
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (6): 618-624.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180425
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jian-Huang KE,Kai XIE,Yu HAN( ),Wei-Wei SUN,Shi-Qiang LUO,Jin-Feng LIU
),Wei-Wei SUN,Shi-Qiang LUO,Jin-Feng LIU
Received:2018-09-13
Revised:2019-01-10
Published:2019-06-20
Online:2019-05-23
Supported by:CLC Number:
Jian-Huang KE, Kai XIE, Yu HAN, Wei-Wei SUN, Shi-Qiang LUO, Jin-Feng LIU. Morphology Controlling of the High-voltage Cathode Materials with Different Co-solvents[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 618-624.
| Sample | LCP-ET | LCP-EG | LCP-DEG | LCP-Theor. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | 1.0197 | 1.0203 | 1.0203 | 1.0200 |
| b/nm | 0.5916 | 0.5922 | 0.5920 | 0.5920 |
| c/nm | 0.4703 | 0.4698 | 0.4698 | 0.4690 |
| α/° | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| β/° | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| γ/° | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| V/nm3 | 0.2837 | 0.2839 | 0.2838 | 0.2832 |
| I(020)/I(200) | 5.975 | 3.208 | 2.836 | 1.576 |
Table 1 Variation of crystal parameters for LCP obtained from various solvents
| Sample | LCP-ET | LCP-EG | LCP-DEG | LCP-Theor. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | 1.0197 | 1.0203 | 1.0203 | 1.0200 |
| b/nm | 0.5916 | 0.5922 | 0.5920 | 0.5920 |
| c/nm | 0.4703 | 0.4698 | 0.4698 | 0.4690 |
| α/° | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| β/° | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| γ/° | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| V/nm3 | 0.2837 | 0.2839 | 0.2838 | 0.2832 |
| I(020)/I(200) | 5.975 | 3.208 | 2.836 | 1.576 |
| Sample | LCP-ET | LCP-EG | LCP-DEG |
|---|---|---|---|
| BET/(m2·g-1) | 1.1446 | 1.5840 | 1.3558 |
Table 2 BET analysis of the three samples
| Sample | LCP-ET | LCP-EG | LCP-DEG |
|---|---|---|---|
| BET/(m2·g-1) | 1.1446 | 1.5840 | 1.3558 |
| Solvent | H2O | ET | EG | DEG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity/(mPa·S) | 1.005 | 1.074 | 19.9 | 35.7 |
| Boiling point/℃ | 100 | 78 | 197.3 | 245 |
Table 3 Physical parameters of four solvents
| Solvent | H2O | ET | EG | DEG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity/(mPa·S) | 1.005 | 1.074 | 19.9 | 35.7 |
| Boiling point/℃ | 100 | 78 | 197.3 | 245 |
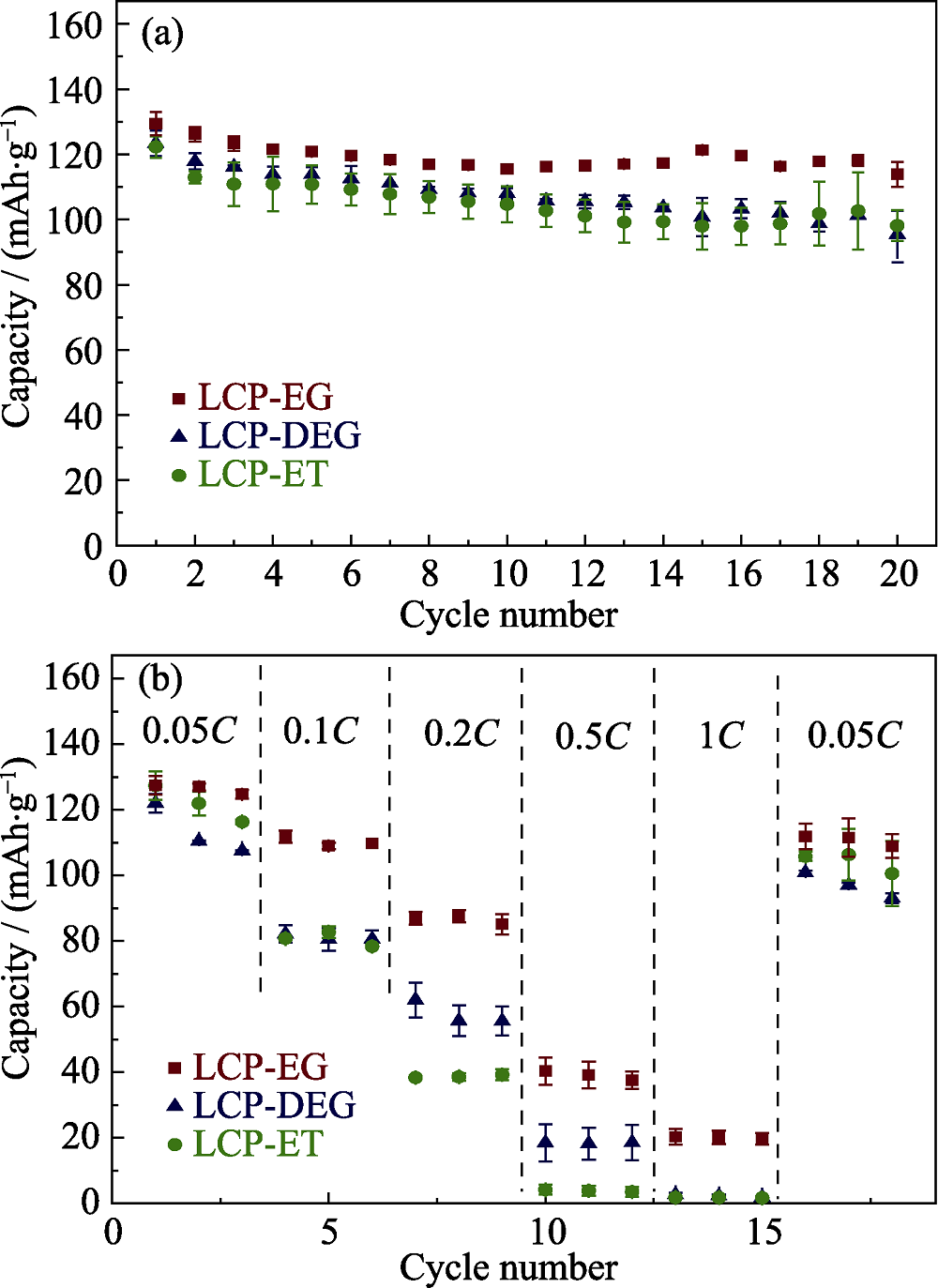
Fig. 5 (a) Capacity retentions and (b) specific capacities vs. C rate obtained in each cycle for LiCoPO4 samples synthesized by solvothermal process using various co-solvents
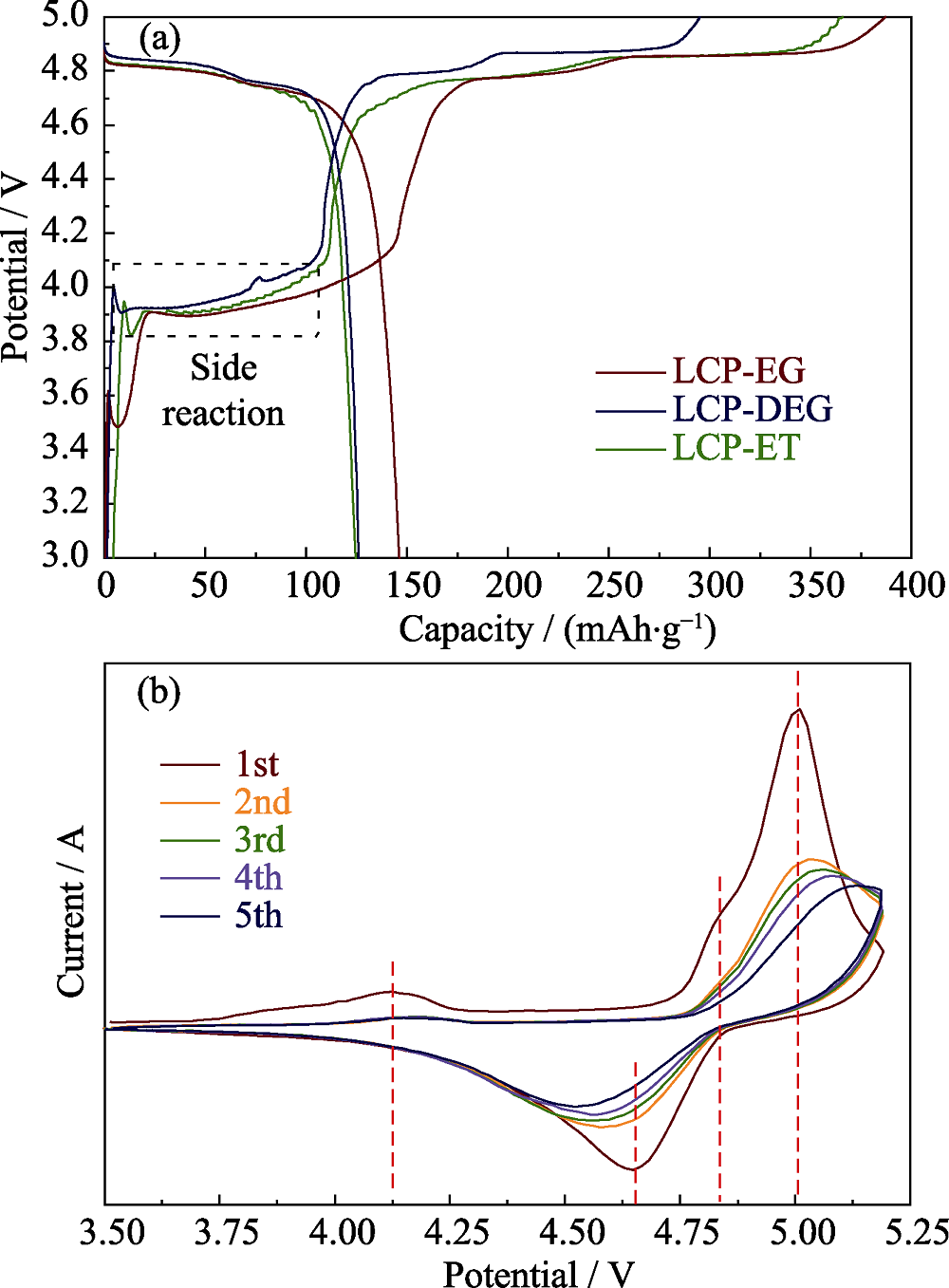
Fig. 6 (a) Charge and discharge profiles of the samples obtained from various solvents; (b) Cyclic voltammetry characteristics of LCP-EG at a scanning rate of 0.05 mV/s
| [1] | 黄可龙, 王兆翔, 刘素琴 . 锂离子电池原理与关键技术. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008: 8. |
| [2] |
PADHI A K, NANJUNDASWAMY K S, GOODENOUGH J B . Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries.[J]. Electrochem. Soc., 1997,144(4):1188-1194.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
WOLFENSTINE J, ALLEN J . LiNiPO4-LiCoPO4 solid solutions as cathodes.[J]. Power Sources, 2004,136(1):150-153.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
WOLFENSTINE J, ALLEN J . Ni 3+/Ni 2+ redox potential in LiNiPO4. [J]. Power Sources, 2005,142(1/2):389-390.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
MAEYOSHI Y, MIYAMOTO S, MUNAKATA H , et al. Enhanced cycle stability of LiCoPO4 by using three-dimensionally ordered macroporous polyimide separator.[J]. Power Sources, 2017,350:103-108.
DOI URL |
| [6] | DU CHENQIANG, TANG ZHIYUAN, XU QIANG . Research progress in preparing cathode material lithium cobalt phosphate. Battery, 2013,43(5):293-295. |
| [7] |
STROBRIDGE F C, CLEMENT R J, LESKES M , et al. Identifying the structure of the intermediate, Li2/3CoPO4, formed during electrochemical cycling of LiCoPO4. Chem. Mater., 2014,26(21):6193-6205.
DOI URL |
| [8] | BRUTTI S, PANERO S . Recent advances in the development of LiCoPO4 as high voltage cathode material for Li-ion batteries.[J]. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013,1140:67-99. |
| [9] |
HOWARD W F, SPOTNITZ R M . Theoretical evaluation of high- energy lithium metal phosphate cathode materials in Li-ion batteries.[J]. Power Sources, 2007,165(2):887-891.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WOLFENSTINE J . Electrical conductivity of doped LiCoPO4.[J]. Power Sources, 2006,158(2):1431-1435.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 栗欢欢 . 新型5V锂离子二次电池正极材料LiCoPO4的制备与改性研究. 天津: 南开大学硕士学位论文, 2009. |
| [12] |
KISHORE M V V M S, VARADARAJU U V . Influence of isovalent ion substitution on the electrochemical performance of LiCoPO4. Mater. Res. Bull., 2005,40(10):1705-1712.
DOI URL |
| [13] | LI HUANHUAN, YANG XIAOLIANG, WEI JINPING . Effect of Mn 2+ doping on electrochemical performance of LiCoPO4 . Electrochemistry, 2008,14:210-212. |
| [14] |
KREDER K J, MANTHIRAM A . Vanadium-substituted LiCoPO4 core with a monolithic LiFePO4 shell for high-voltage lithium-ion batteries. ACS Energy Letters, 2017,2(1):64-69.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
JANG I C, SON C G, YANG S M G , et al. LiFePO4 modified Li1.02(Co0.9Fe0.1)0.98PO4 cathodes with improved lithium storage properties.[J]. Materials Chemistry, 2011,21(18):6510-6514.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LUDWIG J, MARINO C, HAERING D , et al. Morphology- controlled microwave-assisted solvothermal synjournal of high-performance LiCoPO4 as a high-voltage cathode material for Li-ion batteries.[J]. Power Sources, 2017,342:214-223.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG F, YANG J, NULI Y N , et al. Novel hedgehog-like 5V LiCoPO4 positive electrode material for rechargeable lithium battery.[J]. Power Sources, 2011,196(10):4806-4810.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
PENG L, ZHANG X, FANG Z , et al. General facet-controlled synthesis of single-crystalline {010}-oriented LiMPO4 (M=Mn, Fe, Co) nanosheets. Chemistry of Materials, 2017,29(24):10526-10533.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
NI J P, WANG H B, GAO L J , et al. A high-performance LiCoPO4/ C core/shell composite for Li-ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2012,70:349-354.
DOI URL |
| [20] | JAYAPRAKASH N, KALAISELVI N, PERIASAMY P . A preliminary investigation into the new class of lithium intercalating LiNiSiO4 cathode material. Nanotechnology, 2008, 19(2): 025603-1-5. |
| [21] |
JIN B, GU H B, KIM K W . Effect of different conductive additives on charge/discharge properties of LiCoPO4/Li batteries.[J]. Solid State Electr., 2007,12(2):105-111.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
YOSHIDA J, NAKANISHI S, IBA H , et al. Effect of carbon composite on manganese phosphate particles for lithium ion battery properties.[J]. Soc. Powder Technol., 2011,48:389-395.
DOI URL |
| [23] | WANG F, YANG J . Synthesis and electrochemical performance of nano LiCoPO4 by polyol method. Journal of Electrochemistry, 2013,19(6):585-588. |
| [24] |
DOKKO K, KOIZUMI S, NAKANO H , et al. Particle morphology, crystal orientation, and electrochemical reactivity of LiFePO4 synthesized by the hydrothermal method at 443 K. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2007,17:4803-4810.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
BRAMNIK N N, NIKOLOWSKI K, BAEHTZ C , et al. Phase transitions occurring upon lithium insertion-extraction of LiCoPO4. Chem. Mater., 2007,19(4):908-915.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
WU B R, XU H L, MU D B , et al. Controlled solvothermal synjournal and electrochemical performance of LiCoPO4 submicron single crystals as a cathode material for lithium ion batteries.[J]. Power Sources, 2016,304:181-188.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 仲维卓 . 人工水晶, 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994: 515. |
| [28] | OSTWALD W Z . Über die vermeintliche isomerie des roten und gelben quecksilberoxyds und die oberflächenspannung fester körper. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 1900,34:495-503. |
| [29] |
THACKERAY M . Lithium ion batteries: an unexpected conductor. Nature Materials, 2002,1(2):81-82.
DOI |
| [30] |
MANZI J, BRUTTI S . Surface chemistry on LiCoPO4 electrodes in lithium cells: SEI formation and self-discharge. Electrochimica Acta, 2016,222:1839-1846.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
AURBACH D, MARKOVSKY B, SALITRA G , et al. Review on electrode-electrolyte solution interactions, related to cathode materials for Li-ion batteries.[J]. Power Sources, 2007,165(2):491-499.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
JOHNSON L, LI C, LIU Z , et al. The role of LiO2 solubility in O2 reduction in aprotic solvents and its consequences for Li-O2 batteries. Nat. Chem., 2014,6(12):1091-1099.
DOI |
| [33] |
FREUNBERGER S A, CHEN Y, DREWETT N E , et al. The lithium- oxygen battery with ether-based electrolytes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011,50(37):8609-8613.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
BRUTTI S, PANERO S . Recent advances in the development of LiCoPO4 as high voltage cathode material for Li-ion batteries. ACS Symposium Series, 2013,1140:67-99.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
NAKAYAMA M, GOTO S, UCHIMOTO Y , et al. X-ray absorption spectroscopic study on the electronic structure of Li1-xCoPO4 electrodes as 4.8 V positive electrodes for rechargeable lithium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem.B, 2005,109:11197-11203.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
EHRENBERG H, BRAMNIK N N, SENYSHYN A , et al. Crystal and magnetic structures of electrochemically delithiated Li1-xCoPO4 phases. Solid State Sciences, 2009,11(1):18-23.
DOI URL |
| [37] | BRAMNIK N N, BRAMNIK K G, BUHRMESTER T , et al. Electrochemical and structural study of LiCoPO4-based electrodes.[J]. Solid State Eletrochem., 2004,8:558-564. |
| [38] |
BRAMNIK N N, BRAMNIK K G, BAEHTZ C , et al. Study of the effect of different synjournal routes on Li extraction-insertion from LiCoPO4.[J]. Power Sources, 2005,145:74-81.
DOI URL |
| [1] | YANG Zhuo, LU Yong, ZHAO Qing, CHEN Jun. X-ray Diffraction Rietveld Refinement and Its Application in Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [2] | ZHU Hezhen, WANG Xuanpeng, HAN Kang, YANG Chen, WAN Ruizhe, WU Liming, MAI Liqiang. Enhanced Lithium Storage Stability Mechanism of Ultra-high Nickel LiNi0.91Co0.06Al0.03O2@Ca3(PO4)2 Cathode Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1030-1036. |
| [3] | FENG Kun, ZHU Yong, ZHANG Kaiqiang, CHEN Zhang, LIU Yu, GAO Yanfeng. Boehmite Nanosheets-coated Separator with Enhanced Performance for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1009-1015. |
| [4] | SU Nana, HAN Jingru, GUO Yinhao, WANG Chenyu, SHI Wenhua, WU Liang, HU Zhiyi, LIU Jing, LI Yu, SU Baolian. ZIF-8-derived Three-dimensional Silicon-carbon Network Composite for High-performance Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1016-1022. |
| [5] | WANG Yang, FAN Guangxin, LIU Pei, YIN Jinpei, LIU Baozhong, ZHU Linjian, LUO Chengguo. Microscopic Mechanism of K+ Doping on Performance of Lithium Manganese Cathode for Li-ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1023-1029. |
| [6] | CHEN Ying, LUAN Weiling, CHEN Haofeng, ZHU Xuanchen. Multi-scale Failure Behavior of Cathode in Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Stress Field [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 918-924. |
| [7] | WANG Yutong, ZHANG Feifan, XU Naicai, WANG Chunxia, CUI Lishan, HUANG Guoyong. Research Progress of LiTi2(PO4)3 Anode for Aqueous Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 481-492. |
| [8] | LI Kunru, HU Xinghui, ZHANG Zhengfu, GUO Yuzhong, HUANG Ruian. Three-dimensional Porous Biogenic Si/C Composite for High Performance Lithium-ion Battery Anode Derived from Equisetum Fluviatile [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 929-935. |
| [9] | WANG Ying, ZHANG Wenlong, XING Yanfeng, CAO suqun, DAI Xinyi, LI Jingze. Performance of Amorphous Lithium Phosphate Coated Lithium Titanate Electrodes in Extended Working Range of 0.01-3.00 V [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 999-1005. |
| [10] | WANG Yanan, LI Hua, WANG Zhengkun, LI Qingfeng, LIAN Chen, HE Xin. Progress on Failure Mechanism of Lithium Ion Battery Caused by Diffusion Induced Stress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1071-1087. |
| [11] | GUO Rong-Nan, HAN Wei-Qiang. Effects of Structure and Properties of Polar Polymeric Binders on Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(10): 1021-1029. |
| [12] | LI Bo, HAO Wen, WEN Xiao-Gang. Semi-hollow/Solid ZnMn2O4 Microspheres: Synthesis and Performance in Li Ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(3): 307-312. |
| [13] | BAI Xue-Jun, LIU Chan, HOU Min, WANG Biao, CAO Hui, FU Jun-Jie. Silicon/CNTs/Graphene Free-standing Anode Material for Lithium-ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 705-712. |
| [14] | ZHAI Li-Li, ZHANG Jiang, LI Xuan-Ke, CONG Ye, DONG Zhi-Jun, YUAN Guan-Ming. F127 Template on Pore Structure and Electrochemical Performances of Mesoporous SnO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(6): 588-596. |
| [15] | LIAO Li-Xia, WANG Ming, FANG Tao, YIN Ge-Ping, ZHOU Xiao-Guang, LOU Shuai-Feng. Synthesis and Characterization of ZnFe2O4 Anode for Lithium Ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(1): 34-38. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||