
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 307-312.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170169
Special Issue: 离子电池材料
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Bo, HAO Wen, WEN Xiao-Gang
Received:2017-04-12
Revised:2017-05-31
Published:2018-03-20
Online:2018-03-12
About author:LI Bo. E-mail: liboblieve@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LI Bo, HAO Wen, WEN Xiao-Gang. Semi-hollow/Solid ZnMn2O4 Microspheres: Synthesis and Performance in Li Ion Battery[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(3): 307-312.
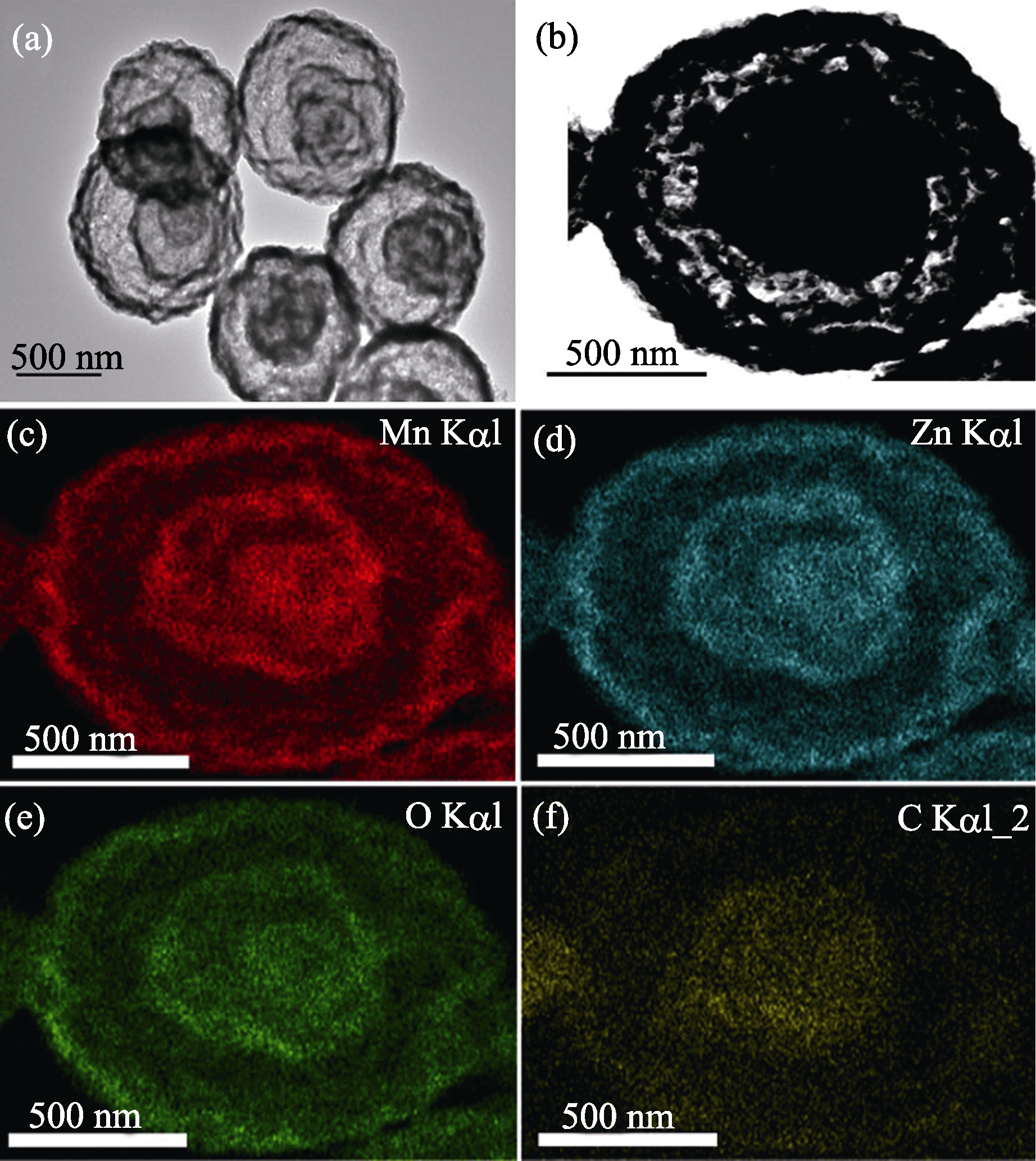
Fig. 4 TEM images and element mappings of the samples calcined at 600℃(a) Bright-field TEM image of ZnMn2O4 hollow microsheres, (b) Dark-field TEM image of a single ZnMn2O4 hollow microshere, (c-f) elements mapping of (c) Mn, (d) Zn, (e) O and (f) C in a single ZnMn2O4 microsphere
| [1] | BRUCE P G, SCROSATI B, TARASCON J M.Nanomaterials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2008, 47(16): 2930-2946. |
| [2] | YUVARAJ S, SELVAN R K, LEE Y S.An overview of AB2O4-and A2BO4-structured negative electrodes for advanced Li-ion batteries. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(26): 21448-21474. |
| [3] | TARASCON J M, ARMAND M.Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature, 2001, 414(6861): 359-367. |
| [4] | GUO B K, WANG X Q, FULVIO P F, et al.Soft-templated mesoporous carbon-carbon nanotube composites for high performance lithium-ion batteries. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(40): 4661-4666. |
| [5] | LAI J, GUO H J, WANG Z X, et al.Preparation and characterization of flake graphite/silicon/carbon spherical composite as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 530: 30-35. |
| [6] | LI H, WANG Z X, CHEN L Q, et al.Research on advanced materials for Li-ion batteries. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(45): 4593-4607. |
| [7] | WANG L, LIU B, RAN S H, et al.Facile synthesis and electrochemical properties of CoMn2O4 anodes for high capacity lithium- ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(6): 2139-2143. |
| [8] | HU L F, WU L M, LIAO M Y, et al.Electrical transport properties of large, individual NiCo2O4 nanoplates. Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(5): 998-1004. |
| [9] | ZHANG G Q, YU L, WU H B, et al.Formation of ZnMn2O4 ball-in-ball hollow microspheres as a high-performance anode for lithium-ion batteries. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(34): 4609-4613. |
| [10] | BAI Z C, FAN N, CHANG C H, et al.Facile synthesis of loaf-like ZnMn2O4 nanorods and their excellent performance in Li-ion batteries. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(6): 2442-2447. |
| [11] | DENG Y F, TANG S D, ZHANG Q M, et al.Controllable synthesis of spinel nano-ZnMn2O4 via a single source precursor route and its high capacity retention as anode material for lithium ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(32): 11987-11995. |
| [12] | ZHENG Z M, CHENG Y L, YAN X B, et al.Enhanced electrochemical properties of graphene-wrapped ZnMn2O4 nanorods for lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(1): 149-154. |
| [13] | ZHANG L H, ZHU S Q, CAO H, et al.Ultrafast spray pyrolysis fabrication of a nanophase ZnMn2O4 anode towards high- performance Li-ion batteries. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(18): 13667-13673. |
| [14] | ZHANG L H, ZHU S Q, CAO H, et al.Hierarchical porous ZnMn2O4 hollow nanotubes with enhanced lithium storage toward lithium-ion batteries. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2015, 21(30): 10771-10777. |
| [15] | ZHANG Y H, ZHANG Y W, GUO C L, et al.Porous ZnMn2O4 nanowires as an advanced anode material for lithium ion battery. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 182: 1140-1144. |
| [16] | LOBO L S, KUMAR A R.Investigation of structural and electrical properties of ZnMn2O4 synthesized by Sol-Gel method. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2016, 27(7): 7398-7406. |
| [17] | ZENG X Y, SHI L X, LI L J, et al.The preparation of flowerlike ZnMn2O4 microspheres assembled with porous nanosheets and their lithium battery performance as anode materials. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(86): 70379-70386. |
| [18] | ZHU S Q, SHI Y Y, CHEN Q L, et al.Self-sacrificial template formation of ultrathin single-crystalline ZnMn2O4 nanoplates with enhanced Li-storage behaviors for Li-ion batteries. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(3): 2024-2027. |
| [19] | GUO N, WEI X Q, DENG X L, et al.Synthesis and property of spinel porous ZnMn2O4 microspheres. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 356: 1127-1134. |
| [20] | LUO L, QIAO H, CHEN K, et al.Fabrication of electrospun ZnMn2O4 nanofibers as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 177: 283-289. |
| [1] | YANG Zhuo, LU Yong, ZHAO Qing, CHEN Jun. X-ray Diffraction Rietveld Refinement and Its Application in Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [2] | SU Nana, HAN Jingru, GUO Yinhao, WANG Chenyu, SHI Wenhua, WU Liang, HU Zhiyi, LIU Jing, LI Yu, SU Baolian. ZIF-8-derived Three-dimensional Silicon-carbon Network Composite for High-performance Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1016-1022. |
| [3] | WANG Yang, FAN Guangxin, LIU Pei, YIN Jinpei, LIU Baozhong, ZHU Linjian, LUO Chengguo. Microscopic Mechanism of K+ Doping on Performance of Lithium Manganese Cathode for Li-ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1023-1029. |
| [4] | ZHU Hezhen, WANG Xuanpeng, HAN Kang, YANG Chen, WAN Ruizhe, WU Liming, MAI Liqiang. Enhanced Lithium Storage Stability Mechanism of Ultra-high Nickel LiNi0.91Co0.06Al0.03O2@Ca3(PO4)2 Cathode Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1030-1036. |
| [5] | FENG Kun, ZHU Yong, ZHANG Kaiqiang, CHEN Zhang, LIU Yu, GAO Yanfeng. Boehmite Nanosheets-coated Separator with Enhanced Performance for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1009-1015. |
| [6] | CHEN Ying, LUAN Weiling, CHEN Haofeng, ZHU Xuanchen. Multi-scale Failure Behavior of Cathode in Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Stress Field [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 918-924. |
| [7] | WANG Yutong, ZHANG Feifan, XU Naicai, WANG Chunxia, CUI Lishan, HUANG Guoyong. Research Progress of LiTi2(PO4)3 Anode for Aqueous Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 481-492. |
| [8] | LI Kunru, HU Xinghui, ZHANG Zhengfu, GUO Yuzhong, HUANG Ruian. Three-dimensional Porous Biogenic Si/C Composite for High Performance Lithium-ion Battery Anode Derived from Equisetum Fluviatile [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 929-935. |
| [9] | WANG Ying, ZHANG Wenlong, XING Yanfeng, CAO suqun, DAI Xinyi, LI Jingze. Performance of Amorphous Lithium Phosphate Coated Lithium Titanate Electrodes in Extended Working Range of 0.01-3.00 V [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 999-1005. |
| [10] | WANG Juhan,WEN Xiong,LIU Chengchao,ZHANG Yuhua,ZHAO Yanxi,LI Jinlin. Preparation and Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Performance of Hierarchical Co/Al-SiO2 Catalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 999-1004. |
| [11] | LU Xiaoqing,WANG Maohuai. Theoretical Investigation on Adsorption and Separation of CO2/N2 in Hybrid Ultramicroporous Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 469-474. |
| [12] | CHENG Fu-Qiang,JI Tian-Tian,XUE Min,MENG Zi-Hui,WU Yu-Kai. Thiohydroxy-functionalized Mesoporous Materials: Preparation and its Adsorption to Cr6+ [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 193-198. |
| [13] | WANG Yanan, LI Hua, WANG Zhengkun, LI Qingfeng, LIAN Chen, HE Xin. Progress on Failure Mechanism of Lithium Ion Battery Caused by Diffusion Induced Stress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1071-1087. |
| [14] | Jian-Huang KE, Kai XIE, Yu HAN, Wei-Wei SUN, Shi-Qiang LUO, Jin-Feng LIU. Morphology Controlling of the High-voltage Cathode Materials with Different Co-solvents [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 618-624. |
| [15] | SUI Li-Li, WANG Run, ZHAO Dan, SHEN Shu-Chang, SUN Li, XU Ying-Ming, CHENG Xiao-Li, HUO Li-Hua. Construction of Hierarchical α-MoO3 Hollow Microspheres and Its High Adsorption Performance towards Organic Dyes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 193-200. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||