
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 141-147.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160290
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Min1,2, JIA Xiao-Peng3, LI Bing-Ke1, DENG Guo-Wei1, WANG Qi-Hui1, LIU Xiao-Yang2
Received:2016-05-03
Revised:2016-06-29
Published:2017-02-20
Online:2017-01-13
About author:YANG Min. E-mail:yangmin820525@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
YANG Min, JIA Xiao-Peng, LI Bing-Ke, DENG Guo-Wei, WANG Qi-Hui, LIU Xiao-Yang. One-pot Synthesis and Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Properties of Zn2GeO4 Microspheres[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(2): 141-147.
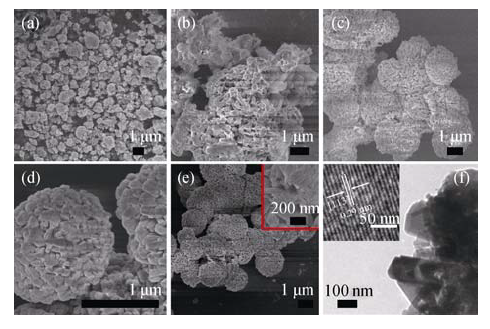
Fig. 2 SEM images of the products at different reaction temperatures(a) 100℃; (b) 120℃; (c) 140℃; (d)170℃; (e) FESEM image of Zn2GeO4 microspheres constructed of randomly packed nanosheets, and (f) TEM and HRTEM images of the individual Zn2GeO4 microspheres
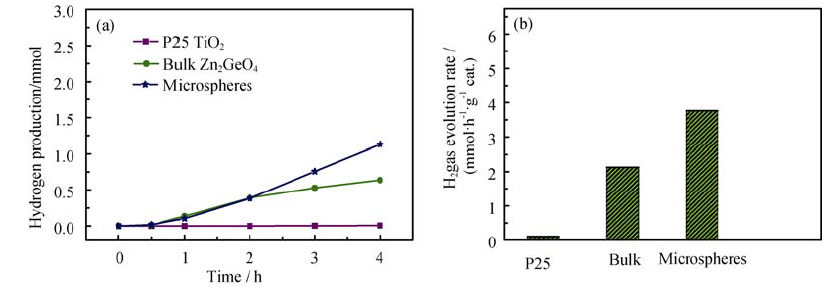
Fig. 8 (a) Photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and (b) hydrogen evolution rate from an aqueous methanol solution over various photocatalysts under exposure to UV lightCatalyst amount:0.075 g; H2O volume:75 mL; CH3OH volume:5 mL
| Material | Prepare method | Energy gap /eV | photosourc (UV-irradiation) | H2 evolution rate (mmol·g-1·h-1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn2GeO4 microspheres | Micrwave-hydrothermal,urea | 4.45 | 125 W Hg | 3.76 | In this work |
| Zn2GeO4 nanobundles | Hydrothermal,triethanolamine | 4.67 | 300 W Xe | 4.90 | [1] |
| Zn2GeO4 nanorods | Microwave-hydrothermal | 4.26 | 125 W Hg | 6.24 | [1] |
| Zn2GeO4 hollow spheres | Hydrothermal, triethanolamine, Sodium hydrate | 4.59 | 500 W Xe | 6.23 | [28] |
| Zn2GeO4 nanopowder | Hydrothermal | 4.77 | 150 W Hg | 0.43 | [29] |
Table 1 Hydrogen evolution rate of some recently-reported methanol-water solutions under exposure to UV light
| Material | Prepare method | Energy gap /eV | photosourc (UV-irradiation) | H2 evolution rate (mmol·g-1·h-1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn2GeO4 microspheres | Micrwave-hydrothermal,urea | 4.45 | 125 W Hg | 3.76 | In this work |
| Zn2GeO4 nanobundles | Hydrothermal,triethanolamine | 4.67 | 300 W Xe | 4.90 | [1] |
| Zn2GeO4 nanorods | Microwave-hydrothermal | 4.26 | 125 W Hg | 6.24 | [1] |
| Zn2GeO4 hollow spheres | Hydrothermal, triethanolamine, Sodium hydrate | 4.59 | 500 W Xe | 6.23 | [28] |
| Zn2GeO4 nanopowder | Hydrothermal | 4.77 | 150 W Hg | 0.43 | [29] |
| [1] | LIANG J, XU J, GU Q, et al. A novel Zn2GeO4 superstructure for effective photocatalytic hydrogen generation.J. Mater. Chem., 2013, 1(26): 7798-7805. |
| [2] | YI R, FENG J K, LV D P,et al. Amorphous Zn2GeO4 nanoparticles as anodes with high reversible capacity and long cycling life for Li-ion batteries.NanoEnergy, 2013, 2(4): 498-504. |
| [3] | GU Z J, LIU F, LI X F,et al. Luminescent Zn2GeO4 nanorod arrays and nanowires. Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys, 2013, 15(20): 7488-7493. |
| [4] | HE H L, ZHANG Y H, PAN Q W,et al. Controllable synthesis of Zn2GeO4:Eu nanocrystals with multi-color emission for white light-emitting diodes.J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015, 3(21):5419-5429. |
| [5] | GAO G J, PENG M Y, WONDRACZEK L,Spectral shifting and NIR down-conversion in Bi3+/Yb3+ co-doped Zn2GeO4.J. Mater. Chem. C, 2014, 2(38): 8083-8088. |
| [6] | ZHAO W W, ZHANG C, SHI Y M,et al. Self-assembled synthesis of hierarchical Zn2GeO4 core-shell microspheres with enhanced photocatalytic activity. DaltonTrans, 2015, 44(1): 75-82. |
| [7] | WANG W, HE J J, CUI F Y,et al. Preparation of Ag2O / TiO2 nanowires heterojunction and their photocatalytic activity under visible-light irradiation.Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(7):1367-1371. |
| [8] | WANG T, LIU Q, LI G,et al. Hydrothermal control growth of Zn2GeO4-diethylenetriamine 3D dumbbell-like nanobundles.Cryst- EngCom, 2014, 16(15): 3222-3227. |
| [9] | YU X Z, SHU W Y, JUN Z,et al. The study of oxygen ion motion in Zn2GeO4 by Raman spectroscopy.Solid State Ionics, 2015, 274: 12-16. |
| [10] | YANG M, JI Y, LIU W,et al. Facile microwave-assisted synthesis and effective photocatalytic hydrogen generation of Zn2GeO4 with different morphology.RSC Adv., 2014, 4(29): 15048-15054. |
| [11] | YAN C Y, LEE P S.Crystallographic alignment of ZnO nanorod arrays on Zn2GeO4 nanocrystals: promising lattice-matched substrates. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114(1): 265-268. |
| [12] | TSAIA M Y, HUANG S H, PERNG T P, et al. Low temperature synthesis of Zn2GeO4 nanorods and their photoluminescence.J. Lumin., 2013, 136: 322-327. |
| [13] | LU Y, YANG M, YANG B, et al. Rapid microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of SrWO4:Eu3+ nanowires and their luminescence properties. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 31(2):175-178. |
| [14] | CHEN F, SUN T W, QI C, et al. Microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis of calcium phosphate microspheres and Polyhedra.J. Inorg. Mater., 2014, 29(7):776-780. |
| [15] | ZHANG J C, WANG X F, ZHANG X H,et al. Microwave synthesis of NaLa(MoO4)2 microcrystals and their near-infrared luminescent properties with lanthanide ion doping (Er3+, Nd3+, Yb3+).Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2011, 14(11): 1723-1727. |
| [16] | ZHANG W X, WANG Q, REN X B, et al. Microwave synthesis and electrochemical property of one dimensional nanostrnctured MnO2.Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(10): 2025-2028. |
| [17] | GUO X, LIN S Y, QIN K, et al. Controllable detemplation of nanozeolites and research of molecular diffusing limitation.Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 713-719. |
| [18] | LIU J, ZHANG G K, YU J C, et al. In situ synthesis of Zn2GeO4 hollow spheres and their enhanced photocatalytic activity for the degradation of antibiotic metronidazole.Dalton Trans, 2013, 42(14): 5092-5099. |
| [19] | NERIA I S, KOLEN’KO Y V,LEBEDEV O I, et al. An effective morphology control of hydroxyapatite crystals via hydrothermal synthesis.Crystal. Growth Des., 2009, 9(1): 466-474. |
| [20] | BAGHBANZADEH M, CARBONE L G, COZZOLI P D,et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of colloidal inorganic nanocrystals.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(48): 11312-11359. |
| [21] | YAN S C, WAN L J, LI Z S,et al. Structural, vibrational and luminescence properties of longitudinal twinning Zn2GeO4 nanowires.Chem. Commun., 2011, 47(19): 5632-5634. |
| [22] | WANG T, LIU Q, LI GAO,et al. Hydrothermal control growth of Zn2GeO4-diethylenetriamine 3D dumbbell-like nanobundles.CrystEngComm., 2014, 16(15):3222-3227. |
| [23] | CHEN F, SUN T W, QI C,et al. Microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis of calcium phosphate microspheres and polyhedra.J. Inorg. Mater., 2014, 29(7): 776-780. |
| [24] | DU S.Q,YUAN Y.F , TU W. X, Microwave-hydrothermal synthesis and photocatalytic activity of Zn2GeO4 nanoribbons.Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin, 2013, 29(9):2062-2068. |
| [25] | ROBERT S, SEBASTIAN L, MILOS R F, et al. Photocatalytic generation of hydrogen from water under aerobic conditions. ChemSusChem., 2014,79(11):1614-1621. |
| [26] | YAN C L, XUE D F.Room temperature fabrication of hollow ZnS and ZnO architectures by a sacrificial template route.J.Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(14): 7102-7106. |
| [27] | ZHANG N, OUYANG S X, KAKO T,Synthesis of hierarchical Ag2ZnGeO4 hollow spheres for enhanced photocatalytic property.Chem. Commun, 2012, 48(79): 9894-9896. |
| [28] | CHEN C, WANG Z Y.Synthesis and crystal growth mechanism of titanium dioxide nanorods. J. Inorg. Mater., 2012, 27(1):45-48. |
| [29] | LIANG J, XU J, LONG J L, et al. Self-assembled micro/nanostructured Zn2GeO4 hollow spheres: direct synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic activity.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(36): 10622-10625. |
| [30] | LIN K Y, MA B J, SU W G,et al. Improved photocatalytic hydrogen generation on Zn2GeO4 nanorods with high crystallinity. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 286 : 61-65. |
| [31] | ZHAO J J, SHEN J, ZOU L P,et al. A low-cost preparation of sio2 aerogel monoliths from silica sol.J. Inorg. Mater., 2015, 30(10): 1081-1084. |
| [1] | WU Zhongcao, HUAN Zhiguang, ZHU Yufang, WU Chengtie. 3D Printing and Characterization of Microsphere Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 601-607. |
| [2] | CAI Miao, CHEN Zihang, ZENG Shi, DU Jianghui, XIONG Juan. CuS Nanosheet Decorated Bi5O7I Composite for the Enhanced Photocatalytic Reduction Activity of Aqueous Cr(VI) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 665-672. |
| [3] | GUO Xiaowei, LI Yuyan, CHEN Nanchun, WANG Xiuli, XIE Qinglin. Construction of Sustainable Release Antimicrobial Microspheres Loaded with Potassium Diformate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 181-187. |
| [4] | LIU Cai, LIU Fang, HUANG Fang, WANG Xiaojuan. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Alga-based CDs-Cu-TiO2 Composite Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1154-1162. |
| [5] | PAN Bichen,REN Penghe,ZHOU Tejun,CAI Zhenyang,ZHAO Xiaojun,ZHOU Hongming,XIAO Lairong. Microstructure and Property of Thermal Insulation Coating on the Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Resin Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 947-952. |
| [6] | XU Shichao,ZHU Tianzhe,QIAO Yang,BAI Xuejian,TANG Nan,ZHENG Chunming. Fabrication of Z-scheme BiVO4/GO/g-C3N4 Photocatalyst with Efficient Visble-light Photocatalytic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 839-846. |
| [7] | ZHU Enquan,MA Yuhua,AINIWA· Munire,SU Zhi. Adsorption-enrichment and Localized-photodegradation of Bentonite-supported Red Phosphorus Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 803-808. |
| [8] | HU Yaping, TIAN Zhengfang, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Controllable Preparation and in Vitro Bioactivity of Bioglass Microspheres via Spray Drying Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1268-1276. |
| [9] | GAO Long, ZHANG Zhaowenbin, CHANG Jiang. Bioglass/Polylactic Acid Porous Microspheres: Preparation and Their Application as Cell Microcarriers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1163-1168. |
| [10] | LI Meng-Xia, LU Yue, WANG Li-Bin, HU Xian-Luo. Controlled Synthesis of Core-shell Structured Mn3O4@ZnO Nanosheet Arrays for Aqueous Zinc-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 86-92. |
| [11] | XIAO Wen-Qian,ZHANG Jing,LI Ke-Jiang,ZOU Xin-Yu,CAI Yu-Dong,LI Bo,LIU Xue,LIAO Xiao-Ling. Litchi-like Superparamagnetic Hydroxyapatite Microspheres with Hierarchically Mesoporous Microspheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 925-932. |
| [12] | SUI Li-Li, WANG Run, ZHAO Dan, SHEN Shu-Chang, SUN Li, XU Ying-Ming, CHENG Xiao-Li, HUO Li-Hua. Construction of Hierarchical α-MoO3 Hollow Microspheres and Its High Adsorption Performance towards Organic Dyes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 193-200. |
| [13] | LI Jian, ZHANG Gang-Hua, FAN Li-Kun, HUANG Guo-Quan, GAO Zhi-Peng, ZENG Tao. Enhanced Visible-light-driven Photocatalytic Activity of Multiferroic KBiFe2O5 by Adjusting pH Value [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(7): 805-810. |
| [14] | WANG Dan-Jun, WANG Chan, ZHAO Qiang, GUO Li, YANG Xiao, WU Jiao, FU Feng. Au Nanoparticles (NPs) Surface Plasmon Resonance Enhanced Photocatalytic Activities of Au/Bi2WO6 Heterogeneous Nanostructures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(6): 659-666. |
| [15] | LI Bo, HAO Wen, WEN Xiao-Gang. Semi-hollow/Solid ZnMn2O4 Microspheres: Synthesis and Performance in Li Ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(3): 307-312. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||