
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 1131-1135.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180107
Special Issue: 离子电池材料
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
GU Feng1,2, WANG You-Wei2, ZHENG Zhi-Hui1,2, LIU Jian-Jun2, LU Wen-Cong1
Received:2018-03-12
Revised:2018-05-02
Published:2018-10-20
Online:2018-09-25
About author:GU Feng. E-mail: fenggu@student.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
GU Feng, WANG You-Wei, ZHENG Zhi-Hui, LIU Jian-Jun, LU Wen-Cong. Catalytic Mechanism of Palladium Catalyst for the Oxidation Reduction and Evolution Reaction of Lithium-air Battery[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1131-1135.

Fig. 1 Fcc, Hcp and Top sites on the Pd (111) surface of oxygen atoms from (a) top view and (b) main view, and (c) relationship between three kinds of adsorption sites on the coverage rate
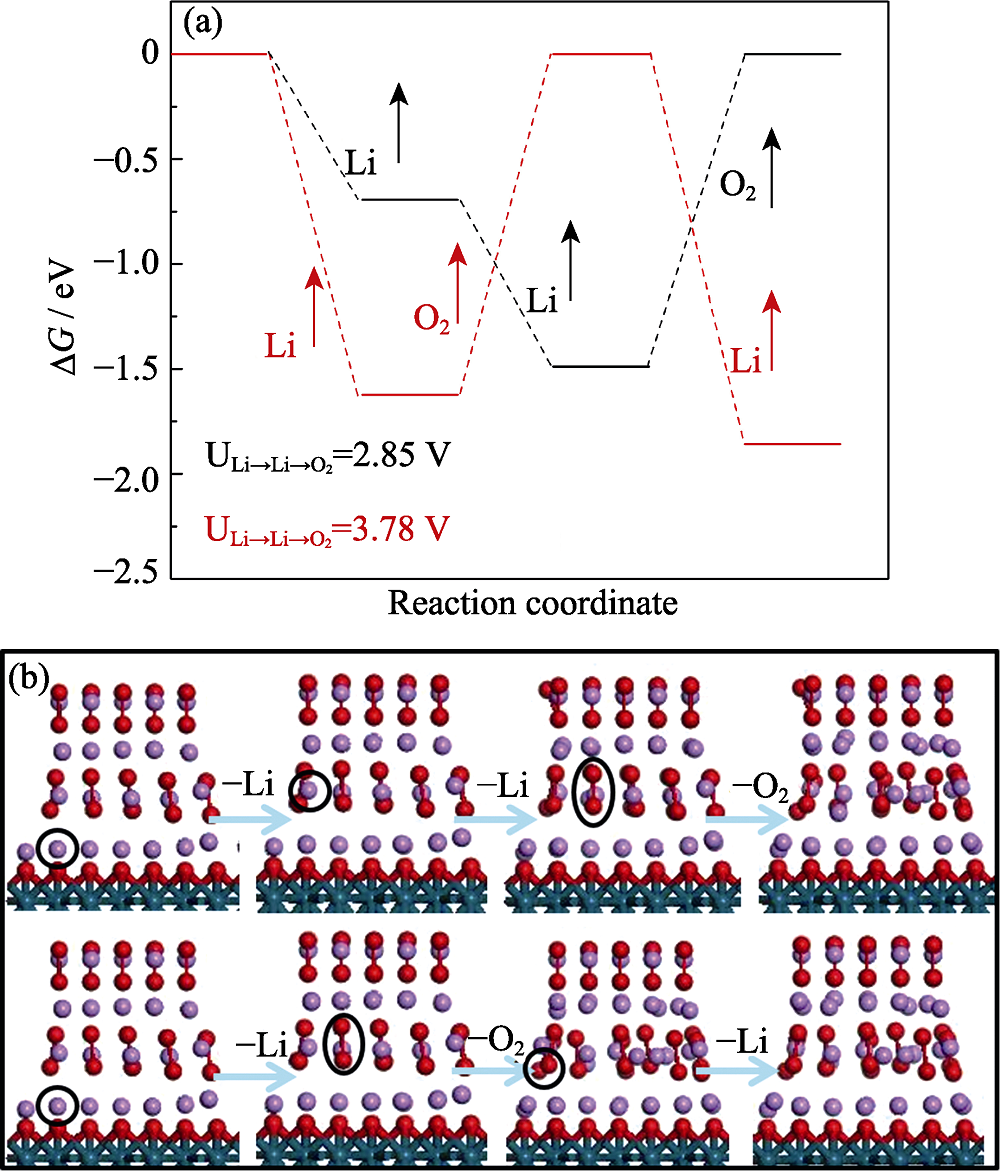
Fig. 2 (a) Energy profiles of two different oxygen evolution reaction paths of Li2O2 for Li+→Li+→O2 with charge voltage of 2.85 V (black line) and Li+→O2→Li+ with charge voltage of 3.78 V (red line); (b) Sketch maps of Li+→Li+→O2 and Li+→O2→ Li+ oxygen evolution reaction paths of Li2O2 with red ball indicating O, blue ball indicating Pd, and purple ball indicating Li
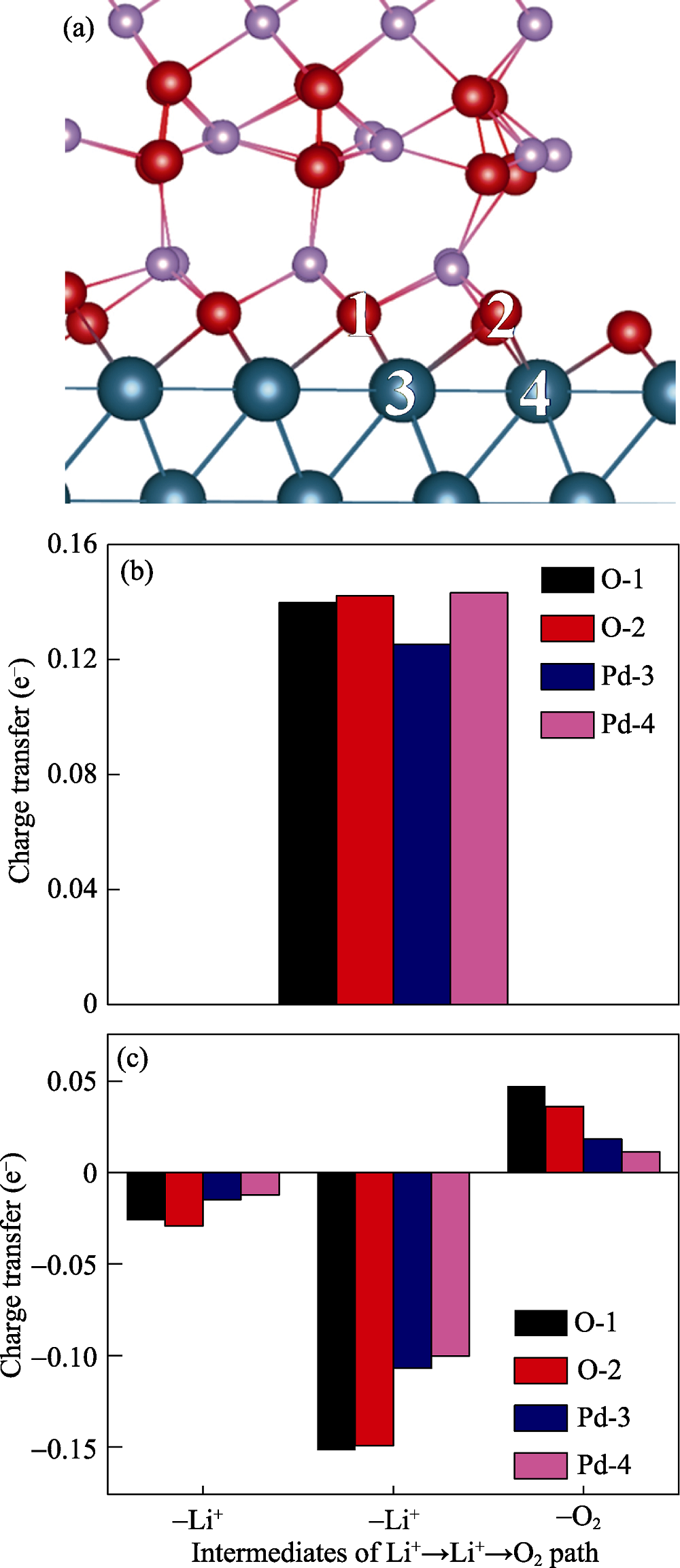
Fig. 3 (a) Calculated structure of Pd(111)/ Li2O2/O2 interface with red ball indicating O, blue ball indicating Pd, and purple ball indicating Li; (b) Bader charge analysis of O and Pd with oxygen reduction reaction of Li2O2, the calculated O atoms and Pd atoms in charge transfer analysis correspond to labeled O atoms and Pd atoms in figure (a); (c) Bader charge analysis of O and Pd with the oxygen evolution reaction of Li2O2, the calculated O atoms and Pd atoms in charge transfer analysis correspond to labeled O atoms and Pd atoms in figure (a)
| [1] | PENG Z Q, FREUNBERGER S A, CHEN Y H, et al. A reversible and higher-rate LiO2 battery. Science, 2012, 337(6094): 563-566. |
| [2] | GIRISHKUMAR G, MCCLOSKEY B, LUNTZ A C, et al. Lithium- air battery: promise and challenges. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2010, 1(14): 2193-2203. |
| [3] | SHAO Y Y, DING F, XIAO J et al. Making Li-air batteries rechargeable: material challenges. Advanced Functional Materials, 2013, 23(8): 987-1004. |
| [4] | LI F J, ZHANG T, ZHOU H S.Challenges of non-aqueous Li-O2 batteries: electrolytes, catalysts, and anodes.Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(4): 1125-1141. |
| [5] | CHRISTENSEN J, ALBERTUS P, SANCHEZ-CARRERA R S, et a. A critical review of Li/Air batteries. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(2): R1-R30. |
| [6] | JUNG H G, HASSOUN J, PARK J B, et al. An improved high-performance lithium-air battery. Nature Chemistry, 2012, 4(7): 579-585. |
| [7] | CHENG H, SCOTT K.Selection of oxygen reduction catalysts for rechargeable lithium-air batteries-metal or oxide?Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2011, 108(1/2): 140-151. |
| [8] | WANG L, ZHAO X, LU Y H, et al. CoMn2O4 spinel nanoparticles grown on graphene as bifunctional catalyst for lithium-air batteries. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2011, 158(12): A1379-A1382. |
| [9] | YANG W, SALIM J, LI S A, et al. Perovskite Sr0.95Ce0.05CoO3-δ loaded with copper nanoparticles as a bifunctional catalyst for lithium-air batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(36): 18902-18907. |
| [10] | DEBART A, BAO J, ARMSTRONG G, et al. An O2 cathode for rechargeable lithium batteries: the effect of a catalyst. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 174(2): 1177-1182. |
| [11] | DEBART A, PATERSON A J, BAO J, et al. α-MnO2 nanowires: a catalyst for the O2 electrode in rechargeable lithium batteries. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2008, 47(24): 4521-4524. |
| [12] | THAPA A K, SAIMEN K, ISHIHARA T.Pd/MnO2 air electrode catalyst for rechargeable lithium/air battery.Electrochemical and Solid State Letters, 2010, 13(11): A165-A167. |
| [13] | LU Y C, XU Z C, GASTEIGER H A,et al. Platinum-gold nanoparticles: a highly active bifunctional electrocatalyst for rechargeable lithium-air batteries. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(35): 12170-12171. |
| [14] | LI P F, ZHANG J K, YU Q L, et al. One-dimensional porous La0.5Sr0.5CoO2. 91 nanotubes as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for rechargeable lithium-oxygen batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 165: 78-84. |
| [15] | KALUBARME R S, PARK G E, JUNG K N, et al. LaNixCo1-xO3-δ perovskites as catalyst material for non-aqueous lithium-oxygen batteries. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2014, 161(6): A880-A889. |
| [16] | SUN N, LIU H X, YU Z Y, et al. The La0.6Sr0.4CoO3 perovskite catalyst for Li-O2 battery. Solid State Ionics, 2014, 268: 125-130. |
| [17] | ZHONG L, MITCHELL R R, LIU Y, et al. In situ transmission electron microscopy observations of electrochemical oxidation of Li2O2. Nano Letters, 2013, 13(5): 2209-2214. |
| [18] | LEI Y, LU J, LUO X, et al. Synthesis of porous carbon supported palladium nanoparticle catalysts by atomic layer deposition: application for rechargeable lithium-O2 battery. Nano Letters, 2013, 13(9): 4182-4189. |
| [19] | MA S, WU Y, WANG J, et al. Reversibility of noble metal- catalyzed aprotic Li-O2 batteries. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(12): 8084-8090. |
| [20] | KRESSE G, FURTHMULLER J.Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Computational Materials Science, 1996, 6(1): 15-50. |
| [21] | KRESSE G, FURTHMüLLER J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Physical Review B, 1996, 54(16): 11169-11186. |
| [22] | SETYAWAN W, CURTAROLO S.High-throughput electronic band structure calculations: challenges and tools.Computational Materials Science, 2010, 49(2): 299-312. |
| [23] | REUTER K, SCHEFFLER M.Composition, structure,stability of RuO2 (110) as a function of oxygen pressure. Physical Review B, 2001, 65(3): 035406-1-11. |
| [24] | REUTER K, SCHEFFLER M.Composition and structure of the RuO2 (110) surface in an O2 and CO environment: implications for the catalytic formation of CO2. Physical Review B, 2003, 68(4): 045407-1-11. |
| [25] | REUTER K, SCHEFFLER M. First-principles atomistic thermodynamics for oxidation catalysis: surface phase diagrams and catalytically interesting regions. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 90(4): 046103-1-4. |
| [26] | ZHANG W, SMITH J R, WANG X G. Thermodynamics from ab initio computations. Physical Review B, 2004, 70(2): 024103-1-8. |
| [27] | MO Y, ONG S P, CEDER G. First-principles study of the oxygen evolution reaction of lithium peroxide in the lithium-air battery. Physical Review B, 2011, 84(20): 205446-1-9. |
| [28] | WEAVER J F, CHEN J J, GERRARD A L.Oxidation of Pt(111) by gas-phase oxygen atoms.Surface Science, 2005, 592(1/2/3): 83-103. |
| [29] | PHATAK A A, DELGASS W N, RIBEIRO F H, et al Density functional theory comparison of water dissociation steps on Cu, Au, Ni, Pd, and Pt. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(17): 7269-7276. |
| [30] | WU C, SCHMIDT D J, WOLVERTON C,et al. Accurate coverage-dependence incorporated into first-principles kinetic models: catalytic NO oxidation on Pt(111). Journal of Catalysis, 2012, 286: 88-94. |
| [31] | TODOROVA M, REUTER K, SCHEFFLER M. Density- functional theory study of the initial oxygen incorporation in Pd (111). Physical Review B, 2005, 71(19): 195403-1-8. |
| [32] | REN X, ZHU J, DU F, et al. B-doped graphene as catalyst to improve charge rate of lithium air battery. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(39): 22412-22418. |
| [1] | GU Xuesu, YIN Jie, WANG Kanglong, CUI Chong, MEI Hui, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Effect of Particle Grading on Properties of Silicon Carbide Ceramics by Binder Jetting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 216-. |
| [2] | CHEN Yu, LIN Pu'an, CAI Bing, ZHANG Wenhua. Research Progress of Inorganic Hole Transport Materials in Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 105-. |
| [3] | TIAN Yubin, TIAN Chaofan, LI Sen, ZHAO Yongxin, XING Tao, LI Zhi, CHEN Xiaoru, XIANG Shuairong, DAI Pengcheng. Biomass-derived High-conductive Carbon Cloth: Preparation and Its Application as Gas Diffusion Layers in Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 127-. |
| [4] | JIANG Runlu, WU Xin, GUO Haocheng, ZHENG Qi, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. UiO-67 Based Conductive Composites: Preparation and its Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 197-. |
| [5] | LI Haiyan, KUANG Fenghua, WU Haolong, LIU Xiaogen, BAO Yiwang, WAN Detian. Temperature Dependence of Residual Tensile Stresses and its Influences on Crack Propagation Behaviour [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 214-. |
| [6] | FANG Wanli, SHEN Lili, LI Haiyan, CHEN Xinyu, CHEN Zongqi, SHOU Chunhui, ZHAO Bin, YANG Songwang. Effect of Film Formation Processes of NiOx Mesoporous Layer on Performance of Perovskite Solar Cells with Carbon Electrodes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 2-. |
| [7] | DING Tongshun, FENG Ping, SUN Xuewen, SHAN Husheng, LI Qi, SONG Jian. Perovskite Film Passivated by Fmoc-FF-OH and Its Photovoltaic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 50-. |
| [8] | XU Hao, QIAN Wei, HUA Yinqun, YE Yunxia, DAI Fengze, CAI Jie. Effects of Micro Texture Processed by Picosecond Laser on Hydrophobicity of Silicon Carbide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 73-. |
| [9] | QIU Haiyang, MIAO Guangtan, LI Hui, LUAN Qi, LIU Guoxia, SHAN Fukai. Effect of Plasma Treatment on the Long-term Plasticity of Synaptic Transistor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 406-412. |
| [10] | DU Jianyu, GE Chen. Recent Progress in Optoelectronic Artificial Synapse Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [11] | YANG Yang, CUI Hangyuan, ZHU Ying, WAN Changjin, WAN Qing. Research Progress of Flexible Neuromorphic Transistors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [12] | WU Junlin, DING Jiyang, HUANG Xinyou, ZHU Danyang, HUANG Dong, DAI Zhengfa, YANG Wenqin, JIANG Xingfen, ZHOU Jianrong, SUN Zhijia, LI Jiang. Fabrication and Microstructure of Gd2O2S:Tb Scintillation Ceramics from Water-bath Synthesized Nano-powders: Influence of H2SO4/Gd2O3 Molar Ratio [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 452-460. |
| [13] | CHEN Xinli, LI Yan, WANG Weisheng, SHI Zhiwen, ZHU Liqiang. Gelatin/Carboxylated Chitosan Gated Oxide Neuromorphic Transistor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 421-428. |
| [14] | YOU Junqi, LI Ce, YANG Dongliang, SUN Linfeng. Double Dielectric Layer Metal-oxide Memristor: Design and Applications [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [15] | FANG Renrui, REN Kuan, GUO Zeyu, XU Han, ZHANG Woyu, WANG Fei, ZHANG Peiwen, LI Yue, SHANG Dashan. Associative Learning with Oxide-based Electrolyte-gated Transistor Synapses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 399-405. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||