
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 1171-1176.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170051
Special Issue: 庆祝上海硅酸盐所独立建所60周年虚拟专刊!
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
QIN Yu-Ting1,2, QIU Peng-Fei1, SHI Xun1, CHEN Li-Dong1
Published:2017-11-20
Online:2017-10-20
CLC Number:
QIN Yu-Ting, QIU Peng-Fei, SHI Xun, CHEN Li-Dong. ThermoelectricProperties for CuInTe2-xSx (x = 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15) Solid Solution[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(11): 1171-1176.
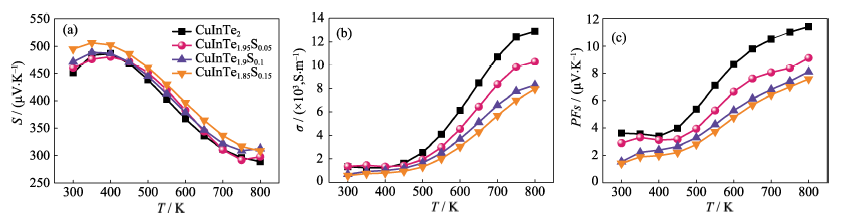
Fig. 3 Temperature dependences of (a) Seebeck coefficient (S), (b) electrical conductivity (σ), and (c) power factors (PFs) for CuInTe2-xSx (x = 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15) compounds
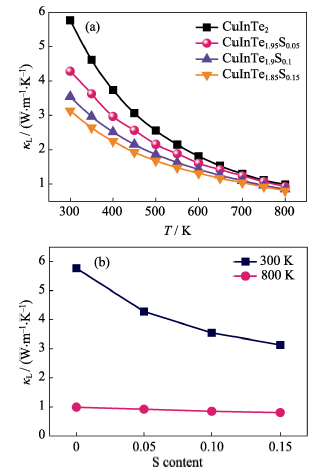
Fig.5 Temperature dependence of thermal conductivity κ (a)and lattice thermal conductivity κL as a function of S contentat 300Κ and 800Κ (b) for CuInTe2-xSx (x = 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15) compounds
| [1] | SHI X, CHEN L D, UHER C.Recent advances in high-performance bulk thermoelectric materials.International Materials Reviews, 2016, 61(6): 379-415. |
| [2] | QIU P F, SHI X, CHEN L D.Cu-based thermoelectric materials.Energy Storage Materials, 2016, 3: 85-97. |
| [3] | GOLDSMID H. Electronic Refrigeration. Pion Limited, 1986. |
| [4] | TRITT TM, SUBRAMANIAN M A.Thermoelectric materials, phenomena, and applications: a bird's eye view.Mrs. Bulletin, 2006, 31(3): 188-194. |
| [5] | SNYDER G J, TOBERER E S.Complex thermoelectric materials.Nature Materials, 2008, 7(2): 105-114. |
| [6] | JOSHI G, LEE H, LAN Y C,et al. Enhanced thermoelectric figure-of-merit in nanostructured p-type silicon germanium bulk alloys. Nano Letters, 2008, 8(12): 4670-4674. |
| [7] | YANG X Y, WU J H, REN D D,et al. Microstructure and thermoelectric properties of p-type Si80Ge20B0.6-SiC nanocomposite. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(9): 997-1003. |
| [8] | HU L P, ZHU T J, WANG Y G,et al. Shifting up the optimum figure of merit of p-type bismuth telluride-based thermoelectric materials for power generation by suppressing intrinsic conduction. Npg Asia Materials, 2014, 6: e88. |
| [9] | SHI X, YANG J, SALVADOR J R,et al. Multiple-filled skutterudites: high thermoelectric figure of merit through separately optimizing electrical and thermal transports. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011,133(5):7837-7846. |
| [10] | ZONG P A, CHEN L D.Preparation and mechanical properties of Ce0.85Fe3CoSb12/rGOthermoelectric nanocomposite.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 33-38. |
| [11] | DING J, LIU R H, GU H,et al. Study on the high temperature stabilityof YbyCo4Sb12/Yb2O3composite thermoelectric material.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(2): 209-214. |
| [12] | TANG Y S, BAI S Q, REN DD,et al.Interface structure and electrical property of Yb0.3Co4Sb12Mo-Cuelement prepared by welding using Ag-Cu-Zn solder. Journal ofInorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 256-260. |
| [13] | CAILLAT T, BORSHCHEVSKY A, FLEURIAL J P.Properties of single crystalline semiconducting CoSb3.Journal of Applied Physics, 1996, 80(8): 4442-4449. |
| [14] | PEI Y Z, LALONDE A, IWANAGA S,et al. High thermoelectric figure of merit in heavy hole dominated PbTe. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(6): 2085-2089. |
| [15] | LIU R H, XI L L, LIU H L,et al. Ternary compound CuInTe2: a promising thermoelectric material with diamond-like structure. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(32): 3818-3820. |
| [16] | PLIRDPRING T, KUROSAKI K, KOSUGA A,et al. Chalcopyrite CuGaTe2: a high-efficiency bulk thermoelectric material. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(27): 3622-3626. |
| [17] | LV Y H, CHEN J K, DOEBELI M,et al. Congruent growth of Cu2Se thermoelectric thin films enabled by using high ablation fluence during pulsed laser deposition. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(10):1115-1120. |
| [18] | LIU H L, SHI X, XU F F,et al. Copper ion liquid-like thermoelectrics. Nature Materials, 2012, 11(5): 422-425. |
| [19] | LIU H L, YUAN X, LU P,et al. Ultrahigh thermoelectric performance by electron and phonon critical scattering in Cu2Se1-xIx. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(45): 6607-6612. |
| [20] | HE Y, DAY T, ZHANG T S,et al. High thermoelectric performance in non-toxic earth-abundant copper sulfide. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(23): 3974-3978. |
| [21] | HE Y, LU P, SHI X,et al. Ultrahigh thermoelectric performance in mosaic crystals. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(24): 3639-3644. |
| [22] | HE Y, ZHANG T S, SHI X,et al. High thermoelectric performance in copper telluride. NPG Asia Materials, 2015,7: e210. |
| [23] | SHI X Y, XI L L, FAN J,et al. Cu-Se bond network and thermoelectric compounds with complex diamondlike structure. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22(22): 6029-6031. |
| [24] | SHI X Y, HUANG F Q, LIU M L,et al. Thermoelectric properties of tetrahedrally bonded wide-gap stannite compounds Cu2ZnSn1-xInxSe4.Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 94(12): 122103. |
| [25] | LIU M L, CHEN I W, HUANG F Q,et al. Improved thermoelectric properties of Cu-doped quaternary chalcogenides of Cu2CdSnSe4. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(37): 3808-3812. |
| [26] | LI D, LI R, QIN X Y,et al. Co-precipitation synthesis of Sn and/or S doped nanostructured Cu3Sb1-xSnxSe4-ySy with a high thermoelectric performance. CrystEngComm, 2013, 15(36): 7166. |
| [27] | YUSUFU A, KUROSAKI K, KOSUGA A,et al. Thermoelectric properties of Ag1-xGaTe2 with chalcopyrite structure. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(6): 061902. |
| [28] | QIN Y T, QIU P F, LIU R H,et al. Optimized thermoelectric properties in pseudocubic diamond-like CuGaTe2 compounds. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(4): 1277-1289. |
| [29] | ZHANG J, LIU R, CHENG N,et al. High-performance pseudocubic thermoelectric materials from non-cubic chalcopyrite compounds. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(23): 3848-3853. |
| [30] | CHENG N, LIU R, BAI S,et al. Enhanced thermoelectric performance in Cd doped CuInTe2 compounds. Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 115(16): 7. |
| [31] | SUZMURA A, WATANABE M, NAGASAKO N,et al. Improvement in thermoelectric properties of Se-free Cu3SbS4 compound. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2014, 43(6): 2356-2361. |
| [32] | WANG H, LALONDE AD, PEI Y, et al. The criteria for beneficial disorder in thermoelectric solid solutions.Advanced Functional Material, 2013, 23(12): 1586-1596. |
| [33] | LIU R H, QIN Y T, CHENG N,et al. Thermoelectric performance of Cu1-x-deltaAgxInTe2 diamond-like materials with a pseudocubic crystal structure. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2016, 3(9): 1167-1177. |
| [34] | LI Y P, MENG Q S, DENG Y,et al. High thermoelectric performance of solid solutions CuGa1-xInxTe2 (x=0-1.0). Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 100(23): 4. |
| [35] | BENCHIKHI M, OUATIB R E, ER-RAKHO L,et al. Synthesis and characterization of CuInS2 nanocrystals prepared bysolvothermal/molten salt method. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(9): 11303-11308. |
| [36] | XIE H, SU X, ZHENG G,et al. The role of Zn in chalcopyrite CuFeS2: enhanced thermoelectric properties of Cu1-xZnxFeS2 with in situ nanoprecipitates. Advanced Energy Material, 2016,7(3):1601299. |
| [37] | SLACK G A, Thermal conductivity of potassium chloride crystals containing calcium.Physical Review, 1957, 105(3): 832-842. |
| [38] | ABELES B.Lattice thermal conductivity of disordered semiconductor alloys at high temperatures. Physical Review, 1963, 131(5):1906-1911. |
| [39] | RINCON C, VALERIGIL M L, WASIM S M.Room-temperature thermal conductivity and Grüneisen parameter of the I-III-VI2 chalcopyrite compounds.Physica Status Solidi A-Applications and Materials Science, 1995, 147(2): 409-415. |
| [40] | FERNANDEZ B, WASIM S M.Sound velocities and elastic-moduli in CuInTe2 and CuInSe2.Physica Status Solidi A-Applied Research,1990, 122(1): 235-242. |
| [1] | WANG Bo, YU Jian, LI Cuncheng, NIE Xiaolei, ZHU Wanting, WEI Ping, ZHAO Wenyu, ZHANG Qingjie. Service Stability of Gd/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 Thermo-electro-magnetic Gradient Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 663-670. |
| [2] | HE Danqi, WEI Mingxu, LIU Ruizhi, TANG Zhixin, ZHAI Pengcheng, ZHAO Wenyu. Heavy-Fermion YbAl3 Materials: One-step Synthesis and Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [3] | LIN Siqi, LI Airan, FU Chenguang, LI Rongbing, JIN Min. Crystal Growth and Thermoelectric Properties of Zintl Phase Mg3X2 (X=Sb, Bi) Based Materials: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [4] | HUA Siheng, YANG Dongwang, TANG Hao, YUAN Xiong, ZHAN Ruoyu, XU Zhuoming, LYU Jianan, XIAO Yani, YAN Yonggao, TANG Xinfeng. Effect of Surface Treatment of n-type Bi2Te3-based Materials on the Properties of Thermoelectric Units [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 163-169. |
| [5] | WANG Pengjiang, KANG Huijun, YANG Xiong, LIU Ying, CHENG Cheng, WANG Tongmin. Inhibition of Lattice Thermal Conductivity of ZrNiSn-based Half-Heusler Thermoelectric Materials by Entropy Adjustment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 717-723. |
| [6] | CHENG Cheng, LI Jianbo, TIAN Zhen, WANG Pengjiang, KANG Huijun, WANG Tongmin. Thermoelectric Property of In2O3/InNbO4 Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 724-730. |
| [7] | LOU Xunuo, DENG Houquan, LI Shuang, ZHANG Qingtang, XIONG Wenjie, TANG Guodong. Thermal and Electrcial Transport Properities of Ge Doped MnTe Thermoelectrics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 209-214. |
| [8] | LIU Dan, ZHAO Yaxin, GUO Rui, LIU Yantao, ZHANG Zhidong, ZHANG Zengxing, XUE Chenyang. Effect of Annealing Conditions on Thermoelectric Properties of Magnetron Sputtered MgO-Ag3Sb-Sb2O4 Flexible Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1302-1310. |
| [9] | REN PeiAn, WANG Cong, ZI Peng, TAO Qirui, SU Xianli, TANG Xinfeng. Effect of Te and In Co-doping on Thermoelectric Properties of Cu2SnSe3 Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1079-1086. |
| [10] | JIN Min, BAI Xudong, ZHANG Rulin, ZHOU Lina, LI Rongbin. Metal Sulfide Ag2S: Fabrication via Zone Melting Method and Its Thermoelectric Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 101-106. |
| [11] | YANG Dongwang, LUO Tingting, SU Xianli, WU Jinsong, TANG Xinfeng. Unveiling the Intrinsic Low Thermal Conductivity of BiAgSeS through Entropy Engineering in SHS Kinetic Process [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 991-998. |
| [12] | ZHANG Cencen, WANG Xue, PENG Liangming. Thermoelectric Transport Characteristics of n-type (PbTe)1-x-y(PbS)x(Sb2Se3)y Systems via Stepwise Addition of Dual Components [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 936-942. |
| [13] | LU Xu, HOU Jichong, ZHANG Qiang, FAN Jianfeng, CHEN Shaoping, WANG Xiaomin. Effect of Mg Content on Thermoelectric Property of Mg3(1+z)Sb2 Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 835-840. |
| [14] | CAI Jianfeng, WANG Hongxiang, LIU Guoqiang, JIANG Jun. Designing High Entropy Structure in Thermoelectrics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 399-404. |
| [15] | YANG Qingyu, QIU Pengfei, SHI Xun, CHEN Lidong. Application of Entropy Engineering in Thermoelectrics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 347-354. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||