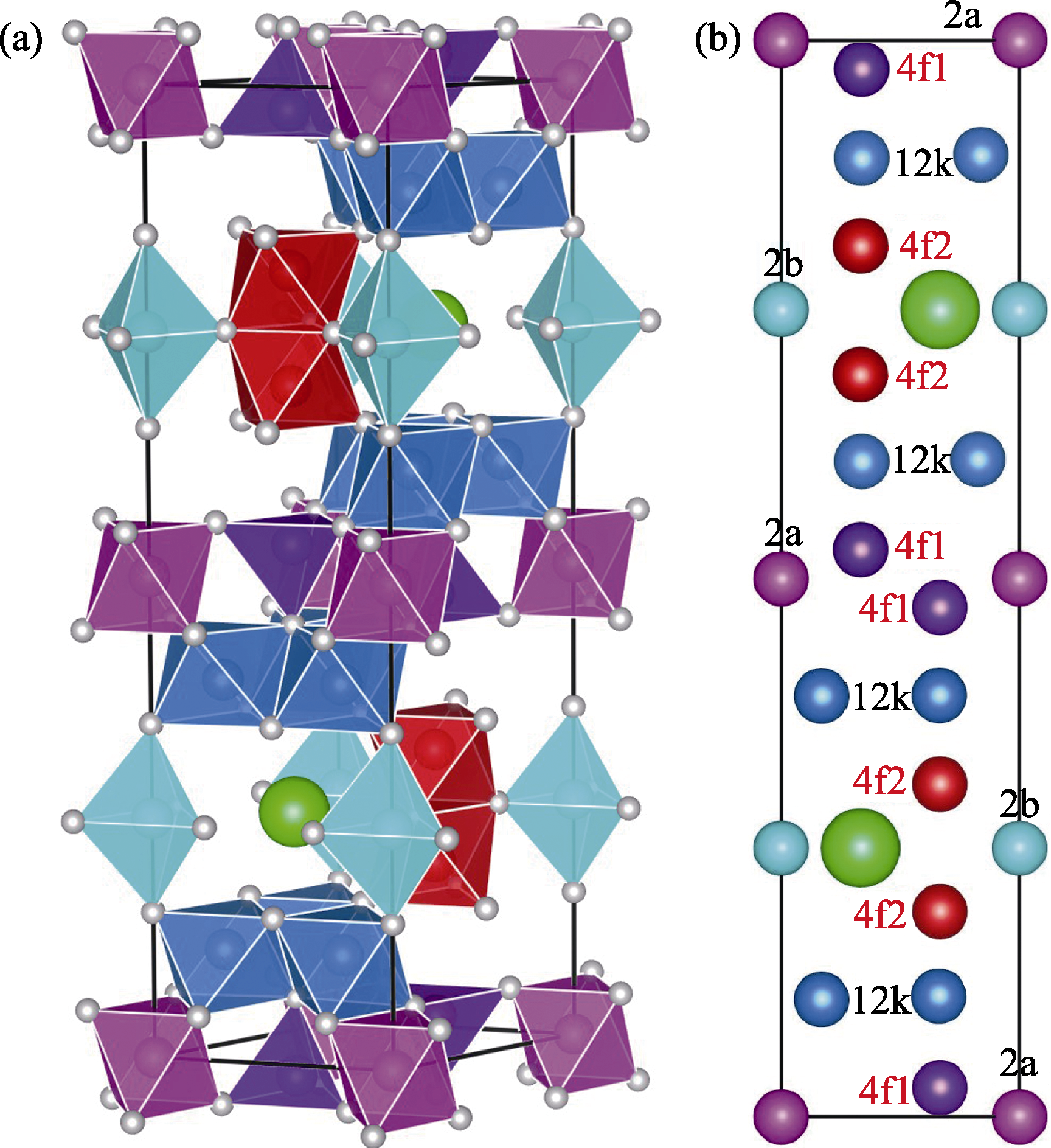
Fig. 1 The unit cell of SrFe12O19 (a) The green ball denotes the Sr atom, the small grey ball denotes the O atom; (b) The blue, red, purple, magenta, and blue-green balls represent the Fe atoms in 12k, 4f2, 4f1, 2a, and 2b sites, respectively. The spin directions for different Fe3+ are labeled with different colors (black and red)
| Spin direction of Fe ions in SrFe12O19 | a/nm | c/nm | Energy/(eV?(unit cell)-1) | Moment/(μB?(unit cell)-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2a | 2b | 4f1 | 4f2 | 12k | ||||
| + | + | + | + | + | 0.5730 | 2.257 | 0 | 25.00 |
| - | + | + | + | + | 0.5690 | 2.239 | 0.5900 | 48.00 |
| + | - | + | + | + | 0.5740 | 2.266 | 0.1300 | 44.00 |
| + | + | - | + | + | 0.5770 | 2.264 | 0.3200 | 39.00 |
| + | + | + | - | + | 0.5870 | 2.324 | 0.4600 | 59.00 |
| + | + | + | + | - | 0.5820 | 2.300 | -1.160 | -7.000 |
| - | - | + | - | + | 0.5840 | 2.269 | 1.040 | 43.00 |
| - | - | - | + | + | 0.5790 | 2.245 | -0.6800 | 28.00 |
| + | + | - | - | + | 0.5860 | 2.310 | -2.820 | 40.00 |
| 0.5880a | 2.304a | |||||||
Table 1 Lattice parameters, relative total energies and magnetic moments of SrFe12O19 in different magnetic configurations
| Spin direction of Fe ions in SrFe12O19 | a/nm | c/nm | Energy/(eV?(unit cell)-1) | Moment/(μB?(unit cell)-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2a | 2b | 4f1 | 4f2 | 12k | ||||
| + | + | + | + | + | 0.5730 | 2.257 | 0 | 25.00 |
| - | + | + | + | + | 0.5690 | 2.239 | 0.5900 | 48.00 |
| + | - | + | + | + | 0.5740 | 2.266 | 0.1300 | 44.00 |
| + | + | - | + | + | 0.5770 | 2.264 | 0.3200 | 39.00 |
| + | + | + | - | + | 0.5870 | 2.324 | 0.4600 | 59.00 |
| + | + | + | + | - | 0.5820 | 2.300 | -1.160 | -7.000 |
| - | - | + | - | + | 0.5840 | 2.269 | 1.040 | 43.00 |
| - | - | - | + | + | 0.5790 | 2.245 | -0.6800 | 28.00 |
| + | + | - | - | + | 0.5860 | 2.310 | -2.820 | 40.00 |
| 0.5880a | 2.304a | |||||||
| Atom | Wyckoff site | Coordinates of atoms | Magnetic moment (GGA) | Magnetic moment (GGA+U) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr | 2d | 1/3, 2/3, 3/4 | 0 | 0 |
| Fe(1) | 2a | 0, 0, 0 | 3.73 | 4.17 |
| Fe(2) | 2b | 0, 0, 1/4 | 3.54 | 4.05 |
| Fe(3) | 4f1 | 1/3, 2/3, 0.0272 | 3.43 | 4.05 |
| Fe(4) | 4f2 | 1/3, 2/3, 0.1909 | 3.17 | 4.10 |
| Fe(5) | 12k | 0.169, 0.338, 0.891 | 3.71 | 4.18 |
| Total | – | – | 38.5 | 40.0 |
Table 2 Magnetic moments (μB) of Fe atoms and total magnetic moments for SrFe12O19 unit cell from GGA and GGA+U
| Atom | Wyckoff site | Coordinates of atoms | Magnetic moment (GGA) | Magnetic moment (GGA+U) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr | 2d | 1/3, 2/3, 3/4 | 0 | 0 |
| Fe(1) | 2a | 0, 0, 0 | 3.73 | 4.17 |
| Fe(2) | 2b | 0, 0, 1/4 | 3.54 | 4.05 |
| Fe(3) | 4f1 | 1/3, 2/3, 0.0272 | 3.43 | 4.05 |
| Fe(4) | 4f2 | 1/3, 2/3, 0.1909 | 3.17 | 4.10 |
| Fe(5) | 12k | 0.169, 0.338, 0.891 | 3.71 | 4.18 |
| Total | – | – | 38.5 | 40.0 |
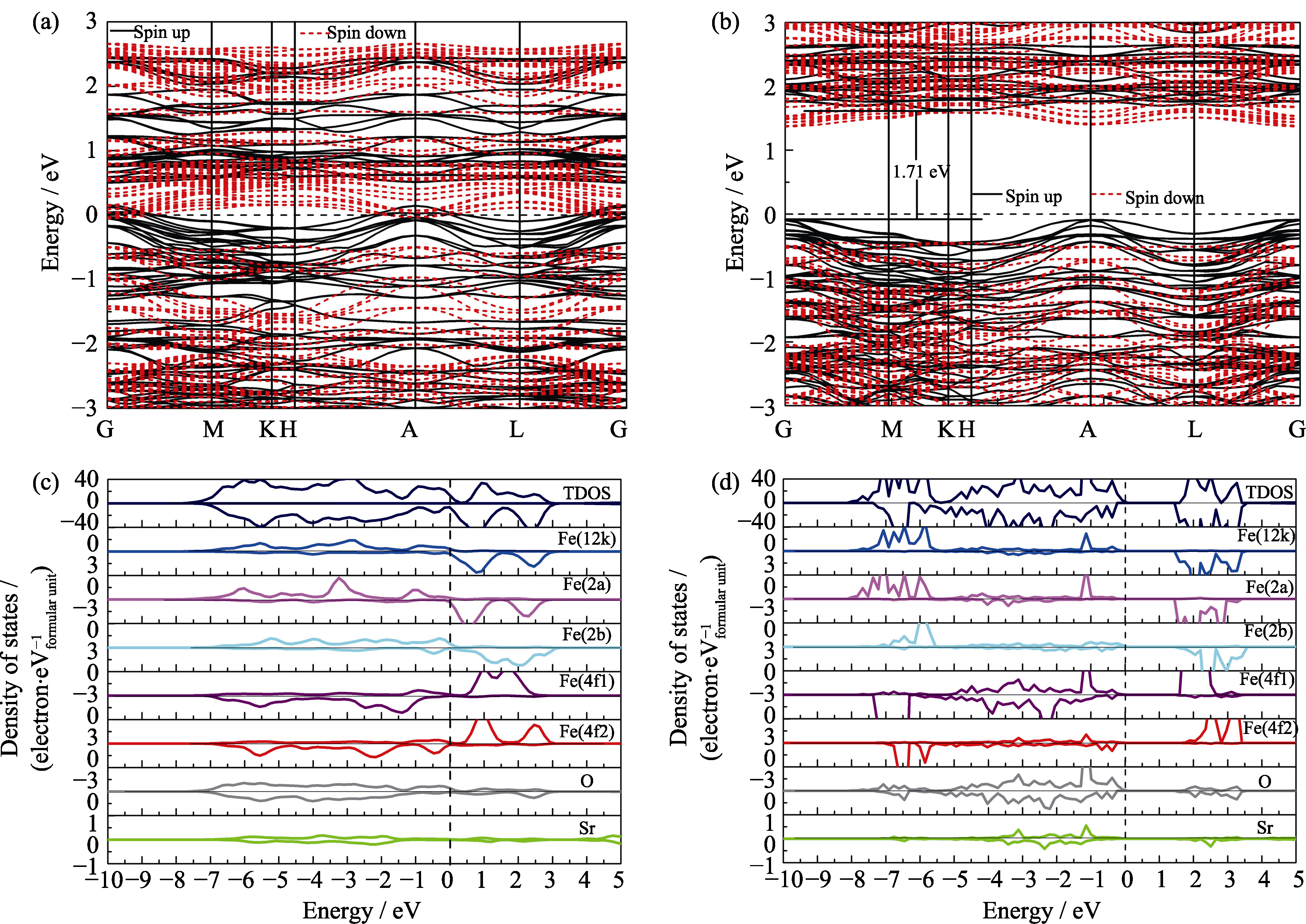
Fig. 2 Electronic band structure (a) and total density of states and atomic projected density (c) of states of SrFe12O19 from GGA, and electronic band structure (b), total density of states and atomic projected density (d) of states of SrFe12O19 from GGA+U
| Substituted site | Esub/eV | mtot/mB | Dmtot |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2a | -2.24 | 39.0 | -1.00 |
| 12k | -2.50 | 39.0 | -1.00 |
| 4f1 | -1.86 | 39.0 | -1.00 |
| 4f2 | -2.03 | 41.0 | 1.00 |
| 2b | -0.34 | 49.0 | 9.00 |
Table 3 Substitution energies of single Mn substituted strontium ferrite with Mn substituted Fe in five different sites, the total magnetic moments of substituted SrFe12-xMnxO19 and their changes relative to the pristine SrFe12O19
| Substituted site | Esub/eV | mtot/mB | Dmtot |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2a | -2.24 | 39.0 | -1.00 |
| 12k | -2.50 | 39.0 | -1.00 |
| 4f1 | -1.86 | 39.0 | -1.00 |
| 4f2 | -2.03 | 41.0 | 1.00 |
| 2b | -0.34 | 49.0 | 9.00 |
| Configurations | Esub/eV | mtot/μB | Dmtot |
|---|---|---|---|
| [2a, 2a] | -2.88 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [2a, 12k].1 | -4.02 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [2a, 12k].2 | -3.98 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].1 | -3.90 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].2 | -3.90 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].3 | -3.97 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].4 | -3.90 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].5 | -3.95 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].6 | -3.99 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].7 | -4.00 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
Table 4 Substitution energies Esub, total magnetic moments mtot and their changes Dmtot relative to that of the pristine SrFe12O19 for different configurations of SrFe12-xMnxO19(x=1.0) with two Mn atoms substituted
| Configurations | Esub/eV | mtot/μB | Dmtot |
|---|---|---|---|
| [2a, 2a] | -2.88 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [2a, 12k].1 | -4.02 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [2a, 12k].2 | -3.98 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].1 | -3.90 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].2 | -3.90 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].3 | -3.97 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].4 | -3.90 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].5 | -3.95 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].6 | -3.99 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| [12k, 12k].7 | -4.00 | 38.0 | -2.00 |
| Site | SFO | [12k] | [2a] | [2a, 12k].1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atoms | M | Atoms | M | Atoms | M | Atoms | M | |
| 2d | 2Sr | -0.004 | 2Sr | -0.003 | 2Fe | -0.004 | 2Sr | -0.003 |
| 2a | 1Fe | 4.165 | 1Fe | 4.171 | 1Mn | 3.866 | 1Mn | 3.786 |
| 1Fe | 4.165 | 1Fe | 4.164 | 1Fe | 4.164 | 1Fe | 4.164 | |
| 2b | 2Fe | 8.108 | 2Fe | 8.135 | 2Fe | 8.132 | 2Fe | 8.137 |
| 4f1 | 4Fe | -16.180 | 4Fe | -16.181 | 4Fe | -16.172 | 4Fe | -16.188 |
| 4f2 | 4Fe | -16.414 | 4Fe | -16.435 | 4Fe | -16.414 | 4Fe | -16.445 |
| 12k | 1Fe | 4.181 | 1Mn | 3.798 | 1Fe | 4.179 | 1Mn | 3.800 |
| 11Fe | 45.983 | 11Fe | 45.958 | 11Fe | 45.955 | 11Fe | 45.950 | |
| 4e | 4O | 0.716 | 4O | 0.563 | 4O | 0.711 | 4O | 0.517 |
| 4f | 4O | 0.696 | 4O | 0.555 | 4O | 0.673 | 4O | 0.218 |
| 6h | 6O | 0.876 | 6O | 0.870 | 6O | 0.860 | 6O | 0.342 |
| 12k | `12O | 0.814 | 12O | 0.683 | 12O | 0.311 | 12O | 1.095 |
| 12k | 12O | 1.916 | 120 | 1.733 | 12O | 1.821 | 12O | 1.812 |
| Sm | 39.02 | 38.07 | 38.08 | 37.09 | ||||
| mtot | 40 | 39 | 39 | 38 | ||||
Table 5 Atomic magnetic moments in four different configurations: pristine strontium ferrite SFO, the [12k] configuration that SFO with one 12k Fe atom replaced by Mn, the [2a] configuration that SFO with one 2a Fe atom replaced by Mn, and the [2a,12k].1 structure that the stable configuration of SFO with two Fe atoms replaced by Mn
| Site | SFO | [12k] | [2a] | [2a, 12k].1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atoms | M | Atoms | M | Atoms | M | Atoms | M | |
| 2d | 2Sr | -0.004 | 2Sr | -0.003 | 2Fe | -0.004 | 2Sr | -0.003 |
| 2a | 1Fe | 4.165 | 1Fe | 4.171 | 1Mn | 3.866 | 1Mn | 3.786 |
| 1Fe | 4.165 | 1Fe | 4.164 | 1Fe | 4.164 | 1Fe | 4.164 | |
| 2b | 2Fe | 8.108 | 2Fe | 8.135 | 2Fe | 8.132 | 2Fe | 8.137 |
| 4f1 | 4Fe | -16.180 | 4Fe | -16.181 | 4Fe | -16.172 | 4Fe | -16.188 |
| 4f2 | 4Fe | -16.414 | 4Fe | -16.435 | 4Fe | -16.414 | 4Fe | -16.445 |
| 12k | 1Fe | 4.181 | 1Mn | 3.798 | 1Fe | 4.179 | 1Mn | 3.800 |
| 11Fe | 45.983 | 11Fe | 45.958 | 11Fe | 45.955 | 11Fe | 45.950 | |
| 4e | 4O | 0.716 | 4O | 0.563 | 4O | 0.711 | 4O | 0.517 |
| 4f | 4O | 0.696 | 4O | 0.555 | 4O | 0.673 | 4O | 0.218 |
| 6h | 6O | 0.876 | 6O | 0.870 | 6O | 0.860 | 6O | 0.342 |
| 12k | `12O | 0.814 | 12O | 0.683 | 12O | 0.311 | 12O | 1.095 |
| 12k | 12O | 1.916 | 120 | 1.733 | 12O | 1.821 | 12O | 1.812 |
| Sm | 39.02 | 38.07 | 38.08 | 37.09 | ||||
| mtot | 40 | 39 | 39 | 38 | ||||
| x | a/nm | c/nm | Volume/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.5940 | 2.319 | 0.7063 |
| 0.5 | 0.5940 | 2.319 | 0.7063 |
| 1.0 | 0.5950 | 2.320 | 0.7071 |
Table 6 Lattice constants and volumes of pristine and Mn-doped strontium ferrites
| x | a/nm | c/nm | Volume/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.5940 | 2.319 | 0.7063 |
| 0.5 | 0.5940 | 2.319 | 0.7063 |
| 1.0 | 0.5950 | 2.320 | 0.7071 |

Fig. 3 Electronic band structure (a), total and projected density of states (c) of single Mn substituted SrFe12O19 (x=0.5), and electronic band structure (b), total and projected density of states (d) of Mn substituted SrFe12O19 (x=1.0) based on the GGA+U approach
| [1] | ZHOU X, MA L, LIU T ,et al. Grystal structure and magnetic property of Si3N4/FePd/Si3N4 thin films.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018,33(8):909-915. |
| [2] | MENG F B, MA X F, ZHANG W ,et al. Structure and magnetic property of Fe and spinel Co2MnO4.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017,32(6):609-614. |
| [3] | XIAO L, CHEN Y, LIU Z ,et al. Growth, magnetic and electrical transport properties of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 thin films on plzst ceramics.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017,32(3):326-330. |
| [4] | ZHANG L, LIU HH, LIU LJ ,et al. Effects of La doping on CaB6 thin films prepared by DC magnetron sputtering.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017,32(5):555-560. |
| [5] | ZHAO X Y, MAN P W, XIE T ,et al. Crystal growth and characterization of the rare-earth orthoferrite Sm0.8Tb0.2FeO3 single crystal.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016,31(9):1004-1008. |
| [6] | SEEMA V, JOY P A, KHOLLAM Y B ,et al. Synthesis of nanosized MgFe2O4 powders by microwave hydrothermal method.Materials Letters, 2004,58(6):1092-1095. |
| [7] | CHEN D, LIU Y, LI Y, , ,et al.Microstructure. Microstructure and magnetic properties of Al-doped barium ferrite with sodium citrate as chelate agent. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2013,337- 338:65-69. |
| [8] | WANG H W, KUNG S C . Crystallization of nanosized Ni-Zn ferrites powders prepared by hydrothermal method. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2004,270(1/2):230-236. |
| [9] | ALMESSIERE M A, SLIMANI Y, BAYKAL A ,et al. Structural and magnetic properties of Ce-doped strontium hexaferrite.Ceramics International, 2018,44:9000-9008. |
| [10] | SEIFERT D ,TÖPFER J, LANGENHORST F ,et al. Synthesis and magnetic properties of La-substituted M-type Sr hexaferrites.Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2009,321(24):4045-4051. |
| [11] | WANG J F, PONTON C B , GRÖSSINGER R, ,et al. A study of La-substituted strontium hexaferrite by hydrothermal systhesis.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004,369(1/2):170-177. |
| [12] | WANG J F, PONTON C B, HARRIS I R ,et al. A study of the magnetic properties of hydrothermally synthesisted Sr hexaferrite with Sm substitution.Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2001,234(2):233-240. |
| [13] | WANG J F, PONTON C B, HARRIS I R ,et al. A study of Pr-substituted strontium hexaferrite by hydrothermal synthesis.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015,403(1/2):104-109. |
| [14] | WANG J F, PONTON C B, HARRIS I R ,et al. A study of Nd-substituted Sr hexaferrite prepared by hydrothermal synthesis.IEEE Transactions on Magnetic, 2002,38(5):2928-2930. |
| [15] | ASHIQ M N, IQBAL M J, GUL I H ,et al. Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Zr-Cd substituted strontium hexaferrite (SrFe12O19).Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009,487(1/2):341-345. |
| [16] | ASHIQ M N, IQBAL M J , NAJAM-UL-HQ M,et al. Synthesis, magnetic and dielectric properties of Er-Ni doped Sr-hexaferrite nanomaterials for applications in high density recording media and microwave divices.Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2012,324(1):15-19. |
| [17] | DAVOODI A, HASHEMI B . Magnetic properties of Sn-Mg substituted strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles synthesized via coprecipitation method.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011,509(19):5893-5896. |
| [18] | CHEN W, WU W W, ZHOU C ,et al. Structural and magnetic properties evolution Co-Nd substituted M-type hexagonal strontium ferrites synthesized by ball-milling-assisted ceramic materials.Journal of Electronic Materials, 2018,47(3):2110-2119. |
| [19] | EBRAHIMI F, ASHRAFIZADEH F . Tuning the ferromagnetic resonance by doping strontium hexaferrite nanopowders. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2018,85(3):621-628. |
| [20] | VIVEK D, CHANDANI N ,NANDADASA,et al. Site occupancy and magnetic properties of Al-substituted M-type strontium hexaferrite.Journal of Applied Physics, 2015,17:243904-243912. |
| [21] | LIYANAGE L S I, KIM S, HONG Y K,et al. Theory of magnetic enhancement in strontium hexaferrite through Zn-Sn pair substitution.Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2013(348):75-81. |
| [22] | KRESSE G , FURTHMÜLLER J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set.Physics Review B, 1996,54(16):11169-11186. |
| [23] | KRESSE G ,FURTHMÜLLER J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set.Computation Material Science, 1996,6:15-50. |
| [24] | PERDEW J P, BURKE K, EMZERHOF M . Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Physics Review Letter, 1996,77:3865-3868. |
| [25] | BLÖCHL P E . Projector augmented-wave method. Physics Review B, 1994,50:17953-17979. |
| [26] | KRESSE G, JOUBERT D . From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Physics Review B, 1999,59:1758-1775. |
| [27] | MONKHORST H, PACK J . Special points for Brillouin-zone interations. Physics Review B, 1976,13:5188-5192. |
| [28] | LIYANAGE L S I, KIM S, HONG Y K ,et al. Theory of magnetic enhancement in strontium hexaferrite through Zn-Sn pair substitution.Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2013,348:75-81. |
| [29] | HUANG L H, ZHU Q S, GE W , et al.Oxygen-vacancy formation in LaMO3( M = Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) calculated at both GGA and GGA + U levels.Computational Materials Science, 2011,50:1800-1805. |
| [30] | SAHU B R, BANERJEE S K . Density-functional study of bulk silicon lightly doped with manganese. Physical Review B, 2008,77(15):155203-155209 |
| [31] | GORTER E W . Saturation magnetization of some ferromagnetic oxides with hexagonal crystal structures. Proc. IEEE-Part B: Radio and Electron. Eng, 1957,104:255-260. |
| [32] | KIMURA K, OHGAKI M, TANAKA K ,et al. Study of the bipyramidal site in magnetoplumbite-like compounds SrM12O19(M=Al, Fe, Ga).Journal Solid State Chemistry, 1990,87:186-194. |
| [33] | IQBAL M J, FAROOQ S . Impact of Pr-Ni substitution on the electrical and magnetic properties of chemically derived nanosized strontium-barium hexaferrites. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010,505:560-567. |
| [1] | WEN Zhiqin, HUANG Binrong, LU Taoyi, ZOU Zhengguang. Pressure on the Structure and Thermal Properties of PbTiO3: First-principle Study [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 787-794. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xian, ZHANG Ce, JIANG Wenjun, FENG Deqiang, YAO Wei. Synthesis, Electronic Structure and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance of Quaternary BiMnVO5 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| [3] | XIANG Hui, QUAN Hui, HU Yiyuan, ZHAO Weiqian, XU Bo, YIN Jiang. Piezoelectricity of Graphene-like Monolayer ZnO and GaN [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 492-496. |
| [4] | ZHAO Linyan, LIU Yangsi, XI Xiaoli, MA Liwen, NIE Zuoren. First-principles Study on Nanoscale Tungsten Oxide: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1125-1136. |
| [5] | ZHAO Yupeng,HE Yong,ZHANG Min,SHI Junjie. First-principles Study on the Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production of a Novel Two-dimensional Zr2CO2/InS Heterostructure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 993-998. |
| [6] | MA Xin-Guo, YAN Jie, CHEN Zi-Meng, ZHU Lin, XU Guo-Wang, HUANG Chu-Yun, LV Hui. First-principles Calculation on Pt- and Au-modified Anatase TiO2(101) Surface [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(3): 291-297. |
| [7] | SHAO Dong-Yuan, CHENG Nan-Pu, CHEN Jing-Jing, LI Xiao, CHEN Zhi-Qian, LI Chun-Mei, HUI Qun. Electronic Structure, Plane Acoustic Velocity and Refractive Property of LiNbO3 and LiTaO3 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(2): 171-179. |
| [8] | YANG Zhi-Huai, ZHANG Yun-Peng, ZHANG Mei-Guang, XU Qiang, ZHANG Ya-Ni, ZHANG Rong. The Electronic and Optical Properties of Tetrahedral Doped Co1-xRexCr2O4 (Re = Li, Na, K, Rb) Spinel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(8): 819-824. |
| [9] |
YU Zhi-Qiang, ZHANG Chang-Hua, LI Shi-Dong, LIAO Hong-Hua.
Electronic Structures and Optoelectronic Properties of C/Ge-doped Silicon Nanotubes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 233-239. |
| [10] | CHEN Xiu-Qin,ZHANG Xing-Wang,LEI Le-Cheng. Electronic Structures and Photocatalysis Properties under Visible Irradiation and of F-doped TiO2 nanotube Nanotube arrays Arrays [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(4): 369-374. |
| [11] | LI Qiao-Ling,ZHANG Cun-Rui,JING Hong-Xia. Preparation of Superior Magnetic SrFe12O19 Microtubules with Template Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(4): 717-720. |
| [12] | WU Zi-Hua,WANG Qun,LIU Xin-Jun,YU Wei-Dong,LI Xiao-Min,CHEN Li-Dong. Change of the Magnetic Moment and Specific Heat of La0.9Ca0.1MnO3 after Heat Treatment in Oxygen and Argon [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(1): 83-86. |
| [13] | TIAN Wu-Bian,WANG Pei-Ling,ZHANG Guo-Jun,KAN Yan-Mei,LI Yong-Xiang. Progress of the Layered Ternary Ceramics: M2AX [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(5): 783-790. |
| [14] | CHEN Ning,ZHANG Bao-Dong,QING Jia,MA Li,LI Fu-Xing. Electronic Structures of REBaCuO Systems and Its Relation withSuperconductivities [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2002, 17(3): 545-551. |
| [15] | ZHANG Zhen-Hua,PENG Jing-Cui,CHEN Xiso-Hua,SWANG Jian-Xiong. Conductance Property of Undoping Metallic Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2001, 16(5): 940-944. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||