
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 1136-1140.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170532
Special Issue: 光催化材料与技术
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIANG Feng1,2, YU Yun1, FENG Ai-Hu1,2, YU Yang1, MI Le1, SONG Li-Xin1
Received:2017-11-13
Published:2018-10-20
Online:2018-09-25
About author:JIANG Feng (1990?), male, candidate of PhD. E-mail: 437432167@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
JIANG Feng, YU Yun, FENG Ai-Hu, YU Yang, MI Le, SONG Li-Xin. Anatase TiO2 Nanoparticles: Facile Synthesis via Non-aqueous Precipitation and Photocatalytic Property[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1136-1140.
| Ti(OBu)4 | Ti(OBu)4 + AcOH | Precipitate slurry | Precipitate | Attribution | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3334 | - | 3334 | - | OH | [19] |
| 2958 | 2958 | 2958 | - | C-H | [20] |
| 2933 | 2933 | 2933 | - | aromatic C-C | [21] |
| 2873 | 2873 | 2873 | - | C-H | [20] |
| 2700 | - | - | - | C-H | [20] |
| 1460 | - | - | - | -CH2 | [22] |
| 1379 | 1419 | - | - | -CH3 | [22] |
| 1124 | - | - | - | Ti-O-C | [23] |
| 1096 | - | - | - | Ti-O-C | [23] |
| 1039 | - | - | - | Ti-O-C- | [23] |
| 611 | 613 | - | - | Ti-O | [24] |
| - | 1724 | 1735 | - | -C==O | [25] |
| - | 1547 | - | - | COO-group | [26] |
| - | 1290 | - | - | C-O | [27] |
| - | 1070 | 1074 | - | C-O | [28] |
| - | 1028 | 1045 | - | C-O | [29] |
| - | - | 1458 | - | CH2 | [30] |
| - | - | 1378 | - | Sym COO | [31] |
| - | - | 1189 | - | C-O | [32] |
| - | - | 881 | - | C-COO | [31] |
| - | - | 438 | 455 | Ti-O-Ti | [33] |
Table 1 Peak position of samples at different reaction stages (cm-1)
| Ti(OBu)4 | Ti(OBu)4 + AcOH | Precipitate slurry | Precipitate | Attribution | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3334 | - | 3334 | - | OH | [19] |
| 2958 | 2958 | 2958 | - | C-H | [20] |
| 2933 | 2933 | 2933 | - | aromatic C-C | [21] |
| 2873 | 2873 | 2873 | - | C-H | [20] |
| 2700 | - | - | - | C-H | [20] |
| 1460 | - | - | - | -CH2 | [22] |
| 1379 | 1419 | - | - | -CH3 | [22] |
| 1124 | - | - | - | Ti-O-C | [23] |
| 1096 | - | - | - | Ti-O-C | [23] |
| 1039 | - | - | - | Ti-O-C- | [23] |
| 611 | 613 | - | - | Ti-O | [24] |
| - | 1724 | 1735 | - | -C==O | [25] |
| - | 1547 | - | - | COO-group | [26] |
| - | 1290 | - | - | C-O | [27] |
| - | 1070 | 1074 | - | C-O | [28] |
| - | 1028 | 1045 | - | C-O | [29] |
| - | - | 1458 | - | CH2 | [30] |
| - | - | 1378 | - | Sym COO | [31] |
| - | - | 1189 | - | C-O | [32] |
| - | - | 881 | - | C-COO | [31] |
| - | - | 438 | 455 | Ti-O-Ti | [33] |
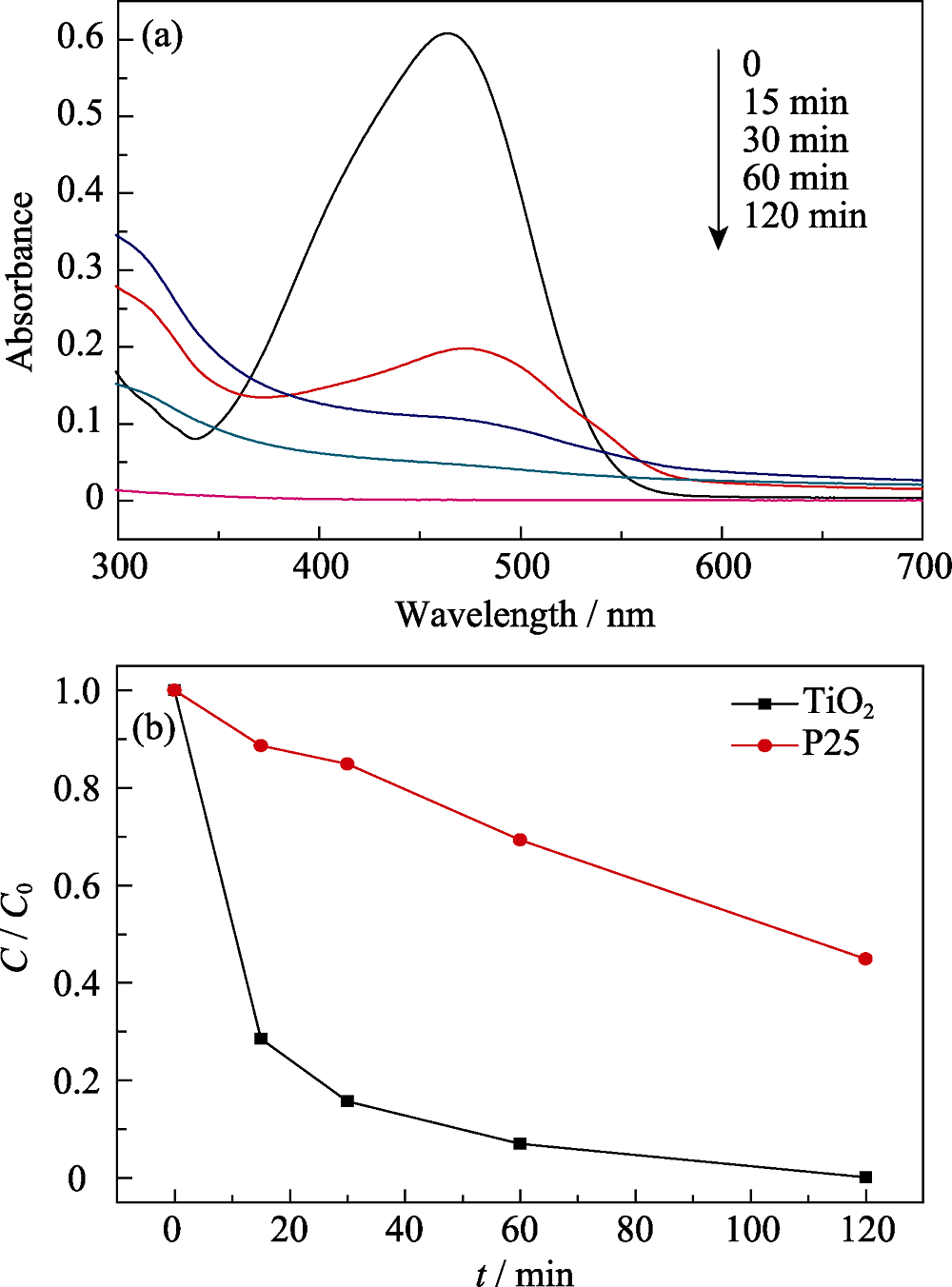
Fig. 6 Photodegradation effect of TiO2 nanoparticles(a) UV-Vis absorption spectra of MO solutions after photocatalytic performance test at different time intervals; (b) Photodegradation rate of MO after photocatalysis by TiO2 nanoparticles and commercial P25 powders
| [1] | KHAN S U M, AL S M, INGLER W B. Efficient photochemical water splitting by a chemically modifiedn-TiO2. Science, 2002, 297(5590): 2243-2245. |
| [2] | BACH U, LUPO D, COMTE P,et al. Solid-state dye-sensitized mesoporous TiO2 solar cells with high photon-to-electronconversion efficiencies. Nature, 1998, 395(6702): 583-585. |
| [3] | GAYA U I, ABDULLAH A H.Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants over titanium dioxide: a review of fundamentals, progress and problems.Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology C Photochemistry Reviews, 2006, 9(1): 1-12. |
| [4] | JUNG K Y, PARK S B, JANG H D.Phase control and photocatalytic properties of nano-sized titania particles by gas-phase pyrolysis of TiCl4.Catalysis Communications, 2004, 5(9): 491-497. |
| [5] | LOOK J L, ZUKOSKI C F.Alkoxide-derived titania particles: use of electrolytes to control size and agglomeration levels.Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 75(6): 1587-1595. |
| [6] | JIANG H Q, WANG P, GUO X L,et al. Preparation and characterization of low-amount Yb3+-doped TiO2 photocatalyst. Russian Chemical Bulletin, 2006, 55(10): 1743-1747. |
| [7] | GUO Y G, HU Y S, SIGLE W.Superior electrode performance of nanostructured mesoporous TiO2 (anatase) through efficient hierarchical mixed conducting networks. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(16): 2087-2091. |
| [8] | ADDAMO M, AUGUGLIARO V, PAOLA A D,et al. Preparation, characterization, and photoactivity of polycrystalline nanostructured TiO2 catalysts. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2004, 35(21): 3303-3310. |
| [9] | SUGIMOTO T, ZHOU X, MURAMATSU A.Synthesis of uniform anatase TiO2 nanoparticles by Gel-Sol method 4. Shape control.Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2003, 259(1): 53-61. |
| [10] | SUGIMOTO T, ZHOU X, MURAMATSU A.Synthesis of uniform anatase TiO2 nanoparticles by Gel-Sol method. 3. Formation process and size control.Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2003, 259(1): 43-52. |
| [11] | ZHANG Y X, LI G H, JIN Y X.Hydrothermal synthesis and photoluminescence of TiO2 nanowires.Chemical Physics Letters, 2002, 365(3/4): 300-304. |
| [12] | HE W, FANG Z, ZHANG K,et al. Continuous synthesis of a co-doped TiO2 photocatalyst and its enhanced visible light catalytic activity using a photocatalysis microreactor. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(68): 54853-54860. |
| [13] | REYES C D, RODRÍGUEZ G G, ESPINOSA P M E,et al. Phase-pure TiO2 nanoparticles: anatase, brookite and rutile. Nanotechnology, 2008, 19(14): 1-10. |
| [14] | CHAN S K, KOICHI N, BIN X,et al. A new observation on the phase transformation of TiO2 nanoparticles produced by a CVD method. Aerosol Science & Technology, 2005, 39(2): 104-112. |
| [15] | FENG Q, WANG T, ZHANG F, et al. Synthesis of TiO2 photocatalytic materials via solid-state reaction and its photodegradation property for methyl orange. Material Research Innovations, 2015, 18(S4): 92-96. |
| [16] | BANNIER E, DARUT G, SÁNCHEZ E,et al. Microstructure and photocatalytic activity of suspension plasma sprayed TiO2 coatings on steel and glass substrates. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2011, 206(2/3): 378-386. |
| [17] | ZHU J, BIAN Z F, REN J,et al. An integrated low temperature approach to highly photoactive nanocrystalline mesostructured titania. Catalysis Communications, 2007, 8(7): 971-976. |
| [18] | ZHU J, YANG J, BIAN Z F,et al. Nanocrystalline anatase TiO2 photocatalysts prepared via a facile low temperature nonhydrolytic Sol-Gel reaction of TiCl4 and benzyl alcohol. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2007, 76(1): 82-91. |
| [19] | PIRES D C, STOCKLERPINTO D V B, SCIAMARELI J,et al. Synthesis and characterization by infrared spectroscopy of hydantoin-based bonding agents, used in composite propellants. Journal of Aerospace Technology & Management, 2009, 1(2): 177-184. |
| [20] | MAX J J, DANEAULT S, CHAPADOS C.1-Propanol hydrate by IR spectroscopy.Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 2002, 80(1): 113-123. |
| [21] | JULKAPLI N M, AHMAD Z, AKIL H M.Preparation and characterization of 1,2,4,5-benzenetetra carboxylic-chitosan. E-Polymers, 2010, 10(1): 841-857. |
| [22] | ENESCU D, FRACHE A.Effects of sterically hindered N-alkoxyamines on photooxidative stability of reinforced polypropylene. E-Polymers, 2013, 12(1): 949-959. |
| [23] | VELASCO M J, RUBIO F, RUBIO J.Hydrolysis of titanium tetrabutoxide. study by FT-IR spectroscopy.Spectroscopy Letters, 1999, 32(2): 289-304. |
| [24] | HWANG J D, CHOU C H.On the origin of leakage current reduction in TiO2 passivated porosus silicon Schottky-barrier diode. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 96(6): 063501-063503. |
| [25] | URBAN M W, KOENIG J L, SHIH L B,et al. Structure of styrene/acrylic acid copolymer in aqueous solution determined by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Applied Spectroscopy, 1987, 41(4): 590-596. |
| [26] | FUGU M B, NDAHI N P, PAUL B B,et al. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial studies of some vanillin schiff base metal (ii) complexes. Journal of Chemical & Pharmaceutical Research, 2013, 5(1): 22-28. |
| [27] | ZHANG W, ZHANG H, XIAO J,et al. Carbon nanotube catalyst for oxidative desulfurization of a model diesel fuel using molecular oxygen. Green Chemistry, 2013, 16(1): 211-220. |
| [28] | GEIGER C, ZELENKA C, WEIGL M,et al. Synthesis of bicyclic sigma receptor ligands with cytotoxic activity. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2007, 50(24): 6144-6153. |
| [29] | SUN S L, WEN J L, MA M G,et al. Successive alkali extraction and structural characterization of hemicelluloses from sweet sorghum stem. Carbohydr. Polym., 2013, 92(2): 2224-2231. |
| [30] | NIKODEM K, GRAŻYNA S G, LIDIA O,et al. A study on the synthesis and properties of substituted EHBG-Fe(iii) complexes as potential MRI contrast agents. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, 2014, 769(1): 100-105. |
| [31] | CHOE J I, KIM G H.Ab initio study of vibrational spectra of p-tert-butylcalix[4]aryl ester complexed with alkali metal cation. Journal of the Korean Chemical Society, 2006, 50(1): 7-13. |
| [32] | SUGIHARTO A B, JOHNSON C M, DUNLOP I E,et al. Delocalized surface modes reveal three-dimensional structures of complex biomolecules. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(20): 7531-7534. |
| [33] | LI Z, HOU B, XU Y,et al. Comparative study of Sol-Gel- hydrothermal and Sol-Gel synthesis of titania-silica composite nanoparticles. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2005, 178(5): 1395-1405. |
| [34] | LIANG C Y, KRIMM S.Infrared spectra of high polymers: Part IX. Polyethylene terephthalate.Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy, 1959, 3(1-6): 554-574. |
| [35] | ZHANG L, LI H, LIU Y,et al. Adsorption-photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange over a facile one-step hydrothermally synthesized TiO2/ZnO-NH2-RGO nanocomposite. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(89): 48703-48711. |
| [1] | AN Lin, WU Hao, HAN Xin, LI Yaogang, WANG Hongzhi, ZHANG Qinghong. Non-precious Metals Co5.47N/Nitrogen-doped rGO Co-catalyst Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Performance of TiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 534-540. |
| [2] | LÜ Qingyang, ZHANG Yuting, GU Xuehong. Fabrication of Hollow Fiber Supported TiO2 Ultrafiltration Membranes via Ultrasound-assisted Sol-Gel Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1051-1057. |
| [3] | XIAO Xiang, GUO Shaoke, DING Cheng, ZHANG Zhijie, HUANG Hairui, XU Jiayue. CsPbBr3@TiO2 Core-shell Structure Nanocomposite as Water Stable and Efficient Visible-light-driven Photocatalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 507-512. |
| [4] | XI Wen, LI Haibo. Preparation of TiO2/Ti3C2Tx Composite for Hybrid Capacitive Deionization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 283-291. |
| [5] | LIU Cai, LIU Fang, HUANG Fang, WANG Xiaojuan. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Alga-based CDs-Cu-TiO2 Composite Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1154-1162. |
| [6] | Li Cuixia, SUN Huizhen, JIN Haize, SHI Xiao, LI Wensheng, KONG Wenhui. Construction and Photocatalytic Performance of 3D Hierarchical Pore rGO/TiO2 Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1039-1046. |
| [7] | WANG Ping,LI Xinyu,SHI Zhanling,LI Haitao. Synergistic Effect of Ag and Ag2O on Photocatalytic H2-evolution Performance of TiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 781-788. |
| [8] | JI Bang, ZHAO Wenfeng, DUAN Jieli, MA Lizhe, FU Lanhui, YANG Zhou. Synthesis of TiO2/WO3 on Nickel Foam for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Ethylene [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 581-588. |
| [9] | HUANG Xieyi,WANG Peng,YIN Guoheng,ZHANG Shaoning,ZHAO Wei,WANG Dong,BI Qingyuan,HUANG Fuqiang. Removal of Volatile Organic Compounds Driven by Platinum Supported on Amorphous Phosphated Titanium Oxide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 482-490. |
| [10] | WANG Xucong, DENG Hao, JIANG Zhongyi, YUAN Liyong. Photocatalytic Reduction of Re (VII) on Amorphous TiO2/g-C3N4 Derived from Different N Sources [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12): 1340-1348. |
| [11] | LIU Jinyun, ZHANG Yuting, HONG Zhou, LIU Hua, WANG Shengxian, GU Xuehong. Fabrication of Dual-layer Hollow Fiber Ceramic Composite Membranes by Co-extrusion [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12): 1333-1339. |
| [12] | CHEN Haoyu, ZHANG Yiwen, WU Zhong, QIN Zhenbo, WU Shanshan, HU Wenbin. Room Temperature Magnetoresistance Property of Co-TiO2 Nanocomposite Film Prepared by Strong Magnetic Target Co-sputtering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1263-1267. |
| [13] | ZHANG Ya-Ping, DING Wen-Ming, ZHU Hai-Feng, HUANG Cheng-Xing, YU Lian-Qing, WANG Yong-Qiang, LI Zhe, XU Fei. Photoelectrochemical Properties of MoSe2 Modified TiO2 Nanotube Arrays [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(8): 797-802. |
| [14] | JIAO Si-Yi, GE Wan-Yin, YIN Li-Xiong, XU Mei-Mei, CHANG Zhe, ZHANG Li. Controllable Synthesis and Growth Mechanism of Two-dimensional TiSe2 Nanosheets [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(8): 834-838. |
| [15] | Xi-Qing LÜ, Huan-Yu ZHANG, Rui LI, Mei ZHANG, Min GUO. Nb2O5 Coating on the Performance of Flexible Dye Sensitized Solar Cell Based on TiO2 Nanoarrays/Upconversion Luminescence Composite Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 590-598. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||