
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 186-192.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180209
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
GONG Yun1,2, LIU Yan3, GU Ping1, ZHU Yu-Fang2, ZHOU Xiao-Xia3
Received:2018-05-04
Revised:2018-08-14
Published:2019-02-20
Online:2019-01-24
About author:GONG Yun. E-mail: 331391649@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
GONG Yun, LIU Yan, GU Ping, ZHOU Xiao-Xia. Synthesis of Nano Manganese Oxide with Assistance of Ultrasonic for Removal of Low Concentration NO[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 186-192.
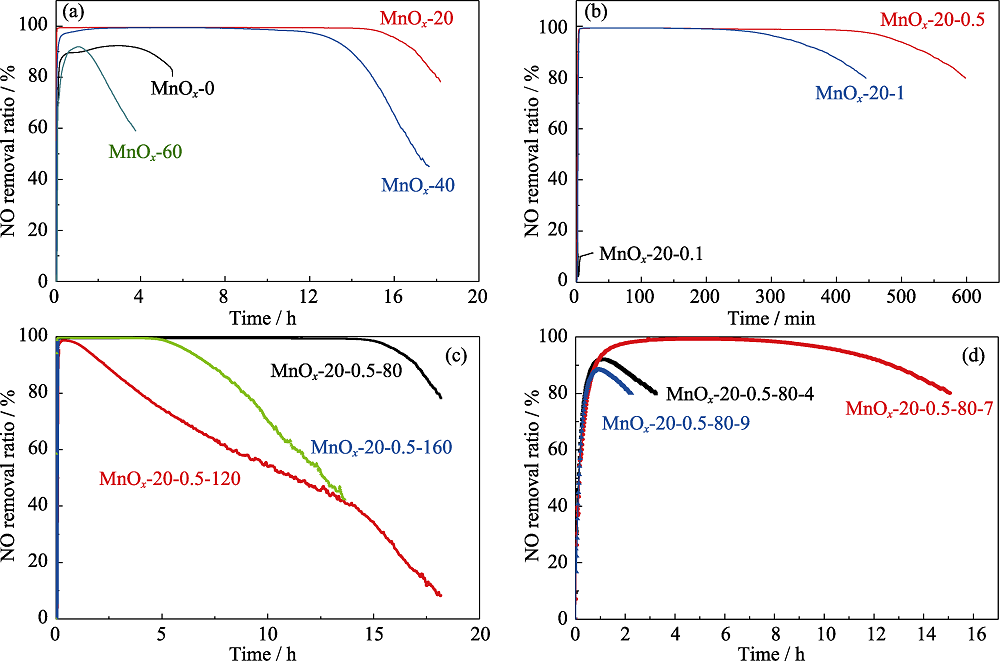
Fig. 1 Effect of process parameters of the sample MnOx on the NO catalytic removal performance (a) Ultrasonic time; (b) Reactants concentration; (c) Dry temperature; (d) pH
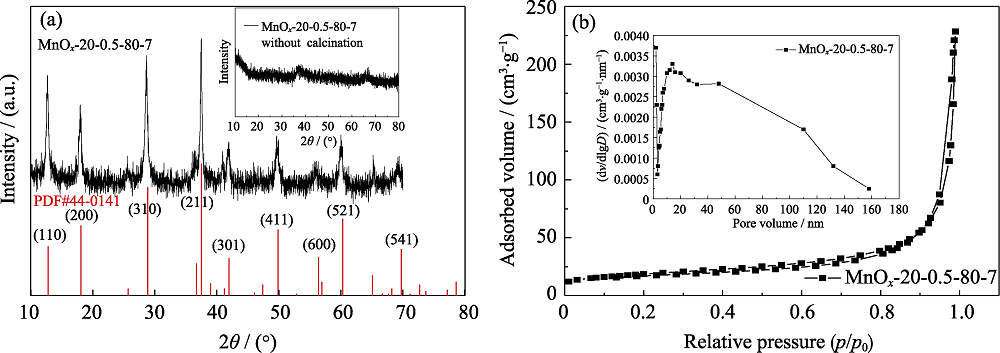
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of MnOx-20-0.5-80-7 before and after calcination (a) and corresponding N2 adsorption-desorption curves and the distribution of pore size (b)
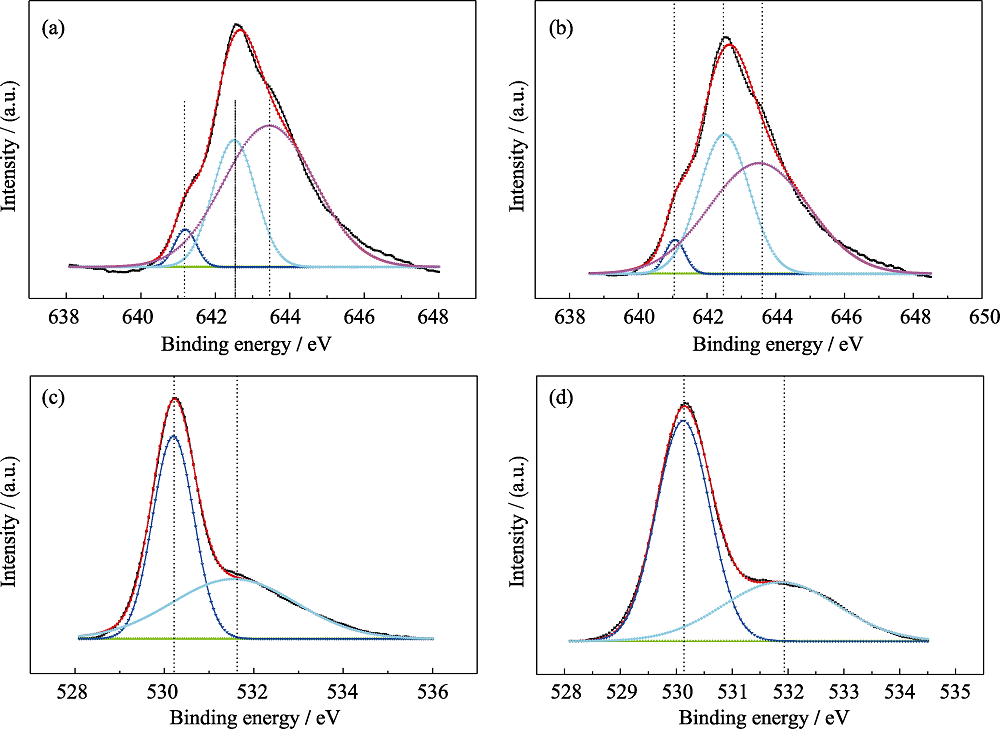
Fig. 4 XPS spectra of the sample MnOx-20-0.5-80-7 before and after catalytic test(a) Mn2p3/2, before; (b) Mn2p3/2, after; (c) O1s, before; (d) O1s, after
| Element | Phase | Before test | After test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binding energy/eV | Percentage/% | Binding energy/eV | Percentage/% | ||
| Mn-surface | Mn2+ | 641.2 | 4.8 | 641.1 | 4.1 |
| Mn3+ | 642.5 | 26.7 | 642.5 | 37.6 | |
| Mn4+ | 643.5 | 66.5 | 643.5 | 58.3 | |
| Mn-etch 10 s | Mn2+ | 640.9 | 13.5 | 640.8 | 10.8 |
| Mn3+ | 642.1 | 54.0 | 642.1 | 56.5 | |
| Mn4+ | 644.3 | 32.5 | 644.3 | 32.7 | |
| O-surface | Olat | 530.1 | 54.5 | 530.1 | 64.0 |
| Oads | 531.5 | 45.5 | 531.8 | 36.0 | |
| O-etch 10 s | Olat | 530.1 | 78.5 | 530.0 | 70.2 |
| Oads | 531.5 | 21.5 | 531.5 | 29.8 | |
Table 1 XPS data of catalyst MnOx-20-0.5-80-7 before and after the NO removal test
| Element | Phase | Before test | After test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binding energy/eV | Percentage/% | Binding energy/eV | Percentage/% | ||
| Mn-surface | Mn2+ | 641.2 | 4.8 | 641.1 | 4.1 |
| Mn3+ | 642.5 | 26.7 | 642.5 | 37.6 | |
| Mn4+ | 643.5 | 66.5 | 643.5 | 58.3 | |
| Mn-etch 10 s | Mn2+ | 640.9 | 13.5 | 640.8 | 10.8 |
| Mn3+ | 642.1 | 54.0 | 642.1 | 56.5 | |
| Mn4+ | 644.3 | 32.5 | 644.3 | 32.7 | |
| O-surface | Olat | 530.1 | 54.5 | 530.1 | 64.0 |
| Oads | 531.5 | 45.5 | 531.8 | 36.0 | |
| O-etch 10 s | Olat | 530.1 | 78.5 | 530.0 | 70.2 |
| Oads | 531.5 | 21.5 | 531.5 | 29.8 | |
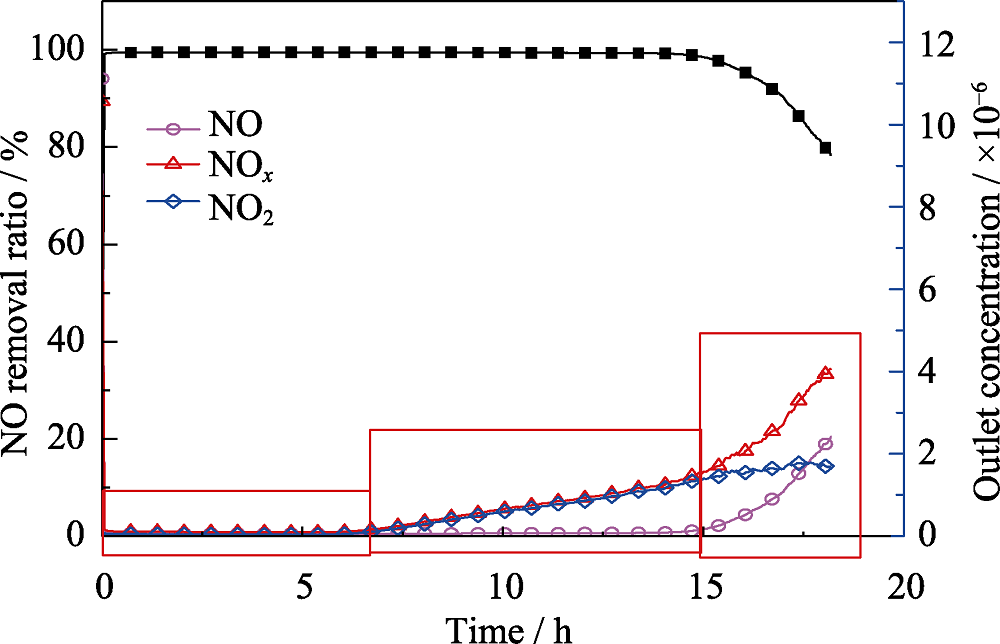
Fig. 5 Catalytic performance of the sample MnOx-20-0.5-80-7 on low-concentration NO removal ratio at room temperature (Reaction conditions: [NO]=10 cm3/m3, [O2]=21%, N2, 25 ℃ and GHSV = 120000 mL•h-1•g-1)
| [1] | LMEIDA-SILVA M, CANHA N, FREITAS M C,et al. Air pollution at an urban traffic tunnel in Lisbon, Portugal: an INAA study. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2011, 69(11): 1586-1591. |
| [2] | GUERRINI G L.Photocatalytic performances in a city tunnel in Rome: NO x monitoring results. Constr. Build. Materials, 2012, 27(1): 165-175. |
| [3] | MONTICELLI O, LOENDERS R, JACOBS P A,et al. NOx removal from exhaust gas from lean burn internal combustion engines through adsorption on FAU type zeolites cation exchanged with alkali metals and alkaline earth metals. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 1999, 21(3): 215-220. |
| [4] | LIU Z M, WOO S I.Recent advances in catalytic DeNOx science and technology. Catalysis Review, 2006, 48(1): 43-89. |
| [5] | HAN X H, WEI X L, SCHNELL U,et al. Detailed modeling of hybrid reburn/SNCR processes for NOx reduction in coal-fired furnaces. Combust Flame, 2003, 132(3): 374-386. |
| [6] | BAE S W, ROH S A, KIM S D.NO removal by reducing agents and additives in the selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) process.Chemosphere, 2006, 65(1): 170-175. |
| [7] | TAKAHASHI N, YAMAZAKI K, SOBUKAWA H,et al. The low-temperature performance of NO(x) storage and reduction catalyst. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2007, 70(1-4): 198-204. |
| [8] | KLEIN J, WU D L, TSCHAMBER V,et al. Carbon-NSR catalyst interaction: impact on catalyst structure and NOx storage efficiency. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2013, 132: 527-534. |
| [9] | CHANG X F, LU G Z, GUO Y,et al. A high effective adsorbent of NOx: preparation, characterization and performance of Ca-beta zeolites. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2013, 165: 113-120. |
| [10] | WEI J C, YU P, CAI B,et al. Absorption of NO in aqueous NaClO2/ Na2CO3 solutions. Chemical Engineering Technology, 2009, 32(1): 114-119. |
| [11] | MOCHIDA I, KISAMORI S, HIRONAKA M,et al. Oxidation of NO into NO2 over active-carbon fibers. Energy & Fuels, 1994, 8(6): 1341-1344. |
| [12] | LIU H Y, ZHANG Z K, XU Y Y,et al. Adsorption-oxidation reaction mechanism of NO on Na-ZSM-5 molecular sieves with a high Si/Al ratio at ambient temperature. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2010, 31(10): 1233-1241. |
| [13] | LIU H Y, LI Y F, XU Y Y,et al. Adsorption and catalysis on the surface of high silica ZSM-5 molecular sieve in NO oxidation at ambient temperature. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2011, 25(4): 615-621. |
| [14] | HUANG H Y, YANG R T.Removal of NO by reversible adsorption on Fe-Mn based transition metal oxides.Langmuir, 2001, 17(16): 4997-5003. |
| [15] | SHU Z, CHEN Y, HUANG W M,et al. Room-temperature catalytic removal of low-concentration NO over mesoporous Fe-Mn binary oxide synthesized using a template-free approach. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2013, 140: 42-50. |
| [16] | DU Y Y, HUA Z L, HUANG W M,et al. Mesostructured amorphous manganese oxides: facile synthesis and highly durable elimination of low-concentration NO at room temperature in air. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(27): 5887-5889. |
| [17] | WANG J, ZHU J Z, ZHOU X X,et al. Nanoflower-like weak crystallization manganese oxide for efficient removal of low-concentration NO at room temperature. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(14): 7631-7638. |
| [18] | DU Y Y, HUANG W M, HUA Z L,et al. A facile ultrasonic process for the preparation of Co3O4 nanoflowers for room-temperature removal of low-concentration NOx. Catalysis Communications. 2014, 57(2): 73-77. |
| [19] | NIAG E C, CHEN C H, GENUINO H,et al. Total oxidation of CO at ambient temperature using copper manganese oxide catalysts prepared by a redox method. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2010, 99(1/2): 103-110. |
| [20] | HADYIIVANOV K I.Identification of neutral and charged NxOy surface species by IR spectroscopy. Catalysis Review, 2000, 42(1/2): 71-144. |
| [21] | BENTRUP U, BRUCKNER A, RICHTER M,et al. NOx adsorption on MnO2/NaY composite: an in situ FT-IR and EPR study. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2001, 32(4): 229-241. |
| [1] | ZHANG Xiangsong, LIU Yetong, WANG Yongying, WU Zirui, LIU Zhenzhong, LI Yi, YANG Juan. Self-assembled Platinum-iridium Alloy Aerogels and Their Efficient Electrocatalytic Ammonia Oxidation Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 511-520. |
| [2] | WANG Lei, LI Jianjun, NING Jun, HU Tianyu, WANG Hongyang, ZHANG Zhanqun, WU Linxin. Enhanced Degradation of Methyl Orange with CoFe2O4@Zeolite Catalyst as Peroxymonosulfate Activator: Performance and Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 469-476. |
| [3] | YU Yefan, XU Ling, NI Zhongbing, SHI Dongjian, CHEN Mingqing. Prussian Blue Modified Biochar: Preparation and Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen from Sewage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 205-212. |
| [4] | TIAN Junting, LI Xiaobing, DING Weiyan, NIE Shengdong, LIANG Zhu. Fabrication of 1-3 Piezocomposites via Soft Mold Method for High-frequency Ultrasound Transducer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 507-512. |
| [5] | LUO Yi, XIA Shuhai, NIU Bo, ZHANG Yayun, LONG Donghui. Preparation and High Temperature Inorganic Transformation of Flexible Silicone Aerogels [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1281-1288. |
| [6] | SHU Chaoqin, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Cobalt-incorporated Chlorapatite: Preparation by Molten Salt Method, Anti-oxidation and Cytocompatibility [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1225-1235. |
| [7] | WANG Haoxuan, LIU Qiaomu, WANG Yiguang. Research Progress of High Entropy Transition Metal Carbide Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 355-364. |
| [8] | ZHANG Wenjin, SHEN Qianqian, XUE Jinbo, LI Qi, LIU Xuguang, JIA Husheng. Preparation and Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation of Hematite Nanobelts Containing Highly Ordered Oxygen Vacancies [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1290-1296. |
| [9] | ZHANG Yachen, MENG Jia, CAI Kun, SHENG Xiaochen, LE Jun, SONG Lixin. Bending Failure Mechanism Study of Si-Cr-Ti High Temperature Oxidation Resistance Coating via Acoustic Emission Technique [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1185-1192. |
| [10] | LEI Yiming, ZHANG Jie, BAI Guanghai, ZHANG Yanwei, WANG Xiaohui, WANG Jingyang. Influence of Al Content on Oxidation Resistance of Phase-pure Ti2AlC under Simulated Loss-of-coolant Accident Conditions [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1097-1102. |
| [11] | WANG Zhihu,ZHANG Jumei,BAI Lijing,ZHANG Guojun. Mg(OH)2 Film on Micro-arc Oxidation Ceramic Coating of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy: Preparation and Corrosion Resistance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(6): 709-716. |
| [12] | HUANG Xieyi,WANG Peng,YIN Guoheng,ZHANG Shaoning,ZHAO Wei,WANG Dong,BI Qingyuan,HUANG Fuqiang. Removal of Volatile Organic Compounds Driven by Platinum Supported on Amorphous Phosphated Titanium Oxide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 482-490. |
| [13] | YANG Shaohui, YAN Shufang, LI Shijiang, CHEN Weidong, DU Pei, MA Wen. Effect of Phase Duty Cycle on the Properties of ZrH1.8 Surface Micro-arc Oxidized Ceramic Layer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1112-1116. |
| [14] | LYU Ziye, TANG Yiping, CAO Huazhen, ZHENG Guoqu, HOU Guangya. Effect of V Doping on Electrocatalytic Performance of Ni-Co-S on Bacterial Cellulose-derived Carbon Aerogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1142-1148. |
| [15] | LI Zhao, SUN Qiangqiang, CHEN Suoqian, ZHOU Chunsheng, CAO Jing, WANG Yongfeng, WANG Yanan. Hydrothermal Synthesized Nickel Copper Composite Phosphides as Bifunctional Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution and Hydrazine Oxidation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1149-1156. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||