
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 191-196.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160247
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Jin1, TAO Ke2, LI Guo-Feng1, LIANG Ke1, CAI Hong-Kun1
Received:2016-04-12
Revised:2016-06-29
Published:2017-02-20
Online:2017-01-13
CLC Number:
WANG Jin, TAO Ke, LI Guo-Feng, LIANG Ke, CAI Hong-Kun. Effect of Hydrogen Annealing on the Property of Low-temperature Epitaxial Growth of Sige Thin Films on Si Substrate[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(2): 191-196.
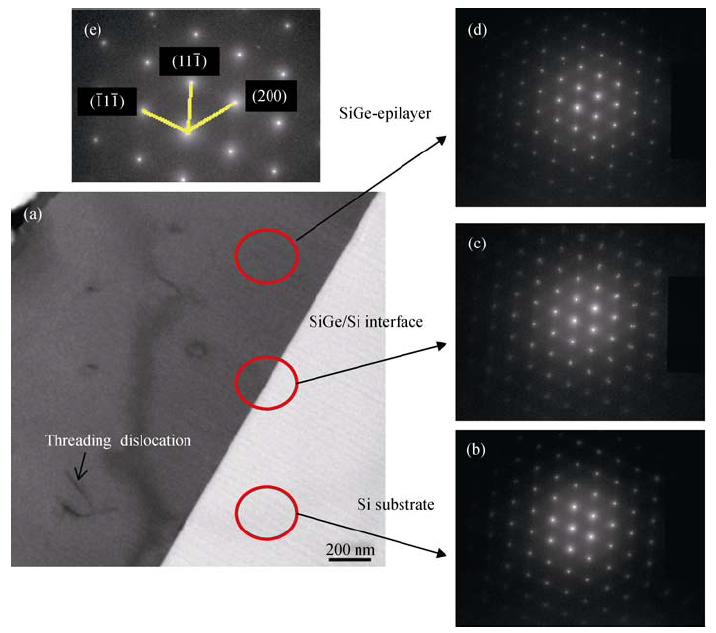
Fig. 1 (a) Cross-sectional TEM image of epitaxial SiGe films on silicon substrate, (b)-(d) electron diffraction patterns for Si substrate, SiGe/Si interface and SiGe epilayer (e) which extracted from (d) for calculation The red circles mark the position for measurement of electron diffraction patterns
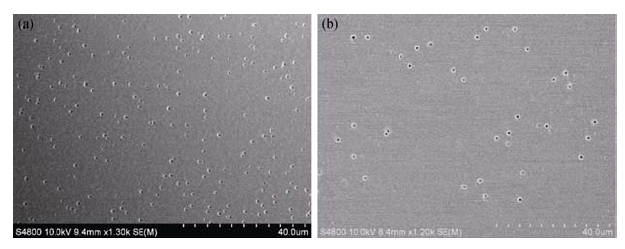
Fig. 5 SEM images of SiGe films after a selective wet etch, and pits with reversed pyramidal structure exhibited on the surface(a) As-deposited sample; (b) 650℃-annealed sample
| SixGe1-x | Resistance /(Ω·cm) | Carrier concentration/cm-3 | Mobility/ (cm2·V-1·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-grown | 0.402 | 6.35×1016 | 244 |
| Annealed | 1.470 | 1.07×1016 | 409 |
Table 1 Electrical properties of SiGe thin films by Hall-effect measurement
| SixGe1-x | Resistance /(Ω·cm) | Carrier concentration/cm-3 | Mobility/ (cm2·V-1·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-grown | 0.402 | 6.35×1016 | 244 |
| Annealed | 1.470 | 1.07×1016 | 409 |
| Ref. | Temp./℃ | Thickness /nm | RMS roughness/nm | TDD/cm-2 | Mobility/(cm2·V-1·s-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-grown | Annealed | As-grown | Annealed | Annealed | ||||
| [21] | LT | 400 | 1224 | 0.40 | 0.7 | 1.70×108 | 1.00×107 | NA |
| HT | 670 | |||||||
| [22] | LT | 350 | 50 | 0.70 | NA | 5.00×105 | NA | 550 |
| HT | 600 | 300 | ||||||
| [23] | LT | 335 | 2000 | 0.60 | 1.6 | NA | 2.00×107 | NA |
| HT | 670 | |||||||
| [24] | LT | 400 | 2500 | 1.20 | 1.0 | NA | 6.00×106 | NA |
| HT | 750 | |||||||
| [25] | LT | 400 | 980 | 3.19 | 0.9 | NA | 6.00×106 | NA |
| HT | 670 | |||||||
Table 2 Summary of the process parameters and film quality from literatures which reported the epitaxial growth of Ge by using low temperature/high temperature method
| Ref. | Temp./℃ | Thickness /nm | RMS roughness/nm | TDD/cm-2 | Mobility/(cm2·V-1·s-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-grown | Annealed | As-grown | Annealed | Annealed | ||||
| [21] | LT | 400 | 1224 | 0.40 | 0.7 | 1.70×108 | 1.00×107 | NA |
| HT | 670 | |||||||
| [22] | LT | 350 | 50 | 0.70 | NA | 5.00×105 | NA | 550 |
| HT | 600 | 300 | ||||||
| [23] | LT | 335 | 2000 | 0.60 | 1.6 | NA | 2.00×107 | NA |
| HT | 670 | |||||||
| [24] | LT | 400 | 2500 | 1.20 | 1.0 | NA | 6.00×106 | NA |
| HT | 750 | |||||||
| [25] | LT | 400 | 980 | 3.19 | 0.9 | NA | 6.00×106 | NA |
| HT | 670 | |||||||
| [1] | PAUL D J.Silicon-germanium strained layer materials in microelectronics.Advanced Materials, 1999, 11(17): 191-204. |
| [2] | CHANG S T, LIAO M H, LIN W K.Si/SiGe hetero-junction solar cell with optimization design and theoretical analysis.Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(15): 5022-5025. |
| [3] | HADI S A,HASHEMI P, NAYFEH A,et al. Thin film a-Si/c- Si1-xGex/c-Si heterojunction solar cells: design and material quality requirements, thin-film si cells.ECS Transactions, 2011, 41(4): 3-14. |
| [4] | CANNON D D, LIU J, DANIELSON D T,et al. Germanium-rich silicon-germanium films epitaxially grown by ultrahigh vacuum chemical-vapor deposition directly on silicon substrates.Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 91(25): 252111. |
| [5] | CHEN J X, ERNST F, HANSSON P O,et al. Liquid phase epitaxy of GeSi on {111} Si substrates: lattice defect structure and electronic properties.Journal of Crystal Growth, 1992, 118(s 3-4): 452-460. |
| [6] | CURRIEM T, SAMAVEDAM S B, LANGDO T A,et al. Controlling threading dislocation densities in Ge on Si using graded SiGe layers and chemical-mechanical polishing.Applied Physics Letters, 1998, 72(14): 1718-1720. |
| [7] | LOH T H, NGUYEN H S, TUNG C H, et al.Ultrathin low temperature SiGe buffer for the growth of high quality Ge epilayer on Si(100) by ultrahigh vacuum chemical vapor deposition.Applied Physics Letters.2007, 90(90): 092108-1-3. |
| [8] | GUO L, ZHAO S, WANG J,et al. Fabrication of strained Ge film using a thin SiGe virtual substrate.Journal of Semiconductors, 2009, 30(9): 16-20. |
| [9] | LOO R, SOURIAU L, ONG P,et al. Smooth and high quality epitaxial strained Ge grown on SiGe strain relaxed buffers with 70-85% Ge.Journal of Crystal Growth, 2011, 324(1): 15-21. |
| [10] | CHOI D, GE Y, HARRIS J S,et al. Low surface roughness and threading dislocation density Ge growth on Si (001) .Journal of Crystal Growth, 2008, 310(18): 4273-4279. |
| [11] | KIM H-W, SHIN K W, LEE G D,et al. High quality Ge epitaxial layers on Si by ultrahigh vacuum chemical vapor deposition.Thin Solid Films, 2009, 517(14): 3990-3994. |
| [12] | YAMAMOTO M, HANNA J, MIYAUCHI M.New low pressure chemical vapor deposition technique for Ge crystalline thin films.Applied Physics Letter, 1993, 63(18): 2508-2510. |
| [13] | YAMAMOTO M, TAKADA Y, HANNA J.Selective growth of Ge in GeF4-Si2H6 system.Applied Physics Letter, 1994, 64(25): 3467-3469. |
| [14] | HANNA J, SHIMIZU K.Low-temperature growth of polycrystalline Si and Ge films by redox reactions of Si2H6 and GeF4.Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, 2000, 611(1): 531-536. |
| [15] | TAO K, KUROSAWA Y, HANNA J.Low-temperature epitaxial growth of high quality Si1-xGex (x≥0.99) films on Si(001) wafer by reactive thermal chemical vapor deposition.Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102: 182109-1-5. |
| [16] | NAYFEH A, CHUI C O, SARASWATK C,et al. Effects of hydrogen annealing on heteroepitaxial-Ge layers on Si: surface roughness and electrical quality.Applied Physics Letters, 2004, 85(14): 2815-2817. |
| [17] | HARTMANN J M, ABBADIEA,BARNES J P,et al.Impact of the H2 anneal on the structural and optical properties of thin and thick Ge layers on Si; low temperature surface passivation of Ge by Si.Journal of Crystal Growth, 2010, 312(4): 532-541. |
| [18] | KOBAYASHI S, NISHI Y, SARASWAT K C.Effect of isochronal hydrogen annealing on surface roughness and threading dislocation density of epitaxial Ge films grown on Si.Thin Solid Films, 2010, 518(6): S136-S139. |
| [19] | LUAN H C, LIM D R, LEE K K,et al. High-quality Ge epilayers on Si with low threading-dislocation densities.Applied Physics Letters, 1999, 75(19): 2909-2911. |
| [20] | PEZZOLI F, BONERA E, GRILLI E,et al. Raman spectroscopy determination of composition and strain in image heterostructures.Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2008, 11(s 5-6): 279-284. |
| [21] | SHAH V A, DOBBIE A, MYRONOV M,et al. High quality relaxed Ge layers grown directly on a Si(001) substrate.Solid-State Electronics, 2011, 62(1): 189-194. |
| [22] | ZHOU Z, LI C, LAI H,et al. The influence of low-temperature Ge seed layer on growth of high-quality Ge epilayer on Si(100) by ultrahigh vacuum chemical vapor deposition.Journal of Crystal Growth, 2008, 310(10): 2508-2513. |
| [23] | OLUBUYIDE O O, DANIELSON D T,KIMERLING L C,et al. Impact of seed layer on material quality of epitaxial germanium on silicon deposited by low pressure chemical vapor deposition.Thin Solid Films, 2006, 508(1): 14-19. |
| [24] | HARTMANN J M, DAMLENCOURT J F, BOGUMILOWICZ Y,et al. Reduced pressure-chemical vapor deposition of intrinsic and doped ge layers on Si(001) for microelectronics and optoelectronics purposes.Journal of Crystal Growth, 2005, 274(1/2): 90-99. |
| [25] | TAN Y H, TAN C S.Growth and characterization of germanium epitaxial film on silicon (001) using reduced pressure chemical vapor deposition. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520(7): 2711-2716. |
| [1] | GU Xuesu, YIN Jie, WANG Kanglong, CUI Chong, MEI Hui, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Effect of Particle Grading on Properties of Silicon Carbide Ceramics by Binder Jetting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 216-. |
| [2] | CHEN Yu, LIN Pu'an, CAI Bing, ZHANG Wenhua. Research Progress of Inorganic Hole Transport Materials in Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 105-. |
| [3] | TIAN Yubin, TIAN Chaofan, LI Sen, ZHAO Yongxin, XING Tao, LI Zhi, CHEN Xiaoru, XIANG Shuairong, DAI Pengcheng. Biomass-derived High-conductive Carbon Cloth: Preparation and Its Application as Gas Diffusion Layers in Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 127-. |
| [4] | JIANG Runlu, WU Xin, GUO Haocheng, ZHENG Qi, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. UiO-67 Based Conductive Composites: Preparation and its Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 197-. |
| [5] | LI Haiyan, KUANG Fenghua, WU Haolong, LIU Xiaogen, BAO Yiwang, WAN Detian. Temperature Dependence of Residual Tensile Stresses and its Influences on Crack Propagation Behaviour [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 214-. |
| [6] | FANG Wanli, SHEN Lili, LI Haiyan, CHEN Xinyu, CHEN Zongqi, SHOU Chunhui, ZHAO Bin, YANG Songwang. Effect of Film Formation Processes of NiOx Mesoporous Layer on Performance of Perovskite Solar Cells with Carbon Electrodes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 2-. |
| [7] | DING Tongshun, FENG Ping, SUN Xuewen, SHAN Husheng, LI Qi, SONG Jian. Perovskite Film Passivated by Fmoc-FF-OH and Its Photovoltaic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 50-. |
| [8] | XU Hao, QIAN Wei, HUA Yinqun, YE Yunxia, DAI Fengze, CAI Jie. Effects of Micro Texture Processed by Picosecond Laser on Hydrophobicity of Silicon Carbide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 0, (): 73-. |
| [9] | QIU Haiyang, MIAO Guangtan, LI Hui, LUAN Qi, LIU Guoxia, SHAN Fukai. Effect of Plasma Treatment on the Long-term Plasticity of Synaptic Transistor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 406-412. |
| [10] | DU Jianyu, GE Chen. Recent Progress in Optoelectronic Artificial Synapse Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [11] | YANG Yang, CUI Hangyuan, ZHU Ying, WAN Changjin, WAN Qing. Research Progress of Flexible Neuromorphic Transistors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [12] | WU Junlin, DING Jiyang, HUANG Xinyou, ZHU Danyang, HUANG Dong, DAI Zhengfa, YANG Wenqin, JIANG Xingfen, ZHOU Jianrong, SUN Zhijia, LI Jiang. Fabrication and Microstructure of Gd2O2S:Tb Scintillation Ceramics from Water-bath Synthesized Nano-powders: Influence of H2SO4/Gd2O3 Molar Ratio [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 452-460. |
| [13] | CHEN Xinli, LI Yan, WANG Weisheng, SHI Zhiwen, ZHU Liqiang. Gelatin/Carboxylated Chitosan Gated Oxide Neuromorphic Transistor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 421-428. |
| [14] | YOU Junqi, LI Ce, YANG Dongliang, SUN Linfeng. Double Dielectric Layer Metal-oxide Memristor: Design and Applications [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [15] | FANG Renrui, REN Kuan, GUO Zeyu, XU Han, ZHANG Woyu, WANG Fei, ZHANG Peiwen, LI Yue, SHANG Dashan. Associative Learning with Oxide-based Electrolyte-gated Transistor Synapses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 399-405. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||