
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (5): 523-528.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160427
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIAO Fan1, MA Jian-Qi1, 2, 3, GE Hong-Guang2, 3
Received:2016-07-18
Revised:2016-09-09
Published:2017-05-20
Online:2017-05-02
About author:LIAO Fan. E-mail: frank_leon@163.com
CLC Number:
LIAO Fan, MA Jian-Qi, GE Hong-Guang. Preparation, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Core-satellite Ag/PDA@SiO2@CoFe2O4 Magnetic Composites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 523-528.
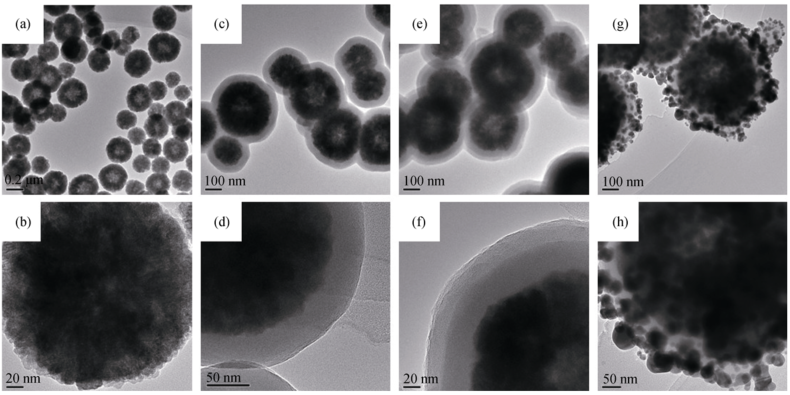
Fig. 1 TEM images of magnetic nanoparticles (a, b), silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles (c, d), polydopamine coated SiO2@CoFe2O4 (e, f) and Ag/PDA@SiO2@CoFe2O4 (g, h) NPs
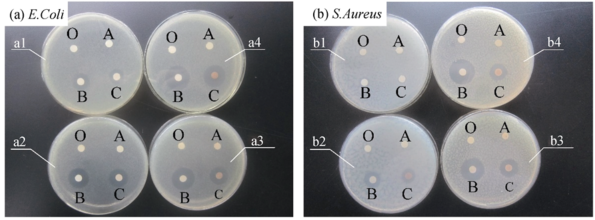
Fig. 5 Inhibition zones of Sterile water, PDA@SiO2@CoFe2O4, Ag/PDA@SiO2@CoFe2O4 and Ag NPs against (a) E.Coli and (b) B.Subtilis (a1-a4, b1-b4 samples containing Ag at concentrations of 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, and 0.8 mg /mL)
| Concentration/(mg·mL-1) | E.coli Inhibition zones/cm | B.subtilis Inhibition zones/cm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | C | B | C | |
| 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| 0.8 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 0.7 |
Table 1 Inhibition zone diameters of the Ag/PDA@SiO2@CoFe2O4 and Ag NPs against E.coli and S.aureas (Diffusion (cm) = final inhibition zonediameter(cm)-initial diameter(cm)
| Concentration/(mg·mL-1) | E.coli Inhibition zones/cm | B.subtilis Inhibition zones/cm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | C | B | C | |
| 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| 0.8 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 0.7 |
| [1] | HOLMES J D, LYONS D M, ZIEGLER K J.Supercritical fluid synthesis of metal and semiconductor nanomaterials.Chemistry, 2003, 9(10): 2145-2151. |
| [2] | VERIANSYAH B, KIM J D, MIN B K, et al.Continuous synthesis of surface-modified zinc oxide nanoparticles in supercritical methanol.the Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 2010, 52: 76-83. |
| [3] | GHODAKE G, LIM S R, LEE D S.Casein hydrolytic peptides mediated green synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles.Colloids & Surfaces B Biointerfaces, 2013, 108(4): 147-151. |
| [4] | VAIDYANATHAN R, KALISHWARALAL K, GOPALRAM S, et al.Nanosilver--the burgeoning therapeutic molecule and its green synthesis.Biotechnology Advances, 2009, 27(6): 924-937. |
| [5] | BORM P J, ROBBINS D, HAUBOLD S, et al.The potential risks of nanomaterials: a review carried out for ECETOC.Particle & Fibre Toxicology, 2006, 3(3): 1-35. |
| [6] | WANG D P, ZENG H C.Creation of interior space, architecture of shell structure, and encapsulation of functional materials for mes- oporous SiO2 spheres.Chemistry of Materials, 2011, 23(22): 4886-4899. |
| [7] | HOFFMANN F, CORNELIUS M, MORELL J, et al.Silica-based mesoporous organic-inorganic hybrid materials.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2006, 45: 3216-3251. |
| [8] | YIN H, YE Y, ZHANG Y, et al.Phosphate removal from wastewaters by a naturally occurring, calcium-rich sepiolite.Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 198(2): 362-369. |
| [9] | DONG Y, LIU T, SUN S, et al.Preparation and characterization of SiO2/polydopamine/Ag nanocomposites with long-term antibacte- rial activity.Ceramics International, 2014, 40(4): 5605-5609. |
| [10] | CHI Y, YUAN Q, LI Y, et al.Synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2-Ag magnetic nanocomposite based on small-sized and highly dispersed silver nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol.Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2012, 383(1): 96-102. |
| [11] | LV B, XU Y, TIAN H, et al.Synthesis of Fe3O4\SiO2\Ag nanoparticles and its application in surface-enhanced Raman scattering.Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2010, 183(12): 2968-2973. |
| [12] | LI L, CHOO E S G, TANG X, et al. Ag/Au-decorated Fe3O4 /SiO2 composite nanospheres for catalytic applications.Acta Materialia, 2010, 58(11): 3825-3831. |
| [13] | LEE H, DELLATORE S M, MILLER W M, et al.Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings.Science, 2007, 318(5849): 426-430. |
| [14] | ZHANG L, WU J, WANG Y, et al.Combination of bioinspiration: a general route to superhydrophobic particles.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(24): 9879-9881. |
| [15] | LIU Y, AI K, LU L.Polydopamine and its derivative materials: synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields.Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(9): 5057-5115. |
| [16] | ZHANG M, ZHENG J, ZHENG Y, et al.Preparation, characterization and catalytic activity of core-satellite Au/Pdop/SiO2/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposites.RSC Advances, 2013, 3(33): 13818-13824. |
| [17] | LIU X C, WANG G C, LIANG R P, et al.Environment-friendly facile synthesis of Pt nanoparticles supported on polydopamine modified carbon materials. J.mater.chem.a, 2013, 1(1): 3945-3953. |
| [18] | ZHANG M, ZHANG X, HE X, et al.A self-assembled polydopamine film on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles for specific capture of protein.Nanoscale, 2012, 4(10): 3141-3147. |
| [19] | WANG W, JIANG Y, LIAO Y, et al.Fabrication of silver-coated silica microspheres through mussel-inspired surface functionalization.Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2011, 358(2): 567-574. |
| [20] | LI W R, XIE X B, SHI Q S, et al.Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli.Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2010, 85(4): 1115-1122. |
| [21] | SUN H, LI G, NIE X, et al.Systematic approach to in-depth understanding of photoelectrocatalytic bacterial inactivation mecha- nisms by tracking the decomposed building blocks.Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(16): 9412-9419. |
| [1] | WANG Bo, YU Jian, LI Cuncheng, NIE Xiaolei, ZHU Wanting, WEI Ping, ZHAO Wenyu, ZHANG Qingjie. Service Stability of Gd/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 Thermo-electro-magnetic Gradient Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 663-670. |
| [2] | WANG Lei, LI Jianjun, NING Jun, HU Tianyu, WANG Hongyang, ZHANG Zhanqun, WU Linxin. Enhanced Degradation of Methyl Orange with CoFe2O4@Zeolite Catalyst as Peroxymonosulfate Activator: Performance and Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 469-476. |
| [3] | LIU Wenlong, ZHAO Jin, LIU Juan, MAO Xiaojian, ZHANG Jian, WANG Shiwei. Microwave Drying of Spontaneous-Coagulation-Cast Wet Alumina Green Body [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 461-468. |
| [4] | YANG Xiaoming, LAN Jianghe, WEI Zhantao, SU Rongbing, LI Yang, WANG Zujian, LIU Ying, HE Chao, LONG Xifa. High Quality and Large Size Yttrium Iron Garnet Crystal Grown by Top Seeded Solution Growth Technique [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 322-328. |
| [5] | RUAN Jing, YANG Jinshan, YAN Jingyi, YOU Xiao, WANG Mengmeng, HU Jianbao, ZHANG Xiangyu, DING Yusheng, DONG Shaoming. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties of SiC Ceramic Matrix Composite Reinforced by Three-dimensional Silicon Carbide Nanowire Network [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 579-584. |
| [6] | XIONG Jinyan, LUO Qiang, ZHAO Kai, ZHANG Mengmeng, HAN Chao, CHENG Gang. Facilely Anchoring Cu nanoparticles on WO3 Nanocubes for Enhanced Photocatalysis through Efficient Interface Charge Transfer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 325-331. |
| [7] | XIA Zhaoyang, WANG Hui, FANG Jinghong, ZHANG Yang, WANG Chaoyue, HE Huan, NI Jinqi, SHI Yun, LI Qin, YU Jianding. Co Incorporation on Structure, Conductivity and Magnetism of GaFeO3 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 319-324. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xiao, LI Youbing, CHEN Ke, DING Haoming, CHEN Lu, LI Mian, SHI Rongrong, CHAI Zhifang, HUANG Qing. Tailoring MAX Phase Magnetic Property Based on M-site and A-site Double Solid Solution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1247-1255. |
| [9] | YANG Conggang, MI Le, FENG Aihu, YU Yang, SUN Dazhi, YU Yun. Synthesis and Performance of KH-560 Modified SiO2 Insulation Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1343-1348. |
| [10] | BAI Jiawei, YANG Jing, LÜ Zhenfei, TANG Xiaodong. Magnetic and Dielectric Properties of Ti 4+-doped M-type Hexaferrite BaFe12-xTixO19 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 43-48. |
| [11] | ZHU Zhengwang,FENG Rui,LIU Yang,ZHANG Yang,XIE Wenhan,DONG Lijie. Preparation and Property of CoFe2O4 Nanofibers with Fishbone-like Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 1011-1016. |
| [12] | XU Dong, ZHU Yufang, ZHENG Yuanyi, LUO Yu, CHEN Hangrong. Injectable Magnetic Liquid-solid Phase Transition Material for MR Imaging and Low-temperature Magnetocaloric Therapy of Osteosarcoma [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1277-1282. |
| [13] | CHEN Haoyu, ZHANG Yiwen, WU Zhong, QIN Zhenbo, WU Shanshan, HU Wenbin. Room Temperature Magnetoresistance Property of Co-TiO2 Nanocomposite Film Prepared by Strong Magnetic Target Co-sputtering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1263-1267. |
| [14] | ZHAO Zhankui, LI Tao, LU Shuhan, WANG Minggang, ZHANG Jingjing, CHENG Daowen, WU Chen, CHI Yue, WANG Hongli. Magnetic Properties and Resistivity of Soft Magnetic Composites Regulated by SPS Enhanced Interface Reaction Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1223-1226. |
| [15] | LIU Zhang-Shuo, LIU Ji, DAI Yang, LI Xiao-Feng, YU Zhong-Zhen, ZHANG Hao-Bin. Bioinspired Ultrathin MXene/CNC Composite Film for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 99-104. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||