
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 93-99.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170164
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
HAO Yan-Xia1,2, QIAN Meng1,2, XU Ji-Jian1, BI Hui1, HUANG Fu-Qiang1,3
Received:2017-04-10
Published:2018-01-23
Online:2017-12-15
Supported by:CLC Number:
HAO Yan-Xia, QIAN Meng, XU Ji-Jian, BI Hui, HUANG Fu-Qiang. Porous Cotton-derived Carbon: Synthesis, Microstructure and Supercapacitive Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(1): 93-99.
| Sample | SBET/(m2•g-1) | VtI/(m3•g-1) | VmII/(m3•g-1) | N/% | (N-5)/% | (N-6)/% | (N-Q)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 397 | 0.1312 | 0.1312 | / | / | / | / |
| CDC-550 | 403 | 0.2682 | 0.1127 | 6.15 | 28.65 | 25.47 | 45.88 |
| CDC-650 | 460 | 0.2619 | 0.1403 | 6.52 | 32.53 | 25.31 | 42.16 |
| CDC-750 | 480 | 0.2458 | 0.1576 | 6.84 | 47.14 | 20.98 | 31.88 |
Table 1 Porous properties and elements composition of the obtained samples
| Sample | SBET/(m2•g-1) | VtI/(m3•g-1) | VmII/(m3•g-1) | N/% | (N-5)/% | (N-6)/% | (N-Q)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | 397 | 0.1312 | 0.1312 | / | / | / | / |
| CDC-550 | 403 | 0.2682 | 0.1127 | 6.15 | 28.65 | 25.47 | 45.88 |
| CDC-650 | 460 | 0.2619 | 0.1403 | 6.52 | 32.53 | 25.31 | 42.16 |
| CDC-750 | 480 | 0.2458 | 0.1576 | 6.84 | 47.14 | 20.98 | 31.88 |
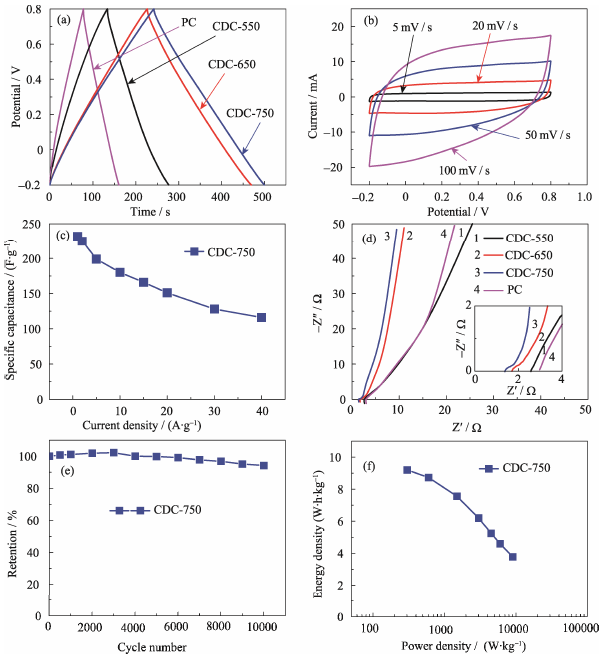
Fig. 5 (a) GCD curves of samples at a current density of 1 A/g, (b) CV curves of CDC-750 at different scan rates, (c) specific capacitance of CDC-750 at different current densities, (d) EIS spectra of the obtained samples, (e) cycle performance of CDC-750 at a current density of 15 A/g, and (f) Ragone plot of symmetrical cell structure of CDC-750
| [1] | ZHU Y, MURALI S, STOLLER M D, et al.Carbon-based supercapacitors produced by activation of graphene. Science, 2011, 332(6037): 1537-1541. |
| [2] | THOUNTHONG P, RAËL S, DAVAT B. Control strategy of fuel cell/supercapacitors hybrid power sources for electric vehicle.J. Power Sources, 2006, 158(1): 806-814. |
| [3] | ZHANG L L, ZHAO X S.Carbon-based materials as supercapacitor electrodes.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38(9): 2520-2531. |
| [4] | FAN L Z, MAIER J.High-performance polypyrrole electrode materials for redox supercapacitors.Electrochem. Commun., 2006, 8(6): 937-940. |
| [5] | LI M, XUE J.Integrated synthesis of nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon from melamine resins with superior performance in supercapacitors.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118(5): 2507-2517. |
| [6] | BI R R, WU X L, CAO F F, et al.Highly dispersed RuO2 nanoparticles on carbon nanotubes: facile synthesis and enhanced supercapacitance performance. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114(6): 2448-2451. |
| [7] | KIM H, POPOV B N.Synthesis and characterization of MnO2-based mixed oxides as supercapacitors.J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, 150(3): D56-D62. |
| [8] | PANDOLFO A G, HOLLENKAMP A F.Carbon properties and their role in supercapacitors.J. Power Sources, 2006, 157(1): 11-27. |
| [9] | LIN T, CHEN I W, LIU F, et al.Nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon of extraordinary capacitance for electrochemical energy storage. Science, 2015, 350(6267): 1508-1513. |
| [10] | LIU C, YU Z, NEFF D, et al.Graphene-based supercapacitor with an ultrahigh energy density.Nano lett., 2010, 10(12): 4863-4868. |
| [11] | LIANG Q, YE L, HUANG Z H, et al.A honeycomb-like porous carbon derived from pomelo peel for use in high-performance supercapacitors.Nanoscale, 2014, 6(22): 13831-13837. |
| [12] | CHEN M, KANG X, WUMAIER T, et al.Preparation of activated carbon from cotton stalk and its application in supercapacitor.J. Solid State Electrochem., 2013, 17(4): 1005-1012. |
| [13] | WANG K, ZHAO N, LEI S, et al.Promising biomass-based activated carbons derived from willow catkins for high performance supercapacitors.Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 166: 1-11. |
| [14] | WANG L, MU G, TIAN C, et al.Porous graphitic carbon nanosheets derived from cornstalk biomass for advanced supercapacitors.ChemSusChem, 2013, 6(5): 880-889. |
| [15] | YANG C S, JANG Y S, JEONG H K.Bamboo-based activated carbon for supercapacitor applications.Curr. Appl. Phys., 2014, 14(12): 1616-1620. |
| [16] | WANG S, REN Z, LI J, et al.Cotton-based hollow carbon fibers with high specific surface area prepared by ammonia etching for supercapacitor application.RSC Adv., 2014, 4(59): 31300-31307. |
| [17] | AHMADPOUR A, DO D D.The preparation of active carbons from coal by chemical and physical activation.Carbon, 1996, 34(4): 471-479. |
| [18] | RODRIGUEZ-REINOSO F, MOLINA-SABIO M.Activated carbons from lignocellulosic materials by chemical and/or physical activation: an overview.Carbon, 1992, 30(7): 1111-1118. |
| [19] | LILLO-RÓDENAS M A, CAZORLA-AMORÓS D, LINARES- SOLANO A. Understanding chemical reactions between carbons and NaOH and KOH: an insight into the chemical activation mechanism. Carbon, 2003, 41(2): 267-275. |
| [20] | FRACKOWIAK E, METENIER K, BERTAGNA V.Supercapacitor electrodes from multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2000, 77: 2421-2423. |
| [21] | XU J, DING W, ZHAO W, et al.In situ growth enabling ideal graphene encapsulation upon mesocrystalline MTiO3 (M= Ni, Co, Fe) Nanorods for stable lithium storage.ACS Energy Lett., 2017, 2: 659-663. |
| [22] | GAMBY J, TABERNA P L, SIMON P, et al.Studies and characterisations of various activated carbons used for carbon/ carbon supercapacitors. J. Power Sources, 2001, 101(1): 109-116. |
| [23] | HAO Y, XU F, QIAN M, et al.Low-cost and massive preparation of nitrogen-doped porous carbon for supercapacitor application. RSC Adv., 2017, 7(18): 10901-10905. |
| [24] | ZHENG C, ZHOU X, CAO H, et al.Synthesis of porous graphene/activated carbon composite with high packing density and large specific surface area for supercapacitor electrode material.J. Power Sources, 2014, 258: 290-296. |
| [25] | XU J, DONG W, SONG C, et al.Black rutile (Sn, Ti)O2 initializing electrochemically reversible Sn nanodots embedded in amorphous lithiated titania matrix for efficient lithium storage.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4(40): 15698-15704. |
| [26] | YOU B, WANG L, YAO L, et al.Three dimensional N-doped graphene-CNT networks for supercapacitor.Chem. Commun., 2013, 49(44): 5016-5018. |
| [27] | LI L, ZHONG Q, KIM N D, et al.Nitrogen-doped carbonized cotton for highly flexible supercapacitors.Carbon, 2016, 105: 260-267. |
| [28] | LU B, HU L, YIN H, et al.Preparation and application of capacitive carbon from bamboo shells by one step molten carbonates carbonization. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(41): 18713-18720. |
| [29] | CHEN L F, ZHANG X D, LIANG H W, et al.Synthesis of nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanofibers as an efficient electrode material for supercapacitors.ACS nano, 2012, 6(8): 7092-7102. |
| [30] | KIM T, JUNG G, YOO S, et al.Activated graphene-based carbons as supercapacitor electrodes with macro-and mesopores. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(8): 6899-6905. |
| [31] | SUBRAMANIAN V, LUO C, STEPHAN A M, et al.Supercapacitors from activated carbon derived from banana fibers.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(20): 7527-7531. |
| [32] | KIM C, CHOI Y O, LEE W J, et al.Supercapacitor performances of activated carbon fiber webs prepared by electrospinning of PMDA-ODA poly (amic acid) solutions.Electrochim. Acta, 2004, 50(2): 883-887. |
| [33] | KALPANA D, CHO S H, LEE S B, et al.Recycled waste paper-a new source of raw material for electric double-layer capacitors.J. Power Sources, 2009, 190(2): 587-591. |
| [1] | DING Ling, JIANG Rui, TANG Zilong, YANG Yunqiong. MXene: Nanoengineering and Application as Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | WU Xishi, ZHU Yunzhou, HUANG Qing, HUANG Zhengren. Effect of Pore Structure of Organic Resin-based Porous Carbon on Joining Properties of Cf/SiC Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1275-1280. |
| [3] | SUN Peng, ZHANG Shaoning, BI Hui, DONG Wujie, HUANG Fuqiang. Tuning Nitrogen Species and Content in Carbon Materials through Constructing Variable Structures for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 766-772. |
| [4] | LIU Fangfang, CHUAN Xiuyun, YANG Yang, LI Aijun. Influence of N/S Co-doping on Electrochemical Property of Brucite Template Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 711-717. |
| [5] | WANG Yiliang, AI Yunlong, YANG Shuwei, LIANG Bingliang, ZHENG Zhenhuan, OUYANG Sheng, HE Wen, CHEN Weihua, LIU Changhong, ZHANG Jianjun, LIU Zhiyong. Facile Synthesis and Supercapacitor Performance of M3O4(M=FeCoCrMnMg) High Entropy Oxide Powders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 425-430. |
| [6] | TANG Jiawei, WANG Yongbang, MA Cheng, YANG Haixiao, WANG Jitong, QIAO Wenming, LING Licheng. Methylnaphthalene Pitch-based Ordered Mesoporous Carbon: Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1031-1038. |
| [7] | CHENG Xiaokun, ZHANG Yue, Lü Haijun, LIU Xinying, HOU Senlin, CHEN Aibing. Porous Carbon Nanomaterials Based Tumor Targeting Drug Delivery System: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 9-24. |
| [8] | LI Zehui,TAN Meijuan,ZHENG Yuanhao,LUO Yuyang,JING Qiushi,JIANG Jingkun,LI Mingjie. Application of Conductive Metal Organic Frameworks in Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 769-780. |
| [9] | CHEN Jun,MA Pei-Hua,ZHANG Cheng,Laurent RUHLMANN,LYU Yao-Kang. Preparation and Electrochemical Property of New Multifunctional Inorganic/Organic Composite Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 217-223. |
| [10] | FEI Mingjie, ZHANG Renping, ZHU Guisheng, YU Zhaozhe, YAN Dongliang. Preparation and Pseudocapacitive Properties of Phosphate Ion-doped MnFe2O4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1137-1141. |
| [11] | DING Zhuofeng, YANG Yongqiang, LI Zaijun. Synthesis and Supercapacitor Performance of Histidine-functionalized Carbon Dots/Graphene Aerogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1130-1136. |
| [12] | LI Teng-Fei, HUANG Lu-Jun, YAN Xu-Dong, LIU Qing-Lei, GU Jia-Jun. Ti3C2Tx/Wood Carbon as High-areal-capacity Electrodes for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 126-130. |
| [13] | ZHANG Tian-Yu, CUI Cong, CHENG Ren-Fei, HU Min-Min, WANG Xiao-Hui. Fabrication of Planar Porous MXene/Carbon Composite Electrodes by Simultaneous Ammonization/Carbonization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 112-118. |
| [14] | MA Ya-Nan, LIU Yu-Fei, YU Chen-Xu, ZHANG Chuan-Kun, LUO Shi-Jun, GAO Yi-Hua. Monolayer Ti3C2Tx Nanosheets with Different Lateral Dimension: Preparation and Electrochemical Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 93-98. |
| [15] | Wei-Jia XU, Da-Ping QIU, Shi-Qiang LIU, Min LI, Ru YANG. Preparation of Cork-derived Porous Activated Carbon for High Performance Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 625-632. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||