
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (3): 269-278.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180248
Special Issue: 热电材料与器件
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
HU Xiao-Kai1,4, ZHANG Shuang-Meng1, ZHAO Fu1,2, LIU Yong1,3, LIU Wei-Shu1
Received:2018-06-21
Revised:2018-08-23
Published:2019-03-20
Online:2019-02-26
Supported by:CLC Number:
HU Xiao-Kai, ZHANG Shuang-Meng, ZHAO Fu, LIU Yong, LIU Wei-Shu. Thermoelectric Device: Contact Interface and Interface Materials[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 269-278.
| T range /℃ | Compositions/wt% | Liquidus T/℃ | Solidus T/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100-200 | 52 In+48 Sn | 118 | 118 |
| 85 Sn+10 Bi+5 Zn | 190 | 168 | |
| 63 Sn+37 Pb | 183 | 183 | |
| 91.2 Sn+8.8 Zn | 198.5 | 198.5 | |
| 200-300 | 50 Sn+50 Pb | 212 | 183 |
| 96.5 Sn+3 Ag+0.5 Cu | 220 | 217 | |
| 95 Sn+5 Sb | 240 | 232 | |
| 300-400 | 5 Sn+95 Pb | 312 | 305 |
| 95 Pb+5 Ag | 364 | 305 | |
| 75 Sn+0.25 Sb+ 0.25 Bi+24.5 Pb | 380 | 370 | |
| 400-500 | 94 Sn+0.2 Pb+5.8 Sb | 461 | 450 |
| 88 Pb+11.75 Sb+0.25 Bi | 473 | 473 | |
| 500-600 | 97 Pb+0.4 Sb + 2.35 Ag+0.25 Bi | 580 | 580 |
| 8.5 Sn+90 Pb+1.5 Ag | 588 | 588 |
Table 1 Compositions of some solders as well as the temperature (T) at liquidus and solidus[16]
| T range /℃ | Compositions/wt% | Liquidus T/℃ | Solidus T/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100-200 | 52 In+48 Sn | 118 | 118 |
| 85 Sn+10 Bi+5 Zn | 190 | 168 | |
| 63 Sn+37 Pb | 183 | 183 | |
| 91.2 Sn+8.8 Zn | 198.5 | 198.5 | |
| 200-300 | 50 Sn+50 Pb | 212 | 183 |
| 96.5 Sn+3 Ag+0.5 Cu | 220 | 217 | |
| 95 Sn+5 Sb | 240 | 232 | |
| 300-400 | 5 Sn+95 Pb | 312 | 305 |
| 95 Pb+5 Ag | 364 | 305 | |
| 75 Sn+0.25 Sb+ 0.25 Bi+24.5 Pb | 380 | 370 | |
| 400-500 | 94 Sn+0.2 Pb+5.8 Sb | 461 | 450 |
| 88 Pb+11.75 Sb+0.25 Bi | 473 | 473 | |
| 500-600 | 97 Pb+0.4 Sb + 2.35 Ag+0.25 Bi | 580 | 580 |
| 8.5 Sn+90 Pb+1.5 Ag | 588 | 588 |
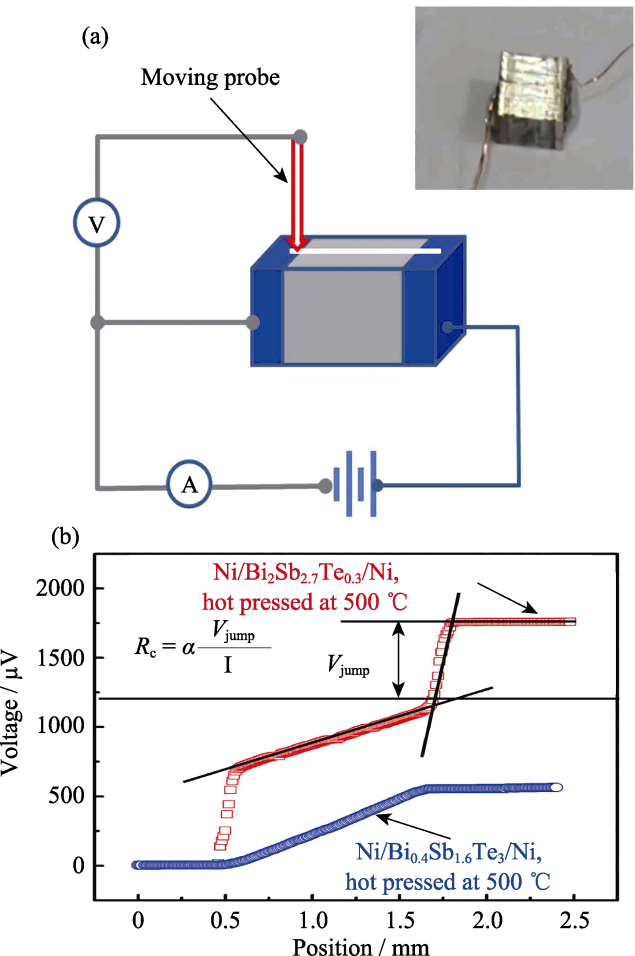
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of a scanning voltage probe for contact resistance measurement, and a Bi2Te3-based leg (inset) (a); contact resistance measurement for both n-type Ni/Bi2Te2.7Se0.3/Ni and p-type Ni/Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3/Ni(b)[21]
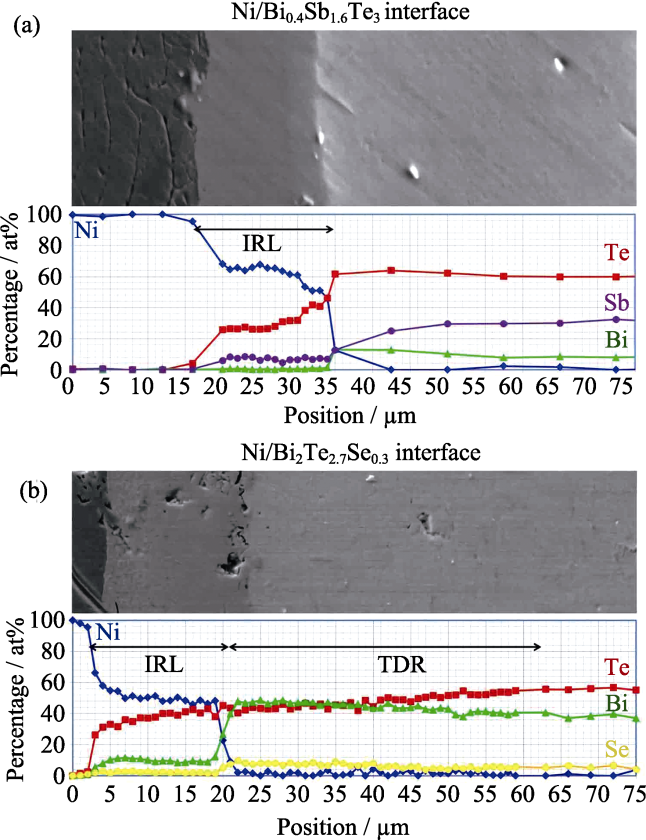
Fig.5 Comparison of composition profile between Ni/Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 interface (a)and Ni/Bi2Te2.7Se0.3Interface (b) obtained from a selected area SEM-EDS[21]IRL: interface reaction layer, TDR: Te-deficient region
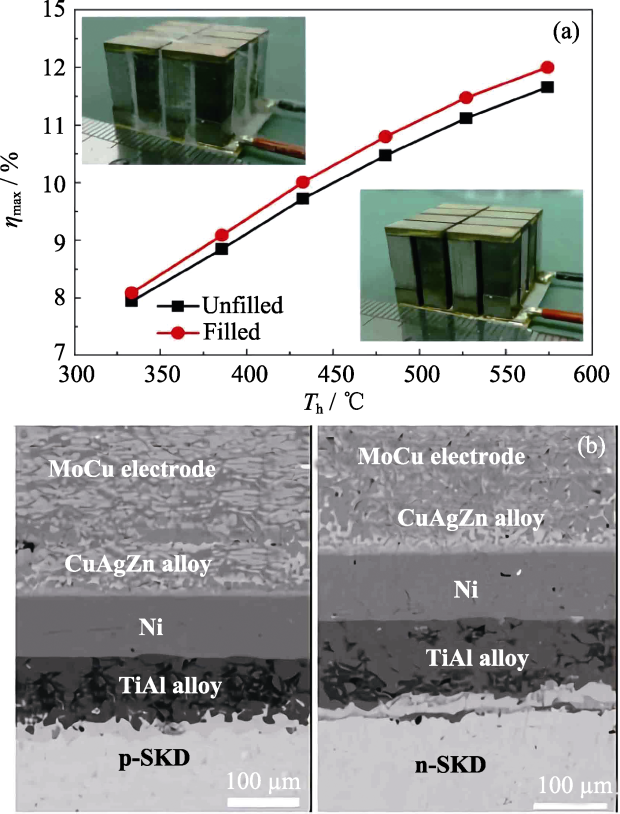
Fig.9 (a) Power generation efficiency of segmented BT/SKD modules and (b) scanning electron microscopy image of SKD/Ti0.88Al0.12/Ni interface and electrode on hot side[13]
| [1] | 中国建筑节能协会. 中国建筑能耗研究报告(2017年), 上海, 2017. |
| [2] | 陈立东, 刘睿恒, 史迅. 热电材料与器件. 北京:科学出版社, 2018:1-14. |
| [3] | LIU W S, HU J Z, ZHANG S M,et al. New trends, strategies and opportunities in thermoelectric materials: a perspective. Mater. Today Phys., 2017, 1: 50-60. |
| [4] | ZHU T J, LIU Y T, FU C G,et al. Compromise and synergy in high efficiency thermoelectric materials. Adv. Mater, 2017, 29(14): 1605884. |
| [5] | LI J F, LIU W S, ZHAO L D,et al. High-performance nanostructured thermoelectric materials. NPGAsia Mater., 2010, 2(4):152-158. |
| [6] | ZEBARJADI M, ESFARJANI K, DRESSELHAUS M S,et al. Perspectives on thermoelectrics: from fundamentals to device applications. Energy Environ. Sci., 2012,5(1): 5147-5162. |
| [7] | CHEN L D, XIONG Z, BAI S Q.Recent progress of thermoelectric nano-composites.Journal ofInorganic Materials, 2010, 25(6): 561-568. |
| [8] | ZHAN B, LAN J Z, LIU Y C,et al. Research progress of oxides thermoelectric materials. Journal ofInorganic Materials, 2014, 29(3): 237-244. |
| [9] | CHEN G, LIU T X, TANG X F,et al. Optimization of electrode material and connecting process for Mg-Si-Sn based thermoelectric device. Journal ofInorganic Materials, 2015, 30(6): 639-646. |
| [10] | FU C, BAI S, LIU Y,et al. Realizing high figure of merit in heavy band p-type half-Heusler thermoelectric materials. Nat. Comm., 2015, 6: 8144-8151. |
| [11] | HU X, JOOD P, OHTA M,et al. Power genaration of nanostructured PbTe-based thermoelectrics: comprehensive development from materials to modules. Energy Environ. Sci., 2016, 9(2): 517-529. |
| [12] | KRAEMER D, JIE Q, MCENANEY K,et al. Concentrating solar thermoelectric generator with a peak efficiency of 7.4%. Nature Energy, 2016, 1: 1-8. |
| [13] | ZHANG Q, LIAO J, TANG Y,et al. Realizing a thermoelectric conversion efficiency of 12% in bismuth telluride/skutterudite segmented modules through full-parameter optimization and energy-loss minimized integration. Energy Environ. Sci., 2017, 10(4): 956-963. |
| [14] | HAO F, QIU P, TANG Y,et al. High efficiency Bi2Te3-based materials and devices for thermoelectric power generation between 100 and 300℃. Energy Environ. Sci.,2016, 9(10): 3120-3127. |
| [15] | 张建中. 温差电技术. 天津:天津科学技术出版社, 2013:131-135, 219-224. |
| [16] | 张文典. 实用表面组装技术, 4版. 北京:电子工业出版社, 2015:162-247. |
| [17] | HATZIKRANIOTIS E, ZORBAS K T, SAMARAS I,et al. Efficiency study of a commercial thermoelectric power generator (TEG) under thermal cycling. J. Electron. Mater., 2010,39(9): 2112-2116. |
| [18] | PARK W, BARAKO M T, MARCONNET A M, et al. Effect of thermal cycling on commercial thermoelectric modules. 13th Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems, San Diego, 2012, 16(12): 107-112. |
| [19] | CLIN TH, TURENNE S, VASILEVSKIY D,et al. Numerical simulation of the thermomechanical behavior of extruded bismuth telluride alloy module. J. Electro. Mater.,2009,38(7): 994-1001. |
| [20] | KIM H S, WANG T, LIU W S,et al.Engineering thermal conductivity for balancing between reliability and performance of bulk thermoelectric generators. Adv. Funct. Mater.,2016, 26(21): 3678-3686. |
| [21] | LIU W S, WANG H, WANG L,et al. Understanding of the contact of nanostructured thermoelectric n-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 legs for power generation applications.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(42): 13093-13100. |
| [22] | LAN Y C, WANG D Z, CHEN G, REN Z F. Diffusion of nickel and tin in p-type (Bi,Sb)2Te3 and n-type Bi2(Te,Se)3 thermoelectric materials. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, 92(10): 101910-1-3. |
| [23] | ROWE D M.CRC Handbook of Thermoelectrics. USA: CRC Press LLC, 1995: 479-485. |
| [24] | LIU W S, QING J, KIM H S,et al. Current progress and future challenges in thermoelectric power generation: from materials to devices. Acta Materialia, 2015, 87: 357-376. |
| [25] | HABA V. Method and Materials For Obtaining Low Resistance Bond to Bismuth Telluride. US Patent, 3017693, 1962. US Patent, 3079455, 1963. |
| [26] | ROSI F D, BERNOFF R A.Method and Materials for Obtaining Low Resistance Bonds to Thermoelectric Bodies. US Patent, 3037064, 1962. |
| [27] | LIAO C N, LEE C H, CHEN W J.Effect of interfacial compound formation on contact resistivity of soldered junction between bismuth telluride based thermoelements and copper.Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 2007,10(9): 23-25. |
| [28] | MENGALI O J, SEILER M R.Contact resistance studies on thermoelectric materials.Adv. Energy Conversion, 1962, 2(62): 59-68. |
| [29] | WEITZMAN L H. Etching Bismuth Telluride.US Patent, 3338765, 1967. |
| [30] | TALOR P J, MADDUX J R, MEISSNER G, ,et al. Controlled improvement in specific contact resistivity for thermoelectric materials by ion implantation. Appl. Phys. Lett.. Controlled improvement in specific contact resistivity for thermoelectric materials by ion implantation. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, 103(4): 043902-1-4. |
| [31] | LIN W P, WESOLOWSKI D E, LEE C C.Barrier/bonding layers on bismuth telluride for high temperature thermoelectric modules.J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2011,22(9): 1313-1320. |
| [32] | IYORE O D.Interface Characterization of Contacts to Bulk Bismuth Telluride Alloys. Richardson, TX: University of Texas at Dallas, Master’s Thesis, UMI No. 1470835, 2009. |
| [33] | FENG H P, YU B, CHEN S,et al. Studies on surface preparation and smoothness of nanostructured Bi2Te3-based alloys by electrochemical and mechanical methods. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(8): 3079-3084. |
| [34] | IYORE O D, LEE T H, GUPTA R P,et al. Interface characterization of nickel contact to bulk bismuth telluride selenide. Surf. Interface Analysis, 2009,41(5): 440-444. |
| [35] | WEINSTEIN M, MLAVSKY A I.Bonding of lead telluride to pure iron electrodes.Rev. Sci. Instrum., 1962, 33(10): 1119-1120. |
| [36] | SINGH A, BHATTACHARYA S, THINAHARAN C, ,et al. Development of low resistance electrical contacts for thermoelectric devices based on n-type PbTe and p-type TAGS-85 ((AgSbTe2)0.15(GeTe)0.85). J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2008, 42(1): 015502- 1-6. |
| [37] | LEAVITT F A, MCCOY J W, MARUDHACHALAM P, ,et al. Segmented Thermoelectric Module with Bonded Legs. US Patent. Segmented Thermoelectric Module with Bonded Legs. US Patent, 2012/0103381 A1, 2012. |
| [38] | XIA H, DRYMIOTIS F, CHEN C L,et al. Bonding and high-temperature reliability of NiFeMo alloy/n-type PbTe joints for thermoelectric module applications. J. Mater. Sci., 2015, 50(7): 2700-2708. |
| [39] | XIA H, DRYMIOTIS F, CHEN C L,et al. Bonding and interfacial reaction between Ni foil and n-type PbTe thermoelectric materials for thermoelectric module applications. J. Mater. Sci., 2014, 49(4): 1716-1723. |
| [40] | XIA H, CHEN C L, DRYMIOTIS F,et al. Interfacial reaction between Nb foil and n-type PbTe thermoelectric materials during thermoelectric contact fabrication. J. Electro. Mater.,2014,43(11): 4064-4069. |
| [41] | ORIHASHI M, NODA Y, CHEN L,et al. Ni/n-PbTe and Ni/p-Pb0.5Sn0.5Te Joining by Plasma Activated Sintering. 17th International Conference on Thermoelectrics, Nagoya, 1998: 543-546. |
| [42] | FERRERES X R, YAMINI S A, NANCARROW M,et al. One-step bonding of Ni electrode to n-type PbTe — a step towards fabrication of thermoelectric generators. Materials and Design, 2016, 107: 90-97. |
| [43] | LI C C, DRYMIOTIS F, LIAO L L,et al. Interfacial reactions between PbTe-based thermoelectric materials and Cu and Ag bonding materials. J. Mater. Chem. C,2015, 3(40): 10590-10596. |
| [44] | GARCIA-CANADAS J, POWELL A V, KALTZOGLOU A,et al. Fabrication and evaluation of a skutterudite-based thermoelectric module for high-temperature applications. J. Electro. Mater., 2013, 42(7): 1369-1374. |
| [45] | FAN X C, GU M, SHI X,et al. Fabrication and reliability evaluation of Yb0.3Co4Sb12/Mo-Ti/Mo-Cu/Ni thermoelectric joints. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(6): 7590-7595. |
| [46] | SALVADOR J R, CHO J Y, YE Z,et al. Conversion efficiency of skutterudite-based thermoelectric modules. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16(24): 12510-12520. |
| [47] | FAN J F, CHEN L D, BAI S Q,et al. Joining of Mo to CoSb3 by spark plasma sintering by inserting a Ti interlayer. Materials Letters, 2004, 58(30): 3876-3878. |
| [48] | ZHAO D G, GENG H R, TENG X Y.Fabrication and reliabilityevaluation of CoSb3/W-Cu thermoelectric element.J. Alloys Compd., 2012, 517(7): 198-203. |
| [49] | ZHAO D G, LI X Y, JIANG W,et al. Fabrication of CoSb3/MoCu thermoelectric joint by one-step SPS and evaluation. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(3): 545-548. |
| [50] | GU M, XIA X G, LI X Y,et al. Microstructural evolution of the interfacial layer in the Ti-Al/Yb0.6Co4Sb12 thermoelectric joints at high temperature. J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 610: 665-670. |
| [51] | TANG Y S, BAI S Q, REN D D,et al. Interface structure and electrical property of Yb0.3Co4Sb12/Mo-Cu element prepared by welding using Ag-Cu-Zn solder. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 256-260. |
| [52] | GU M, XIA X G, HUANG X Y, BAI S Q,et al. Study on the interfacial stability of p-type Ti/CeyFexCo4-xSb12 thermoelectric joints at high temperature. J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 671: 238-244. |
| [53] | CAILLAT T, FLEURIAL J P, SNYDER G J, et al. Development of High Efficiency Segmented Thermoelectric Unicouples. Proceedings of 20th Int. Conf. on Thermoelectrics, Beijing, 2001, 504(1): 282-285. |
| [54] | FLEURIAL J P, CAILLAT T, CHI S C.Electrical Contacts for Skutterudite Thermoelectric Materials.US Patent, 20120006376 A1, 2012. |
| [55] | GUO J Q, GENG H Y, OCHI T,et al. Development of skutterudite thermoelectric materials and modules. J. Electro. Mater., 2012, 41(6): 1036-1042. |
| [56] | MUTO A, YANG J, POUDEL B, et al. Skutterudite unicouple characterization for energy harvesting applications. Adv. Energy Mater., 2013, 3(2): 245-251. |
| [1] | DING Ling, JIANG Rui, TANG Zilong, YANG Yunqiong. MXene: Nanoengineering and Application as Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | YANG Zhuo, LU Yong, ZHAO Qing, CHEN Jun. X-ray Diffraction Rietveld Refinement and Its Application in Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | CHEN Qiang, BAI Shuxin, YE Yicong. Highly Thermal Conductive Silicon Carbide Ceramics Matrix Composites for Thermal Management: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | LIN Junliang, WANG Zhanjie. Research Progress on Ferroelectric Superlattices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [5] | NIU Jiaxue, SUN Si, LIU Pengfei, ZHANG Xiaodong, MU Xiaoyu. Copper-based Nanozymes: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [6] | YUAN Jingkun, XIONG Shufeng, CHEN Zhangwei. Research Trends and Challenges of Additive Manufacturing of Polymer-derived Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [7] | YOU Junqi, LI Ce, YANG Dongliang, SUN Linfeng. Double Dielectric Layer Metal-oxide Memristor: Design and Applications [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [8] | DU Jianyu, GE Chen. Recent Progress in Optoelectronic Artificial Synapse Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [9] | YANG Yang, CUI Hangyuan, ZHU Ying, WAN Changjin, WAN Qing. Research Progress of Flexible Neuromorphic Transistors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [10] | QI Zhanguo, LIU Lei, WANG Shouzhi, WANG Guogong, YU Jiaoxian, WANG Zhongxin, DUAN Xiulan, XU Xiangang, ZHANG Lei. Progress in GaN Single Crystals: HVPE Growth and Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [11] | LIN Siqi, LI Airan, FU Chenguang, LI Rongbing, JIN Min. Crystal Growth and Thermoelectric Properties of Zintl Phase Mg3X2 (X=Sb, Bi) Based Materials: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [12] | ZHANG Chaoyi, TANG Huili, LI Xianke, WANG Qingguo, LUO Ping, WU Feng, ZHANG Chenbo, XUE Yanyan, XU Jun, HAN Jianfeng, LU Zhanwen. Research Progress of ScAlMgO4 Crystal: a Novel GaN and ZnO Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [13] | CHEN Kunfeng, HU Qianyu, LIU Feng, XUE Dongfeng. Multi-scale Crystallization Materials: Advances in in-situ Characterization Techniques and Computational Simulations [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [14] | LIU Yan, ZHANG Keying, LI Tianyu, ZHOU Bo, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Electric-field Assisted Joining Technology for the Ceramics Materials: Current Status and Development Trend [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 113-124. |
| [15] | XIE Bing, CAI Jinxia, WANG Tongtong, LIU Zhiyong, JIANG Shenglin, ZHANG Haibo. Research Progress of Polymer-based Multilayer Composite Dielectrics with High Energy Storage Density [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||