
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (6): 653-659.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180359
Previous Articles Next Articles
Chang-Xing HUANG,Jun CUI,Yuan-Sheng PEI( )
)
Received:2018-08-02
Revised:2018-10-10
Published:2019-06-20
Online:2019-05-23
Supported by:CLC Number:
Chang-Xing HUANG, Jun CUI, Yuan-Sheng PEI. B2O3-SiO2-Na2O Controlled-release Material: Synthetic Parameters Optimization and Release Mechanisms Exploration[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 653-659.
| Components | Na2B4O7·10H2O | H3BO3 | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight/g | 33.02 | 32.16 | 14.82 |
Table 1 Chemical components and their corresponding composition per 80 g BCRM
| Components | Na2B4O7·10H2O | H3BO3 | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight/g | 33.02 | 32.16 | 14.82 |
| Release exponent, n | Release mechanism |
|---|---|
| Cylinder | |
| n ≤ 0.45 | Fickian diffusion |
| 0.45 < n < 0.89 | Non-Fickian diffusion |
| n = 0.89 | Case II transport |
| n > 0.89 | Super Case II transport |
Table 2 Values of diffusional exponent, n, for polymer matrices with cylinder in Korsmeyer-Peppas model[18]
| Release exponent, n | Release mechanism |
|---|---|
| Cylinder | |
| n ≤ 0.45 | Fickian diffusion |
| 0.45 < n < 0.89 | Non-Fickian diffusion |
| n = 0.89 | Case II transport |
| n > 0.89 | Super Case II transport |
| Conditions | Parameters | Boron concentration /(mg·L-1) | Recovery/% | Theoretical values of B2O3 /wt% | Test values of B2O3 /wt% | B2O3 volatilization/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating rate/ (℃?min-1) | 4 | 91.728 | 95.02-102.32 | 60 | 59.08 | 1.53 |
| 6 | 90.657 | 58.39 | 2.68 | |||
| 8 | 89.278 | 57.50 | 4.17 | |||
| 10 | 87.638 | 56.44 | 5.93 | |||
| Holding time/h | 0.5 | 92.372 | 95.41-104.29 | 60 | 59.49 | 0.85 |
| 1 | 91.808 | 59.13 | 1.45 | |||
| 1.5 | 90.491 | 58.28 | 2.87 | |||
| 2 | 90.442 | 58.25 | 2.92 | |||
| Melting temperature/℃ | 1025 | 90.612 | 100.27-105.42 | 60 | 58.36 | 2.73 |
| 1050 | 90.144 | 58.06 | 3.23 | |||
| 1075 | 88.986 | 57.31 | 4.48 | |||
| Initial temperature/℃ | 300 | 90.404 | 100.63-106.42 | 60 | 58.22 | 2.97 |
| 800 | 91.300 | 58.80 | 2.00 | |||
| 1050 | 92.148 | 59.35 | 1.08 |
Table 3 The test and calculation data of samples under various process parameters
| Conditions | Parameters | Boron concentration /(mg·L-1) | Recovery/% | Theoretical values of B2O3 /wt% | Test values of B2O3 /wt% | B2O3 volatilization/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating rate/ (℃?min-1) | 4 | 91.728 | 95.02-102.32 | 60 | 59.08 | 1.53 |
| 6 | 90.657 | 58.39 | 2.68 | |||
| 8 | 89.278 | 57.50 | 4.17 | |||
| 10 | 87.638 | 56.44 | 5.93 | |||
| Holding time/h | 0.5 | 92.372 | 95.41-104.29 | 60 | 59.49 | 0.85 |
| 1 | 91.808 | 59.13 | 1.45 | |||
| 1.5 | 90.491 | 58.28 | 2.87 | |||
| 2 | 90.442 | 58.25 | 2.92 | |||
| Melting temperature/℃ | 1025 | 90.612 | 100.27-105.42 | 60 | 58.36 | 2.73 |
| 1050 | 90.144 | 58.06 | 3.23 | |||
| 1075 | 88.986 | 57.31 | 4.48 | |||
| Initial temperature/℃ | 300 | 90.404 | 100.63-106.42 | 60 | 58.22 | 2.97 |
| 800 | 91.300 | 58.80 | 2.00 | |||
| 1050 | 92.148 | 59.35 | 1.08 |
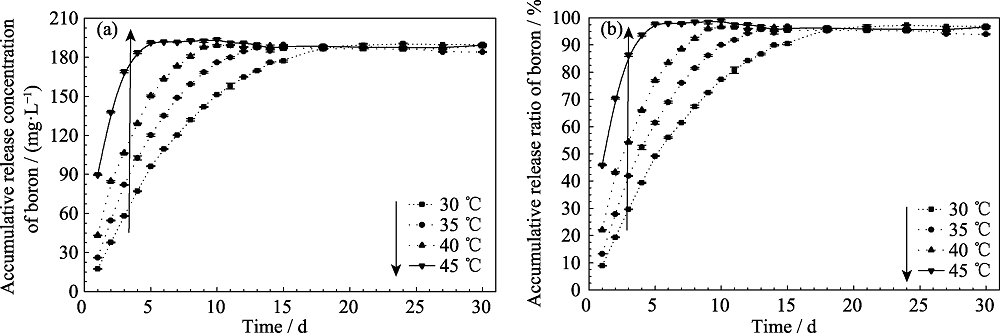
Fig. 2 (a) Accumulative release concentration and (b) accumulative release rate of boron from the BCRM in deionized water under different temperatures
| Before controlled-release | After controlled-release | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavenumber/cm-1 | Corresponding characteristic vibrations ascription | Wavenumber/cm-1 | Corresponding characteristic vibrations ascription |
| 463.46 | Si-O-Si bending vibrations | 466.53 | Si-O-Si bending vibrations |
| 694.02 | [BO3] bending vibrations | 798.51 | O-Si-O stretching vibrations |
| 1061.16 | Si-O-Si asymmetric stretching vibrations | 1083.89 | Si-O-Si asymmetric stretching vibrations |
| 1268.39 | [BO3] stretching vibrations | 1637.42 | H2O |
| 1392.97 | [BO3] antisymmetry stretching vibrations | 3448.34 | H-O stretching vibrations |
| 3448.20 | H-O stretching vibrations | ||
Table 4 Characteristic vibrations reflected by infrared absorption spectrum of each group in the BCRM before and after controlled-release
| Before controlled-release | After controlled-release | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavenumber/cm-1 | Corresponding characteristic vibrations ascription | Wavenumber/cm-1 | Corresponding characteristic vibrations ascription |
| 463.46 | Si-O-Si bending vibrations | 466.53 | Si-O-Si bending vibrations |
| 694.02 | [BO3] bending vibrations | 798.51 | O-Si-O stretching vibrations |
| 1061.16 | Si-O-Si asymmetric stretching vibrations | 1083.89 | Si-O-Si asymmetric stretching vibrations |
| 1268.39 | [BO3] stretching vibrations | 1637.42 | H2O |
| 1392.97 | [BO3] antisymmetry stretching vibrations | 3448.34 | H-O stretching vibrations |
| 3448.20 | H-O stretching vibrations | ||
| Temperature/℃ | Models | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | ${{M}_{t}}/{{M}_{\infty }}=10.06{{t}^{0.97}}$ | 0.9959 |
| 35 | ${{M}_{t}}/{{M}_{\infty }}=14.33{{t}^{0.95}}$ | 0.9935 |
| 40 | ${{M}_{t}}/{{M}_{\infty }}=23.75{{t}^{0.77}}$ | 0.9574 |
| 45 | - | - |
Table 5 Release kinetics model fitting of the BCRM at different temperatures
| Temperature/℃ | Models | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | ${{M}_{t}}/{{M}_{\infty }}=10.06{{t}^{0.97}}$ | 0.9959 |
| 35 | ${{M}_{t}}/{{M}_{\infty }}=14.33{{t}^{0.95}}$ | 0.9935 |
| 40 | ${{M}_{t}}/{{M}_{\infty }}=23.75{{t}^{0.77}}$ | 0.9574 |
| 45 | - | - |
| [1] |
BENGISU M . Borate glasses for scientific and industrial applications: a review. Journal of Materials Science, 2016,51(5):2199-2242.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
YIN HAI-RONG, YANG CHEN, GAO YANG , et al. Fabrication and characterization of strontium-doped borate-based bioactive glass scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018,743:564-569.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BALASUBRAMANIAN P BÜTTNER T, MIGUEZ PACHECO V, , et al. Boron-containing bioactive glasses in bone and soft tissue engineering. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018,38(3):855-869.
DOI URL |
| [4] | LÓPEZ-NARANJO E J, ALZATE-GAVIRIA L M, HERNÁNDEZ- ZÁRATE G , et al. Termite resistance of wood-plastic composites treated with zinc borate and borax. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, 2014,29(2):281-293. |
| [5] | RAHIMNEJAD YAZDI A, TOWLER M . The effect of the addition of gallium on the structure of zinc borate glass with controlled gallium ion release. Materials & Design, 2016,92:1018-1027. |
| [6] |
ZHANG XING, JIA WEI-TAO, GU YI-FEI , et al. Borate bioglass based drug delivery of teicoplanin for treating osteomyelitis. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010,25(3):293-298.
DOI URL |
| [7] | CUI JUN, YUAN WEN-JIAO, YUAN DONG-HAI , et al. Effect of pH on the passivation of carbon steel by sodium borosilicate controlled-release inhibitor in simulated recirculating cooling water. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017,56(25):7239-7252. |
| [8] |
SHI RUI-RUI, LI MENG, PEI YUAN-SHENG . Synthesis and characterizations of B2O3-SiO2-Na2O controlled-release antibacterial agent. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017,32(5):529-534.
DOI URL |
| [9] | CUI JUN, YANG YAN-GE, LI XIU-QING , et al. Toward a slow-release borate inhibitor to control mild steel corrosion in simulated recirculating water. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018,10(4):4183-4197. |
| [10] | LIU XIAO-QING, HE FENG, FANG YU , et al. Technical researches on volatilization reduction of B2O3 in borosilicate glasses. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2013,35(5):13-17. |
| [11] | QIAN DA-XING, ZHOU NAI, SUN DAO-BING , et al. Factors on volatilization of B2O3 in glass melting. Journal of Building Materials, 1998(2):93-96. |
| [12] |
SNYDER M J, MESKO M G, SHELBY J E . Volatilization of boron from E-glass melts. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2006,352(6/7):669-673.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
PEDRO R D O, PEREIRA S, GOYCOOLEA F M , et al. Self-aggregated nanoparticles of N-dodecyl, N°-glycidyl(chitosan) as pH-responsive drug delivery systems for quercetin. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2018,135(2):45678.
DOI URL |
| [14] | RUIZ-CARO R, GAGO-GUILLAN M, OTERO-ESPINAR F J , et al. Mucoadhesive tablets for controlled release of acyclovir. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2012,60(10):1249-1257. |
| [15] |
SINHA P, UBAIDULLA U, HASNAIN M S , et al. Alginate-okra gum blend beads of diclofenac sodium from aqueous template using ZnSO4 as a cross-linker. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2015,79:555-563.
DOI URL |
| [16] | XU XIAO-YUN, JIA DE-HUA, LIU JUN , et al. Determination of boron in silica refractory raw materials by ICP-OES. Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2015(4):29-31. |
| [17] |
KIM YOUNG-JAE, YANABA YUTAKA, MORITA KAZUKI . The effect of borate and silicate structure on thermal conductivity in the molten Na2O-B2O3-SiO2 system. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2015,415:1-8.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SITTA D L A, GUILHERME M R, DA SILVA E P , et al. Drug release mechanisms of chemically cross-linked albumin microparticles: effect of the matrix erosion. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2014,122:404-413.
DOI URL |
| [19] | VARNER J R SEWARD III T P, SCHAEFFER H A, . Boron chemistry in flue gases from borosilicate glass furnaces. Advances in Fusion and Processing of Glass III, John Wiley & Sons,Inc, 2012, 387-395. |
| [20] | VARNER J R SEWARD III T P, SCHAEFFER H A, . Effect of water in the melting atmosphere on the transformation temperature of commercial glasses. Advances in Fusion and Processing of Glass III, John Wiley & Sons,Inc, 2012, 345-354. |
| [21] |
BOLORÉ D, PIGEONNEAU F . Spatial distribution of nucleated bubbles in molten glasses undergoing coalescence and growth. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018,101(5):1892-1905.
DOI URL |
| [22] | KRAXNER J, KLEMENT R, LIŠKA M . High-temperature viscosity and density of alumino-borosilicate glasses as a model system for commercial E-glass. Ceramics Silikaty, 2008,52(3):148-154. |
| [23] |
GAO XIANG-LONG, ZHANG QIAN, YU JING-BO , et al. Effect of replacement of Al2O3 by Y2O3 on the structure and properties of alkali-free boro-aluminosilicate glass. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2018,481:98-102.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
FERREIRA E B, ZANOTTO E D, FELLER S , et al. Critical analysis of glass stability parameters and application to lithium borate glasses. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2011,94(11):3833-3841.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
MARCHAND B, LANIER S, DAVY C A , et al. Are calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H) present in alkali-activated glass cullet cement? Materials Letters, 2018,219:104-108.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
NING JIA, YAO AI-HUA, WANG DE-PING , et al. Synthesis and in vitro bioactivity of a borate-based bioglass. Materials Letters, 2007,61(30):5223-5226.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
HUANG YUN-YUN, ZHANG YI-JUN, LIN SAI , et al. Sol-Gel synthesis of NiO nanoparticles doped sodium borosilicate glass with third-order nonlinear optical properties. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016,686:564-570.
DOI URL |
| [28] | HAN JUAN, HE FENG, MEI SHU-XIA , et al. Effect of Na2O/B2O3 on structure and properties of borosilicate glass. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2015,37(3):1-4. |
| [29] |
OTHMAN H A, ELTABEY M M, IBRAHIM S E , et al. Synthesis, electrical and magnetic properties of sodium borosilicate glasses containing Co-ferrites nanoparticles. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2017,506:115-121.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
HASSAAN M Y, OSMAN H M, HASSAN H H , et al. Optical and electrical studies of borosilicate glass containing vanadium and cobalt ions for smart windows applications. Ceramics International, 2017,43(2):1795-1801.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ROHNKE M, PFITZENREUTER S, MOGWITZ B , et al. Strontium release from Sr 2+-loaded bone cements and dispersion in healthy and osteoporotic rat bone . Journal of Controlled Release, 2017,262:159-169.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
BARBOSA J, CORREIA D M, GONÇALVES R , et al. Magnetically controlled drug release system through magnetomechanical actuation. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2016,5(23):3027-3034.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
SONAWANE S J, KALHAPURE R S, RAMBHAROSE S , et al. Ultra-small lipid-dendrimer hybrid nanoparticles as a promising strategy for antibiotic delivery: in vitro and in silico studies. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2016,504(1/2):1-10.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
FAYYAZBAKHSH F, SOLATI-HASHJIN M, KESHTKAR A , et al. Release behavior and signaling effect of vitamin D3 in layered double hydroxides-hydroxyapatite/gelatin bone tissue engineering scaffold: an in vitro evaluation. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2017,158:697-708.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
JIN XIAO-QI, WANG QIAN, SUN JI-HONG , et al. Dual (pH- and temperature-) stimuli responsive nanocarrier with bimodal mesoporous silica nanoparticles core and copolymer shell for controlled ibuprofen-releasing: fractal feature and diffusion mechanism. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017,254:77-85.
DOI URL |
| [1] | LI Hai-Bin, WANG De-Ping, WU Ying-Ying, YAO Ai-Hua, YE Song. Effect of Citric Acid Concentration on the Properties of Borate Glass Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 831-836. |
| [2] | WU Ying-Ying, YE Song,YAO Ai-Hua, LI Hai-Bin, JIA Wei-Tao, HUANG Wen-Hai, WANG De-Ping. Effect of Gas-foaming Porogen-NaHCO3 and Citric Acid on the Properties of Injectable Macroporous Borate Bioactive Glass Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 777-784. |
| [3] | ZHU Kai-Ping, WANG De-Ping, FAN Hong-Yuan, WANG Hui, YAO Ai-Hua, YE Song. In-situ Transformation of Borate Glass and Its Effect on pH of Soaking-liquid [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(10): 1069-1074. |
| [4] | ZHOU Hong-Ming,LIU Fu-Rong, LI Jian, FANG Zhen-Qi, LI Yan-Fen, ZHU Yu-Hua. Research on the LiODFB Electrolyte’s Electrochemical Performance and Its Compatibility with LTO Electrode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(5): 507-514. |
| [5] | LI Tian-Bao, LIANG Jian, XU Bing-She, WANG Jin. Preparation and Characteristic of One-dimensional Magnesium Borate Nanomaterials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(9): 947-951. |
| [6] | ZHANG Xin,JIA Wei-Tao,GU Yi-Fei,ZHANG Chang-Qing,HUANG Wen-Hai,WANG De-Ping. Borate Bioglass Based Drug Delivery of Teicoplanin for Treating Osteomyelitis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(3): 293-298. |
| [7] | HAO Li-Feng, LI Jiu-Sheng, XU Xiao-Hong, REN Tian-Hui. Preparation and Tribological Properties of Surface-modified Borate Magnesium Nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(12): 1330-1334. |
| [8] | YAO Ai-Hua,AI Fan-Rong,LIU Xin,WANG De-Ping,HUANG Wen-Hai. Study on Hollow Hydroxyapaptite Microspheres Prepared by a Borate Glass Conversion Process [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(1): 53-57. |
| [9] |
YU Jing,ZHAO Di,HUANG Wen-Hai,ZHOU Nai,WANG De-Ping,YIN Wei,CHEN Ya-Qing.
Study on the Performance of Radioactive Dysprosium Lithium Borate Glass Mircrospheres used for Synovectomy Treatment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(1): 58-62. |
| [10] | TIAN Yan,LIU Jun-Feng,REN Nan-Qi,HUANG Yu-Dong. Preparation and Investigation on Extreme-pressure Performance of PyDDP Surface Modified Borate-molybdenum Agent [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(6): 1249-1253. |
| [11] | LIU Jian-Wen,LI Xin-Hai,WANG Zhi-Ying,GUO Hua-Jun,HU Qi-Yang. Novel Preparation, Characterization, Property of Lithium Bis(oxalate) Borate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(4): 808-812. |
| [12] | PAN Shang-Ke,LU Sheng,DING Dong-Zhou,YANG Fan,REN Guo-Hao,WANG Guo-Fu. Effects of Different Dopants on the Growth and Phase Transition of Ba3Y(BO3)3 Crystal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(3): 567-570. |
| [13] | CHEN Jun-Feng,LI Yun,SONG Gui-Lan,YAO Dong-Min,YUAN Lan-Ying,QI Xue-Jun,WANG Shao-Hua. Czochralski Growth and Scintillation Properties of Cerium-doped Li6Gd(BO3)3 Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(5): 1053-1059. |
| [14] |
ZHU Dong-Mei,LUO Fa,ZHOU Wan-Cheng,RAY C S,DAY D E.
Effects of Gravity Level on Phase Separation of PbO-B2O3 Glasses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(4): 855-860. |
| [15] | HU Yun-Chu,WU Zhi-Ping,SUN Han-Zhou,Zhou Ying,LIU Yuan. Synthesis of Nano Zinc Borate Fire Retardant by Solid State Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(4): 815-820. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||